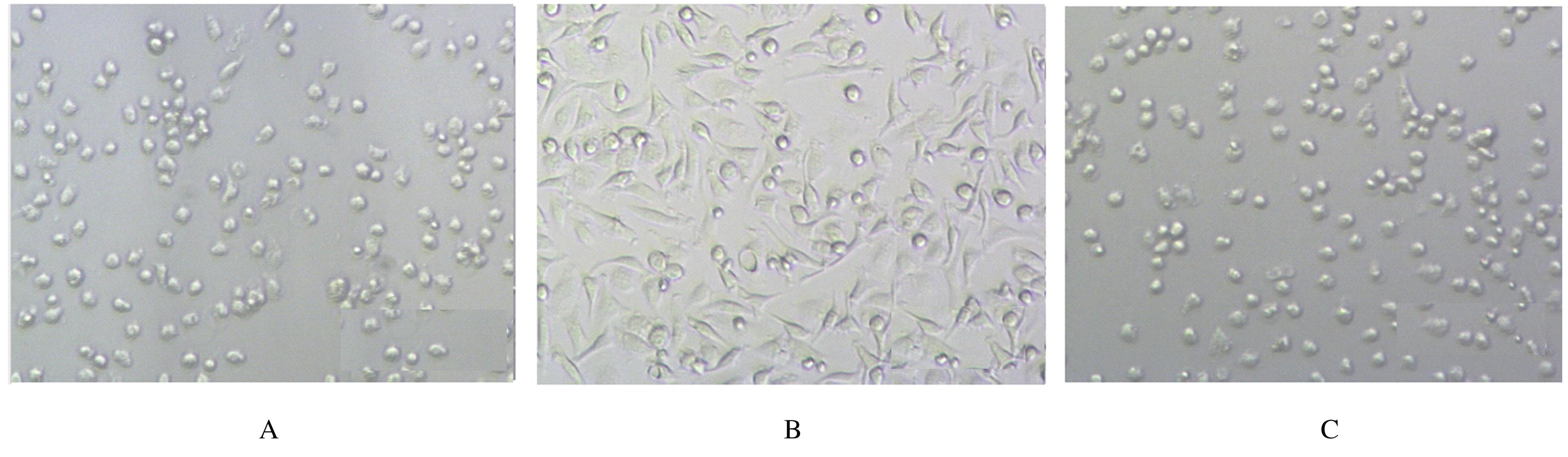
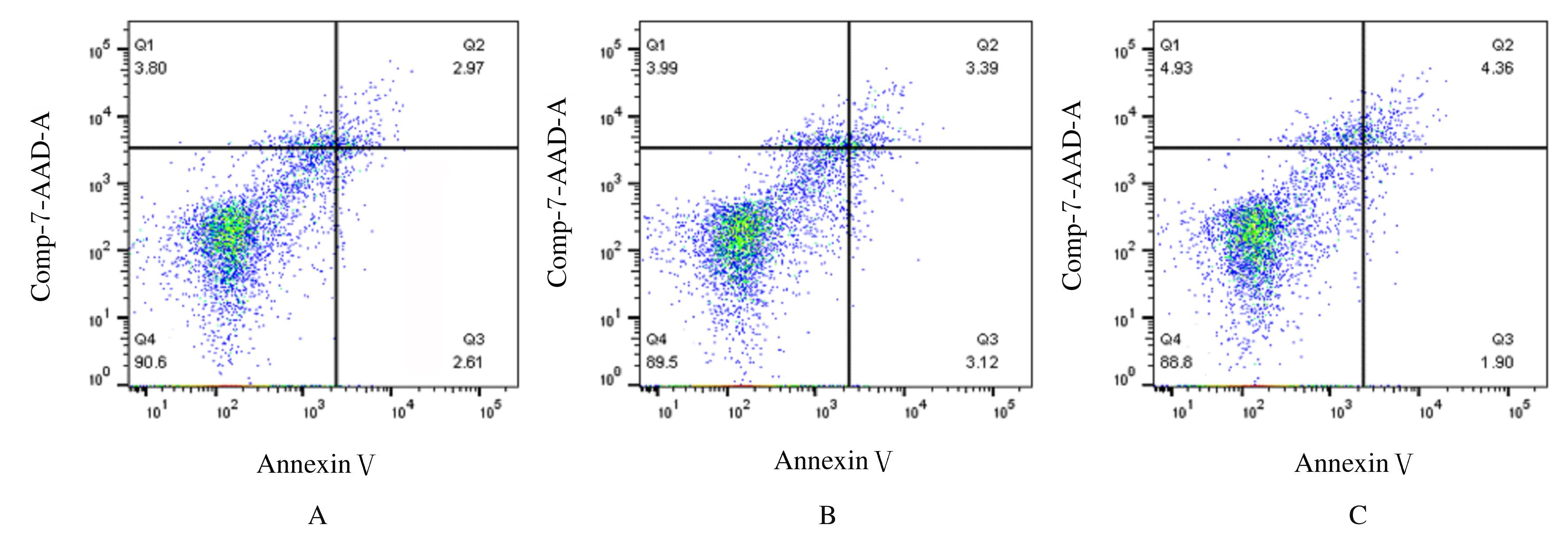
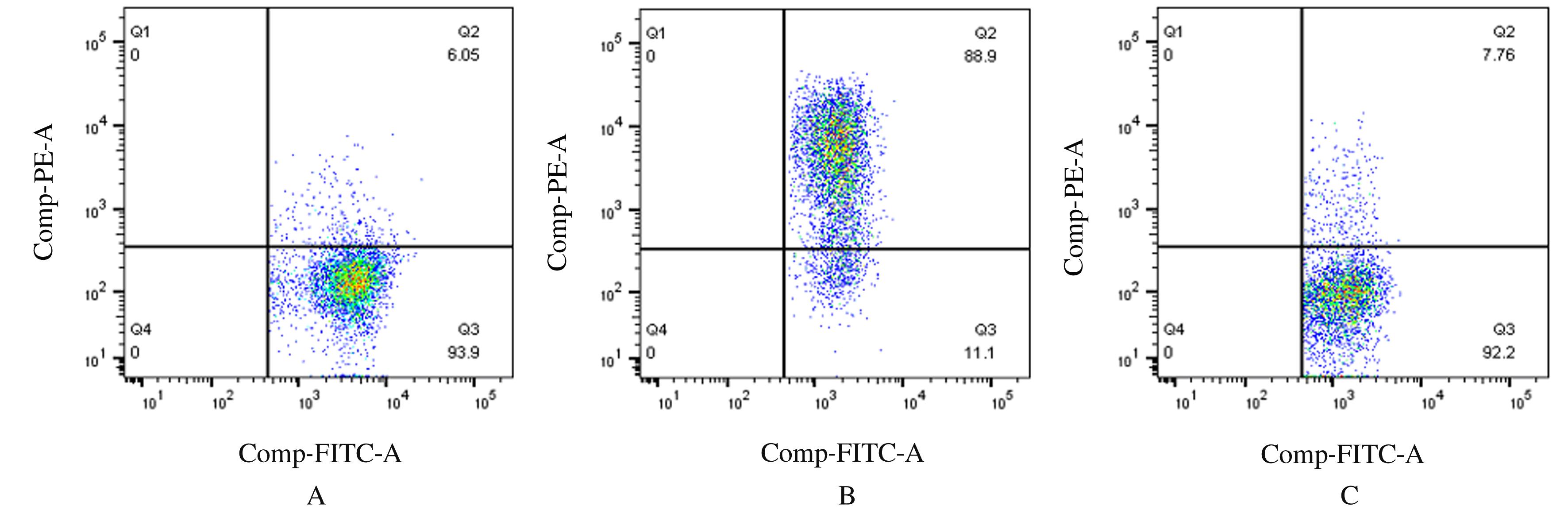
| 1 |
LECOULTRE M, DUTOIT V, WALKER P R. Phagocytic function of tumor-associated macrophages as a key determinant of tumor progression control: a review[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2020, 8(2): 1408.
|
| 2 |
KONG X Y, GAO J. Macrophage polarization: a key event in the secondary phase of acute spinal cord injury[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2017, 21(5): 941-954.
|
| 3 |
LEOPOLD WAGER C M, HOLE C R, WOZNIAK K L,et al. STAT1 signaling within macrophages is required for antifungal activity against Cryptococcus neoformans[J].Infect Immun,2015,83(12):4513-4527.
|
| 4 |
SICA A, ERRENI M, ALLAVENA P, et al. Macrophage polarization in pathology[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2015, 72(21): 4111-4126.
|
| 5 |
PARISI L, GINI E, BACI D, et al. Macrophage polarization in chronic inflammatory diseases: killers or builders? [J]. J Immunol Res, 2018, 2018: 1-25.
|
| 6 |
OZ H. Chronic inflammatory diseases and green tea polyphenols[J]. Nutrients, 2017, 9(6): 561.
|
| 7 |
AFZAL M, SAFER A M, MENON M. Green tea polyphenols and their potential role in health and disease[J]. Inflammopharmacology,2015,23(4): 151-161.
|
| 8 |
NGUYEN-NGO C, SALOMON C, LAI A, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Gallic acid in human gestational tissues in vitro [J]. Reprod Camb Eng, 2020, 160(4): 561-578.
|
| 9 |
黄丽华, 侯 林, 薛海南, 等. 没食子酸通过拮抗脂多糖诱导的TLR4/NF-κB活化抑制RAW264.7巨噬细胞炎性反应[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2016, 32(12): 1610-1614.
|
| 10 |
AHN C B, JUNG W K, PARK S J, et al. Gallic acid-g-chitosan modulates inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells via NF-κB, AP-1, and MAPK pathways[J]. Inflammation, 2016, 39(1): 366-374.
