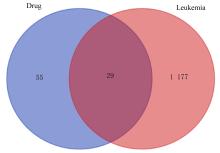
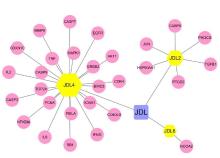
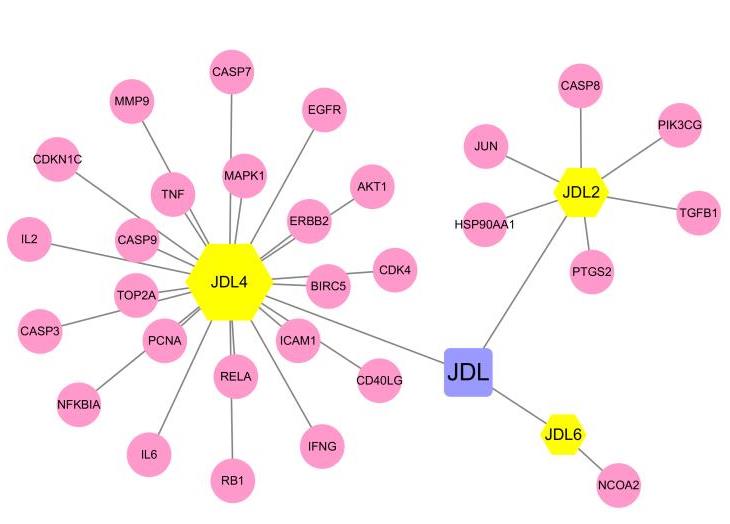
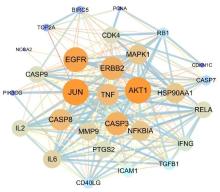
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (1): 74-83.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230110
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics analysis of network pharmacology and molecular docking technology based on mechanism of Physalis Calyx seu Fructus on leukemia
Minghui WANG,Moyi LIU,Helin WANG,Ying LI,Xiangjun WANG,Hetong HUI,Xinyuan FAN,Tianqi WANG,Limei LIU( )
)
- Department of Microbiology Laboratory,School of Medical Technology,Beihua University,Jilin 132000,China
-
Received:2022-04-07Online:2023-01-28Published:2023-02-08 -
Contact:Limei LIU E-mail:Liulm74@163.com
CLC Number:
- R733.7
Cite this article
Minghui WANG,Moyi LIU,Helin WANG,Ying LI,Xiangjun WANG,Hetong HUI,Xinyuan FAN,Tianqi WANG,Limei LIU. Bioinformatics analysis of network pharmacology and molecular docking technology based on mechanism of Physalis Calyx seu Fructus on leukemia[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 74-83.
share this article
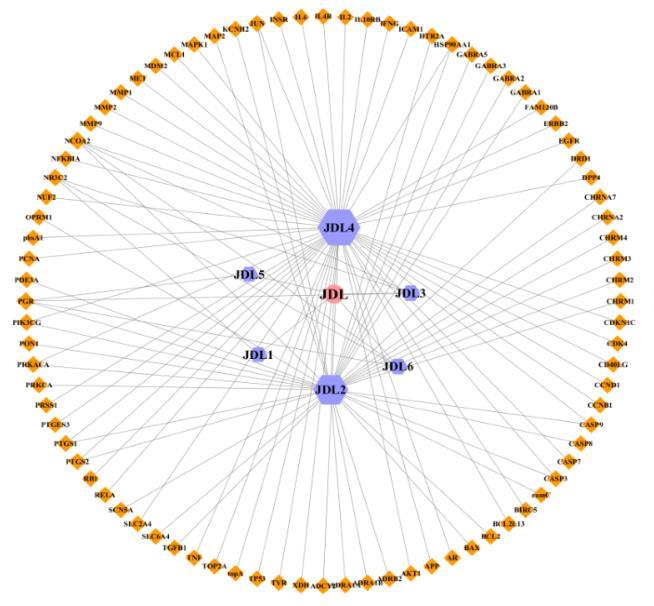
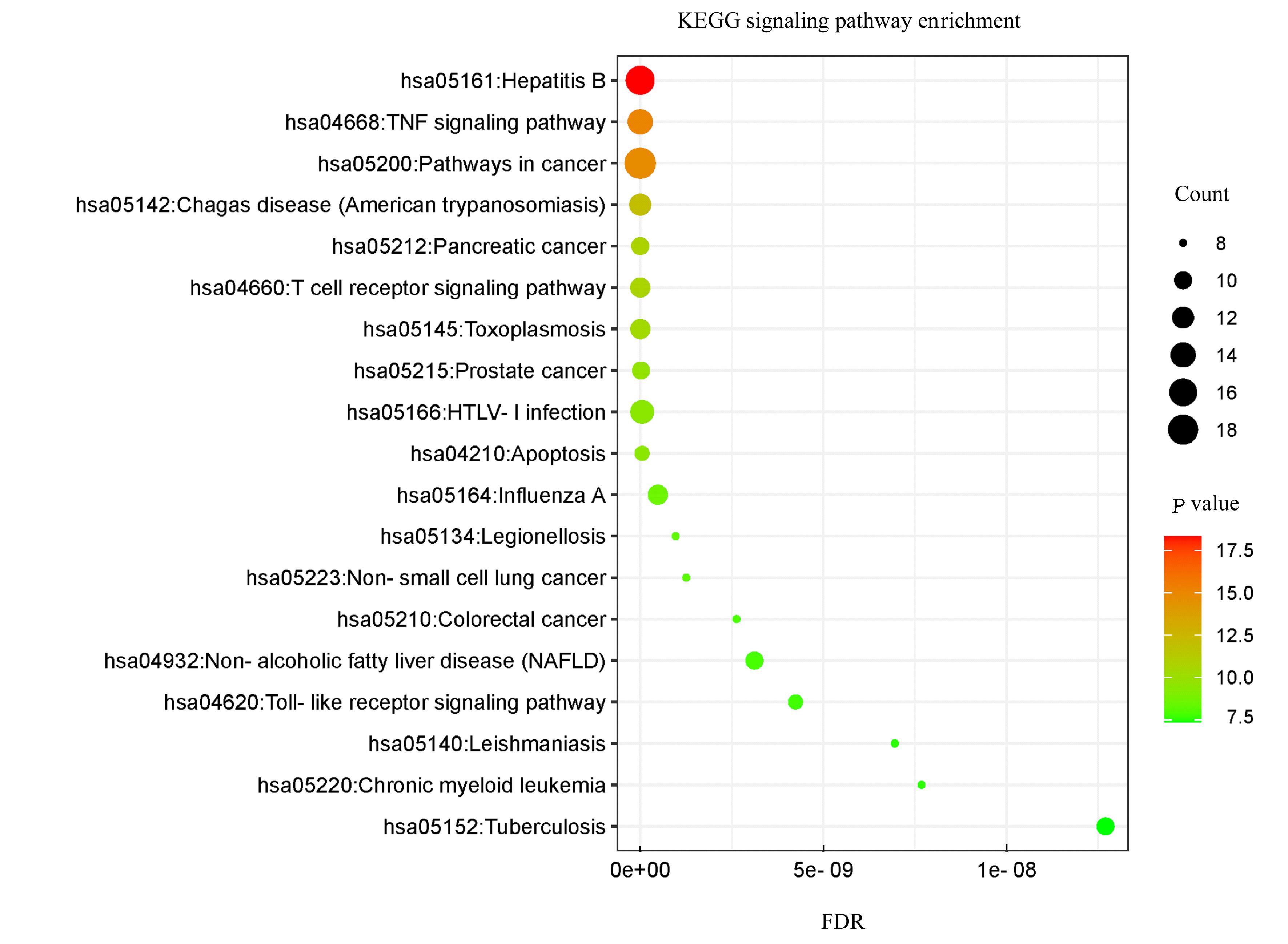
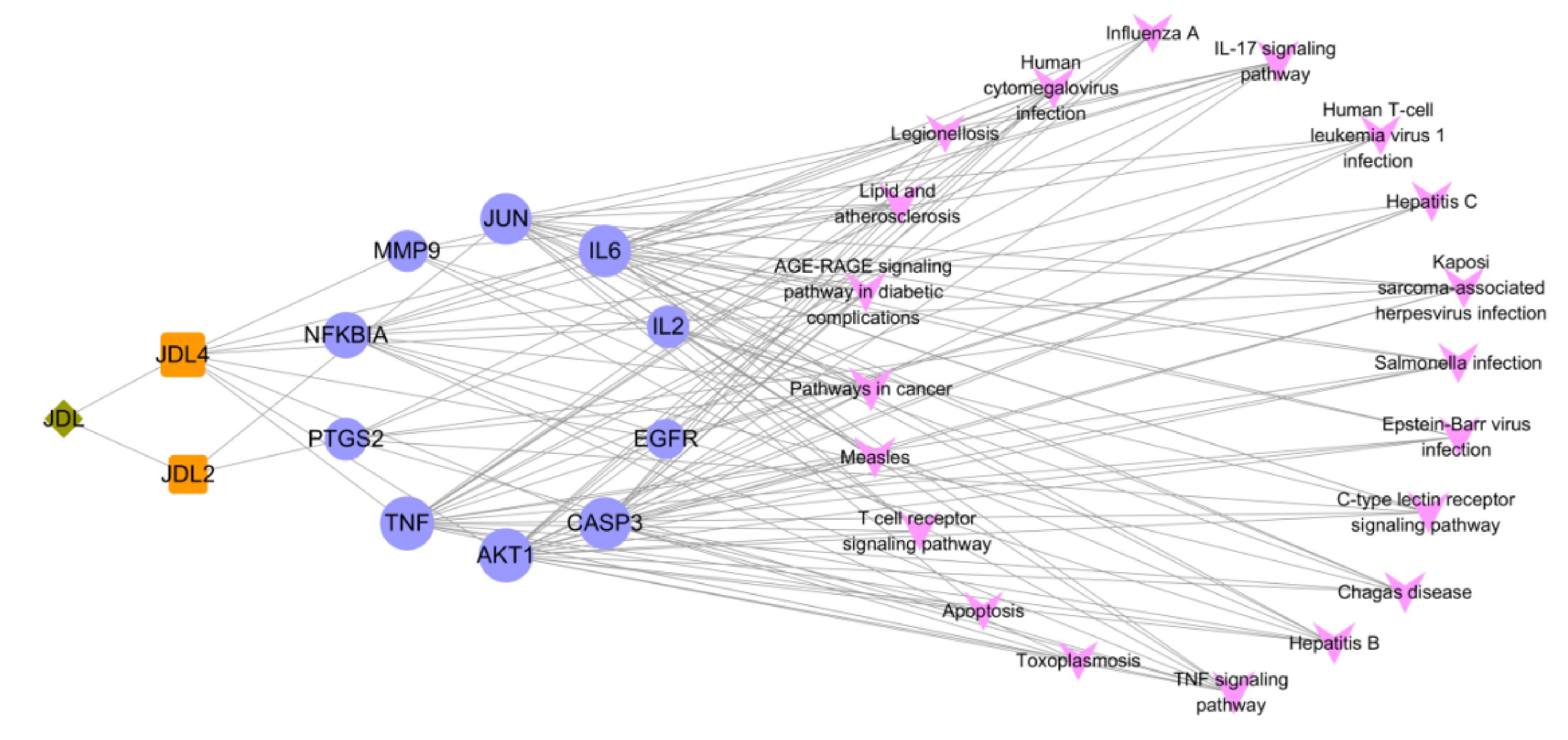
Tab.1
Main active components of PCF"
| Number | Mol ID | Molecule name | Oral bioavail ability (η/%) | Drug likeness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JDL1 | MOL000006 | Luteolin | 36.162 6 | 0.245 5 |
| JDL2 | MOL000359 | Sitosterol | 36.913 9 | 0.751 2 |
| JDL3 | MOL000358 | Beta-sitosterol | 36.913 9 | 0.751 2 |
| JDL4 | MOL007231 | Gramisterol | 44.192 6 | 0.754 4 |
| JDL5 | MOL009681 | Obtusifoliol | 42.552 0 | 0.756 5 |
| JDL6 | MOL003578 | Cycloartenol | 38.685 7 | 0.780 9 |
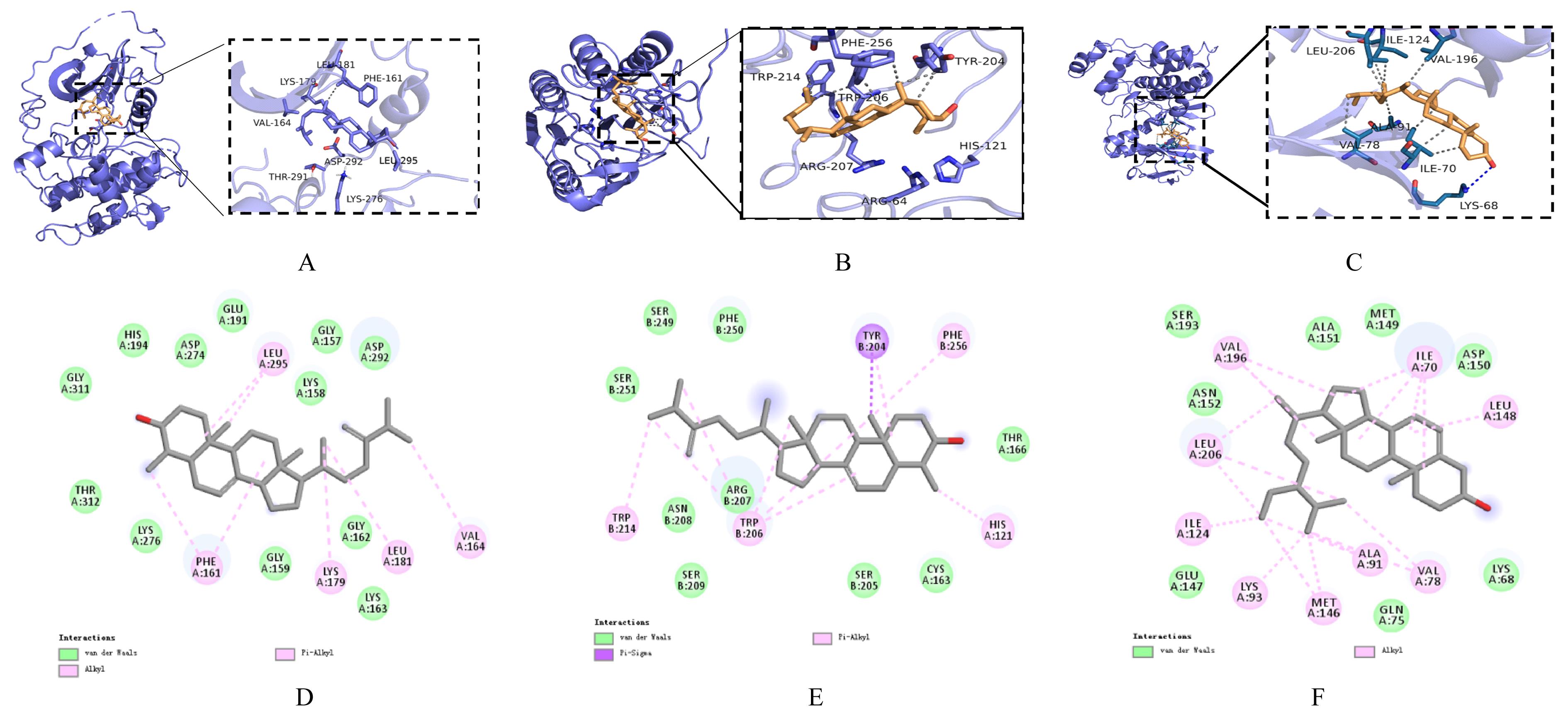
Tab. 2
Molecular docking results"
| Target gene | PDBID | Ligand | Affinity (kcal·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | 4GV1 | Gramisterol | -8.6 |
