Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (1): 139-149.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230118
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Bioinformatics analysis of splicing factor-alternative splicing regulatory network based on alternative splicing data in lung adenocarcinoma tissue
Wuyue TANG1,2,Shuojie LI1,2,Lijuan PANG1,2,3( )
)
- 1.Department of Pathology, School of Medical Sciences, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832002, China
2.Department of Pathology, First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medical Sciences, Shihezi University Shihezi 832002, China
3.Department of Pathology, Central People’s Hospital of Zhanjiang, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524000, China
-
Received:2022-01-03Online:2023-01-28Published:2023-02-03 -
Contact:Lijuan PANG E-mail:ocean123456@shzu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R738.6
Cite this article
Wuyue TANG,Shuojie LI,Lijuan PANG. Bioinformatics analysis of splicing factor-alternative splicing regulatory network based on alternative splicing data in lung adenocarcinoma tissue[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 139-149.
share this article
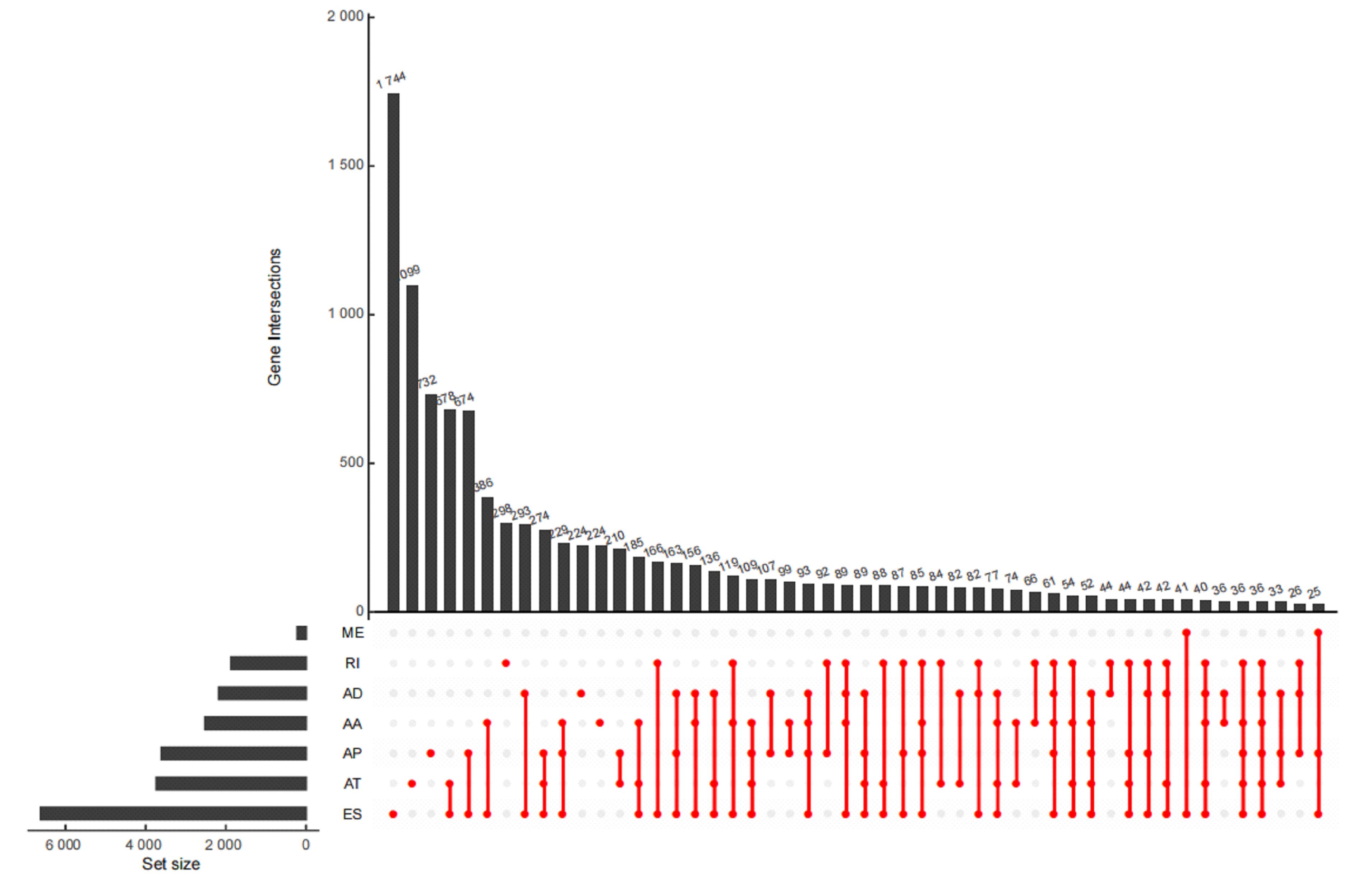
Tab.1
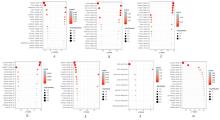
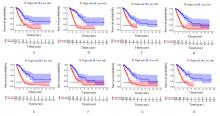
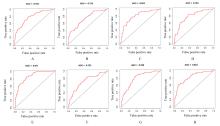
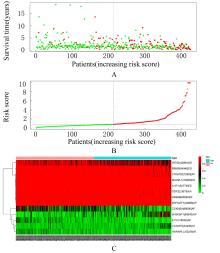
Univariate Cox regression analysis of prognostic factors in LUAD patients"
| Item | P value | Hazard ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.883 | 0.999(0.979-1.019) |
| Gender | 0.977 | 1.006(0.688-1.471) |
| TNM stage | <0.001 | 1.655(1.393-1.966) |
| T stage | <0.001 | 1.594(1.270-2.001) |
| M stage | 0.077 | 1.762(0.941-3.298) |
| N stage | <0.001 | 1.803(1.457-2.231) |
| AA-risk score | 0.021 | 1.402(1.044-1.982) |
| AD-risk score | 0.003 | 1.671(1.245-2.390) |
| AP-risk score | 0.008 | 0.608(0.459-0.895) |
| AT-risk score | 0.002 | 1.667(1.241-2.288) |
| ES-risk score | 0.006 | 1.486(1.092-2.176) |
| ME-risk score | <0.001 | 1.677(1.243-2.339) |
| RI-risk score | 0.026 | 1.367(0.997-1.871) |
| 1 | ZHANG G H, DONG R, KONG D M, et al. The effect of GLUT1 on the survival rate and immune cell infiltration of lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma: a meta and bioinformatics analysis[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2022, 22(2): 223-238. |
| 2 | JIA K R, WU Y C, HUANG J, et al. Survival-associated alternative splicing events in pan-renal cell carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 1317. |
| 3 | WAN Q, SANG X, JIN L, et al. Alternative splicing events as indicators for the prognosis of uveal melanoma[J]. Genes (Basel), 2020, 11(2): E227. |
| 4 | CHEN H Q, CARROT-ZHANG J, ZHAO Y, et al. Genomic and immune profiling of pre-invasive lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 5472. |
| 5 | RAVEH E, MATOUK I J, GILON M, et al. The H19 long non-coding RNA in cancer initiation, progression and metastasis—a proposed unifying theory[J]. Mol Cancer, 2015, 14: 184. |
