Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 834-841.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210403
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Improvement effect of angiotensin(1-7) on kidney injury induced by limb ischemia-reperfusion in mice and its mechanism
Liyan ZHU1,2,Yaoming WANG1,Zheng QIN1,Huanhuan ZHAO1,Zengying WANG1,Xiuhong YANG1,2( )
)
- 1.Functional Laboratory,School of Basic Medical Sciences,North China University of Science and Technology,Hebei Province,Tangshan 063000,China
2.Key Laboratory of Chronic Diseases of Tangshan City,Hebei Province,Tangshan 063000,China
-
Received:2020-11-13Online:2021-07-28Published:2021-07-22 -
Contact:Xiuhong YANG E-mail:ljkyxhljn@163.com
CLC Number:
- R363
Cite this article
Liyan ZHU,Yaoming WANG,Zheng QIN,Huanhuan ZHAO,Zengying WANG,Xiuhong YANG. Improvement effect of angiotensin(1-7) on kidney injury induced by limb ischemia-reperfusion in mice and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 834-841.
share this article
Tab. 1
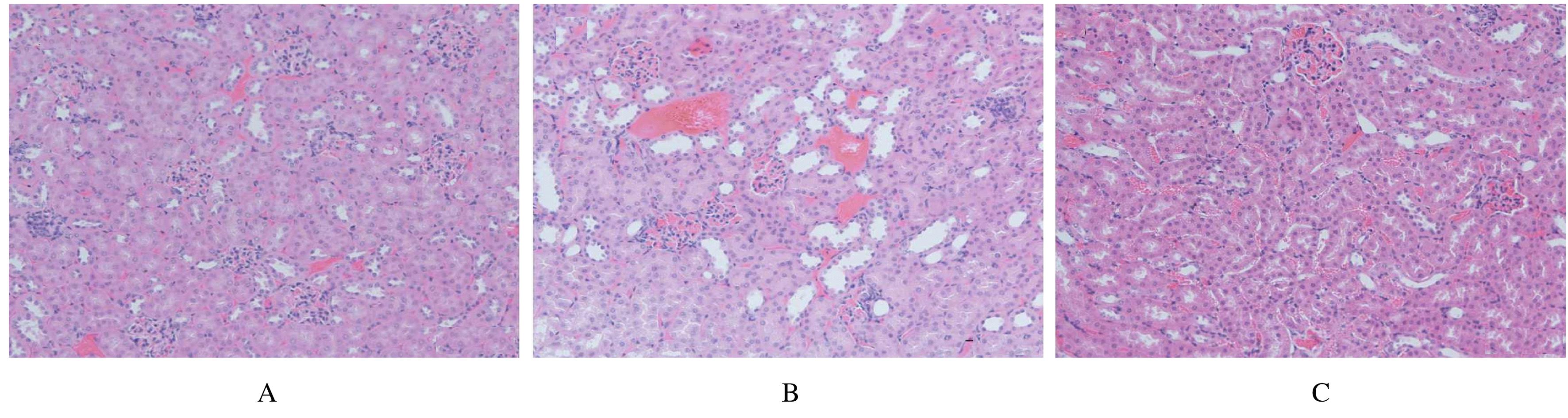
Indexes of kidney function and pathological injury scores of kindey tissue of mice in various groups"
| Group | Scr [cB/(μmol·L-1)] | BUN [cB/(mmol·L-1)] | Pathological injury score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 19.92±1.96 | 7.95±2.06 | 14.67±3.54 |
| LIR | 30.35±5.09* | 13.36±2.45* | 55.20±9.13* |
| LIR+Ang-(1-7) | 24.94±2.72△ | 9.91±1.69△ | 36.80±4.02△ |
| *P<0.05 vs control group;△P<0.05 vs LIR group. | |||
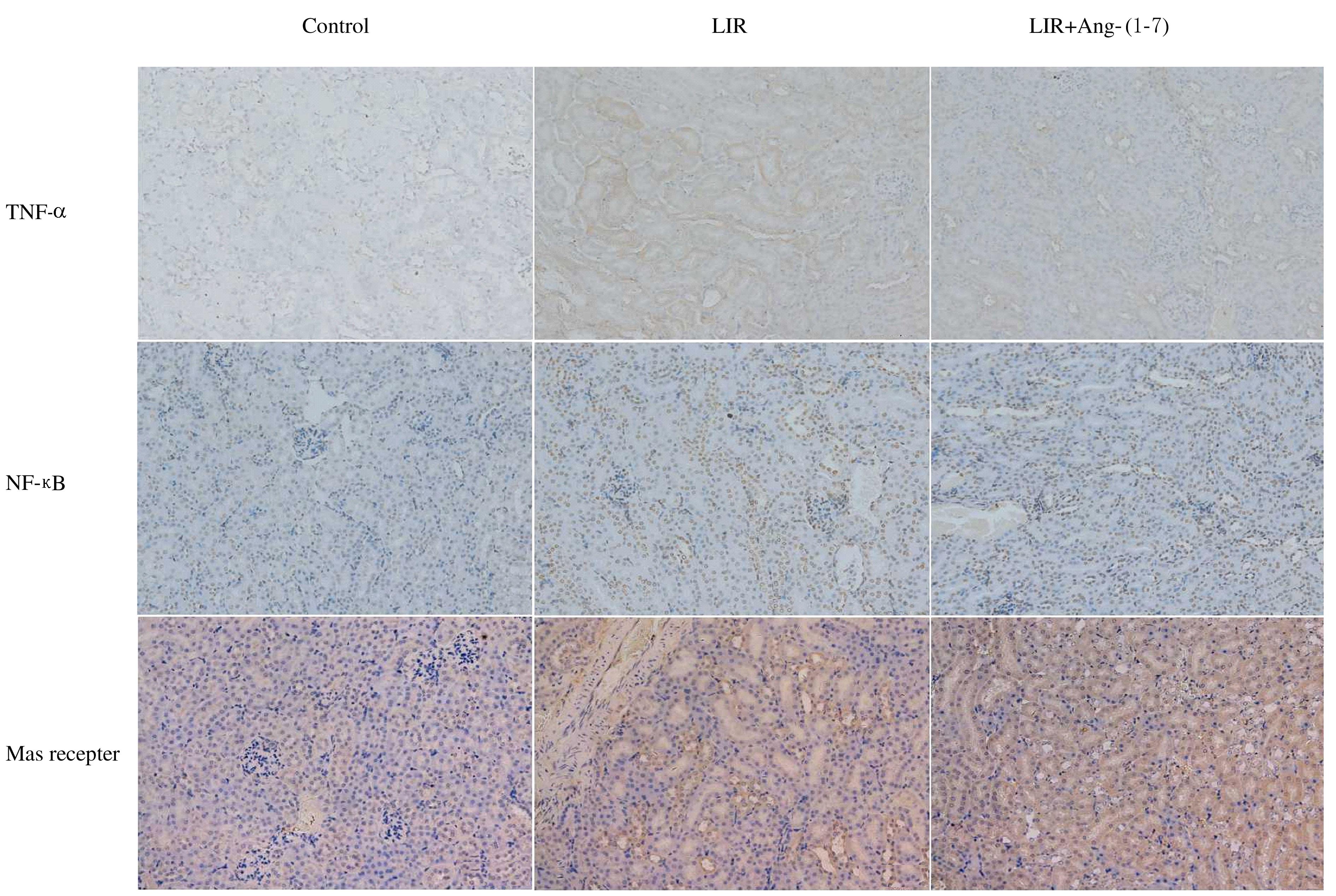
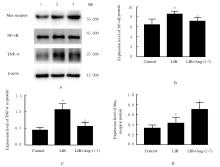
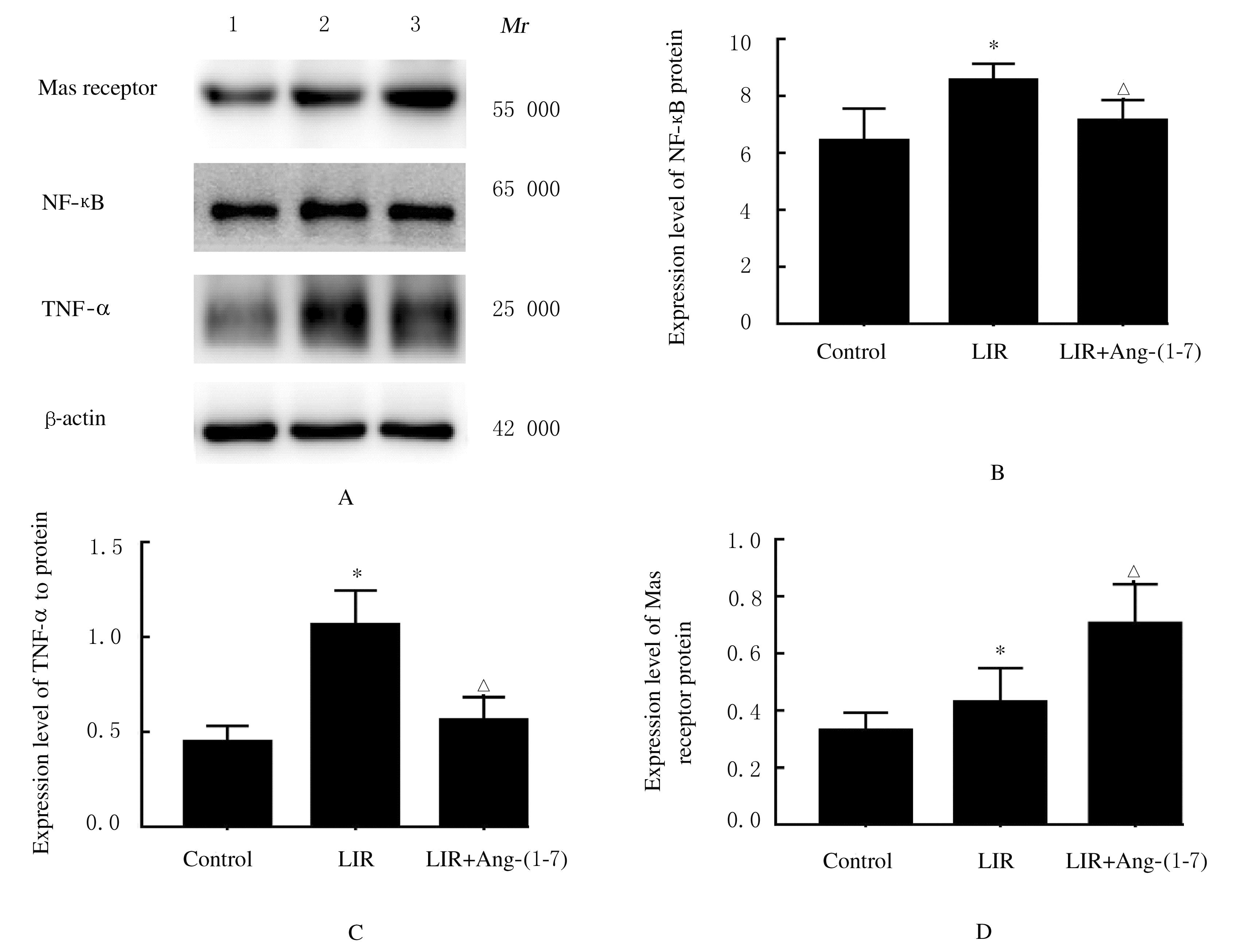
Tab. 3
Expression levels of TNF-α,NF-κB, and Mas receptor proteins in kidney tissue of mice in various groups"
| Group | TNF-α | NF-κB | Mas receptor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.08±0.02 | 0.10±0.01 | 0.16±0.01 |
| LIR | 0.21±0.03* | 0.22±0.02* | 0.21±0.01* |
| LIR+Ang-(1-7) | 0.13±0.02△ | 0.19±0.02△ | 0.28±0.01△ |
| *P<0.05 vs control group;△P<0.05 vs LIR group. | |||
