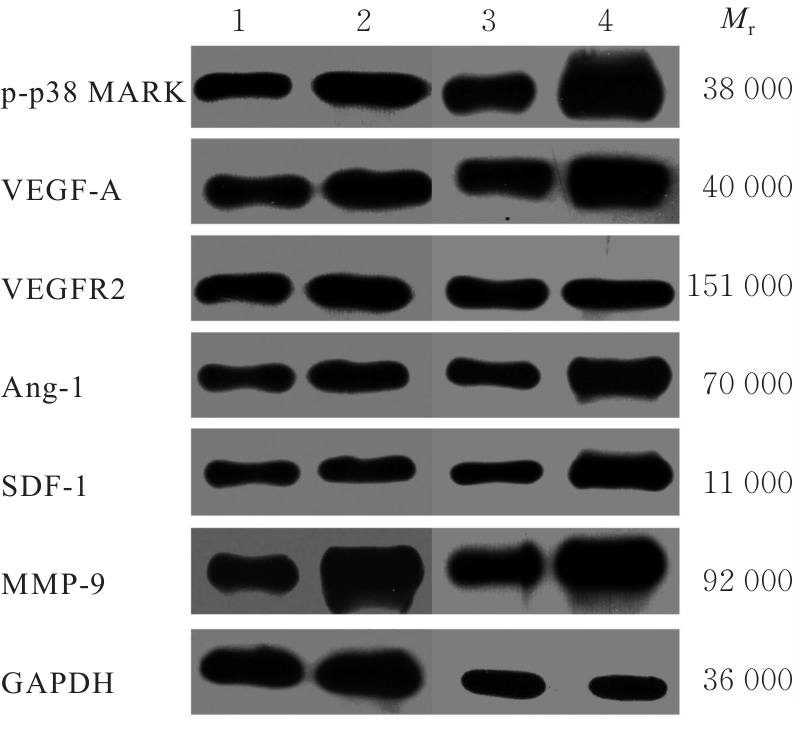
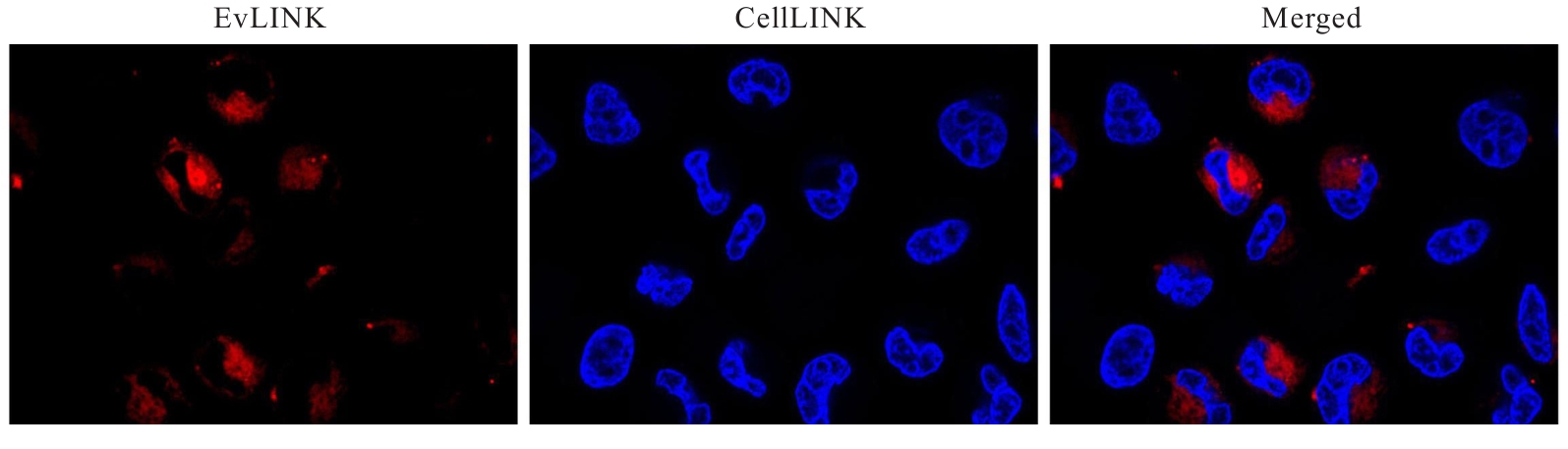
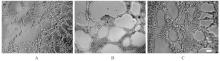
| [1] |
DUNCAN H F, KIRKEVANG L L, PETERS O A, et al. Treatment of pulpal and apical disease: The European Society of Endodontology (ESE) S3-level clinical practice guideline[J]. Int Endodontic J, 2023, 56(S3): 238-295.
|
| [2] |
吴加豪, 乔建瓯. 口腔常见微生物与哮喘患者肺功能及口腔免疫特征相关性研究[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版), 2024, 45(1): 75-80.
|
| [3] |
TIBÚRCIO-MACHADO C S, MICHELON C, ZANATTA F B, et al. The global prevalence of apical periodontitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int Endodontic J, 2021, 54(5): 712-735.
|
| [4] |
SOLETE P. Comparative evaluation of various analgesics in irreversible pulpitis to reduce pain[J]. Bioinformation, 2021, 17(2): 313-319.
|
| [5] |
KIM S G, MALEK M, SIGURDSSON A, et al. Regenerative endodontics: a comprehensive review[J]. Int Endodontic J, 2018, 51(12): 1367-1388.
