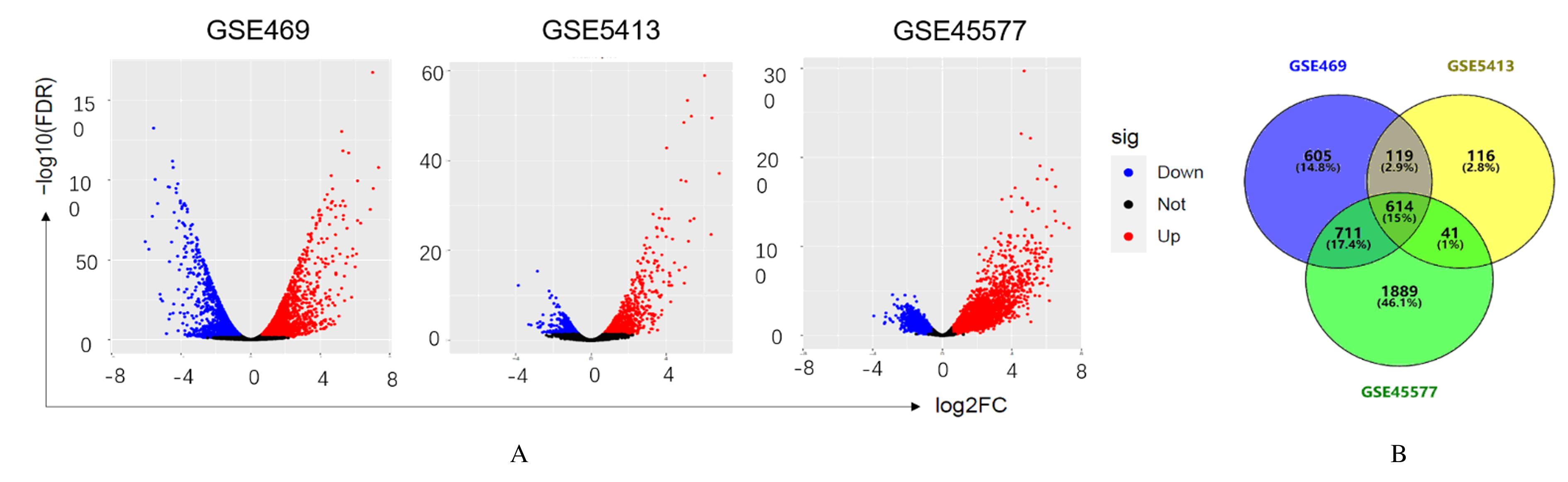
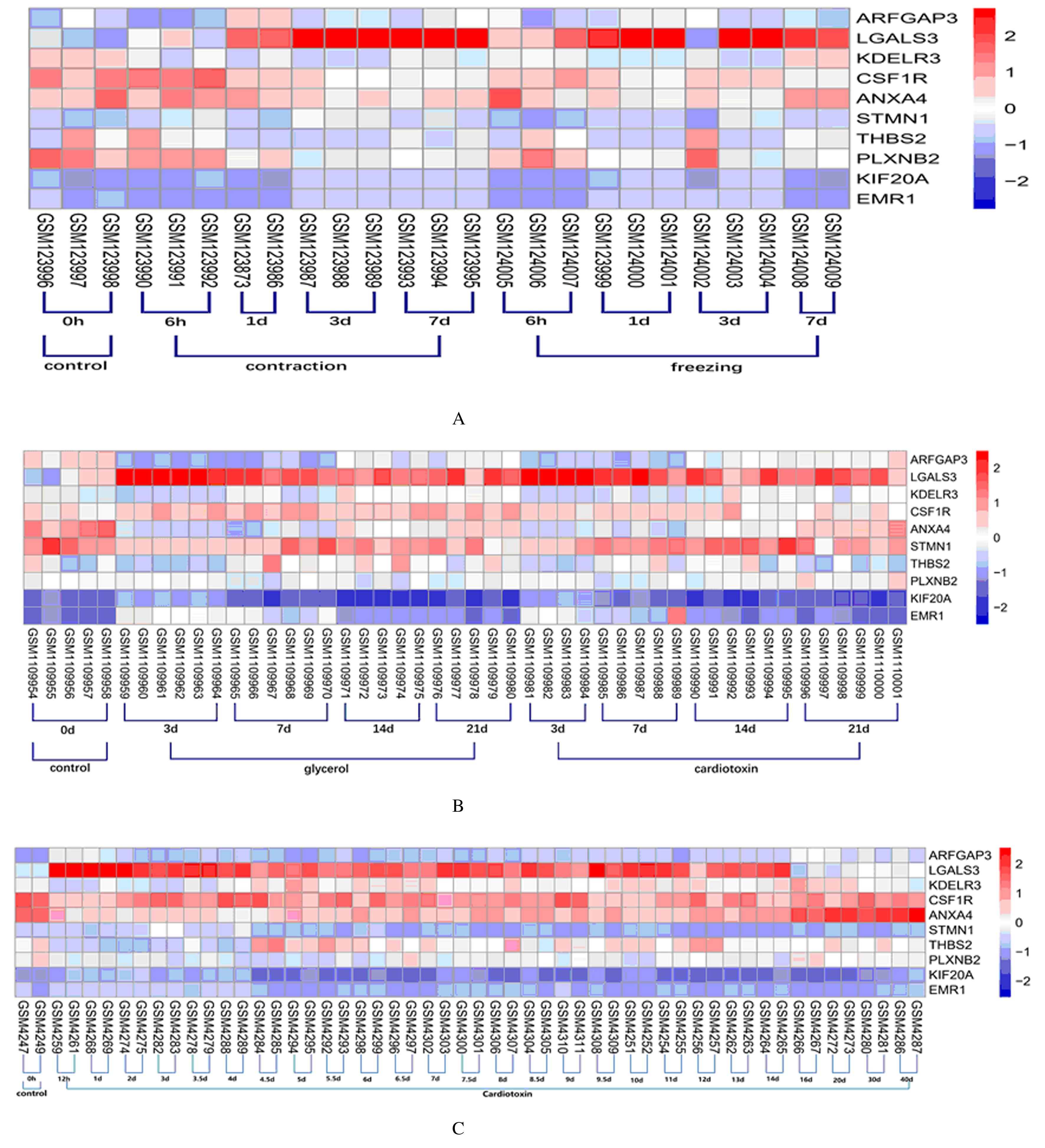
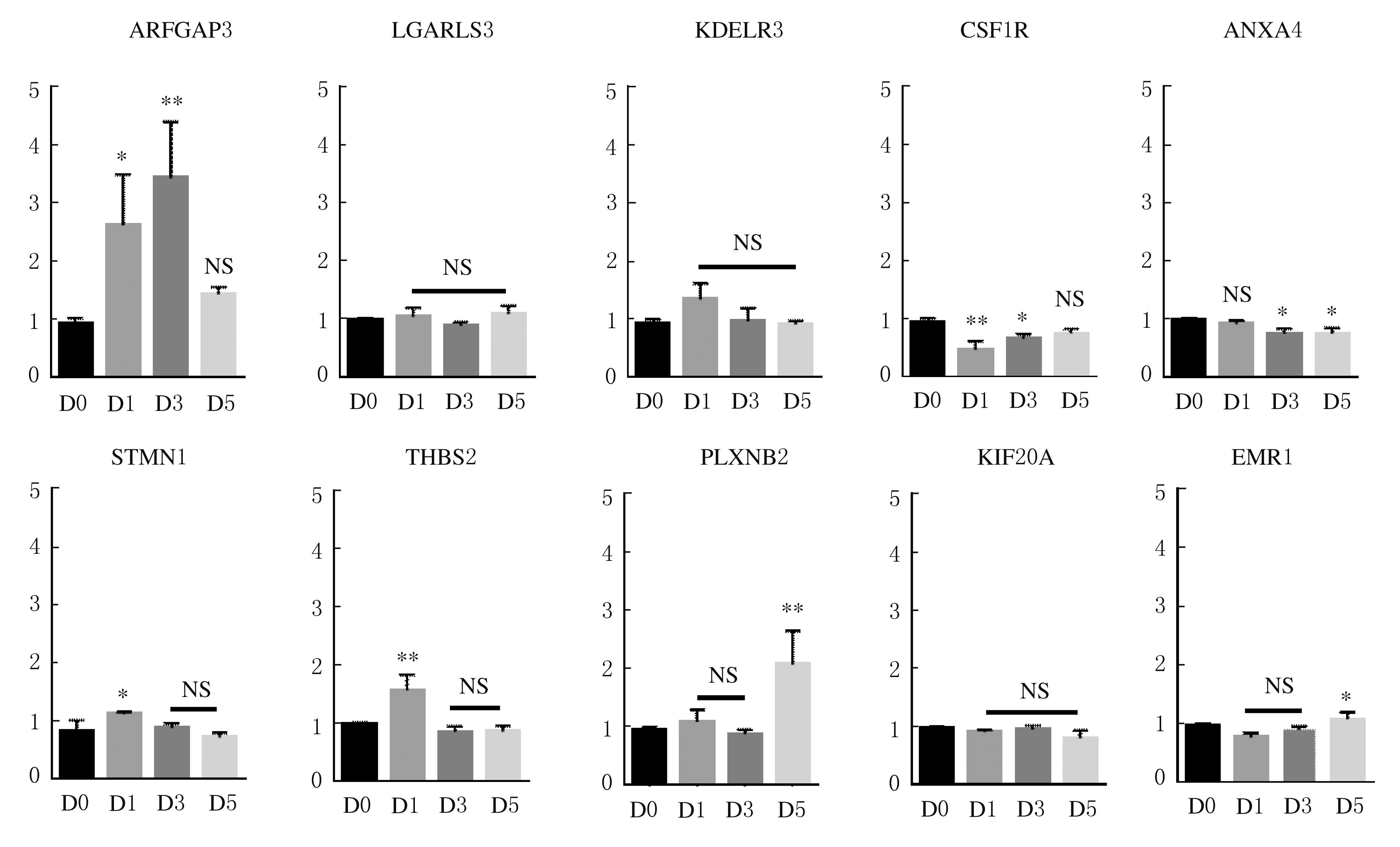
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 1092-1098.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210503
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Expressions of vesicle transport-related genes during repair of pelvic floor muscles after injury
Jue CHEN,Li HONG( ),Suting LI,Zhi WANG,Mao CHEN,Menglei HAO,Ya XIAO,Jie MIN,Ming HU
),Suting LI,Zhi WANG,Mao CHEN,Menglei HAO,Ya XIAO,Jie MIN,Ming HU
- Department of Gynecology and Obestetrics,People’s Hospital,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430060,China
-
Received:2021-01-05Online:2021-09-28Published:2021-10-26 -
Contact:Li HONG E-mail:dr_hongli@whu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R711.4
Cite this article
Jue CHEN,Li HONG,Suting LI,Zhi WANG,Mao CHEN,Menglei HAO,Ya XIAO,Jie MIN,Ming HU. Expressions of vesicle transport-related genes during repair of pelvic floor muscles after injury[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1092-1098.
share this article
Tab.1
Primer sequences of RT-qPCR"
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| ARFGAP3 | 5'-CGAGGAGGAAGTACCAGGAGGAC-3' | 5'-CCAGTAGGAATCGGCACCATCATC-3' |
| LGARLS3 | 5'-CAGGACAGGCTCCTCCTAGTGC-3' | 5'-GCAGCAGGATAGCCTCCAGGAG-3' |
| KDELR3 | 5'-TGAACTACAGTTACACGCCGATGG-3' | 5'-AGTGGTGATGGTCTCAGCCTCTC-3' |
| CSF1R | 5'-CCTCCTCTGGTCCTGCTGCTG-3' | 5'-TTCCACACTGCCATTGCTCACAC-3' |
| ANXA4 | 5'-GGCTTAGGCACTGATGACAACACC-3' | 5'-CACAGAGAACGAGCAGAACCTTCC-3' |
| STMN1 | 5'-GCAAGATGGCGGAGGAGAAGC-3' | 5'-TTGTTCTTCCGCACCTCTTCCAC-3' |
| THBS2 | 5'-CAGATTGGCTACGCAGGTGATGG-3' | 5'-CATCGTCCTCGTCACAAGCATCTC-3' |
| PLXNB2 | 5'-CAGAAGCGAGACACGGCACAC-3' | 5'-TACCATGACCAGAGGCAGGATGAG-3' |
| KIF20A | 5'-CCAGCAATCCAGCCGCAGTC-3' | 5'-TCAGAGCCAGCCAGGTCACAG-3' |