| 1 | SHIH J M, SHIH Y M, HOU Y C, et al. Effects of fish oil-based lipid emulsion on inflammation and kidney injury in mice subjected to unilateral hind limb ischemia/reperfusion[J]. Cytokine, 2018, 111: 49-57. |
| 2 | 王建军, 杨秀红, 邓 巍,等. 小鼠止血带休克后肾组织ACE/ACE2表达变化及意义[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2011, 27(12): 2399-2402. |
| 3 | XU Z, LI W X, HAN J B, et al. Angiotensin Ⅱ induces kidney inflammatory injury and fibrosis through binding to myeloid differentiation protein-2 (MD2)[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 44911. |
| 4 | HASSANSHAHI J, NEMATBAKHSH M. The role of mas receptor on renal hemodynamic responses to angiotensin 1-7 in both irreversible and reversible unilateral ureteral obstruction rats[J]. Adv Biomed Res, 2018, 7: 12. |
| 5 | CHEN J F, ZHANG W, XU Q, et al. Ang-(1-7) protects HUVECs from high glucose-induced injury and inflammation via inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2018, 41(5): 2865-2878. |
| 6 | PALLER M S, HOIDAL J R, FERRIS T F. Oxygen free radicals in ischemic acute renal failure in the rat[J]. J Clin Invest, 1984, 74(4): 1156-1164. |
| 7 | ZHAO Y L, FENG Q Z, HUANG Z J, et al. Simvastatin inhibits inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Inflammation, 2014, 37(5): 1865-1875. |
| 8 | DILAURO M, ZIMPELMANN J, ROBERTSON S J, et al. Effect of ACE2 and angiotensin-(1-7) in a mouse model of early chronic kidney disease[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2010, 298(6): F1523-F1532. |
| 9 | SILVEIRA K DDA, POMPERMAYER BOSCO K S, DINIZ L R, et al. ACE2-angiotensin-(1-7)-Mas axis in renal ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2010, 119(9): 385-394. |
| 10 | SINER J M, BHANDARI V, ENGLE K M, et al. Elevated serum angiopoietin 2 levels are associated with increased mortality in sepsis[J]. Shock, 2009, 31(4): 348-353. |
| 11 | RUIZ-ORTEGA M, RUPÉREZ M, ESTEBAN V,et al.Angiotensin Ⅱ: a key factor in the inflammatory and fibrotic response in kidney diseases[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2006, 21(1): 16-20. |
| 12 | LIU X J, MEI Z G, QIAN J P, et al. Puerarin partly counteracts the inflammatory response after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion via activating the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2013,8(34): 3203-3215. |
