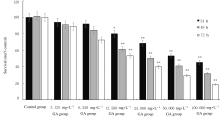
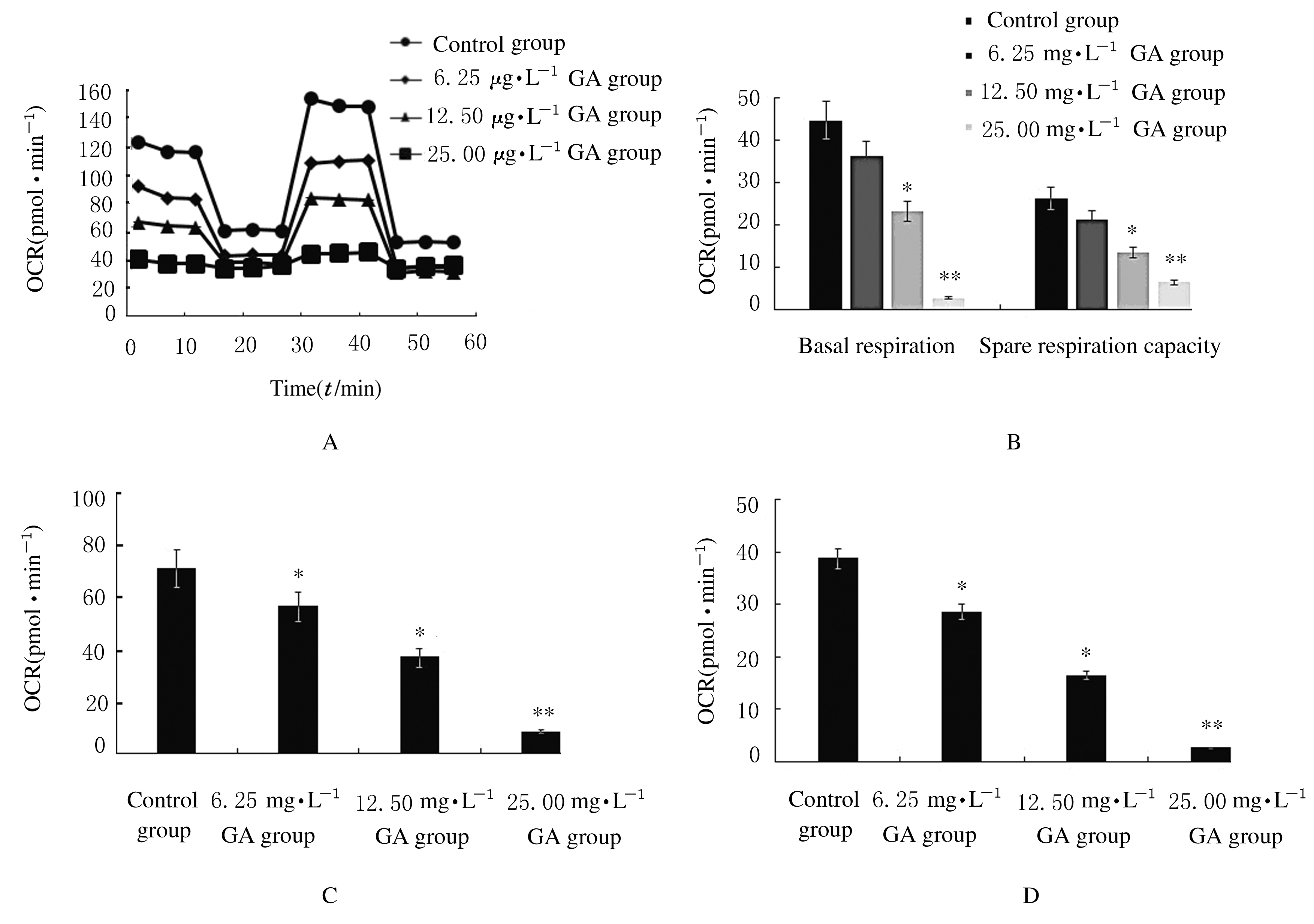
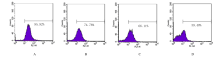
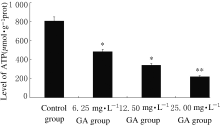
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 125-132.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20210117
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
