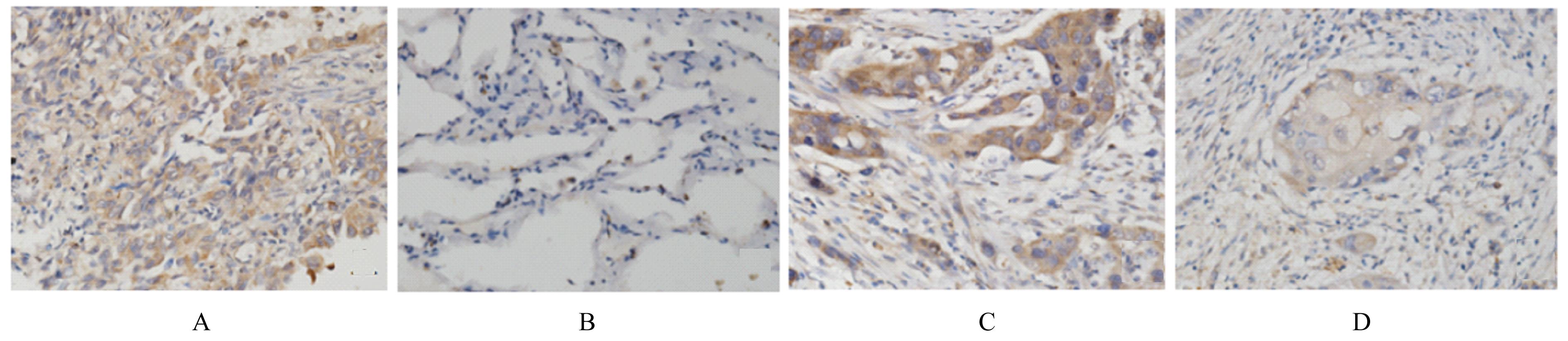
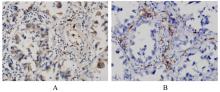
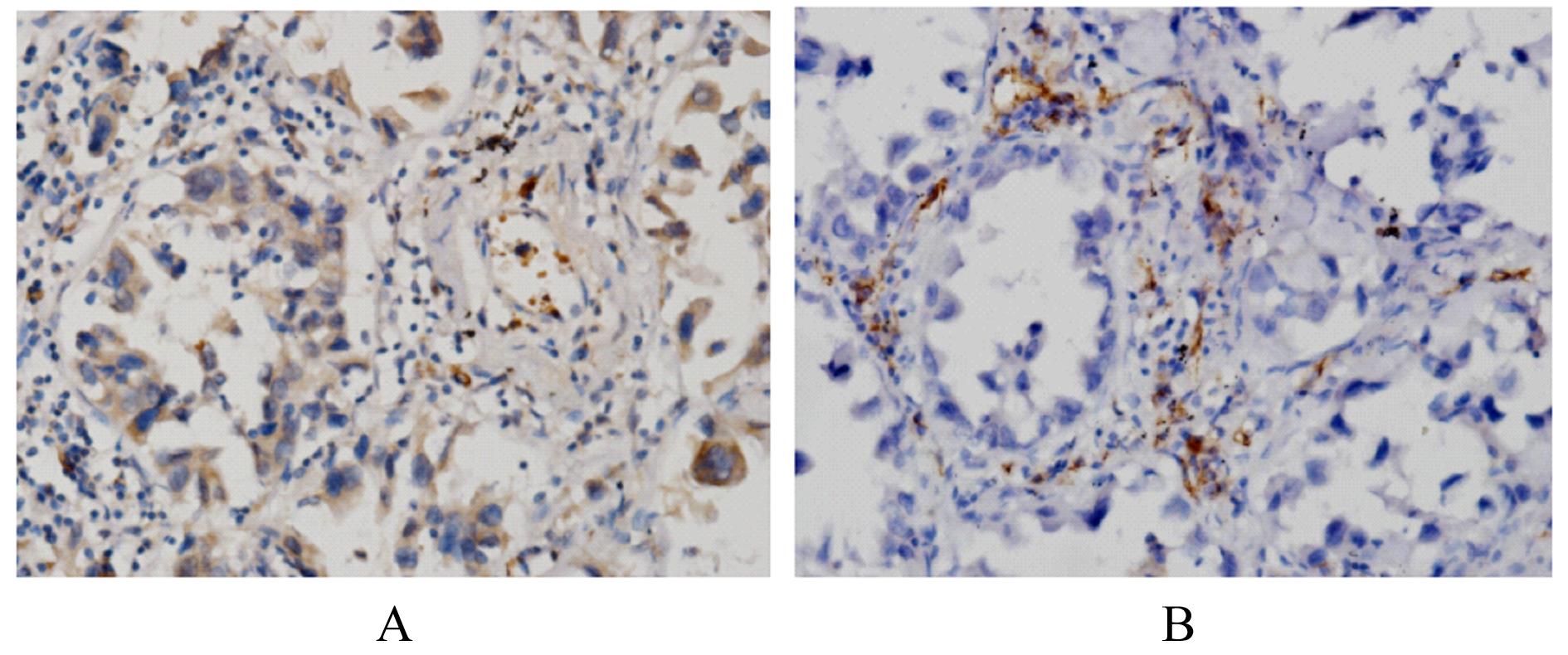
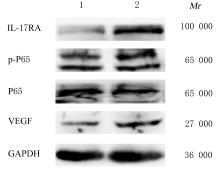
| 1 |
BALATA H, FONG K M, HENDRIKS L E, et al. Prevention and early detection for NSCLC: advances in thoracic oncology 2018[J].J Thorac Oncol,2019,14(9): 1513-1527.