| 13 | CHOI H S, KIM I J, KIM C S,et al.Angiotensin-[1-7] attenuates kidney injury in experimental Alport syndrome[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 4225. |
| 14 | PATEL V B, JUN M R, MCLEAN B A, et al. ACE2 deficiency worsens epicardial adipose tissue inflammation and cardiac dysfunction in response to diet-induced obesity[J]. Diabetes, 2016, 65(1): 85-95. |
| 15 | PROKOP J W, SANTOS R A, MILSTED A. Differential mechanisms of activation of the Ang peptide receptors AT1, AT2, and MAS: using in silico techniques to differentiate the three receptors[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6): e65307. |
| 16 | AL-MAGHREBI M, BENTER I F, DIZ D I. Endogenous angiotensin-(1-7) reduces cardiac ischemia-induced dysfunction in diabetic hypertensive rats[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2009, 59(4): 263-268. |
| 17 | 陈健芳, 陈景福, 陈 巍, 等. 血管紧张素(1-7)通过抑制JAK/STAT信号通路对抗高糖诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞损伤[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2017, 33(3): 481-488. |
| 18 | MENDES A C R, FERREIRA A J, PINHEIRO S V B,et al. Chronic infusion of angiotensin-(1-7) reduces heart angiotensin II levels in rats[J]. Regul Pept, 2005, 125(1-3): 29-34. |
| 19 | 张晓翠, 侯兆玉, 张红利, 等. 血管紧张素1-7通过Mas受体减轻血管紧张素Ⅱ所致人肾小球内皮细胞损伤[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2018, 34(5): 893-898. |
| 20 | 刘 菁,曾筱茜,程一鸣,等.肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统抑制剂相关联合用药策略的降压疗效及肾脏保护作用[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2019,39(5): 470-473. |
| 21 | NIE W, YAN H, LI S, et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) enhances angiotensin Ⅱ induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells[J]. Mol Immunol, 2009, 46(3): 355-361. |
| 22 | JIANG T, GAO L, GUO J, et al. Suppressing inflammation by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway contributes to the neuroprotective effect of angiotensin-(1-7) in rats with permanent cerebral ischaemia[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2012, 167(7): 1520-1532. |