| EMR1 | 5'-TGGCAAGCATCATGGCATACCTG-3' | 5'-TGACGGTTGAGCAGACAGTGAATG-3' |
| GAPDH | 5'-AGGAGCGAGACCCCACTAACA-3' | 5'-AGGGGGGCTAAGCAGTTGGT-3' |
| 1 | ZHU L, LANG J, LIU C, et al. The epidemiological study of women with urinary incontinence and risk factors for stress urinary incontinence in China[J]. Menopause, 2009, 16(4): 831-836. |
| 2 | EICKMEYER S M. Anatomy and physiology of the pelvic floor[J]. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am, 2017, 28(3): 455-460. |
| 3 | CHAN S S, CHEUNG R Y, YIU K W, et al. Pelvic floor biometry in Chinese primiparous women 1 year after delivery: a prospective observational study[J]. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol,2014, 43(4): 466-474. |
| 4 | ZAMMIT P S. Function of the myogenic regulatory factors Myf5, MyoD, Myogenin and MRF4 in skeletal muscle, satellite cells and regenerative myogenesis[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol,2017, 72:19-32. |
| 5 | 郑 琪,睢梦华,凌英会. 骨骼肌卫星细胞增殖与成肌分化过程中关键信号通路的作用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2017, 48(11): 2005-2014. |
| 6 | BECK R, RAWET M, WIELAND F T, et al. The COPI system: molecular mechanisms and function[J]. FEBS Lett, 2009, 583(17): 2701-2709. |
| 7 | NAKAMURA Y, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H,et al. Mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived exosomes accelerate skeletal muscle regeneration[J]. FEBS Lett,2015, 589(11): 1257-1265. |
| 8 | 张潜英,李 虎,李常银,等. 骨骼肌组织来源的外泌体促进骨骼肌干细胞增殖并抑制其分化[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2018, 40(7): 1171-1178. |
| 9 | 李云霞,陈世益. 胰岛素样生长因子促进骨骼肌损伤修复[J]. 体育科研, 2003(1): 33-40. |
| 10 | 王大鹏,张桂梅,罗力佳. 细胞生长因子修复骨骼肌损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(2): 273-278. |
| 11 | 左 群,于新凯,李 男. 骨骼肌损伤和修复中炎症细胞因子作用的研究进展[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2012, 27(9): 878-881. |
| 12 | 孙 茹. 骨骼肌损伤与修复过程中炎症反应与肌卫星细胞再生关系的研究[D]. 长春:东北师范大学, 2009. |