| Caspase-3 | 3KJF | Gramisterol | -8.3 |
| EGFR | 5D41 | Gramisterol | -7.0 |
| IL-2 | 1M48 | Gramisterol | -7.4 |
| IL-6 | 4O9H | Gramisterol | -6.1 |
| MMP9 | 6ESM | Gramisterol | -6.4 |
| NFKBIA | LIKN | Gramisterol | -6.0 |
| TNF | 7JRA | Gramisterol | -7.4 |
| JUN | 3PTG | Sitosterol | -8.8 |
| PTGS2 | 5IKR | Sitosterol | -4.4 |
| 1 | KANTARJIAN H M, KEATING M J, FREIREICH E J.Toward the potential cure of leukemias in the next decade[J]. Cancer, 2018, 124(22): 4301-4313. |
| 2 | MEDINGER M, HEIM D, HALTER J P, et al. Diagnosis and therapy of acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Ther Umsch, 2019, 76(9): 481-486. |
| 3 | HU H X, XU L T, GAO H, et al. Chemical constituents from physalis calyx seu fructus and their inhibitory effects against oxidative stress and inflammatory response[J]. Planta Med, 2020, 86(16): 1191-1203. |
| 4 | 孙佳旻. 锦灯笼化学成分及抗炎、抗氧化活性研究[D]. 济南: 山东中医药大学, 2021. |
| 5 | 胡慧心. 锦灯笼化学成分及生物活性研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020. |
| 6 | LI A L, CHEN B J, LI G H,et al. Physalis alkekengi L. var. franchetii (mast.) makino: an ethnomedical, phytochemical and pharmacological review[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2018, 210: 260-274. |
| 7 | SOMINTARA S, LEARDKAMOLKARN V, SUTTIARPORN P, et al. Anti-tumor and immune enhancing activities of rice bran gramisterol on acute myelogenous leukemia[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1): e0146869. |
| 8 | 伍振辉, 张 欢, 吴欣平, 等. 基于网络药理学及体外实验探讨青黄散抗急性髓系白血病的分子机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(7): 179-189. |
| 9 | 房伟进. 基于网络药理学与分子对接探究龙葵抗白血病机制[D]. 石家庄: 河北经贸大学, 2021. |
| 10 | 朱章志, 施岚尔, 刘江涛, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨青蒿治疗人急性髓系白血病作用机制[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2021, 39(1): 1-4, 259. |