| 23 | NI J, YANG F Y, HUANG X R, et al. Dual deficiency of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 and Mas receptor enhances angiotensin II-induced hypertension and hypertensive nephropathy[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24(22): 13093-13103. |
| 24 | 王建辉, 张 伟, 刘 燕, 等. 小鼠肢体缺血再灌注后肾组织AT1和Mas受体蛋白差异性表达与肾损伤的关系[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2016, 41(3): 184-188. |
| [1] | Xin SHEN,Yang LIU,Hongyu CHEN,Jie ZHANG,Qingli CHENG,Guang YANG. Regulatory effect of high glucose on polarization of RAW264.7 macrophages via miR-125b in mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 847-857. |
| [2] | Tao LIN,Yinghua LI,Yawen LIAN,Xiaowei CHEN,Qi WAN. Improvement effect of recombinant human growth hormone on motor function in mice with focal cerebral ischemia- reperfusion and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 568-574. |
| [3] | Zhihui ZHAO,Xianghua BAI,Jinling HE,Weiqin DUAN,Min LIU,Shengmao ZHANG. Inhibitory effect of sufentanil on apoptosis of myocardial cells in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 364-373. |
| [4] | Na HAN,Fanping LIU,Yanqing TIAN,Zhiqing ZHENG,Weiming LANG,Qian WANG,Yatao LIU,Jianguang ZHU. Regulatory effect of miRNA-27a on immune function in experimental pulmonary tuberculosis rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 104-110. |
| [5] | Song SU,Hongbo WANG,Yucong MA,Xin FANG,Junrong LIU,Hongmei QIAO. Kawasaki disease with inflammatory changes in parapharyngeal space:A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 228-233. |
| [6] | Mimi REN,Menghan GAO,Jing WANG,Jiamei LAI,Jinyu YU,Hang YUAN. Protective effect of 12/15-lipoxygenase gene knockout on kidney tissue of obesity-related glomerulopathy model mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1337-1346. |
| [7] | Xue LUAN, Guanghai YAN, Haibo LI, Bo ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Yuanyuan HUANG. Effect of salidroside on airway inflammation in mice with asthma and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 537-544. |