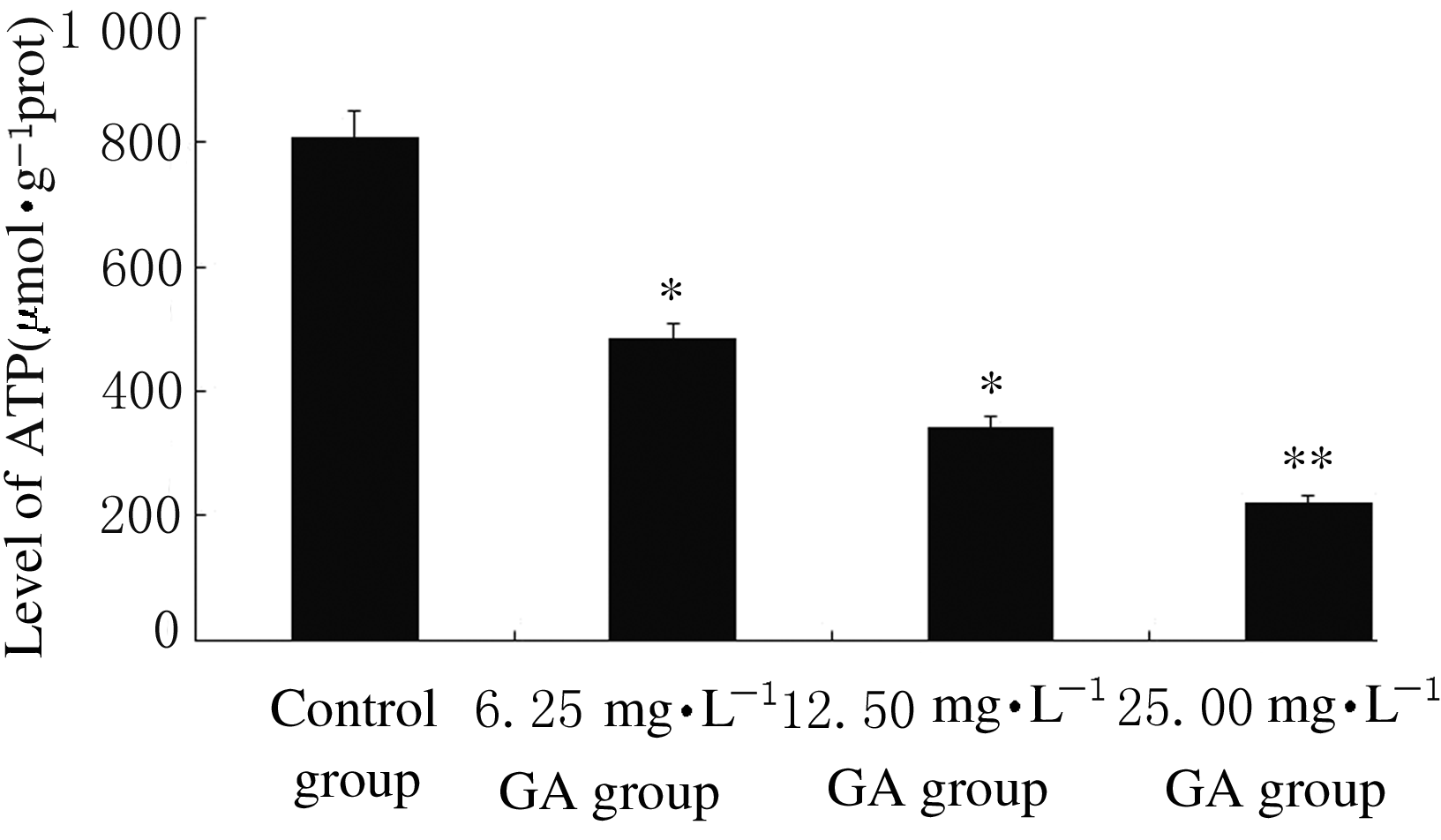
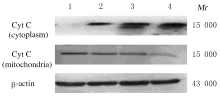
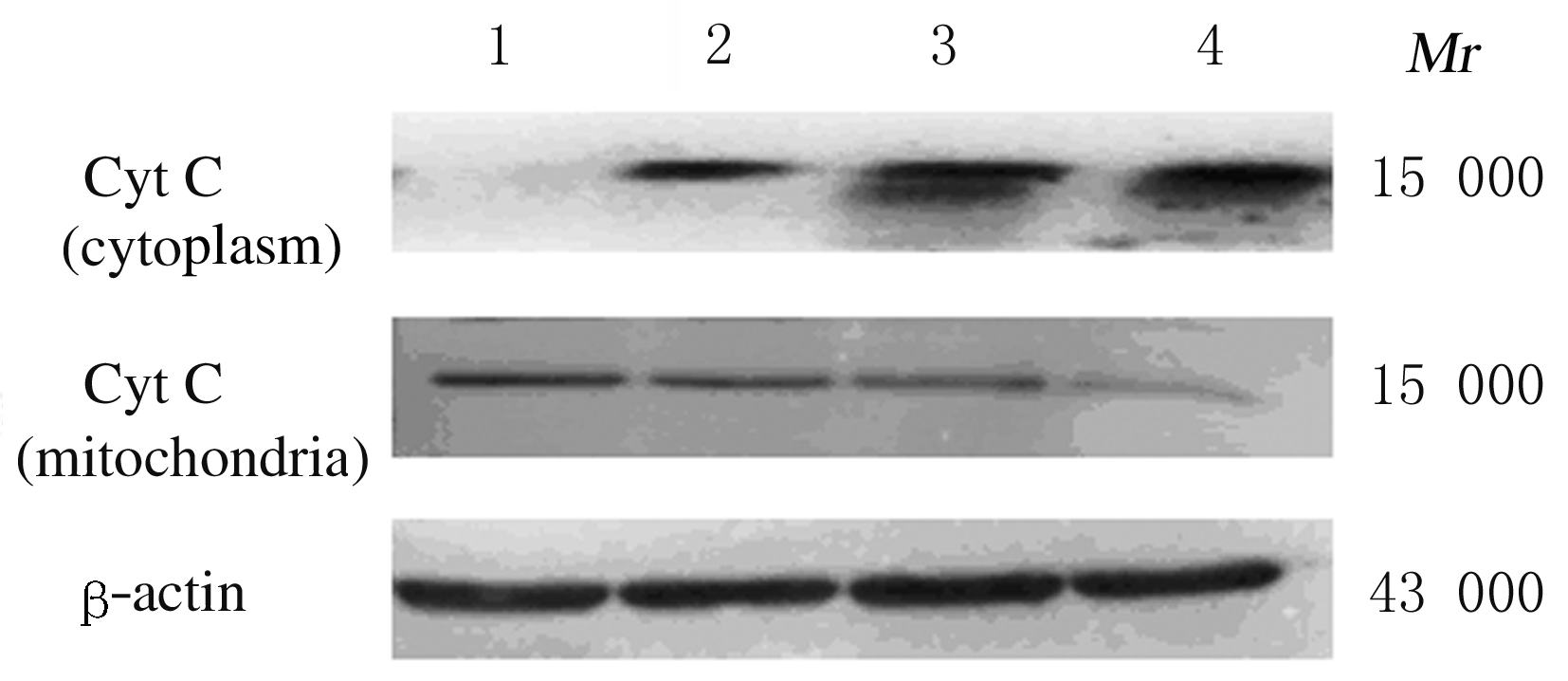
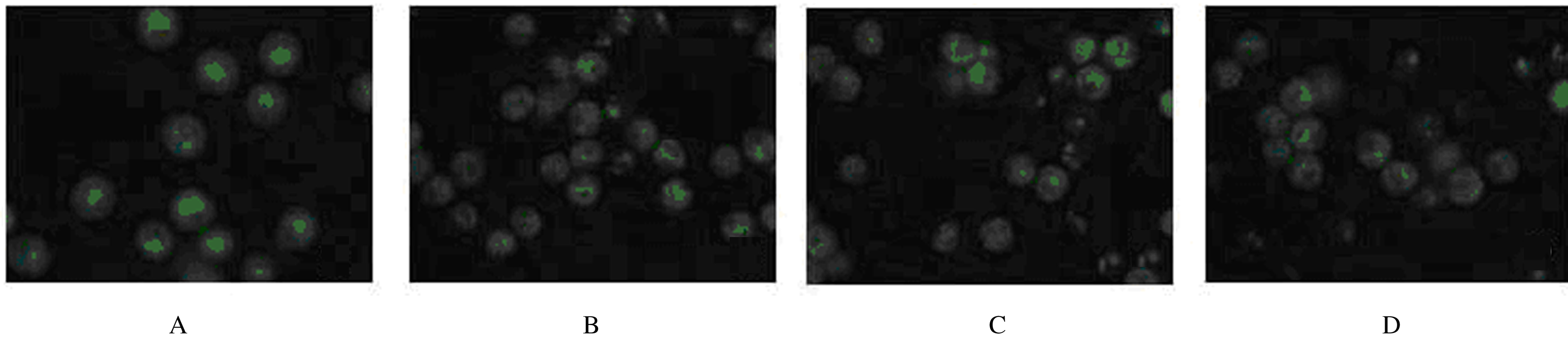
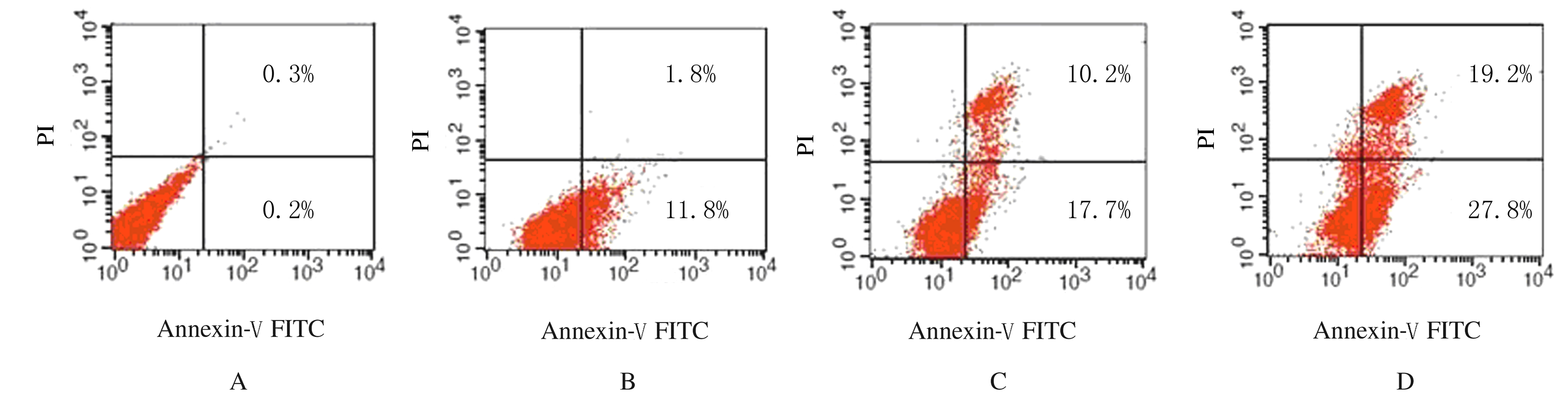
Induction effect of gallic acid on apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG-2 cells through regulating mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation
Haiying ZHANG1,Wenxin ZHANG1,2,Wenjing ZHAO2,Wei LI1( )
)
- 1.Key Laboratory of Pathology,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.Central Laboratory,Hepatobiliary Disease Hospital of Jilin Province,Changchun 130062,China
-
Received:2020-03-31Online:2021-01-28Published:2021-01-27 -
Contact:Wenjing ZHAO,Wei LI E-mail:liwei2006@jlu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R285.5
Cite this article
Haiying ZHANG,Wenxin ZHANG,Wenjing ZHAO,Wei LI. Induction effect of gallic acid on apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG-2 cells through regulating mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 125-132.