| 11 | JIAO X Y, JIN X, MA Y Y, et al. A comprehensive application: molecular docking and network pharmacology for the prediction of bioactive constituents and elucidation of mechanisms of action in component-based Chinese medicine[J]. Comput Biol Chem, 2021, 90: 107402. |
| 12 | PINZI, RASTELLI G. Molecular docking: shifting paradigms in drug discovery[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(18): E4331. |
| 13 | 章晓云, 李华南, 陈 锋, 等. 网络药理学结合分子对接技术揭示桂枝芍药知母汤治疗痛风性关节炎的潜在分子机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(2): 245-252. |
| 14 | JULIUSSON G, HOUGH R. Leukemia [J]. Prog Tumor Res,2016,43:87-100. |
| 15 | 王卫东, 何小花, 杨庆敏, 等. 治疗急性髓系白血病的中药活性成分研究进展[J]. 时珍国医国药,2021,32(6): 1444-1449. |
| 16 | 李海霞, 姚 旭, 田雪飞, 等. 中医药治疗白血病的研究进展[J]. 中医药导报, 2019, 25(12): 119-123. |
| 17 | JIANG Q F, ISQUITH J, LADEL L, et al. Inflammation-driven deaminase deregulation fuels human pre-leukemia stem cell evolution[J]. Cell Rep, 2021, 34(4): 108670. |
| 18 | CAIADO F, PIETRAS E M, MANZ M G. Inflammation as a regulator of hematopoietic stem cell function in disease, aging, and clonal selection[J]. J Exp Med, 2021, 218(7): e20201541. |
| 19 | MITROULIS I, KALAFATI L, BORNHÄUSER M, et al. Regulation of the bone marrow niche by inflammation[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1540. |
| 20 | 杨丽军, 王丹丹, 吴红杰, 等. 锦灯笼抗炎活性成分作用机制的网络药理学研究[J]. 天津中医药大学学报, 2018, 37(5): 399-403. |
| 21 | GONÇALVES PEREIRA R C, GONTIJO EVANGELISTA F C, DOS SANTOS JÚNIOR V S, et al. Cytotoxic activity of triterpenoids from cheiloclinium cognatum branches against chronic and acute leukemia cell lines[J]. Chem Biodivers, 2020, 17(12): e2000773. |
| 22 | SHI G Q, LIU J, ZHAO W E, et al. Separation and purification and in vitro anti-proliferative activity of leukemia cell K562 of Galium aparine L. petroleum ether phase[J]. Saudi Pharm J, 2016, 24(3): 241-244. |
| 23 | HUANG H M, LIU J C. C-Jun blocks cell differentiation but not growth inhibition or apoptosis of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells induced by STI571 and by histone deacetylase inhibitors[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2009, 218(3): 568-574. |
