Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 315-322.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210209
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
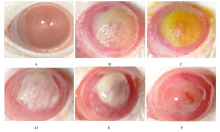
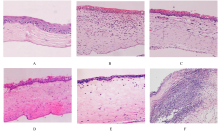
Regulatory effect of luteolin on Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis through TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in rats
- Department of Ophthalmology,Affiliated Third Hospital,Qiqihar Medical College,Qiqihar 161000,China
-
Received:2020-05-08Online:2021-03-28Published:2021-03-25 -
Contact:Shurong ZHANG E-mail:hk122221@163.com
CLC Number:
- R772.21
Cite this article
Shurong ZHANG,Qiying ZHANG. Regulatory effect of luteolin on Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis through TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in rats[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 315-322.
share this article
Tab. 1
Levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-12 in cornea tissue of rats in various of groups [n=5,x±s,ρB/(μg·L-1)]"
| Group | IL-1β | TNF-α | IL-12 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sham operation | 25.39±3.11 | 265.71±35.12 | 161.04±26.17 |
| Model | 47.67±4.03* | 487.82±42.37* | 350.87±30.58* |
| Luteolin | |||
| Low dose | 41.00±3.95*△▲ | 430.69±45.69*△▲ | 306.24±31.69*△▲ |
| Medium dose | 35.46±3.26*△#▲ | 382.11±40.33*△#▲ | 245.19±31.24*△#▲ |
| High dose | 30.28±3.87*△#○▲ | 329.03±38.74*△#○▲ | 203.08±30.57*△#○▲ |
| LPS+luteolin | 56.50±5.15*△ | 523.19±12.17*△ | 401.55±35.24*△ |
Tab. 2
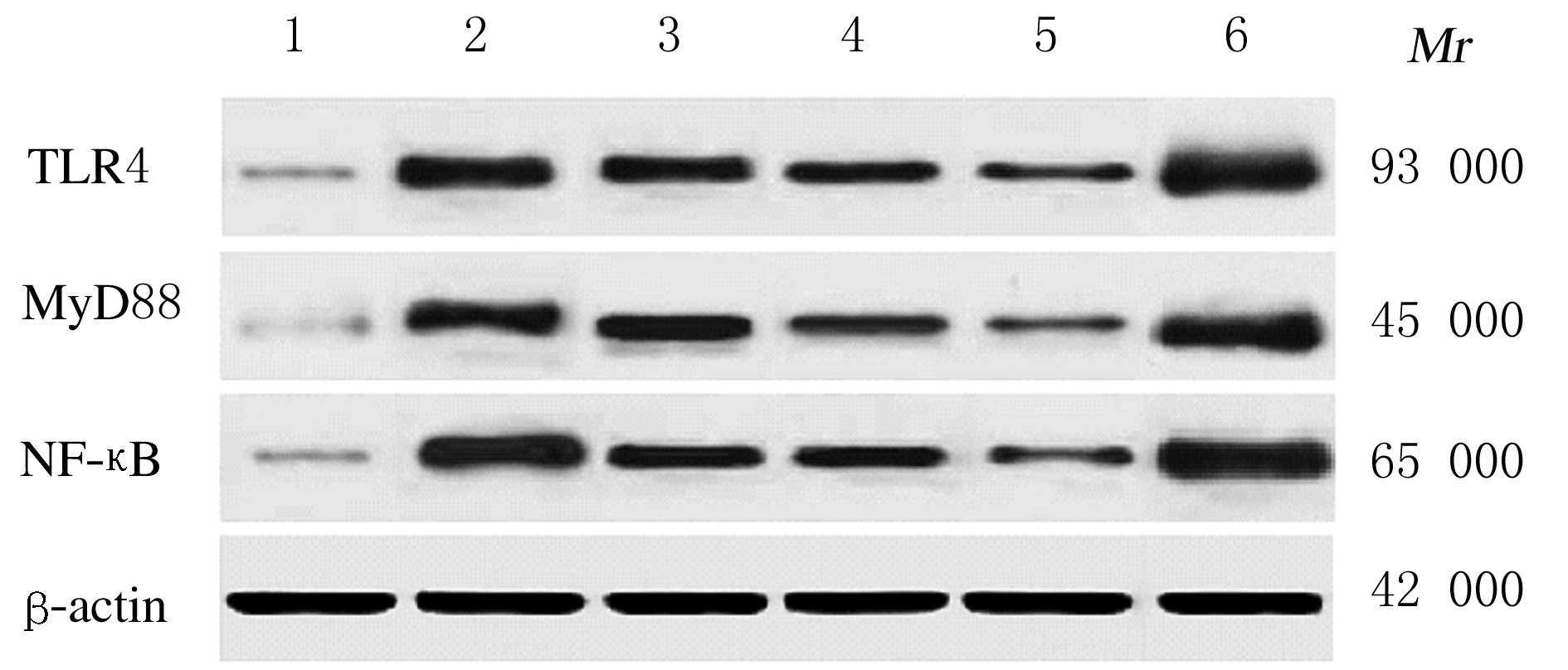
Expression levels of TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB proteins in cornea tissue of rats in various groups"
| Group | TLR4 | MyD88 | NF-κB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sham operation | 0.20±0.02 | 0.19±0.02 | 0.17±0.02 |
| Model | 1.12±0.10* | 1.07±0.09* | 1.13±0.08* |
| Luteolin | |||
| Low dose | 0.91±0.07*△▲ | 0.94±0.07*△▲ | 0.93±0.08*△▲ |
| Medium dose | 0.81±0.07*△#▲ | 0.76±0.06*△#▲ | 0.80±0.07*△#▲ |
| High dose | 0.53±0.06*△#○▲ | 0.40±0.05*△#○▲ | 0.47±0.05*△#○▲ |
| LPS+luteolin | 1.59±0.14*△ | 1.26±0.12*△ | 1.60±0.13*△ |
| 1 | 龚 桦, 谭奕炜, 龚向明, 等. 中国华南地区真菌性角膜炎致病菌谱变化[J].中华实验眼科杂志,2017,35(2):161-164. |
| 2 | JIANG J Q, LI C, CUI C X, et al. Inhibition of LOX-1 alleviates the proinflammatory effects of high-mobility group box 1 in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis [J]. Int J Ophthalmol, 2019, 12(6):898-903. |
| 3 | KURE A, NAKAGAWA K, KONDO M, et al. Metabolic fate of luteolin in rats: Its relationship to anti-inflammatory effect[J].J Agric Food Chem,2016,64(21):4246-4254. |
| 4 | AZIZ N, KIM M Y, CHO J Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin: A review of in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies [J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2018, 225:342-358. |
| 5 | 周霄楠, 韩 超, 宋鹏琰, 等. 木犀草素和槲皮素体外抗炎作用研究[J]. 动物医学进展, 2017, 38(10):60-65. |
| 6 | 沈瑞明, 马丽辉, 郑颜萍. 木犀草素通过TLR/MyD88/NF-κB通路参与急性痛风性关节炎大鼠的抗炎作用[J]. 中南大学学报:医学版, 2020, 45(2):115-122. |
