| [1] |
Wei ZHONG,Zhiyin DAI,Xinggang CUI,Bo LI,Yu JIANG.
Effect of nuclear factor of activated T lymphocytes 5 on senescence of smooth muscle cells of mice induced by high-salt and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 567-575.
|
| [2] |
DILIXIATI·Dilidaer,Lin JIA.
Improvement effect of exosomes derived from human adipose-derived stem cells and human dermal fibroblasts on ultraviolet-induced photoaging skin wrinkles in nude mice
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 621-631.
|
| [3] |
Fanjun SUN,Xingchen PAN,Dan TONG.
Research progress in MRI neuroimaging for patients with functional gastrointestinal diseases and inflammatory bowel disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 541-548.
|
| [4] |
Zilong GAO,Biao LIU,Le QI,Jingyu LANG,Yan LIU.
Giant cell-rich osteosarcoma with special imaging findings: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 222-227.
|
| [5] |
Hong LI,Hui WANG,Lishu WANG,Chaonan WANG,Xiaohao XU,Liwei SUN.
Ameliorating effect of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides on intestinal mucosal barrier damage in elderly mice by regulating intestinal microbial metabolites
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 76-84.
|
| [6] |
Weichao WU,Yan GUO,Xiangkai ZHAO,Zhiguang GU,Yijia GUO,Zipeng LAN,Hui HUANG,Lei KUANG,Ming ZHANG,Dongsheng HU,Yongli YANG,Wei WANG,Jinru CHEN.
Correlation analysis on occupational acid fog exposure and accelerated biological aging in workers
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1741-1750.
|
| [7] |
Xueting CHI,Fangyuan CHEN,Zifeng PI,Guangfu LYU,Yuchen WANG,Yinqing LI,Xiaowei HUANG,Zhe LIN.
Improvement effect of velvet antler polypeptide on postmenopausal osteoporosis in rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 963-969.
|
| [8] |
Xueting CHI,Xiaowei HUANG,Fangyuan CHEN,Gaofeng ZHOU,Jinji WANG,Guangfu LYU,Zhe LIN,Qing GONG.
Improvement effect of velvet antler polypeptide in osteoporosis model rats and its effect on SIRT1/FOXO1 signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 120-127.
|
| [9] |
Xiaodong WEN,Chunling WANG,Yuanjing JIANG,Xinmei ZHOU,Yi ZHANG,Yuan WU.
Effect of fructus mume total flavone on injury of SH-SY5Y cells induced by MPP+ through regulating miR-145-3p expression and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1415-1423.
|
| [10] |
Canfei XU,Yan HUANG,Kaizhi ZHANG.
Acute ischemic stroke patients with onset time within 4.5 h identified by machine learning combined with magnetic resonance diffusion weighted imaging
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1635-1641.
|
| [11] |
Hongli CUI,Siqi FAN,Wenfei GUAN,E MENG,Jiatong LIU,Xuetong SUN,Chunxu CAO,Lixin LIU,Yali QI,Fang FANG,Zhicheng WANG.
Inhibitory effect of irradiation enhanced by gallic acid-lecithin complex-induced oxidative stress on proliferation of A549 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 941-946.
|
| [12] |
Naixu SHI,Miao HAO,Tianfu ZHANG,Kelin ZHAO,Ziyan HUANG,Chunyan LI,Xiaofeng WANG.
Inhibitory effect of baicalein on proliferation of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma CAL27 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 985-993.
|
| [13] |
Chang LI,Zishan MA,Shanmei HUANG,Bangqiao YIN,Zhifan CHEN,Sha NIE,Ziqian ZHANG,Li LI,Ying LIU,Yaoping TANG.
Protective effect of Yiyi Fuzisan on myocardium ischemia and vascular endothelial function injury in mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 580-589.
|
| [14] |
Desheng HUANG,Yanan ZHAO,Yun CHEN,Yiyao SUN,Weilin QIN,Moujie LIU,Juhua XIE.
Improvement effect of metformin on hypertrophy of H9C2 cardiomyocytes and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 675-681.
|
| [15] |
Gaofeng ZHOU,Jing XIAO,Jia ZHOU,Junxiu LIU,Guangfu LYU,Yuchen WANG,He LIN,Xiaowei HUANG.
