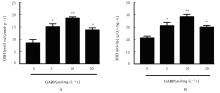
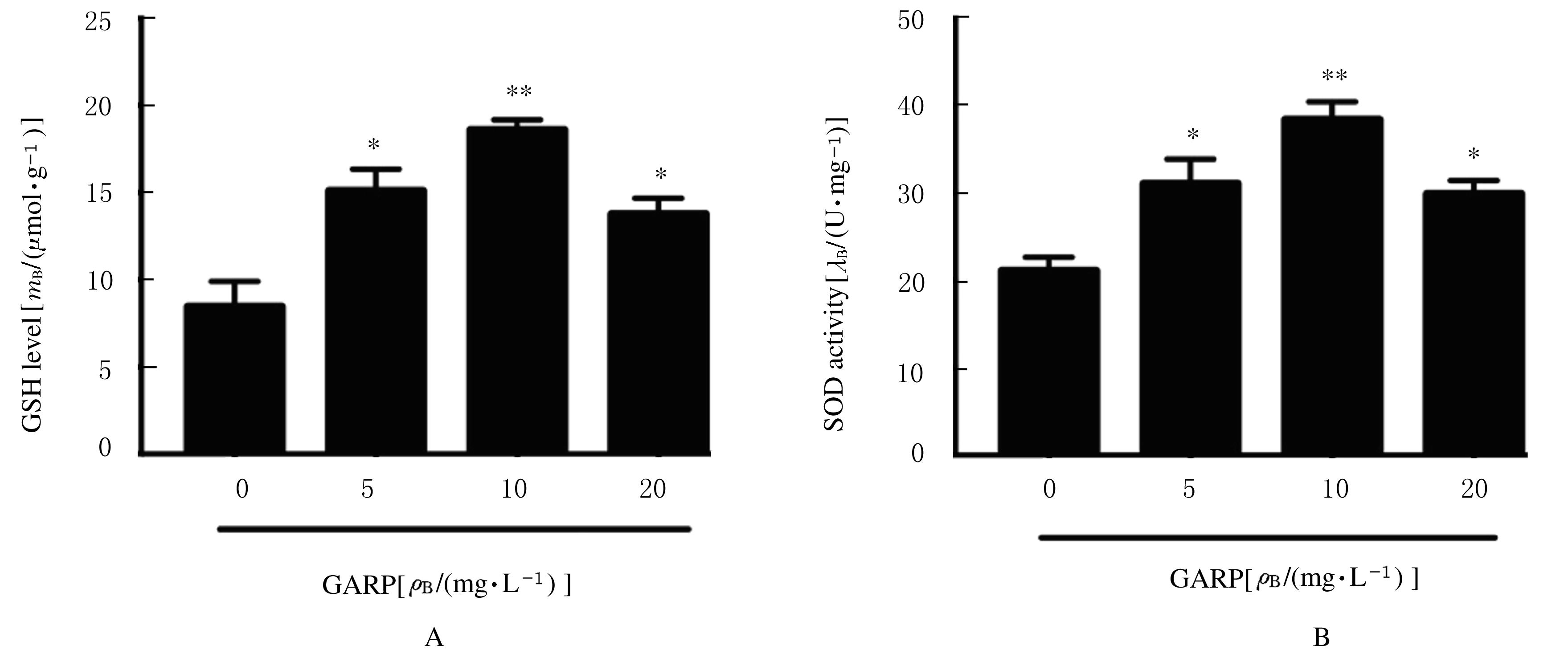
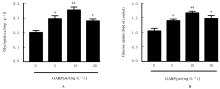
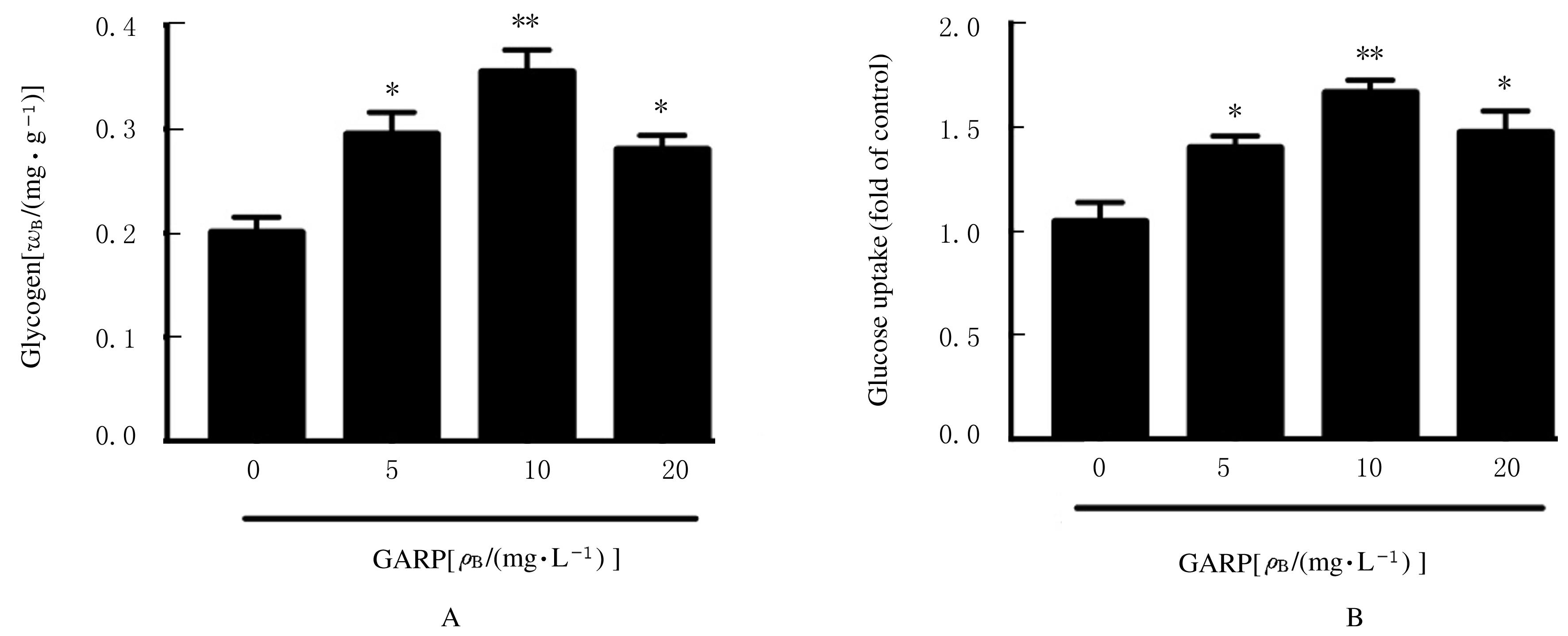
| 1 |
WAN J J, QIN Z, WANG P Y, et al. Muscle fatigue: general understanding and treatment[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2017, 49(10): e384.
|
| 2 |
朱海林. 野山参化学成分及抗慢性阻塞性肺疾病活性的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020.
|
| 3 |
WANG J, LI S S, FAN Y Y, et al. Anti-fatigue activity of the water-soluble polysaccharides isolated from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2010, 130(2): 421-423.
|
| 4 |
徐云凤, 赵 雨, 邢楠楠, 等. 人参蛋白对小鼠抗疲劳作用的研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2011, 32(11): 406-407, 436.
|
| 5 |
陈双越. 人参组培体系建立研究[D]. 延吉: 延边大学, 2019.
|
| 6 |
郝悦君, 孙浩丁, 车成来, 等. 2种培养方式下人参不定根生长动态观察及活性物质含量测定[J]. 延边大学农学学报, 2020, 42(2): 14-20.
|
| 7 |
LIANG W X, WANG S H, YAO L, et al. Quality evaluation of Panax ginseng adventitious roots based on ginsenoside constituents, functional genes, and ferric-reducing antioxidant power[J]. J Food Biochem, 2019, 43(8): e12901.
|
| 8 |
NIRANJANA MURTHY H, DANDIN V S, YOEUP PAEK K. Hepatoprotective activity of ginsenosides from Panax ginseng adventitious roots against carbon tetrachloride treated hepatic injury in rats[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2014, 158(Pt A): 442-446.
|
| 9 |
MURTHY H N, DANDIN V S, LEE E J, et al. Efficacy of ginseng adventitious root extract on hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2014, 153(3): 917-921.
|
| 10 |
WAN J J, QIN Z, LEI H, et al. Erythromycin has therapeutic efficacy on muscle fatigue acting specifically on orosomucoid to increase muscle bioenergetics and physiological parameters of endurance[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2020, 161: 105118.
|
| 11 |
FENG T, HUANG Y Y, TANG Z H, et al. Anti-fatigue effects of pea (Pisum sativum L.) peptides prepared by compound protease[J]. J Food Sci Technol, 2021, 58(6): 2265-2272.