| 7 | SZEKALSKA M, SOSNOWSKA K,TOMCZYKOWA M,et al. In vivo anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic activities of cynaroside evaluated by using hydrogel formulations [J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 121:109681. |
| 8 | 刘 廷, 徐园园, 陈 豪, 等. 改良角膜表面镜片术法建立兔曲霉菌性角膜炎动物模型[J]. 中华实验眼科杂志,2011, 29(2):101-106. |
| 9 | 周 芳, 肖启国. TLR-2、TLR-4与大鼠角膜碱烧伤早期炎症反应相关性研究[J]. 眼科新进展, 2017, 37(3):230-234. |
| 10 | ROCHA-AZEVEDO B D, JAMERSON M, CABRAL G A, et al. Acanthamoeba culbertsoni: analysis of amoebic adhesion and invasion on extracellular matrix components collagen Ⅰ and laminin-1 [J].Exp Parasitol, 2010, 126(1):79-84. |
| 11 | RAGHAVAN A, BAIDWAL S, VENKATAPATHY N,et al. The acanthamoeba-fungal keratitis study [J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2019, 201:31-36. |
| 12 | XU Q, HU L T, WANG Q, et al. Expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis [J]. Int J Ophthalmol, 2019, 12(5):711-716. |
| 13 | CRASCÌ L, CARDILE V, LONGHITANO G, et al. Anti-degenerative effect of Apigenin, Luteolin and Quercetin on human keratinocyte and chondrocyte cultures: SAR evaluation [J]. Drug Res (Stuttg), 2018, 68(3):132-138. |
| 14 | 程 钧, 翟华蕾, 王君怡, 等. 角膜后部真菌感染的临床特点和治疗策略[J]. 中华眼科杂志, 2017, 53(10):758-765. |
| 15 | HELLMANN A M,LOTHER J,WURSTER S,et al.Human and murine innate immune cell populations display common and distinct response patterns during their in vitro interaction with the pathogenic mold Aspergillus fumigatus [J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8:1716. |
| 16 | 张雨点, 谢锦艳, 李小川, 等. 木犀草素是具有PPARγ激动剂活性的新型AMPK激活剂[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2019, 19(9):1601-1607. |
| 17 | 刘 娟, 王 军, 邓庆华. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病炎症机制及中药单体成分对其治疗作用的研究进展[J]. 中国药房, 2018, 29(8):1145-1149. |
| 18 | ZHAO W, CHE C, LIU K, et al. Fenretinide inhibits neutrophil recruitment and IL-1β production in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis[J].Cornea,2018,37(12):1579-1585. |
| 19 | LIU M, LI C, ZHAO G Q, et al. Boxb mediate BALB/c mice corneal inflammation through a TLR4/MyD88-dependent signaling pathway in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis [J]. Int J Ophthalmol, 2018, 11(4):548-552. |
| 20 | SIGOLA L B, FUENTES A L, MILLIS L M, et al. Effects of Toll-like receptor ligands on RAW 264.7 macrophage morphology and zymosan phagocytosis [J]. Tissue Cell, 2016, 48(4):389-396. |
| 21 | LIU M,LI C,ZHAO G Q,et al. Boxb mediate BALB/c mice corneal inflammation through a TLR4/MyD88-dependent signaling pathway in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis [J]. Int J Ophthalmol, 2018, 11(4):548-552. |
| [1] | Guangwen LONG,Qian ZHANG,Xiulin YANG,Chunling JI,Yukang DONG. Regulation effect of miR-146b on expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in lung tissue of rats with acute respiratory distress syndrome [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 587-594. |
| [2] | Lei XIE,Xiaoli LIU,Jing GE,Yawei LI. Effects of baicalin combined with metformin on endocrine, inflammatory factors and insulin resistance in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 623-629. |