|
| [6] |
MOUSSA D G, APARICIO C. Present and future of tissue engineering scaffolds for dentin-pulp complex regeneration[J]. J Tissue Eng Regen Med, 2018: term.2769.
|
| [7] |
TSUTSUI T. Dental pulp stem cells: advances to applications[J]. Stem Cells Cloning Adv Appl, 2020, 13: 33-42.
|
| [8] |
KIM J H, KIM G H, KIM J W, et al. In vivo angiogenic capacity of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth with human umbilical vein endothelial cells[J]. Mol Cells, 2016, 39(11): 790-796.
|
| [9] |
CHEN L L. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21(8): 475-490.
|
| [10] |
董惠贤, 钟嘉琳, 江千舟. 环状RNA在成骨分化中的作用[J]. 医学新知, 2021, 31(1): 23-32.
|
| [11] |
XIONG H C, CHEN K. Multipotent stem cells from apical pulp of human deciduous teeth with immature apex[J]. Tissue Cell, 2021, 71: 101556.
|
| [12] |
JI F, PAN J, SHEN Z C, et al. The circular RNA circRNA124534 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells through modulation of the miR-496/β-catenin pathway[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 230.
|
| [13] |
JI F, ZHU L Y, PAN J, et al. hsa_circ_0026827 promotes osteoblast differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells through the Beclin1 and RUNX1 signaling pathways by sponging miR-188-3p[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 470.
|
| [14] |
QAZI R E M, SAJID Z, ZHAO C Q, et al. Lyophilization based isolation of exosomes[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(13): 10477.
|
| [15] |
MATSUI M, KOBAYASHI T, TSUTSUI T W. CD146 positive human dental pulp stem cells promote regeneration of dentin/pulp-like structures[J]. Hum Cell, 2018, 31(2): 127-138.
|
| [16] |
JI F, ZHU L Y, PAN J, et al. hsa_circ_0026827 promotes osteoblast differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells through the Beclin1 and RUNX1 signaling pathways by sponging miR-188-3p[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 470.
|
| [17] |
李东雨, 朱小苗, 赵继荣, 等.组蛋白去乙酰化酶及其抑制剂在牙源性干细胞成骨和成牙本质分化中的研究进展[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2024, 49(4): 468-474.
|
| [18] |
GE X Y, LI Z H, ZHOU Z, et al. Circular RNA SIPA1L1 promotes osteogenesis via regulating the miR-617/Smad3 axis in dental pulp stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11(1): 364.
|
| [19] |
CHENG W, LIAO Y H, XIE Y, et al. Helicobacter pylori-induced fibroblast-derived Serpin E1 promotes gastric cancer growth and peritoneal dissemination through p38 MAPK/VEGFA-mediated angiogenesis[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2023, 23(1): 326.
|
| [20] |
WANG T Q, ZHAO H Q, JING S Z, et al. Magnetofection of miR-21 promoted by electromagnetic field and iron oxide nanoparticles via the p38 MAPK pathway contributes to osteogenesis and angiogenesis for intervertebral fusion[J]. J Nanobiotechnol, 2023, 21(1): 27.
|
| [21] |
李召宝, 李召静, 王婧. 山柰酚激活p38MAPK信号通路促进人牙周韧带间充质干细胞的迁移和成骨细胞分化[J]. 湖南师范大学学报(医学版), 2023, 20(4): 18-25.
|
| [22] |
ZHOU Z Z, ZOU M L, CHEN H P, et al. Forkhead box A1 induces angiogenesis through activation of the S100A8/p38 MAPK axis in cutaneous wound healing[J]. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol, 2023, 45(6): 742-753.
|
| [23] |
CHO H D, KIM J H, PARK J K, et al. Kochia scopariaseed extract suppresses VEGF-induced angiogenesis via modulating VEGF receptor 2 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways[J]. Pharm Biol, 2019, 57(1): 684-693.
|
| [24] |
ZHAO Y Q, YU B, WANG Y X, et al. Ang-1 and VEGF: central regulators of angiogenesis[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2025, 480(2): 621-637.
|
| [25] |
BADR G, EL-HOSSARY F M, LASHEEN F E M, et al. Cold atmospheric plasma induces the curing mechanism of diabetic wounds by regulating the oxidative stress mediators iNOS and NO, the pyroptotic mediators NLRP-3, Caspase-1 and IL-1β and the angiogenesis mediators VEGF and Ang-1[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 169: 115934.
|
| [26] |
QIN H J, ZHAO X Q, HU Y J, et al. Inhibition of SDF-1/CXCR4 axis to alleviate abnormal bone formation and angiogenesis could improve the subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis[J]. BioMed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 8852574.
|
| [27] |
LIU Y, ZHANG H Y, YAN L X, et al. MMP-2 and MMP-9 contribute to the angiogenic effect produced by hypoxia/15-HETE in pulmonary endothelial cells[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2018, 121: 36-50.
|
| [28] |
TU Y-A, CHOU C H, YANG P-K, et al. Intentional endometrial injury enhances angiogenesis through increased production and activation of MMP-9 by TNF-α and MMP-3 in a mouse model[J]. Mol Hum Reprod, 2021, 27(10): gaab055.
|
| [29] |
NESSBACH P, SCHWARZ S, BECKE T D, et al. Angiogenic potential of co-cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells and adipose stromal cells in customizable 3D engineered collagen sheets[J]. J Funct Biomater, 2022, 13(3): 107.
|