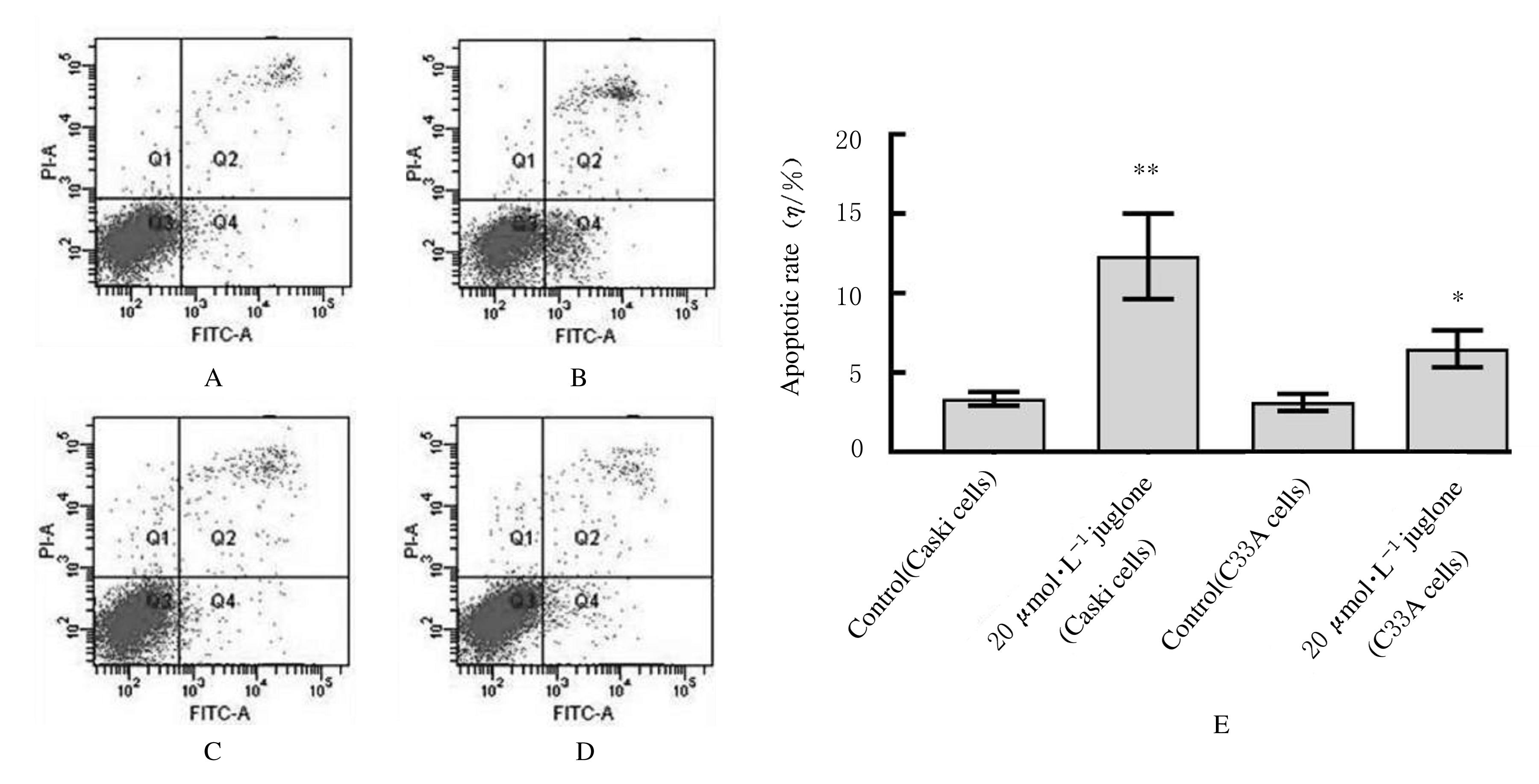
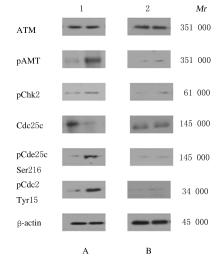
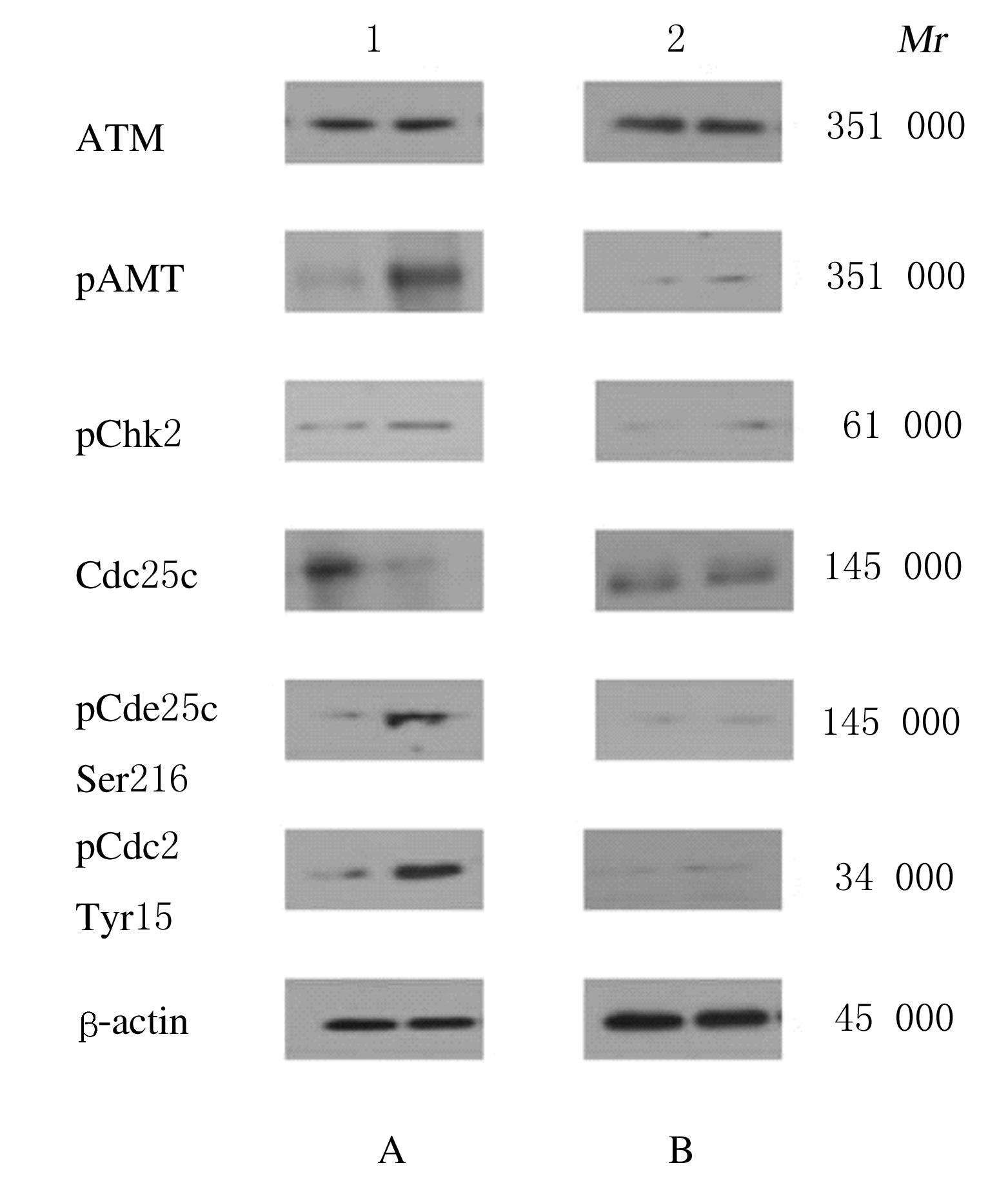
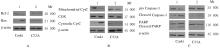
| 1 |
VU M, YU J, AWOLUDE O A,et al.Cervical cancer worldwide[J].Curr Probl Cancer,2018,42(5):457-465.
|
| 2 |
GUPTA S M, MANIA-PRAMANIK J .Molecular mechanisms in progression of HPV-associated cervical carcinogenesis [J].J Biomed Sci,2019,26(1): 28-46.
|
| 3 |
JOHNSON-MALLARD V, DARVILLE G, MERCADO R,et al . How health care providers can use digital health technologies to inform human papillomavirus (HPV) decision making and promote the HPV vaccine uptake among adolescents and young adults[J].Biores Open Access,2019,8(1) : 84-93.