| 13 | EDGAR R, DOMRACHEV M, LASH A E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2002, 30(1): 207-210. |
| 14 | BARRETT T, WILHITE S E, LEDOUX P, et al. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets--update[J]. Nucleic Acids Res,2013,41(Database issue): D991-D995. |
| 15 | 李素廷,洪 莉,汤剑明,等. 模拟产伤法构建小鼠肛提肌损伤模型及效果评价[J]. 中国计划生育和妇产科, 2019, 11(10): 88-91. |
| 16 | YI Y, WANG L, Li S, et al. Effects of mechanical trauma on the differentiation and ArfGAP3 expression of C2C12 myoblast and mouse levator ani muscle[J]. Int Urogynecol J, 2020, 31(9): 1913-1924. |
| 17 | WARREN G L, SUMMAN M, GAO X, et al. Mechanisms of skeletal muscle injury and repair revealed by gene expression studies in mouse models[J].J Physiol, 2007, 582(Pt 2): 825-841. |
| 18 | LUKJANENKO L, BRACHAT S, PIERREL E,et al. Genomic profiling reveals that transient adipogenic activation is a hallmark of mouse models of skeletal muscle regeneration[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(8): e71084. |
| 19 | ZHAO P, IEZZI S, CARVER E, et al. Slug is a novel downstream target of MyoD. Temporal profiling in muscle regeneration[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(33): 30091-30101. |
| 20 | DADGAR S, WANG Z, JOHNSTON H, et al. Asynchronous remodeling is a driver of failed regeneration in Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. J Cell Biol, 2014, 207(1): 139-158. |
| 21 | SANGSAWANG B, SANGSAWANG N. Stress urinary incontinence in pregnant women: a review of prevalence, pathophysiology, and treatment[J]. Int Urogynecol J, 2013, 24(6): 901-912. |
| 22 | 陈 娟,郎景和,朱 兰,等. 压力性尿失禁及盆底组织膨出患者肛提肌形态学的观察[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2004(8): 19-21. |
| 23 | STAER-JENSEN J, SIAFARIKAS F, HILDE G,et al. Postpartum recovery of levator hiatus and bladder neck mobility in relation to pregnancy[J].Obstet Gynecol, 2015, 125(3): 531-539. |
