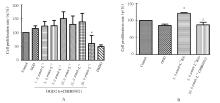
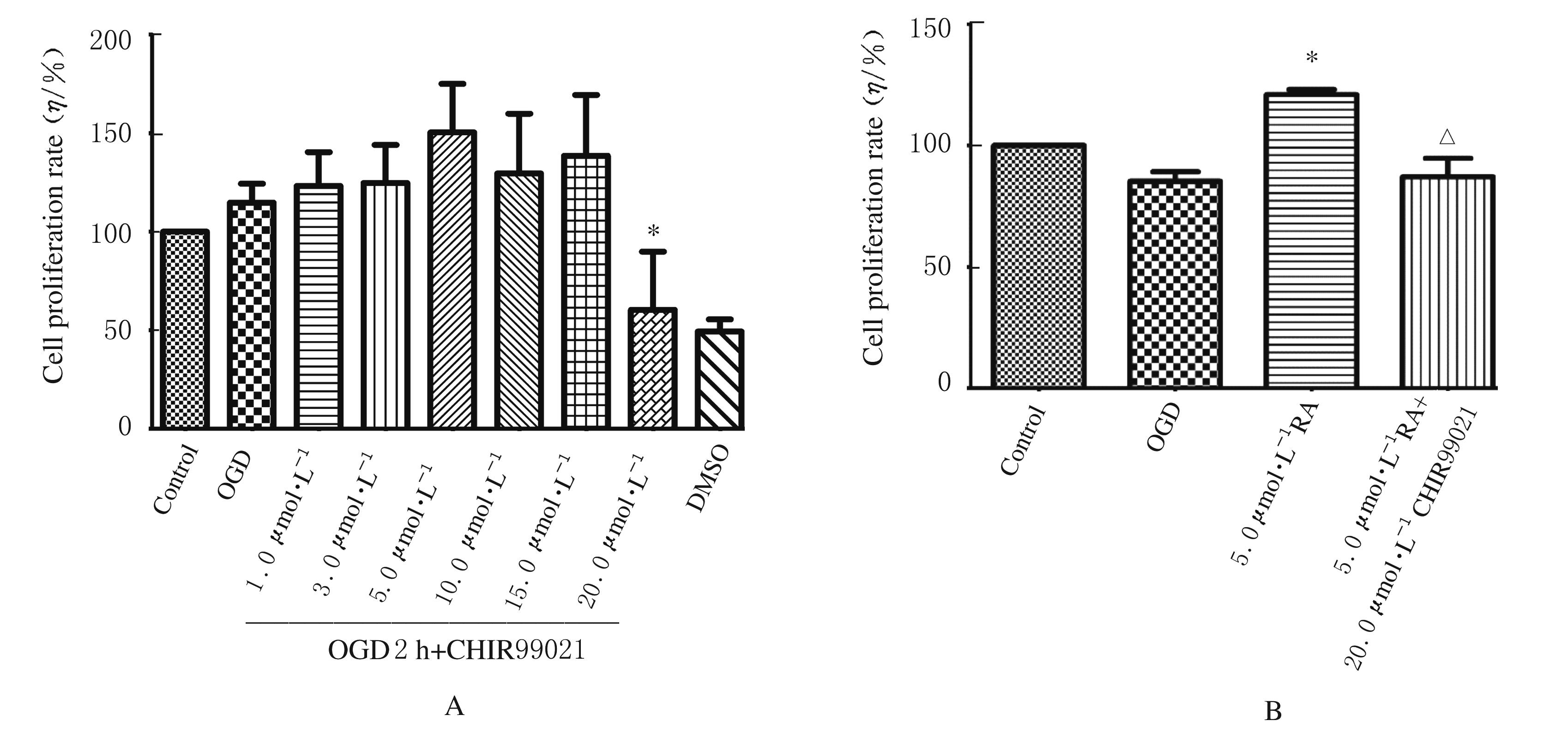
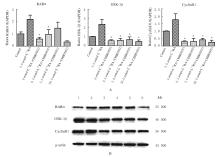
| [1] |
Zhijuan WANG,Mingshu ZHANG,Liping YE.
Effects of platelet-derived growth factor D on proliferation, migration and invasion of lung cancer H1299 cells through ERK signaling pathway and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 898-904.
|
| [2] |
Yandi MA,Xiangyun LU,Shangfeng HE,Xueyan YU,Yunhua HU,Haixia GAO,Yunzhao CHEN,Jie YU,Wenjie WANG,Feng LI,Xiaobin CUI.
Expression of m6A methylation binding protein YTHDF2 in esophageal carcinoma tissue and its effect on proliferation and migration of esophageal carcinoma cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 962-970.
|
| [3] |
Guowu WANG,Yuan YAO,Yu ZHANG,Na XU,Fang LIU.
Inhibitory effect of miR-152 on proliferation and invasion of endometrial carcinoma cells by reducing low-density lipoprotein receptor expression
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 591-599.
|
| [4] |
Guanhu LI,Qingxu LANG,Chunyan LIU,Qin LIU,Mengrou GENG,Xiaoqian LI,Zhenqi WANG.
Inhibitory effect of valproic acid combined with X-ray irradiation on proliferation of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 622-629.
|
| [5] |
Peiyu YAN,Aichen ZHANG,Hong ZHANG,Yang LI,Mengmeng ZHANG,Mengze LUO,Ying PAN.
Therapeutic effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on premature ovarian failure model rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 648-656.
|
| [6] |
Cuilan LIU,Fengai HU,Jing LIU,Dan WANG,Changyun QIU,Dunjiang LIU,Di ZHAO.
Effect of adiponectin receptor agonist AdiopRon on biological behaviors of glioma cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 702-710.
|
| [7] |
Zhuangzhi WU,Xiaoning HE,Siqi CHEN.
Inhibitory effect of miR-124-3p on proliferation and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 718-727.
|
| [8] |
Xiaoyan LI,Wei ZHANG,Jie HE.
Promotion effect of REG1A on proliferation and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 444-453.
|
| [9] |
Guangsong XU,Haibing JIANG,Jing PAN,Guoqing LI.
Inhibitory effects of betulinic acid on migration and invasion of gastric cancer MGC-803 cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 122-128.
|
| [10] |
Chaofeng ZHOU,Shifan ZHOU,Qing TIAN,Sai WANG,Honglin LI,Chunzheng MA.
Effect of lncRNA-NORAD overexpression on biological behaviors of esophageal cancer Eca-109 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 33-43.
|
| [11] |
Xin ZHANG,Chaojuan JU,Xin JIN,Chaohui XIONG,Yan ZHAO.
Protective effect of exogenous nerve growth factor on scleral tissue of guinea pigs with form-deprived myopia and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1455-1461.
|
| [12] |
Naigao TANG,Genjian ZHENG.
Effects of miR-762 on proliferation and apoptosis of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting NCOR1 expression
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1099-1107.
|
| [13] |
Yajie CAO,Xiaohong BAO,Shuzhen LI,Haiying GENG,Zengxiaorui CAI,Chunmei DAI,Ning LI.
Effects of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor NVP-AEW541 on proliferation, migration and invasion of ESCC cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1131-1138.
|
| [14] |
Chen WANG,Jun TIAN,Hailing CHENG.
Effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer HeLa cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1187-1193.
|
| [15] |
Meng QU,Shiya WENG,Hong ZHENG,Yan LI,Runze GAO,Shenggao WANG,Chunyan YU,Boxue CHEN,Zhiheng DONG.
Protective effect of fermented red ginseng total saponins on rat myocardial interstitial fibroblasts cultured with high glucose and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1201-1208.
|
 )
)