| 24 | ROSZAK J, SMOK-PIENIĄŻEK A, STĘPNIK M. Transcriptomic analysis of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway reveals the dual role of the c-Jun oncogene in cytotoxicity and the development of resistance in HL-60 leukemia cells in response to arsenic trioxide[J]. Adv Clin Exp Med, 2017, 26(9): 1335-1342. |
| 25 | BESTACH Y, TOLOZA M J, FERRI C, et al. The dynamic of TNF and IL6 gene expression in chronic myeloid leukemia patients reveals early responders to imatinib[J]. Leuk Res, 2019, 86: 106221. |
| 26 | BISHT K, TAY J, WELLBURN R N, et al. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides suppress erythroblastic Islands and erythropoiesis in the bone marrow in an extrinsic and G-CSF-,IL-1-,and TNF-independent manner[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 583550. |
| 27 | SALEH M, KHALIL M, ABDELLATEIF M S,et al. Role of matrix metalloproteinase MMP-2, MMP-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP-1) in the clinical progression of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J]. Hematology, 2021, 26(1): 758-768. |
| 28 | SHARMA K, SINGH U, RAI M, et al. Interleukin 6 and disease transformation in chronic myeloid leukemia: a Northeast Indian population study[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2020, 16(1): 30-33. |
| 29 | BERNARD A, CHEVRIER S, BELTJENS F, et al. Cleaved caspase-3 transcriptionally regulates angiogenesis-promoting chemotherapy resistance[J]. Cancer Res, 2019, 79(23): 5958-5970. |
| 30 | KÜÇÜKCANKURT F, ERBILGIN Y, FıRTıNA S, et al. PTEN and AKT1 variations in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J]. Turk J Haematol, 2020, 37(2): 98-103. |
| 31 | OUYANG S, ZENG Q M, TANG N, et al. Akt-1 and Akt-2 differentially regulate the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by controlling proliferation of thymus-derived regulatory T cells[J]. J Immunol, 2019, 202(5): 1441-1452. |