share this article
| 1 | WARBURG O, WIND F, NEGELEIN E. The metabolism of tumors in the body[J]. J Gen Physiol, 1927, 8(6):519-530. |
| 2 | CHENG M H, HUANG H L, LIN Y Y, et al. BA6 induces apoptosis via stimulation of reactive oxygen species and inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation in human lung cancer cells[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 6342104. |
| 3 | ASHTON T M, MCKENNA W G, KUNZ-SCHUGHART L A, et al. Oxidative phosphorylation as an emerging target in cancer therapy[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 24(11):2482-2490. |
| 4 | CHANG J C, CHANG H S, WU Y C, et al. Mitochondrial transplantation regulates antitumour activity, chemoresistance and mitochondrial dynamics in breast cancer[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2019,38(1): 30-46. |
| 5 | RYU Y, JIN L, KEE H J, et al. Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity [J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 34790. |
| 6 | PARK B, LEE S, LEE B, et al.New ethanol extraction improves the anti-obesity effects of black tea [J]. Arch Pharm Res, 2016, 39(3): 310-320. |
| 7 | ASNAASHARI M, FARHOOSH R, SHARIF A. Antioxidant activity of gallic acid and methyl gallate in triacylglycerols of Kilka fish oil and its oil-in-water emulsion [J]. Food Chem, 2014, 159: 439-444. |
| 8 | JIN L,PIAO Z H,LIU C P, et al. Gallic acid attenuates calcium calmodulin-dependent kinase Ⅱ-induced apoptosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats [J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(3):1517-1526. |
| 9 | XINTAQROPOULOU C, WARD C, WISE A, et al. Expression of glycolytic enzymes in ovarian cancers and evaluation of the glycolytic pathway as a strategy for ovarian cancer treatment [J]. BMC Cancer, 2018,18(1): 636. |
| 10 | 王丽萍,丁一,刘国红,等.五倍子酸对人纤维肉瘤HT1080细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版),2015, 50(1):58-61. |
| 11 | SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, JEMAL A, et al. Cancer ststistics, 2019 [J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2019, 69(1):7-34. |
| 12 | GLOBAL BURDEN OF DISEASE CANCER COLLABORATION,FITZMAURICE C, ALLEN C, et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2017,3(4): 524-548. |
| 13 | YANG J D, HAINAUT P, GORES G J, et al. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management [J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019,16 (10):589-604. |
| 14 | 顾 欢,白长川, 刘 柳,等. 中医药调控自噬治疗肝癌的研究现状[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2019,35(11): 2582-2587. |
| 15 | 万敏婕,高普均.诱导和利用肿瘤细胞弱点治疗肝癌[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2020,36(2):318. |
| 16 | ZHANG L, YAO Y X, ZHANG S J, et al. Metabolic reprogramming toward oxidative phosphorylation identifies a therapeutic target for mantle cell lymphoma[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2019,11 (491):eaau1167. |
| 17 | ZHAO L J, ZHAO X Y , ZHAO K, et al. The α-tocopherol derivative ESeroS-GS induces cell death and inhibits cell motility of breast cancer cells through the regulation of energy metabolism [J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2014, 745:98-107. |
| 18 | 范霞霞,苏 楠,黄晓婧,等. 天然二萜衍生物Jar-TTA双重抑制糖酵解及氧化磷酸化诱导食管癌细胞凋亡[J].中国药理学通报,2019,35(7):950-958. |
| 19 | CHEN Y F, SHIH P C, KUO H M, et al. TP3, an antimicrobial peptide, inhibits infiltration and motility of glioblastoma cells via modulating the tumor microenvironment [J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(11): 3918-3931. |
| 20 | CHENG M H, PAN C Y, CHEN N F, et al. Piscidin-1 induces apoptosis via mitochondrial reactive oxygen species-regulated mitochondrial dysfunction in human osteosarcoma cells [J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10: 5045. |
| 21 | ZHANG L, CHINNATHAMBI A, ALHARBI S A, et al. Punicalagin promotes the apoptosis in human cervical cancer (ME-180) cells through mitochondrial pathway and by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Saudi J Biol Sci, 2020, 27(4): 1100-1106. |
| 22 | CHEN Y C, LU M C, EL-SHAZLY M, et al. Breaking down leukemia walls: heteronemin, a sesterterpene derivative, induces apoptosis in leukemia Molt4 cells through oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and induction of talin expression [J]. Mar Drugs, 2018,16(6):E212. |
