• •
lncRNA尿路上皮癌胚抗原1对人胃肠道间质瘤细胞失巢凋亡的调控作用及其机制
赵宇1,何小双2,董晓寅1,高丰毅1,何家赓1
- 1.石河子大学第一附属医院胃肠外科,新疆 石河子 832000
2.石河子大学第一附属医院呼吸与 危重症医学科,新疆 石河子 832000
Regulatory effect of lncRNA urothelial carcinoembryonic antigen 1 on anoikis in human gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells and its mechanism
Yu ZHAO1,Xiaoshuang HE2,Xiaoyin DONG1,Fengyi GAO1,Jiageng HE1
- 1.Department of Gastroenterology,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
2.Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
摘要:
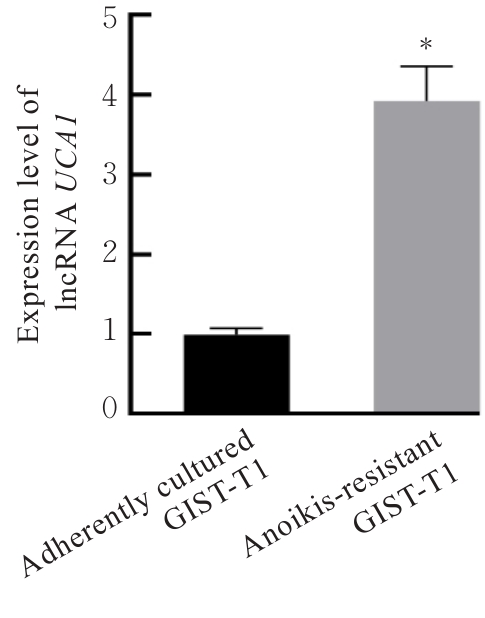
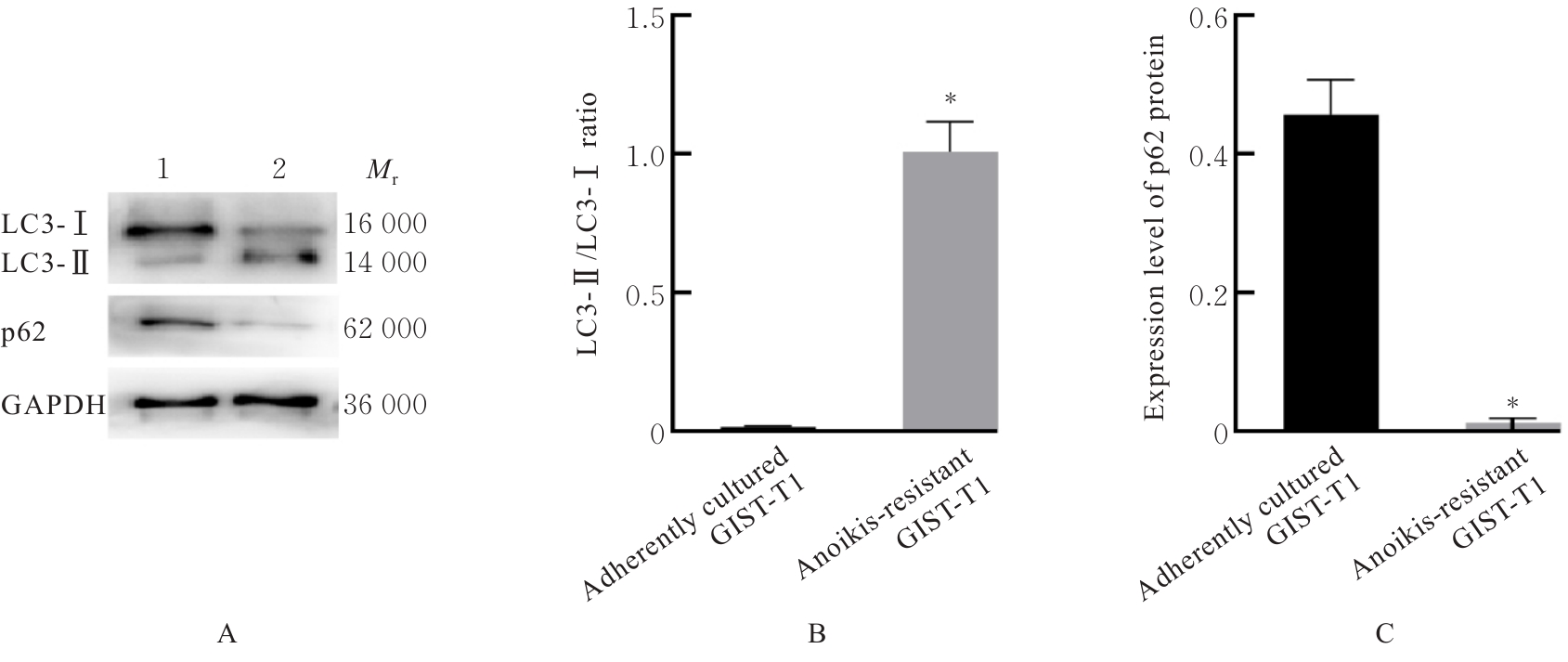
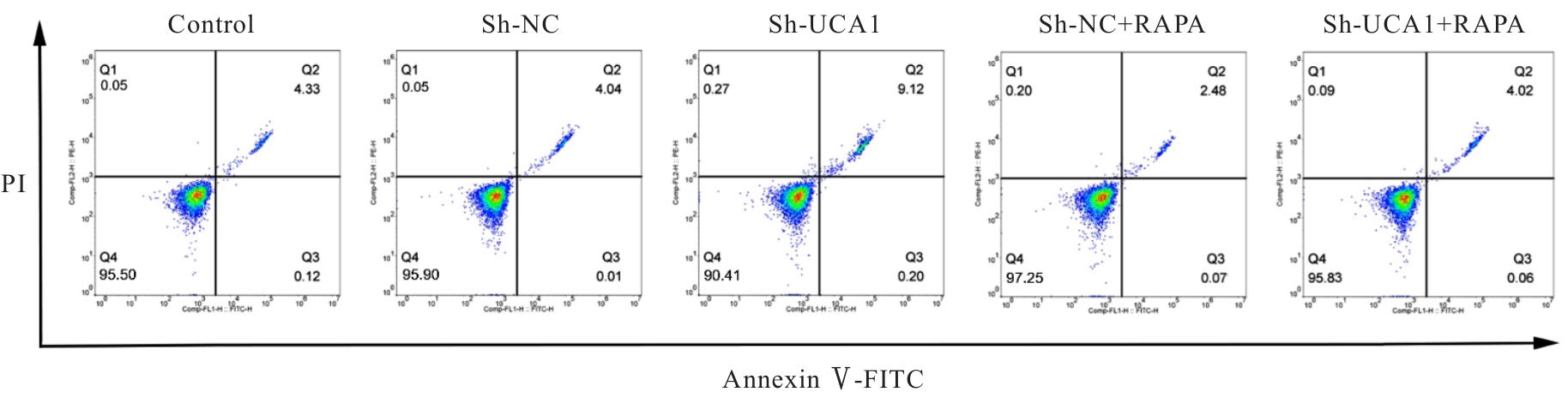
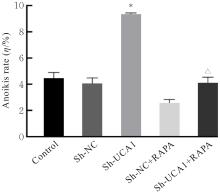
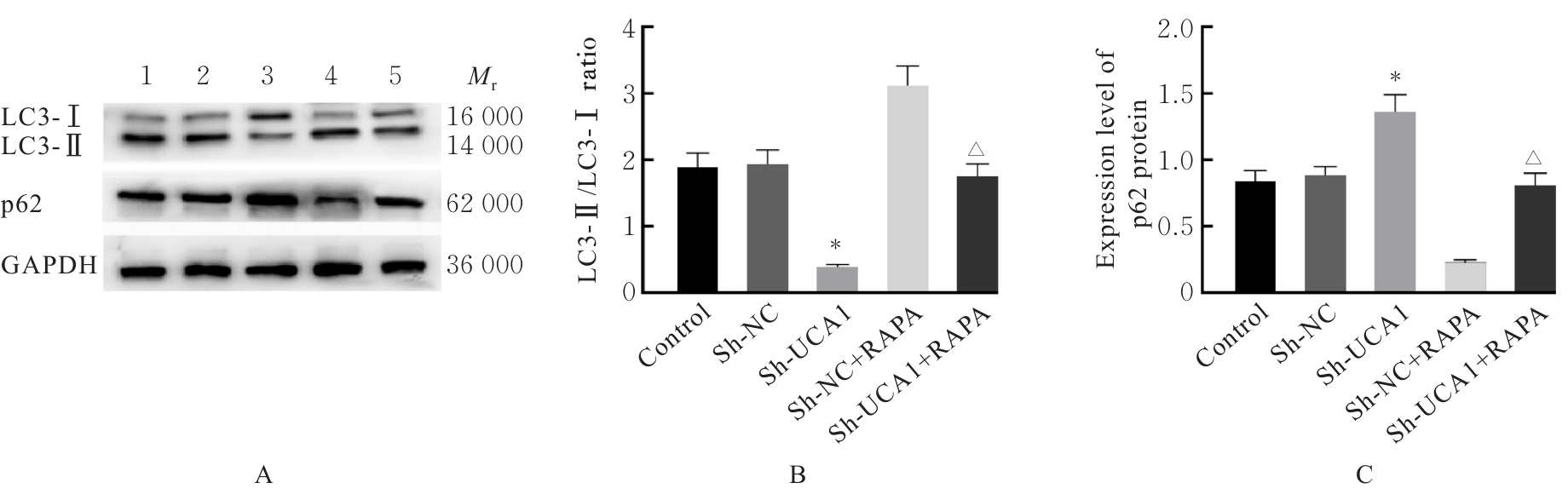
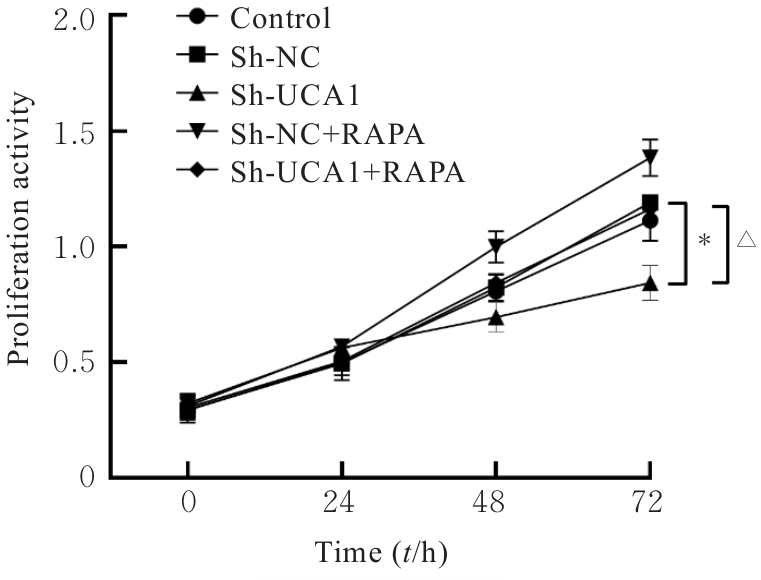
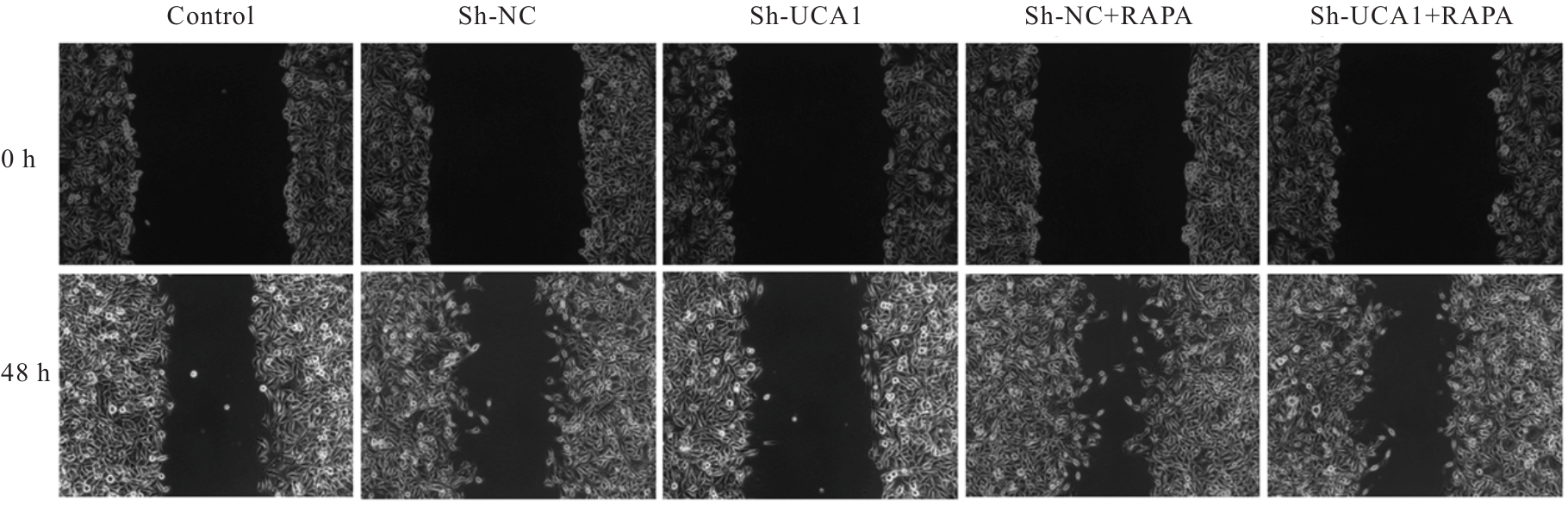
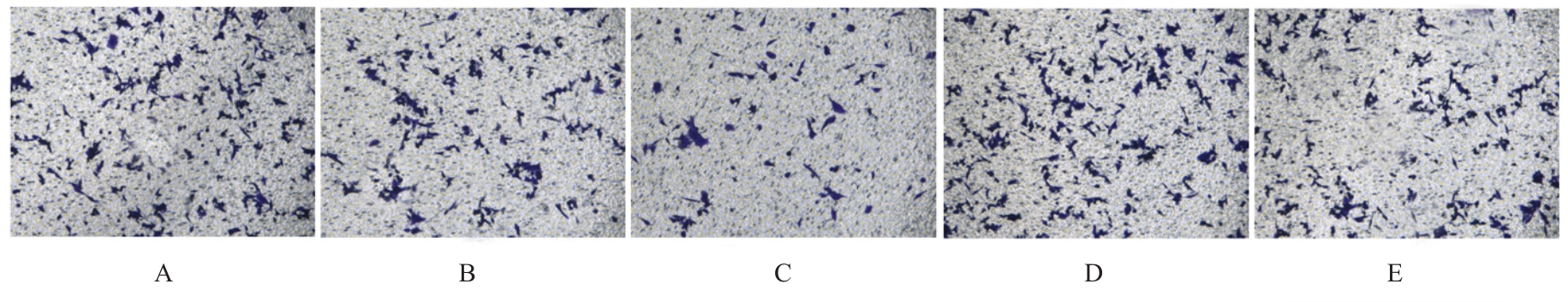
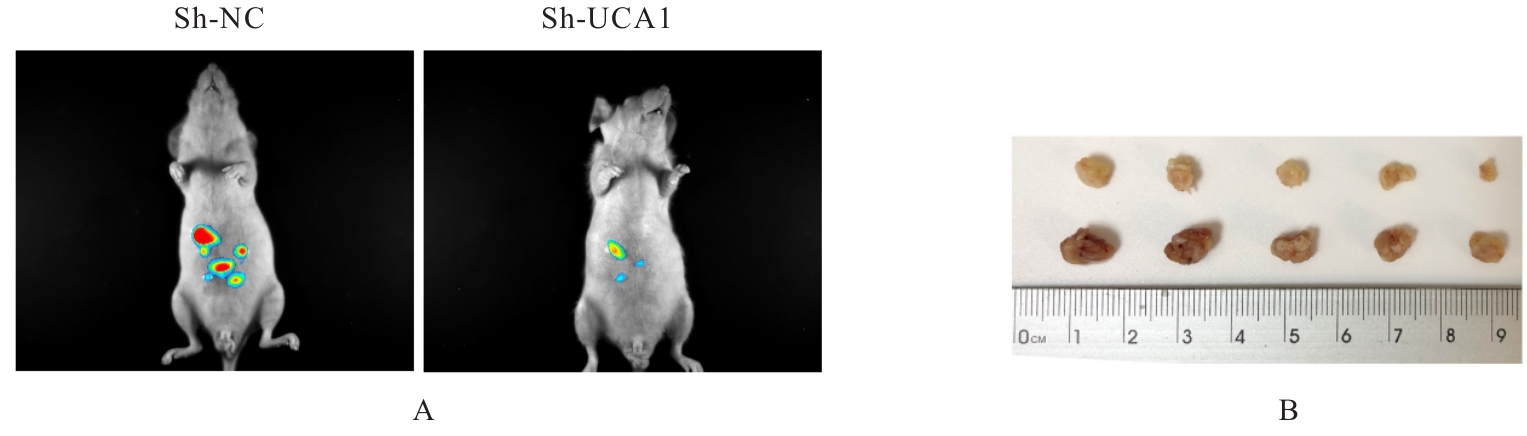
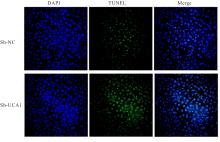