|
| 2 |
O’CALLAGHAN D S, O’DONNELL D, O’CONNELL F,et al. The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2010,5(12): 2024-2036.
|
| 3 |
RIVAS-FUENTES S, SALGADO-AGUAYO A, PERTUZ BELLOSO S, et al. Role of chemokines in non-small cell lung cancer: angiogenesis and inflammation[J]. J Cancer, 2015, 6(10): 938-952.
|
| 4 |
WANG S M, LI Z A, HU G M. Prognostic role of intratumoral IL-17A expression by immunohistochemistry in solid tumors: a meta-analysis[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(39): 66382-66391.
|
| 5 |
CHANG S H. T helper 17 (Th17) cells and interleukin-17 (IL-17) in cancer[J]. Arch Pharm Res,2019,42(7): 549-559.
|
| 6 |
LI S, CONG X L, GAO H Y, et al. Tumor-associated neutrophils induce EMT by IL-17a to promote migration and invasion in gastric cancer cells[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 6.
|
| 7 |
RAZI S, BARADARAN NOVEIRY B, KESHAVARZ-FATHI M, et al. IL-17 and colorectal cancer: from carcinogenesis to treatment[J]. Cytokine, 2019, 116: 7-12.
|
| 8 |
WU Y Z, KONATÉ M M, LU J M, et al. IL-4 and IL-17A cooperatively promote hydrogen peroxide production, oxidative DNA damage, and upregulation of dual oxidase 2 in human colon and pancreatic cancer cells[J]. J Immunol, 2019, 203(9): 2532-2544.
|
| 9 |
HUANG Q, DUAN L M, QIAN X, et al. IL-17 promotes angiogenic factors IL-6, IL-8, and vegf production via Stat1 in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 36551.
|
| 10 |
CHAO X, YI L, LAN L L, et al. Long-term PM2.5 exposure increases the risk of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression by enhancing interleukin-17a (IL-17a)-regulated proliferation and metastasis[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2020, 12(12): 11579-11602.
|
| 11 |
FREZZETTI D, GALLO M, MAIELLO M R, et al. VEGF as a potential target in lung cancer[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2017, 21(10): 959-966.
|
| 12 |
APTE R S, CHEN D S, FERRARA N. VEGF in signaling and disease: beyond discovery and development[J]. Cell, 2019, 176(6): 1248-1264.
|
| 13 |
房 惠, 杨红宇, 马绪哲, 等. 叉头蛋白3对肺腺癌细胞增殖和化疗药物顺铂敏感性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(6): 1261-1266, 1481.
|
| 14 |
LI C, MA X Z, TAN C S, et al. IL-17F expression correlates with clinicopathologic factors and biological markers in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2019, 215(10): 152562.
|
| 15 |
马守宝, 林丹丹, 刘海燕. 炎症细胞因子在肿瘤微环境中的作用及其作为治疗靶点的研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2016, 28(2): 182-191.
|
| 16 |
GORCZYNSKI R M. IL-17 signaling in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2020, 1240: 47-58.
|
| 17 |
FABRE J, GIUSTINIANI J, GARBAR C, et al. Targeting the tumor microenvironment: the protumor effects of IL-17 related to cancer type[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2016, 17(9): E1433.
|
| 18 |
XU B B, GUENTHER J F, POCIASK D A, et al. Promotion of lung tumor growth by interleukin-17[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2014, 307(6): L497-L508.
|
| 19 |
LV Q Y, WU K J, LIU F L, et al. Interleukin‑17A and heparanase promote angiogenesis and cell proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer[J]. Int J Oncol, 2018, 53(4): 1809-1817.
|
| 20 |
WU X Q, YANG T, LIU X, et al. IL-17 promotes tumor angiogenesis through Stat3 pathway mediated upregulation of VEGF in gastric cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(4): 5493-5501.
|
| 21 |
LIU L G, SUN H Z, WU S, et al. IL‑17A promotes CXCR2‑dependent angiogenesis in a mouse model of liver cancer[J]. Mol Med Report, 2019, 20 (2): 1065-1074.
|
| 22 |
姜一弘, 张 丹, 张天择, 等. 核因子κB(NF-κB)信号通路在炎症与肿瘤中作用的研究进展[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2018, 34(12): 1130-1135.
|
| 23 |
TANIGUCHI K, KARIN M. NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: coming of age[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2018, 18(5): 309-324.
|
| 24 |
石焕英, 陈海飞, 李群益, 等. VEGF及其靶向药物的研究进展[J]. 上海医药, 2020, 41(15): 4-7, 17.
|
| 25 |
张文英, 季 爽, 李永怀, 等. ACE2通过调节A549细胞中VEGF的表达抑制肺腺癌微血管形成[J]. 国际呼吸杂志, 2020, 40(16): 1209-1215.
|
| 26 |
博 伦,张 琼,王祥旭,等. 血管内皮生长因子/血管内皮生长因子受体通路在胆管细胞癌发生发展及治疗中的作用[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2020,36(8): 1866-1869.
|
 )
)