| 6 | ZHANG Y J, YAO X Y, ZHOU H, et al. OncoSplicing: an updated database for clinically relevant alternative splicing in 33 human cancers[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2022, 50(D1): D1340-D1347. |
| 7 | SONG Q L, YI F T, ZHANG Y H, et al. CRKL regulates alternative splicing of cancer-related genes in cervical cancer samples and HeLa cell[J]. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19(1): 499. |
| 8 | LIN C W, YU B W, ZHANG M, et al. Systematic analyses of the differentially expressed alternative splicing events in gastric cancer and its clinical significance[J]. Front Genet, 2020, 11: 522831. |
| 9 | COOMER A O, BLACK F, GREYSTOKE A, et al. Alternative splicing in lung cancer[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech, 2019, 1862(11/12): 194388. |
| 10 | DE FRAIPONT F, GAZZERI S, CHO W C, et al. Circular RNAs and RNA splice variants as biomarkers for prognosis and therapeutic response in the liquid biopsies of lung cancer patients[J]. Front Genet, 2019, 10: 390. |
| 11 | WAN L D, YU W Y, SHEN E H, et al. SRSF6-regulated alternative splicing that promotes tumour progression offers a therapy target for colorectal cancer[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(1): 118-129. |
| 12 | URBANSKI L M, LECLAIR N, ANCZUKÓW O. Alternative-splicing defects in cancer: Splicing regulators and their downstream targets, guiding the way to novel cancer therapeutics[J]. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, 2018, 9(4): e1476. |
| 13 | CERASUOLO A, BUONAGURO L, BUONAGURO F M, et al. The role of RNA splicing factors in cancer: regulation of viral and human gene expression in human papillomavirus-related cervical cancer[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 474. |
| 14 | SOUBISE B, JIANG Y, DOUET-GUILBERT N,et al. RBM22, a key player of pre-mRNA splicing and gene expression regulation, is altered in cancer[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14(3): 643. |
| 15 | HUANG X Y, SHI H Y, SHI X H, et al. LncRNA FBXL19-AS1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of cervical cancer through upregulating COL1A1 as a sponge of miR-193a-5p[J]. J Biol Res (Thessalon), 2021, 28(1): 20. |
| 16 | MELNYK J E, STERI V, NGUYEN H G, et al. The splicing modulator sulfonamide indisulam reduces AR-V7 in prostate cancer cells[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2020, 28(20): 115712. |
| 17 | WOJTUSZKIEWICZ A, ASSARAF Y G, MAAS M J,et al. Pre-mRNA splicing in cancer: the relevance in oncogenesis, treatment and drug resistance[J]. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol, 2015, 11(5): 673-689. |
| 18 | LIM B, KIM C, KIM J H, et al. Genetic alterations and their clinical implications in gastric cancer peritoneal carcinomatosis revealed by whole-exome sequencing of malignant ascites[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(7):8055-8066. |
| 19 | SONG H, WANG Y P, SHI C J, et al. SH3KBP1 promotes glioblastoma tumorigenesis by activating EGFR signaling[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 583984. |