|
| 11 |
吴 静, 付海英, 张英林, 等. DNA-PKcs协同自身免疫调节因子调控小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞toll样受体的表达及其意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版),2012,38(6):1063-1067.
|
| 12 |
吴 琼, 王乐锋, 张妍淞, 等. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯通过NF-κB通路抑制脂多糖诱导的巨噬细胞向M1表型极化[J]. 食品科学, 2018, 39(1): 142-148.
|
| 13 |
LEE W J, TATEYA S, CHENG A M, et al. M2 macrophage polarization mediates anti-inflammatory effects of endothelial nitric oxide signaling[J]. Diabetes, 2015, 64(8): 2836-2846.
|
| 14 |
MAURO A, RUSSO V, DI MARCANTONIO L,et al. M1 and M2 macrophage recruitment during tendon regeneration induced by amniotic epithelial cell allotransplantation in ovine[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2016, 105: 92-102.
|
| 15 |
XING J, LI R, LI N, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of procyanidin B1 on LPS-treated THP1 cells via interaction with the TLR4-MD-2 heterodimer and p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2015, 407(1/2): 89-95.
|
| 16 |
SAKHARWADE S C, MUKHOPADHAYA A. Vibrio cholerae porin OmpU induces LPS tolerance by attenuating TLR-mediated signaling[J]. Mol Immunol, 2015, 68(2): 312-324.
|
| 17 |
SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(9): 6425-6440.
|
| 18 |
MÜLLER C, CHARNIGA C, TEMPLE S, et al. Quantified F-actin morphology is predictive of phagocytic capacity of stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelium[J]. Stem Cell Res, 2018, 10(3):1075-1087.
|
| 19 |
MCGARRITY S, ANUFORO Ó, HALLDÓRSSON H,et al. Metabolic systems analysis of LPS induced endothelial dysfunction applied to sepsis patient stratification[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 6811.
|
| 20 |
孙 颖, 刘 玲, 施晓艳, 等. 丹皮酚通过下调miR-155/JAK1-STAT1通路抑制巨噬细胞M1极化[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2020, 45(9): 2158-2164.
|
| 21 |
KAWADA M, OHNO Y, RI Y, et al. Anti-tumor effect of Gallic acid on LL-2 lung cancer cells transplanted in mice[J].Anticancer Drugs,2001,12(10):847-852.
|
| 22 |
WEN L, QU T B, ZHAI K, et al. Gallic acid can play a chondroprotective role against AGE-induced osteoarthritis progression[J]. J Orthop Sci,2015,20(4): 734-741.
|
| 23 |
SAKALAUSKAS A, ZIAUNYS M, SMIRNOVAS V.Gallic acid oxidation products alter the formation pathway of insulin amyloid fibrils[J].Sci Rep, 2020,10(1): 14466.
|
| 24 |
籍 辰, 张文娟, 关 宁, 等. M1型巨噬细胞对慢性牙周炎模型小鼠免疫状态的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2020, 46(6): 1137-1142, 1346.
|
| 25 |
吴柏霖, 李森茂, 胡 嘏, 等. 一水草酸钙晶体介导巨噬细胞炎症反应的体外研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报(医学版), 2015, 44(5): 505-509.
|
| 26 |
张晓静, 崔梦珂, 辛广远, 等. 花青素Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside对脂多糖和白介素-4刺激的小鼠骨髓巨噬细胞极化的影响[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2019, 35(11): 1320-1324.
|
| 27 |
BAEK H S, MIN H J, HONG V S, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of the novel PIM kinase inhibitor KMU-470 in RAW 264.7 cells through the TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(14): 5138.
|
| 28 |
LIU Y L, HSU C C, HUANG H J, et al. Gallic acid attenuated LPS-induced neuroinflammation: protein aggregation and necroptosis[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2020, 57(1): 96-104.
|
| 29 |
尹学红, 庞春燕, 白 力, 等. 脂肪间充质干细胞促进M1型巨噬细胞向M2型巨噬细胞转化[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2016, 32(3): 332-338.
|
| 30 |
ADHYA D, DUTTA K, KUNDU K, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibition by Japanese encephalitis virus in monocyte/macrophages: a novel viral immune evasion strategy[J]. Immunobiology, 2013,218(10):1235-1247.
|
| 31 |
寇玥婷,成颖莹,王 娟,等.5-羟色胺4受体激动剂对糖尿病小鼠结肠黏膜巨噬细胞极化的影响[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2021,42(4):453-458,466.
|
| 32 |
DE PALMA M, LEWIS C E. Macrophage regulation of tumor responses to anticancer therapies[J]. Cancer Cell, 2013, 23(3): 277-286.
|
| 33 |
LIN W H, KUO H H, HO L H, et al. Gardenia jasminoides extracts and Gallic acid inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by suppression of JNK2/1 signaling pathways in BV-2 cells[J]. Iran J Basic Med Sci, 2015, 18(6): 555-562.
|
 ),Ning GUAN2,Xiuqiu GAO1
),Ning GUAN2,Xiuqiu GAO1