| 24 | 陈犹白,张 巍,栗 利,等. 脂肪干细胞成肌分化及修复骨骼肌损伤:应用现状及未来研究方向[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(1): 126-132. |
| [1] | Xia LI,Yi YU,Haiwei ZUO,Fengjuan ZHOU,Yong XIN. Inhibitory effect of circRNA on colorectal cancer and its bioinformatics analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1283-1287. |
| [2] | WANG Zhi, HONG Li, LI Suting, ZENG Wanling. Analysis on endometrial cancer-related genes and candidate pathways based on GEO database bioinformatics methods [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 804-809. |
| [3] | CHEN Bingpeng, REN Ming, LI Ronghang, HAN Qing, WANG Jincheng. Regulatory effect of NOB1 on osteosarcoma cell-related genes detected by gene microarray technique [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(05): 929-934. |
| [4] | TIAN Dan, SUN Xin, AN Xiaoting, ZHANG Liyan, LIU Yang, TONG Haibin, LI Tan, SHEN Ye, MAN Fanglin, YAN Weiqun. Construction and eukaryotic expression of recombinant HSA-TP5 fusion gene expression vector [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(05): 948-952. |
| [5] | XIN Guijie, ZHU Haichao, LI Hao, WEN Jianping. Induction of cellular immunity by HCV multi-epitope DNA vaccine prepared with minimalistic immunologically defined gene expression method in mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(06): 1071-1075. |
| [6] | QI Ling, WANG Weiyao, ZHENG Zhonghua, ZHANG Yizhong, ZHAO Liwei, ZHONG Xiuhong, ZHAO Donghai, YANG Shuyan, YANG Ningjiang, REN Kuang, YU Hongquan. Effects of SUMO and proteins modified by SUMO on occurrence of malignant gliomas [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(01): 7-10. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xue,CHEN Ping,BI Yun-feng,QU Ning-ning,LIU Qiong,SUN Xin-ze. Cloning and expression of nitrite reductase gene from Alcaligenes xylosoxidans [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(4): 690-693. |