| 32 | SABNIS H, BRADLEY H L, BUNTING S T, et al. Capillary nano-immunoassay for Akt 1/2/3 and 4EBP1 phosphorylation in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. J Transl Med, 2014, 12: 166. |
| 33 | ZHOU X X, LI Z Y, ZHOU J F. Tumor necrosis factor α in the onset and progression of leukemia[J]. Exp Hematol, 2017, 45: 17-26. |
| 34 | WANG M, ZHANG C, TIAN T, et al. Increased regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of acute myeloid leukemia patients rely on tumor necrosis factor(TNF)-α-TNF receptor-2 pathway[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 1274. |
| 35 | DOS SANTOS N R, GHYSDAEL J, TRAN QUANG C. The TCR/CD3 complex in leukemogenesis and as a therapeutic target in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J]. Adv Biol Regul, 2019, 74: 100638. |
| 36 | HARDY I R, SCHAMEL W W, BAEUERLE P A,et al.Implications of T cell receptor biology on the development of new T cell therapies for cancer[J]. Immunotherapy, 2020, 12(1): 89-103. |
| 37 | 卢启明, 胡小英. 基于网络药理学和分子对接探析健脾丸治疗慢性胃炎的作用机制[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志,2021,38(11): 1421-1429. |
| 38 | AUCAR M G, CAVASOTTO C N. Molecular docking using quantum mechanical-based methods[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2020, 2114: 269-284. |
| [1] | Shaojie FU,Sensen SU,Yiying CHEN,Zhonggao XU. Analysis on network pharmacology and molecular docking technique based on mechanism of Shenqi Dihuang Decoction in treatment of membranous nephropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1518-1527. |
| [2] | Weibo LI,Juan CAO,Xiu GUO,Chunling DONG,Bo LI. Promotion effect of tumor associated macrophages-derived IL-6 on invasion and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma Cal27 cells by upregulating LIF expression in tumor cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 946-953. |