|
| 4 |
王若汗,李庆杰,成光宇,等.胡桃醌对人胃癌细胞SGC-7901凋亡相关基因p53蛋白表达的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(14):3090-3094.
|
| 5 |
辛国松. 基于线粒体损伤胡桃醌抗乳腺癌作用机制研究[J].哈尔滨商业大学学报(自然科学版),2018,34(5):516-521,559.
|
| 6 |
聂珍贵,王世全,高春艳,等.两种萘醌类化合物对人结肠癌Caco-2细胞增殖的影响[J].西部中医药,2017,30(11):44-46.
|
| 7 |
方 芳,赵良中,李 强,等.胡桃醌对卵巢癌SKOV3细胞氧化应激和凋亡的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2016,32(1):156-159.
|
| 8 |
WANG J Z, LIU G J, LI Z Y,et al. Pin1 in cardiovascular dysfunction: A potential double-edge role[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2016, 212: 280-283.
|
| 9 |
LIAO X H, ZHANG A L, ZHENG M,et al.Chemical or genetic Pin1 inhibition exerts potent anticancer activity against hepatocellular carcinoma by blocking multiple cancer-driving pathways[J]. Sci Rep, 2017,7:43639.
|
| 10 |
CHENG H L, HAO Y L, YU C L, et al.Landscape of Pin1 in the cell cycle[J].Exp Biol Med(Maywood),2015,240(3):403-408.
|
| 11 |
LU Z, HUNTER T. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 in cancer [J]. Cell Res, 2014, 24(9):1033-1049.
|
| 12 |
MOORE J D, POTTER A.Pin1 inhibitors: pitfalls,progress and cellular pharmacology[J]. Bioorganic,2013, 23(15):4283-4291.
|
| 13 |
AITHAL B K, SUNIL KUMAR M R, RAO B N,et al. Evaluation of harmacokinetic,biodistribution,pharmacodynamic,and toxicity profile of free juglone and its sterically stabilized liposomes[J].J Pharm Sci,2011(8):3517-3528.
|
| 14 |
季宇彬,曲中原,邹 翔,等. 青龙衣中胡桃醌对S180肉瘤小鼠的抑瘤作用研究[J].中国药学杂志,2009,44(3):195-199.
|
| 15 |
孙 卉,何志贵,师俊玲. 核桃青皮活性成分胡桃醌抗肿瘤作用研究进展[J]. 农产品加工,2021(14):86-90.
|
| 16 |
吴建安,尚 厦,胡 倩. 胡桃醌通过调节CDK4表达调控口腔鳞癌Tca8113细胞增殖和凋亡[J]. 河北医学,2020,26(2):329-333.
|
| 17 |
王昌高,昝 慧,张万里,等. 胡桃醌对胃癌细胞耐药性及细胞中ANXA2、ERCC1表达和AKT/mTOR信号通路的影响[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2020,29(2):136-141.
|
| 18 |
李庆杰,王若汗,冯佳亮,等. 胡桃醌对小鼠SH-SY5Y神经母细胞瘤干预后相关差异基因表达变化及通路分析[J]. 吉林中医药,2020,40(6):784-787.
|
| 19 |
张 静,马丽娟,王幼辉. 胡桃醌对人卵巢癌细胞株SKOV3自噬水平的影响及其机制研究[J]. 中国药物与临床,2019,19(18):3091-3092.
|
| 20 |
孙红亚,袁爱娟,李纪鹏. 胡桃醌对人卵巢癌SKOV3和IOSE80细胞增殖和侵袭的抑制作用及其机制研究[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学,2019,24(1):32-37.
|
| 21 |
岳武恒,梅 瑞,蔡 娟,等. 胡桃醌-PLGA纳米粒制备及对A375恶黑细胞的体外抗肿瘤作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(4):87-93.
|
| 22 |
CHIASSON VL, MUNSHI N, CHATTERJEE P,et al. Pin1 deficiency causes endothelial dysfunction and hypertension[J]. Hypertension,2011,58(3):431- U199.
|
| 23 |
RUAN L, TORROS CM, QIAN J,et al.Pin1 prolyl isomerase regulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2011, 31(2):392-398.
|
| 24 |
CHIASSON VL, MUNSHI N, YOUNG KJ,et al.Inhibition of the prolyl isomerase pin1 increases eNOS Ser116phosphorylation,endothelial dysfunction,and blood pressure[J].Hypertension,2009,54(4):E95-E95.
|
 )
)