| [8] | SUN Xiao-yu,HE Zhong-qin,LIU Xiao-hong,GAO Xin,ZHONG Cheng,XUE Ying. Cloning,expression,and purification of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase gene of Veillonella dispar [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(4): 704-709. |
| [9] | JIA Xiao-hui,LUO Jian-min,LIU Ya-ping,YIN Wan-yi,ZHANG LI-hong. Expressions of SHIP and Caspase-3 mRNA in bone marrow tissue of [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(3): 554-558. |
| [10] | WU Xian-jun,MIAO Xuan,CHENG Xiu,WANG Yan-qing,TSUJI Ichiro,LI Xiao-meng. Recombination of GFP-SUMO-3 fusion protein and its expression and localization in LNCaP cells [J]. J4, 2011, 37(6): 1024-1027. |
| [11] | SUN Ling,LIU Hui-ying,LI Shu-hong,GONG Peng-tao,ZHANG Xi-chen,NING Jing. Cloning and prokaryotic expression of GRA1 gene of Toxoplasma gondii [J]. J4, 2011, 37(4): 631-635. |
| [12] | LIU Ji, JIA Tian-Jun, LIU Xue-Qing, JIA Xiao-Hui, ZHAI Xue-Qiong. Cloning and identification of C-terminal gene encoding human mannose-binding lectin associated serine protein kinase-2 [J]. J4, 2011, 37(1): 51-55. |
| [13] | ZHAO Li-Jing, XUDuo, CHENG Hong, LIANG Zuo-Wen, LU Yu-Ming, HAN Xiang-Bei, GUO Ya-Xiong, ZHAO Li-Juan, DONG Yan. Effects of 20(s)-proto-panaxdiol oncaspase-3 expression and activation in Siha cells in vitro [J]. J4, 2011, 37(1): 26-29. |
| [14] | LI Zhi, LANG Xiao-Ou, ZHANG Shao-Jun, Jiang Wen-Hua. Expressions of Stat3 and Stat5 in differentiated thyroid carcinoma tissues |and significances [J]. J4, 2010, 36(4): 708-712. |
| [15] |
LI Jing, PIAO Yun-Feng, JIANG Zheng, AN Ding-Wei, JIN Li-Jun.
Expressions of STAT3 gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines HepG2,Bel7402,SMMC7721 and hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and their significances [J]. J4, 2010, 36(3): 531-535. |