Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5): 1131-1138.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220505
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles
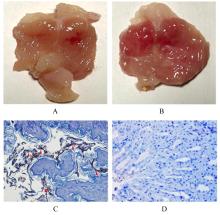
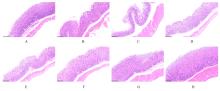
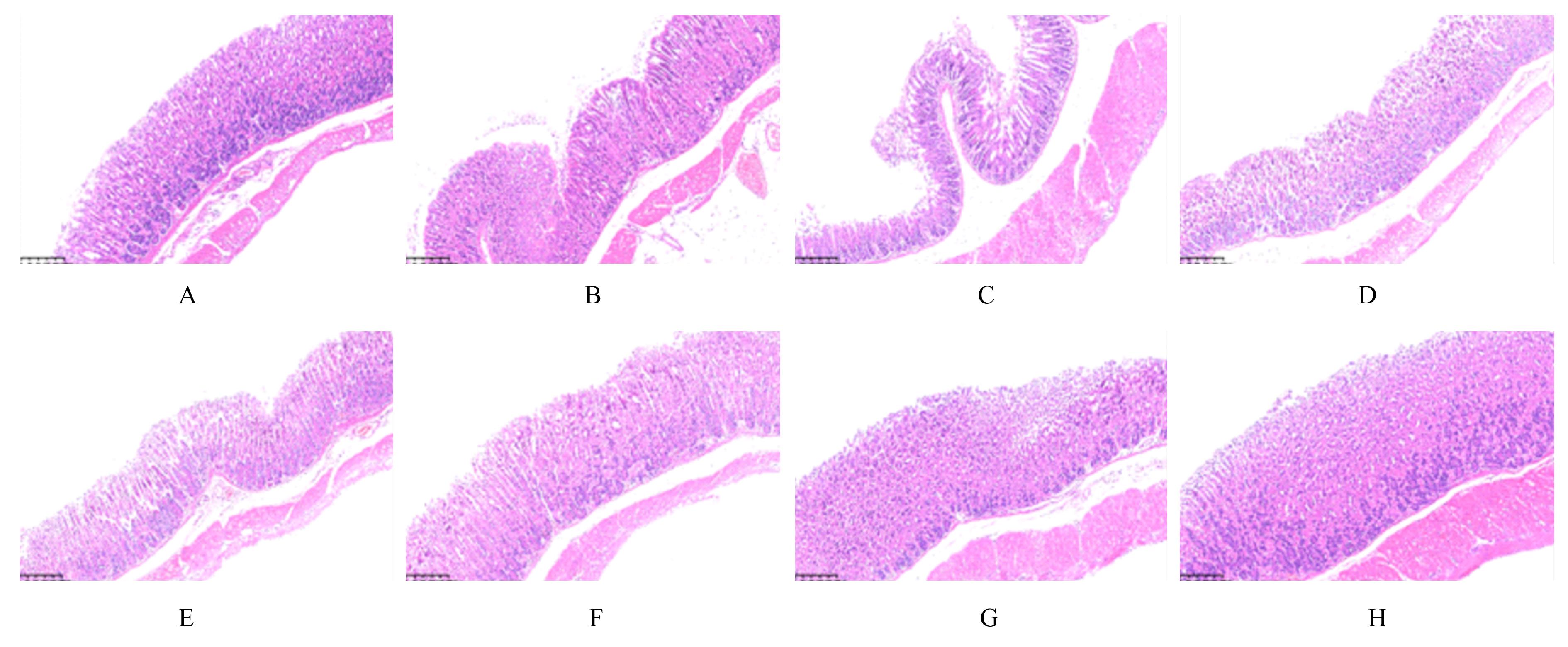
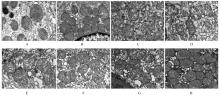
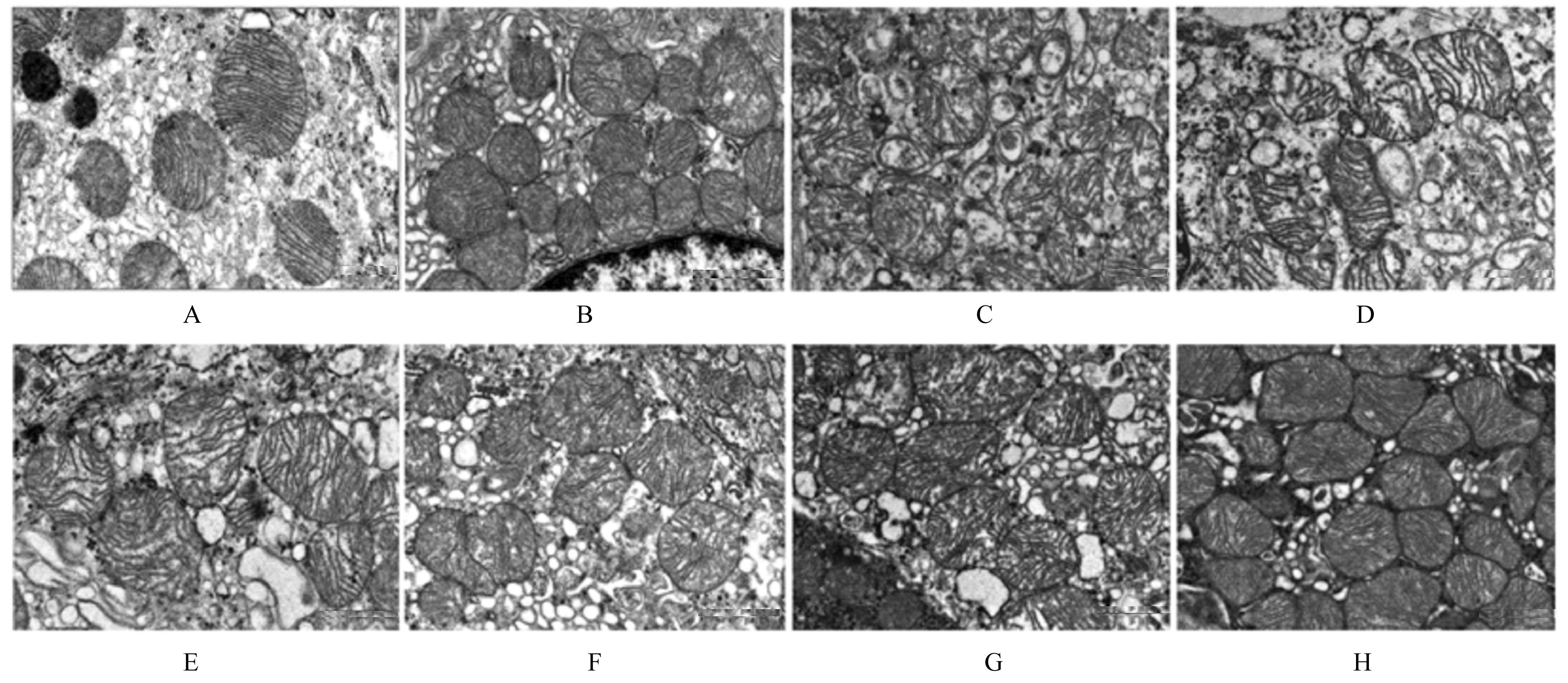
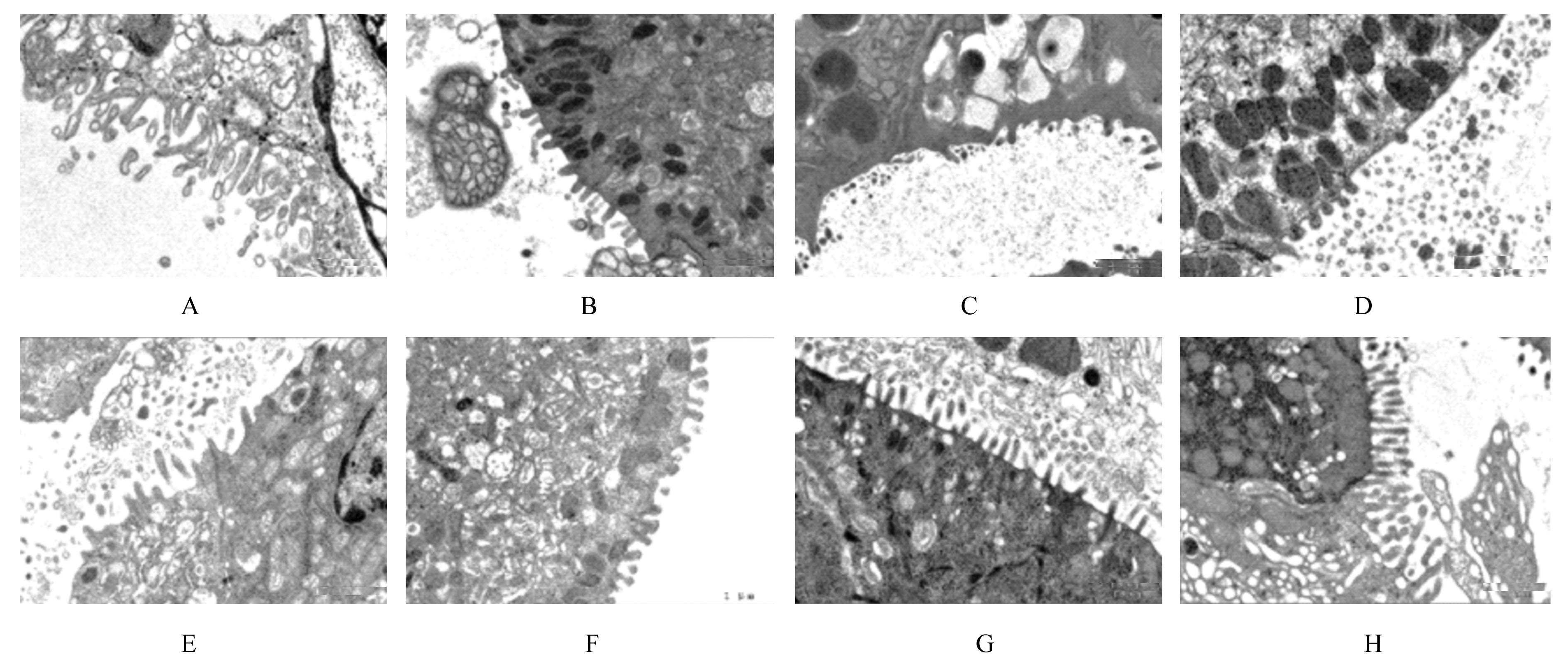
Effect of Parnassia palustris Linn extracts on Helicobacter pylori colonization in gastric mucosa and its mechanism
Zhao JIN1,Rushuai WANG1,Zhaoyang WANG2,zhanbiao HE3,Fuming TIAN3,Ruijun WANG3( )
)
- 1.Department of Imaging Diagnosis,Affiliated Hospital,Inner Mongolia Medical University,Hohhot 010050,China
2.Department of Gastroenterology Surgery,Affiliated Hospital,Inner Mongolia Medical University,Hohhot 010050,China
3.Clinical Medical Research Center for Neurological Disease,Department of Neurosurgery,Affiliated Hospital,Inner Mongolia Medical University,Hohhot 010050,China
CLC Number:
- R856.5