| [3] | Lijun YAN,Shengquan TONG,Jing LIU,Dongmei GAO,Nanfang CHEN,Jie HU. Therapeutic effect of total glucosides of paeony in model rats with rheumatoid arthritis by mediating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway and its mechanisim [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 390-396. |
| [4] | Xue BAI,Lu YU,Wenqiang YANG,Xin HE,Xinsheng YANG,Jing YANG. Inhibitory effect of carnosine on LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine release in astrocytes and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 330-337. |
| [5] | Zhenjie MA,Lan MA,Zhen JIA. Effect of celiac plexus block on stress response and immune inflammation of rats after partial hepatectomy and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 407-413. |
| [6] | Jie WU,Xuehua YANG,Ling MA,Wenqiang FAN,Dongdong FU,Xiao GAO,Shufei ZUO,Shu LIANG,Yilu QIN,Peishan WANG,Jinyan GUO. Effect of miR-26a-5p on apoptosis of human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells through JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 460-468. |
| [7] | LI Wei, ZHANG Haifeng, WANG Miao, HUO Jing, ZHANG Ying, ZHAO Cui. Protective effect of Astragalus Injection on heart of rats with sleep deprivation and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 998-1003. |
| [8] | WAN Qi, YU Baogang. Effects of miR-125b on proliferation and migration of cardiac fibroblasts by TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 286-291. |
| [9] | DU Xingxu, QIAO Zijing, YANG Shuo, XU Zhiying, YANG Bo, LI He, CHEN Jianguang, WANG Chunmei. Effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide on serum inflammatory factors in T2DM rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(01): 50-55. |
| [10] | ZHAO Miao, WANG Yi, ZHANG Ying, FENG Yumei, CAO Yawen, JIANG Haisen, LI Wei. Improvement effect of curcumin on cognitive function in mice with sleep deprivation and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1373-1378. |
| [11] | CAO Shuang, FAN Ziwei, WANG Yingying, SUN Lijuan, GU Hong, LI He, SUN Jinghui, WANG Chunmei, CHEN Jianguang, CHEN Xi, ZHANG Chengyi. Effects of prunus tomentosa thunb total flavonoids on levels of inflammatory factors in RAW264.7 cells and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 836-842. |
| [12] | CUI Yan, WANG Ruonan, WU Jiuru, WEI Shu, LIN Shengjuan, WANG Zhongnan. Effect of water extract of spina date seed and albizzia julibrissin flower on hpa axis and inflammatory cytokines in anxious depression model rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 539-545. |
| [13] | HE Qi, SHI Hua, DAN Yang, SHAO Suju. Effects of Jiawei Danshen Yin on cardiac function and serum inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α in rats with chronic heart failure [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 63-68. |
| [14] | CHEN Qiong, CAO Jie, ZHAO Lijun, YI Nan. Effects of different exercise modes on body composition, inflammatory factors,and exercise capacity of obese teenagers [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(05): 1070-1075. |
| [15] | YANG Kun, TIAN Zhenzhen, WANG Shuhua, XIU Ming, GUO Xiangling, QI Lina, LI Min, SUN Li, GAO Runping. Effect of LPS-TLR4 pathway in hepatic fibrogenesis of rats with chronic alcohol intake [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(04): 751-755. |