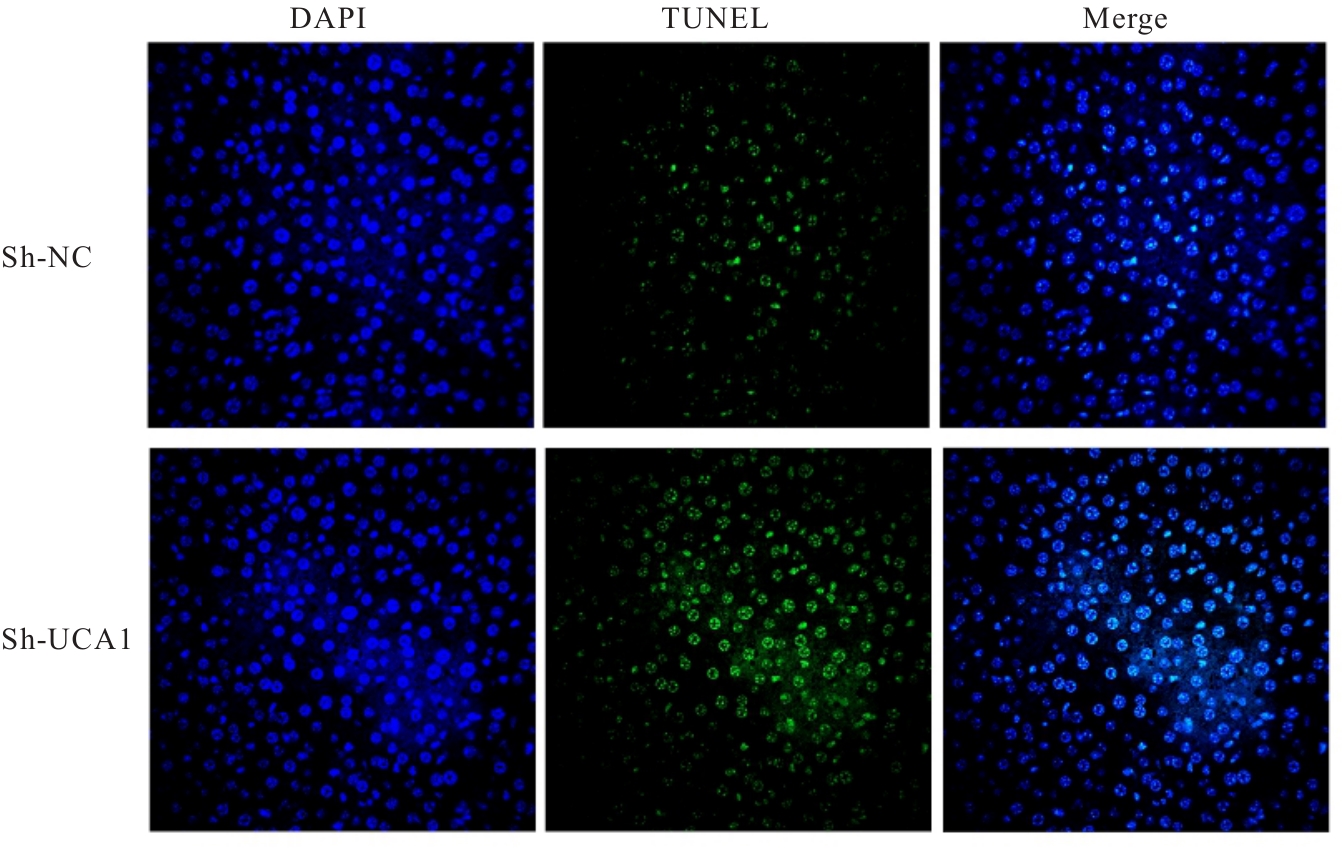
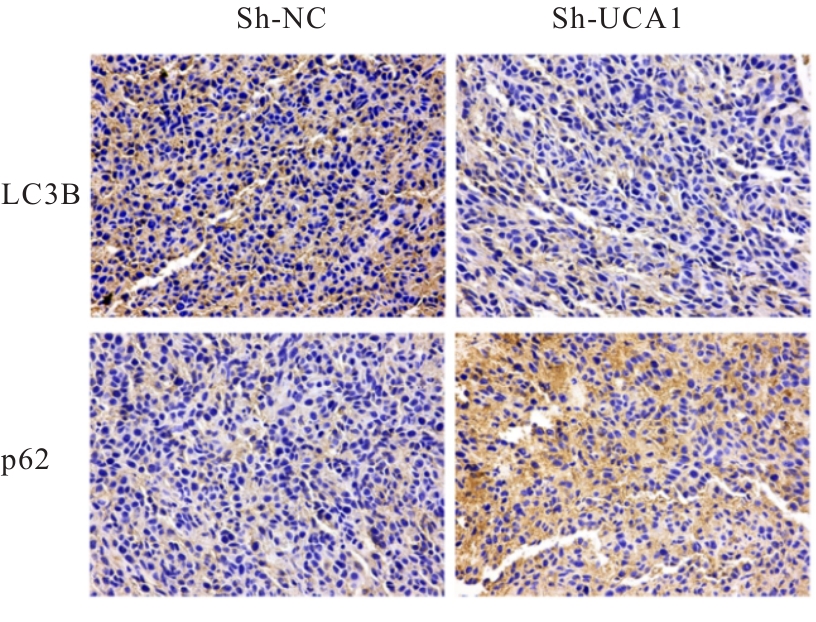
目的 探讨长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)尿路上皮癌胚抗原1(UCA1)对人胃肠道间质瘤(GIST)细胞失巢凋亡的影响,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 分别于贴壁和失巢状态下培养G1ST细胞株GIST-T1并诱导失巢凋亡抵抗的GIST-T1细胞,采用实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测2种细胞中lncRNA UCA1表达,Western blotting法检测细胞中自噬标志物微管相关蛋白轻链3(LC3)-Ⅰ、LC3-Ⅱ和p62表达水平,并计算LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ比值。