| [3] | Yihan WANG,Yidan WANG,Hetong HUI,Xinyuan FAN,Tianqi WANG,Wei XIA,Limei LIU. Detection of promoter methylation levels of Wnt5A and LINE-1 in serum during extramedullary infiltration in acute lymphoblastic leukemia transplanted tumor model mice and its significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 284-290. |
| [4] | Yan LI,Yue HOU,Xingwei MU,Bingqing LIU,Hong WAN,Chang LIU,Wei XIA. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on mechanism of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus in occurrence and development of thoracic aortic aneurysm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 414-425. |
| [5] | Shuqing FENG,Yanhong YAO,Yue SHI,Zhibin LIU,Feng GAO. Application of real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR for detection of BCR/ABL gene expression in peripheral blood in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation therapy in patients with Ph + acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 180-187. |
| [6] | Yanyan FAN,Na WANG,Wen XU,Yajie GE,Lina WANG. Preventive effect of fresh amniotic membrane on intrauterine adhesion and its improvement effect on endometrial receptivity in rabbits [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 990-998. |
| [7] | Yuqing PAN, Yunyan SUN, Yixun LI, Liying WANG, Zhuoma SINAN, Rui CHEN, Xi ZHANG, Yan DU. Construction and analysis of competitive endogenous RNA networks in acute myeloid leukemia based on high-throughput microarray [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 669-676. |
| [8] | Xi ZHANG,Yuqing PAN,Xin YU,Yating ZHENG,Chengbin GUO,Na XU,Liangxiao WANG,Liang HE,Li YANG. Screening and identification of target proteins interacting with GINS2 in human promyelocytic leukemia cDNA library [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 66-72. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xi, ZHAI Li, SUN Yunyan, YANG Wei, GAO Yanzhang, LEI Ming, PAN Yuqing. Bioinformatics analysis of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia based on high-throughput microarray [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1036-1042. |