| [8] | Lijun YAN,Shengquan TONG,Jing LIU,Dongmei GAO,Nanfang CHEN,Jie HU. Therapeutic effect of total glucosides of paeony in model rats with rheumatoid arthritis by mediating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway and its mechanisim [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 390-396. |
| [9] | QIAO Liangwei, QU Qingshan, LI Ming. Effect of LncRNA-ATB on acute rejection of kidney transplanted rats by regulating miR-200c expression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 955-962. |
| [10] | ZHANG Li, CUI Xiaoqian, SHANG Yunlong, CHENG Yuanjuan, SONG Debiao. Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome caused by diabetic ketoacidosis combined with hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state:A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1070-1073. |
| [11] | ZHAO Liping, HUANG Shubing, ZHANG Boping, ZHOU Zhilan, JIA Xuebing, SUN Mengfei, QIAO Chenmeng, CHEN Xue, SHEN Yanqin, CUI Chun. Inhibitory effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus on intestinal inflammation after spinal cord injury in zebrafishes and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 680-686. |
| [12] | WEN Ying, WU Qiaoling, LIU Guoli. Protective effect of sufentanil post-conditioningthrough ERK1/2-mediated p70S6K signaling pathway on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injuryof rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 792-797. |
| [13] | WANG Yazhou, HE Peng, WANG Danhong. Effects of montelukast on proliferation and apoptosis of airway smooth muscle cells in asthmatic rats by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 274-279. |
| [14] | ZHOU Yabin, HUA Jin, QI Lingli, DAI Lu, PANG Xiaoli. Protective effect of curcumin pre-treatment on liver of acute ischemia-reperfusion model rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 297-301. |
| [15] | WANG Jianjun, LIU Yanan, WANG Jianhui, LIU Yan, LI Ying, WANG Ruixue, YANG Xiuhong. Protective effect of diminazene on kidney injury of limb ischemia-reperfusion model mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(01): 14-19. |