采用敲减lncRNA UCA1或阴性对照慢病毒转染GIST-T1细胞并给予自噬激活剂雷帕霉素(RAPA)干预,将GIST-T1细胞分为对照组、sh-NC组、sh-UCA1组、sh-NC+RAPA组和sh-UCA1+RAPA组,并对细胞进行失巢诱导。采用流式细胞术检测各组细胞失巢凋亡率,Western blotting法检测各组细胞中LC3-Ⅰ、LC3-Ⅱ和p62蛋白表达水平,细胞计数试剂盒8(CCK-8)法检测各组细胞增殖活性,细胞划痕实验检测各组细胞划痕愈合率,Transwell小室实验检测各组细胞的侵袭细胞数。收集sh-NC组和sh-UCA1组GIST-T1细胞,分别通过尾静脉注射建立2组裸鼠移植瘤模型,4周后采用荧光活体成像仪检测2组裸鼠体内肿瘤生长和肝脏转移情况,测量2组裸鼠肿瘤组织质量。采用TUNEL染色法观察2组裸鼠肿瘤组织中细胞凋亡情况,免疫组织化学染色法检测2组裸鼠肿瘤组织中LC3B和p62蛋白表达水平。 结果 与贴壁培养的GIST-T1细胞比较,失巢凋亡抵抗的GIST-T1细胞中lncRNA UCA1表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ比值明显升高(P<0.05),p62蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05)。与sh-NC组比较,sh-UCA1组GIST-T1细胞凋亡率升高(P<0.05),LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ比值明显降低(P<0.05),p62蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),细胞增殖活性和划痕愈合率明显降低(P<0.05),侵袭细胞数明显减少(P<0.05);与sh-UCA1组比较,sh-UCA1+RAPA组GIST-T1细胞失巢凋亡率明显降低(P<0.05),LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ比值明显升高(P<0.05),p62蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),细胞增殖活性和划痕愈合率明显升高(P<0.05),侵袭细胞数明显增加(P<0.05)。裸鼠体内移植瘤实验, 与sh-NC组比较,sh-UCA1组裸鼠肝组织荧光强度减弱,肿瘤质量明显降低(P<0.05),肿瘤组织中细胞凋亡率明显升高(P<0.05),LC3B蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),p62蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05)。 结论 lncRNA UCA1在失巢凋亡抵抗的GIST-T1细胞中高表达,下调其表达可通过降低自噬水平来促进GIST-T1细胞失巢凋亡,从而抑制细胞生长、迁移和侵袭。
中图分类号:
- R735