| [10] | SONG Hongyun, PAN Ying, AN Furun, ZHANG Jiakui, YANG Dongdong, ZHAI Zhimin. Clinical characteristics of acute leukemia patients with complex karyotypes and their effects on prognosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 377-382. |
| [11] | SU Long, ZHANG Yunwei, WANG Zhuo, SONG Fei, QIN Tianxue, GAO Sujun. Proliferation inhibition and pro-apoptotic effects of shikonin on human leukemia MV4-11 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(01): 96-101. |
| [12] | ZHANG Xi, PAN Yuqing, LI Jingfang, YANG Wei, GAO Yanzhang, WEI Ying, SHI Qiong, XIA Quansong, YANG Li. Construction of human promyelocytic cDNA library and its identification [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1015-1019. |
| [13] | CAO Wenbin, LIU Qingzhen, ZHOU Lukun, ZHENG Xiaohui, CHEN Shulian, ZHANG Rongli, HE Yi, FENG Sizhou, HAN Mingzhe, YANG Donglin. Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in non-HIV-infected patients with acute leukemia after chemotherapy: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 148-152. |
| [14] | ZHI Dingming, SUI Dianjun, QI Rui, MIAO Yongdi, HAN Dong, LOU Shilei, QIU Yue, SUN Cong. Potential targets of pueraria in treatment of hyperlipoproteinemia based on network pharmacology [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(04): 724-730. |
| [15] | HUANG Qi, SHA Hui, CHEN Long, LYU Longlong, XU Shengming, ZHANG Zetian, ZHAO Song, JIN Fengyan, NIU Feng. Expression levels of plasma lncRNA MALAT1, LincRNA-p21 and GAS5 in patients with multiple myeloma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia and their diagnostic significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 339-345. |
|
||