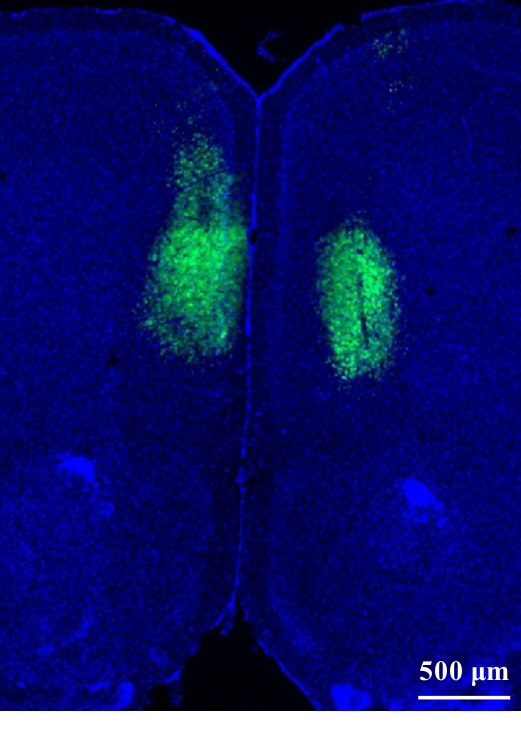
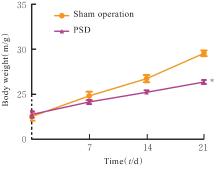
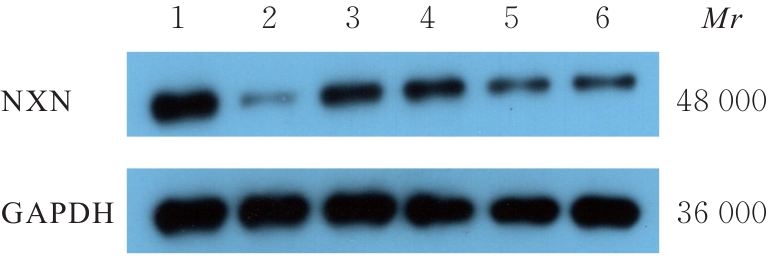
| 1 |
STRONG B, FRITZ M C, DONG L M, et al. Changes in PHQ-9 depression scores in acute stroke patients shortly after returning home[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(11): e0259806.
|
| 2 |
YU Y, ZHANG G, LIU J, et al. Network meta-analysis of Chinese patent medicine adjuvant treatment of poststroke depression[J]. Medicine, 2020, 99(31): e21375.
|
| 3 |
BABKAIR L A, CHYUN D, DICKSON V V, et al. The effect of psychosocial factors and functional independence on poststroke depressive symptoms: a cross-sectional study[J]. J Nurs Res, 2021, 30(1): e189.
|
| 4 |
赵紫岐, 马 睿, 屈 云. 基于临床实践的卒中后抑郁评估现状分析[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2022, 37(6): 860-863.
|
| 5 |
IDELFONSO-GARCÍA O G, ALARCÓN-SÁNCHEZ B R, VÁSQUEZ-GARZÓN V R, et al. Is nucleoredoxin a master regulator of cellular redox homeostasis? its implication in different pathologies[J]. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(4): 670.
|
| 6 |
TRAN B N, VALEK L, WILKEN-SCHMITZ A, et al. Reduced exploratory behavior in neuronal nucleoredoxin knockout mice[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 45: 102054.
|
| 7 |
VALEK L, TRAN B N, TEGEDER I. Cold avoidance and heat pain hypersensitivity in neuronal nucleoredoxin knockout mice[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 192: 84-97.
|
| 8 |
KNOUSE M C, MCGRATH A G, DEUTSCHMANN A U, et al. Sex differences in the medial prefrontal cortical glutamate system[J]. Biol Sex Differ, 2022, 13(1): 66.
|
| 9 |
HEIN M, ZOREMBA N, BLEILEVENS C, et al. Levosimendan limits reperfusion injury in a rat middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model[J]. BMC Neurol, 2013, 13: 106.
|
| 10 |
LONGA E Z, WEINSTEIN P R, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats[J]. Stroke, 1989, 20(1): 84-91.
|
| 11 |
周丽萍, 章宸一瑜, 马世平, 等. 柴胡-黄芩药对配伍及用量比例对抑郁小鼠行为学及脑海马BDNF/TrkB信号通路的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2020, 38(4): 67-71.
|
| 12 |
PAN C S, LI G, SUN W Z, et al. Neural substrates of poststroke depression: current opinions and methodology trends[J]. Front Neurosci, 2022, 16: 812410.
|
| 13 |
JOBSON D D, HASE Y, CLARKSON A N, et al. The role of the medial prefrontal cortex in cognition, ageing and dementia[J]. Brain Commun, 2021, 3(3): fcab125.
|
| 14 |
WANG R R, LIU Z H, BI N X, et al. Dysfunction of the medial prefrontal cortex contributes to BPA-induced depression-and anxiety-like behavior in mice[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2023, 259: 115034.
|
| 15 |
王存强, 贺顺岭, 顾韵泽, 等. 脑卒中后抑郁者海马和前额叶皮质氢质子波谱分析研究[J]. 中国实用医刊, 2016, 43(17): 1-4.
|
| 16 |
LIU J, MENG F T, WANG W T, et al. Medial prefrontal cortical PPM1F alters depression-related behaviors by modifying p300 activity via the AMPK signaling pathway[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2023, 29(11): 3624-3643.
|
| 17 |
TANG W Q, LIU Y, JI C H, et al. Virus-mediated decrease of LKB1 activity in the mPFC diminishes stress-induced depressive-like behaviors in mice[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2022, 197: 114885.
|
| 18 |
XU J, GUO C P, LIU Y, et al. Nedd4l downregulation of NRG1 in the mPFC induces depression-like behaviour in CSDS mice[J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2020, 10(1): 249.
|
| 19 |
ARELLANES-ROBLEDO J, REYES-GORDILLO K, IBRAHIM J, et al. Ethanol targets nucleoredoxin/dishevelled interactions and stimulates phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate production in vivo and in vitro [J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2018, 156: 135-146.
|
| 20 |
CHA J Y, AHN G, JEONG S Y, et al. Nucleoredoxin 1 positively regulates heat stress tolerance by enhancing the transcription of antioxidants and heat-shock proteins in tomato[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2022, 635: 12-18.
|
| 21 |
VILLA R F, FERRARI F, MORETTI A. Post-stroke depression: mechanisms and pharmacological treatment[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2018, 184: 131-144.
|
| 22 |
白 露, 宋 雪, 王 珑, 等. 氧化应激在卒中后抑郁病理机制中的作用及研究进展[J]. 河北医学, 2022, 28(12): 2105-2108.
|
| 23 |
李传斌, 夏 磊. 圣约翰草提取物对卒中后抑郁患者氧化应激损伤的影响[J]. 临床心身疾病杂志, 2022, 28(4): 100-103.
|
| 24 |
汪海潮, 毛森林, 王澎伟. 卒中后抑郁的发病机制及危险因素的研究进展[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2023, 40(9): 785-788.
|
 ),Bo SHI,Zhixuan WEI,Qunjian CUI
),Bo SHI,Zhixuan WEI,Qunjian CUI