| 23 | LIU M D, XIONG S J, TAN F, et al. Physcion 8-O-β-glucopyranoside induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis of human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via suppressing survivin expression[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2016,37 (5):687-697. |
| 24 | JIN L M, MIAO J H, LIU Y J, et al. Icaritin induces mitochondrial apoptosis by up-regulating miR-124 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells[J].Biomed Pharmacother, 2017,85:287-295. |
| 25 | OH H N, OH K B, LEE M H, et al.JAK2 regulation by licochalcone H inhibits the cell growth and induces apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma [J].Phytomedicine, 2019,52: 60-69. |
| [1] | Xue LUAN,Guanghai YAN,Haibo LI,Bo ZHANG,Wei ZHANG,Yuanyuan HUANG. Effect of salidroside on airway inflammation in mice with asthma and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 537-544. |
| [2] | Runhong MU,Xinzhu LIU,Rui LIN,Yupeng LI,Luyao WANG,Chunyu WANG,Xiao GUO. Effect of PRDX6 over-expression of proliferation, invasion and migration of liver cancer cells and its molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 559-565. |
| [3] | Cuilan LIU,Jianjun LI,He JIANG,Jing LIU,Dan WANG,Chen LI,Di ZHAO. Effect of urolithin B on biological behaviors of human glioblastome U118 MG cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 566-574. |
| [4] | Jia FENG,Haichan XU,Jian WEN,Zehua WU,Yi CHEN. Effect of betulinic acid on proliferation and apoptosis of myeloma cells by regulating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 615-622. |
| [5] | Pei GONG,Jingran LIU,Shimin ZHAO,Yuzhen WANG,Jiming XIE. Inhibitory effect of MCM10 silencing on proliferation of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 652-659. |
| [6] | Xiaohui LI,Ziwei QU,Xin LU,Qingbin MENG,Huatao CHEN,Jun REN,Chengpei TAN. Regulatory effect of exosomes carrying miR-196b-5p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological characteristics of colon cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 660-668. |
| [7] | Tianqi ZOU,Lin BAI,Zhengxu ZHANG,He LI,Chunmei WANG,Jinghui SUN,Jianguang CHEN,Xi CHEN,Chengyi ZHANG. Inhibitory effect of prunus tomentosa thunb total flavonoids on skin hypertrophic scar in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 265-274. |
| [8] | Bingxue QI,Yan MA,Yixian ZHANG,Yadong SUN,Lining MIAO. Effect of liraglutide on expressions of mRNA and protein of related proteins after podocyte injury induced by high glucose and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 275-283. |
| [9] | Zhanqi ZHAO,Chengjin ZHANG,Juan TIAN. Inhibitory effect of Ndfip1 on ferrion-induced neuronal apoptosis and its neuroprotective mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 338-343. |
| [10] | Haoxuan TANG,Nanfeng MENG,Meiling DU,Wei WANG,Tao HE. Inhibitory effect of new VEGF monoclonal antibody combined with all-trans retinoic acid on proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 344-351. |
| [11] | Jie WU,Xuehua YANG,Ling MA,Wenqiang FAN,Dongdong FU,Xiao GAO,Shufei ZUO,Shu LIANG,Yilu QIN,Peishan WANG,Jinyan GUO. Effect of miR-26a-5p on apoptosis of human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells through JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 460-468. |
| [12] | . Inhibitory effect of curcumin on tumor growth in colorectal cancer mice and its mechanism of PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathwayPEI Yongbin, WANG Guiqi, LI Wei, JIANG Xia, JIANG Haibo, ZHAO Zengren (Department of General Surgery,First Hospital,Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050031,China) [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 145-151. |
| [13] | LI Qi, XU Rui, LI Tengteng, JIANG Yichuan, LI Min. Effect of pirarubicin on cardiomyocyte injury in rats and establishment of its model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 948-954. |
| [14] | LI Wei, ZHANG Haifeng, WANG Miao, HUO Jing, ZHANG Ying, ZHAO Cui. Protective effect of Astragalus Injection on heart of rats with sleep deprivation and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 998-1003. |
| [15] | JIA Daqi, KONG Wencong, SU Rongjian, DU Xiaoyuan, HE Wubin. Effects of macrophage stimulating 1 receptor inhibitor BMS777607 on proliferation and apoptosis of lung cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 739-744. |