| 20 | SHI Y X, ZHU T, ZOU T, et al. Prognostic and predictive values of CDK1 and MAD2L1 in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(51): 85235-85243. |
| 21 | LI J F, HE X, WU X T, et al. miR-139-5p inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting MAD2L1[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2020, 2020: 2953598. |
| 22 | ZHANG J F, ZHANG J, XU S P, et al. Hypoxia-induced TPM2 methylation is associated with chemoresistance and poor prognosis in breast cancer[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 45(2): 692-705. |
| 23 | LIU S W, ZENG F P, FAN G W, et al. Identification of hub genes and construction of a transcriptional regulatory network associated with tumor recurrence in colorectal cancer by weighted gene co-expression network analysis[J]. Front Genet, 2021, 12: 649752. |
| 24 | VARISLI L. Identification of new genes downregulated in prostate cancer and investigation of their effects on prognosis[J].Genet Test Mol Biomarkers,2013,17(7): 562-566. |
| 25 | LIU Q, FANG L M, WU C J. Alternative splicing and isoforms: from mechanisms to diseases[J]. Genes, 2022, 13(3): 401. |
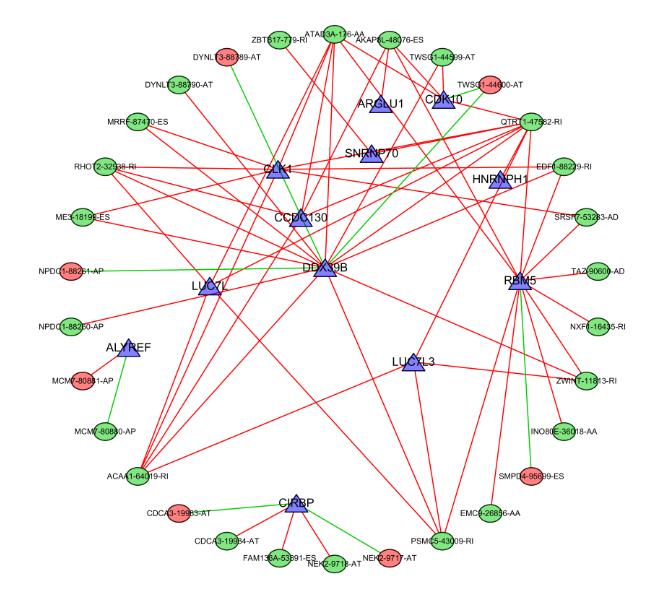
| 26 | PÉREZ-CALERO C, BAYONA-FELIU A, XUE X Y, et al. UAP56/DDX39B is a major cotranscriptional RNA-DNA helicase that unwinds harmful R loops genome-wide[J].Genes Dev,2020,34(13/14): 898-912. |
| 27 | AWASTHI S, CHAKRAPANI B, MAHESH A,et al. DDX39B promotes translation through regulation of pre-ribosomal RNA levels[J]. RNA Biol, 2018, 15(9): 1157-1166. |
| 28 | ZHANG H N, HE C C, GUO X X, et al. DDX39B contributes to the proliferation of colorectal cancer through direct binding to CDK6/CCND1[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2022, 8(1): 30. |
| 29 | XU Z Z, LI X M, LI H X, et al. Suppression of DDX39B sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to DNA-damaging chemotherapeutic agents via destabilizing BRCA1 mRNA[J].Oncogene,2020,39(47):7051-7062. |
| 30 | WEI J H, LU J, CAO Y, et al. DDX39B predicts poor survival and associated with clinical benefit of anti-PD-L1 therapy in ccRCC[J]. Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 2021, 21(10): 849-859. |
| 31 | ISHIMI Y. Regulation of MCM2-7 function[J]. Genes Genet Syst, 2018, 93(4): 125-133. |
| 32 | WANG J Z, ZHU W, HAN J, et al. The role of the HIF-1α/ALYREF/PKM2 axis in glycolysis and tumorigenesis of bladder cancer[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2021, 41(7): 560-575. |
| [1] | Junjie HOU,Xuguang MI,Xiaonan LI,Xiaonan LI,Ying YANG,Xiaodan LU,Yanqiu FANG,Ningyi JIN. Establishment and evaluation of prognostic model of lung adenocarcinoma based on lactate metabolism gene [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1546-1554. |
| [2] | Liantao HU,Wenjun DENG,Shizhen LU,Luo SUN,Xuebing LI,Chuhao LI,Xinran WANG,chunbing ZHANG,Yue LI,Weiqun WANG. Bioinformatics analysis on CC chemokine ligand 20 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and its effect on prognostic assessment of liver hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1010-1017. |