|
| 12 |
LIU G Y, YANG X, ZHANG J X, et al. Synthesis, stability and anti-fatigue activity of selenium nanoparticles stabilized by Lycium barbarum polysaccharides[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 179: 418-428.
|
| 13 |
HU G S, GAO S, MOU D H. Water and alcohol extracts from Diaphragma juglandis on anti-fatigue and antioxidative effects in vitro and vivo [J]. J Sci Food Agric, 2021, 101(8): 3132-3139.
|
| 14 |
WANG M Y, REN J X, CHEN X N, et al. 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 promotes myoblast differentiation and protects against myotube atrophy via regulation of the Akt/mTOR/FoxO3 pathway[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2020, 180: 114145.
|
| 15 |
RAJIZADEH M A, NAJAFIPOUR H, SAMAREH FEKR M, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of myrtenol in the rats with allergic asthma[J]. Iran J Pharm Res, 2019, 18(3): 1488-1498.
|
| 16 |
LI Y, DENG Y, LI Z, et al. Composition, physicochemical properties, and anti-fatigue activity of water-soluble okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) stem pectins[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2020, 165(Pt B): 2630-2639.
|
| 17 |
JIANG R, WANG M Y, SHI L, et al. Panax ginseng total protein facilitates recovery from dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy through the activation of glucose consumption in C2C12 myotubes[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2019, 2019: 3719643.
|
| 18 |
龙光文, 张 谦, 杨秀林, 等. miR-146b对急性呼吸窘迫综合征大鼠肺组织中ICAM-1表达的调控作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2021, 47(3): 587-594.
|
| 19 |
张颖捷, 杜万红. 国内外抗疲劳研究进展[J]. 实用预防医学, 2012, 19(7): 1112-1116.
|
| 20 |
何恩鹏, 李艳红. 天然抗疲劳药物研究现状及展望[J]. 新疆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 38(1): 80-84.
|
| 21 |
LIN H J, ZHANG X Y, LIU J W, et al. Schisantherin A improves learning and memory abilities partly through regulating the Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling pathway in chronic fatigue mice[J].Exp Ther Med,2021,21(4): 385.
|
| 22 |
杨凤雯, 韦秋菊, 刘雪婷, 等. 宽筋藤对小鼠抗疲劳、耐缺氧作用研究[J]. 右江医学, 2020, 48(1): 23-27.
|
| 23 |
ZHU H K, XU W Q, WANG N, et al. Anti-fatigue effect of Lepidium meyenii Walp. (Maca) on preventing mitochondria-mediated muscle damage and oxidative stress in vivo and vitro[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12(7): 3132-3141.
|
| 24 |
GOMEZ-CABRERA M C, CARRETERO A, MILLAN-DOMINGO F, et al. Redox-related biomarkers in physical exercise[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 42: 101956.
|
| 25 |
RAJPUT S A, SHAUKAT A, RAJPUT I R, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 prevents deoxynivalenol-induced immune injury via alleviating oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2021, 220: 112333.
|
| 26 |
ZAI J A, KHAN M R, MUGHAL Z U N, et al. Methanol extract of Iphiona aucheri ameliorates CCl4 induced hepatic injuries by regulation of genes in rats[J]. Toxicol Res (Camb), 2019, 8(6): 815-832.
|
| 27 |
KJØBSTED R, ROLL J L W, JØRGENSEN N O,et al.AMPK and TBC1D1 regulate muscle glucose uptake after, but not during, exercise and contraction[J]. Diabetes, 2019, 68(7): 1427-1440.
|
| 28 |
谢飞飞. 远志多糖对力竭运动小鼠体内抗疲劳和体外抗氧化作用研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2021, 42(6): 332-336.
|
| 29 |
LEE A, BAE E, PARK J, et al. Identification of the genes related to the glycogen metabolism in hyperthermophilic archaeon, Sulfolobus acidocaldarius [J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12: 661053.
|
| 30 |
LI S, HUANG Q, ZHANG L W, et al. Effect of CAPE-pNO2 against type 2 diabetes mellitus via the AMPK/GLUT4/ GSK3β/PPARα pathway in HFD/STZ-induced diabetic mice[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2019, 853: 1-10.
|
| 31 |
GAO J B, WANG H J, LI Y J, et al. Resveratrol attenuates cerebral ischaemia reperfusion injury via modulating mitochondrial dynamics homeostasis and activating AMPK-Mfn1 pathway[J]. Int J Exp Pathol, 2019, 100(5/6): 337-349.
|
 )
)