| [3] | Xiaoyan LI,Wei ZHANG,Jie HE. Promotion effect of REG1A on proliferation and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 444-453. |
| [4] | Ying ZHAO,Danyu ZHAO,Chao LIU. Bioinformatics analysis on prognostic evaluation value of TXNDC11 gene in pan-cancer and its immunity regulation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 142-153. |
| [5] | Shuzhen LI,Yajie CAO,Haiying GENG,Zengxiaorui CAI,Chunmei DAI,Youfeng WEN,Ning LI. Bioinformatics analysis based on expression level of HMMR in lung adenocarcinoma tissue and its impact on prognosis of LUAD patients [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1502-1509. |
| [6] | Yao LIN,Chunlin LIN,Qin WANG,Bin ZHANG,Shaoyu WANG,Guangwei ZHU. Expressions of minichromosome maintenance proteins and structural maintenance of chromosomes 4 genes in cervical squamous cell carcinoma tissue and bioinformation analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 430-437. |
| [7] | GUO Weiwei, QIN Yue, YANG Haibo, MI Zhanhu. Promotion effect of LncRNA MALAT1 on osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells through miR-34c/SATB2 axis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 963-971. |
| [8] | ZHAO Min, JIN Xin, DI Xin, TIAN Chang, LIU Jiaying, CONG Shan, WANG Ke. Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 634-638. |
| [9] | FANG Hui, YANG Hongyu, MA Xuzhe, CHEN Lisong, GAI Xiaodong, LI Chun. Effects of FOXP3 on cell proliferation and chemosensitivity to cisplatin in lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1261-1266. |
| [10] | DU Yayan, LIU Yang, LU Mu, HUAI Shitao, LYU Zuoli, WEI Yutao. Expressions of adiponectin-related miR-371b-5p in epicardial adipose tissue and plasma of patients with coronary heart disease and its effect on secretion of adipocytokines [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 643-650. |
| [11] | YANG Yi, BAO Kangda, ZHOU Yanbing, YUAN Chao, LI Yong, LIU Xiaoming, XU Jinrui. Regulation of Wnt5a in apoptosis of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 229-234. |
| [12] | WANG Chaoyi, WANG Qiang, ZHENG Yueyong, LI Cong, GUO Dunwei, TANG Hua. Effect of follistatin on skeletal muscle wasting of cancer cachexia mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(04): 653-658. |
| [13] | CAO Xin-mei,ZHANG Dai-quan,WANG Xu,XIA Ji-yi,HUANG Li,GAO Yan. Effect of C-erbB-2 shRNA on chemosensitivity of mouse lung adenocarcinoma cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(04): 777-781. |
| [14] | YANG Yan-ming,FANG Fang,LIU Nian,QU Zhi-jie,WANG Zhi-cheng,ZHANG Yan-qiu. Influence of pEgr1-hsTRAL plasmid on radiosensitivity and DR4 and DR5 expression levels in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(2): 199-203. |
| [15] | LI Ping|ZHANG Jie|LI Ya-rong|WANG Ke|SU Zhen-zhong . Reversal effect of Ku70-targeted siRNA on chemoresistance to cisplatin in human lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. J4, 2012, 38(2): 240-245. |
|
||