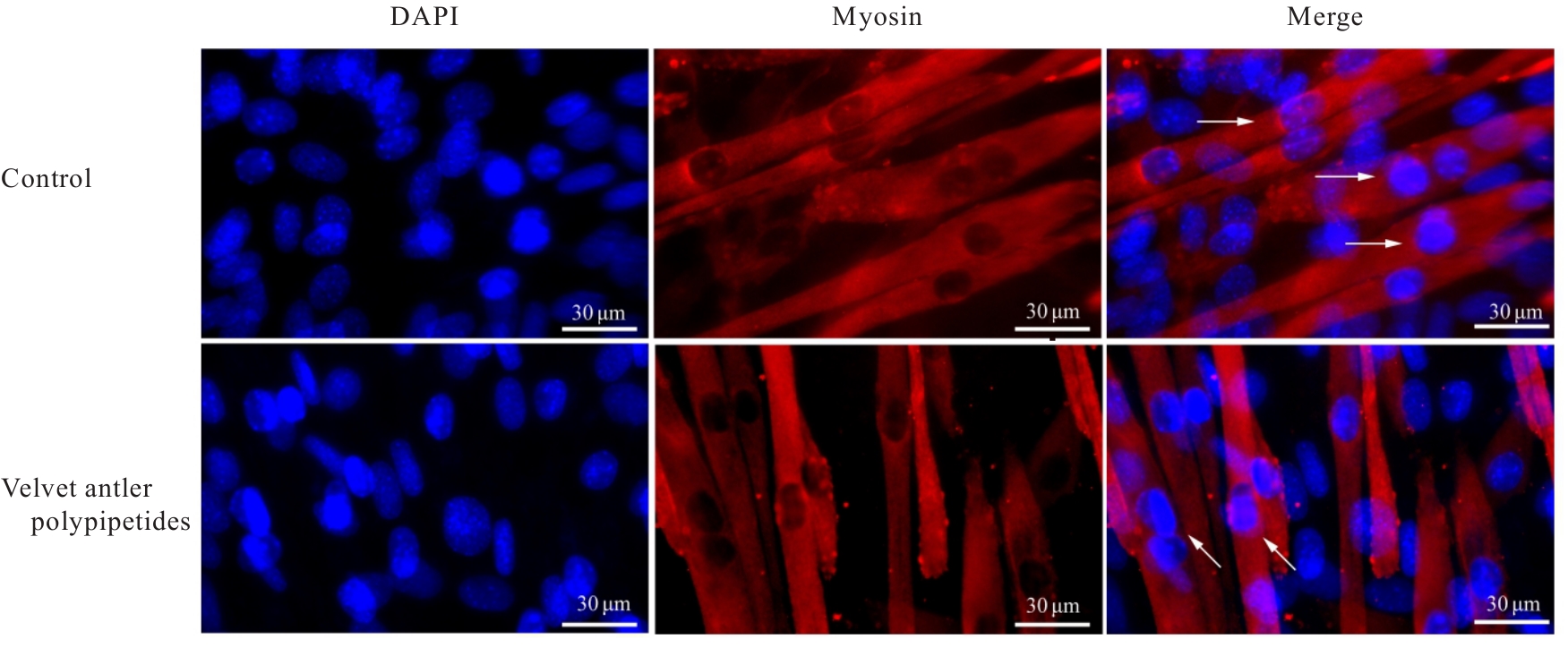
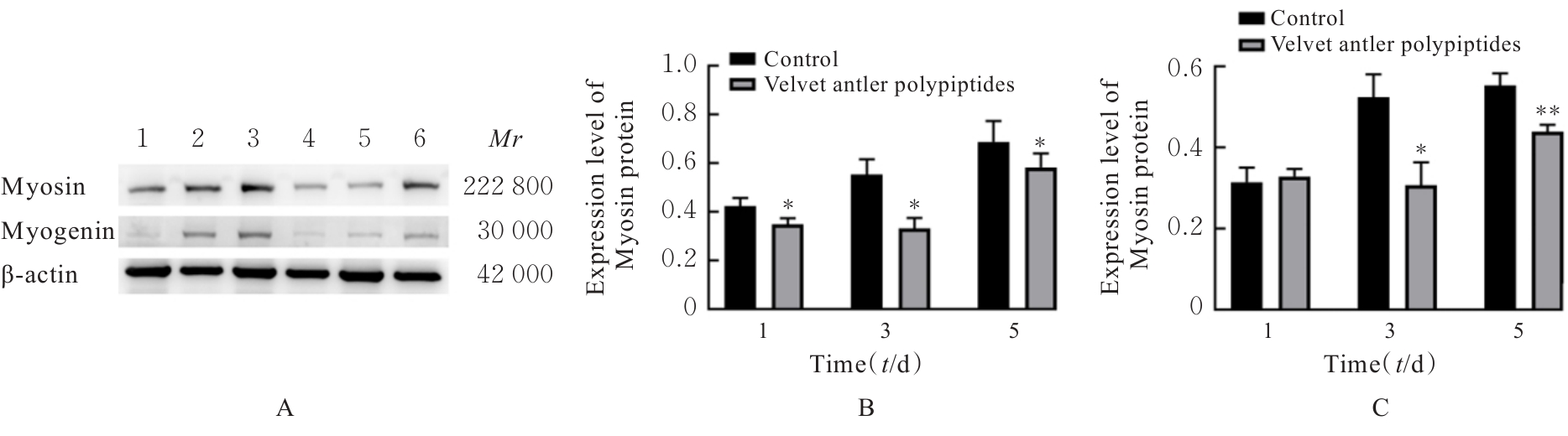
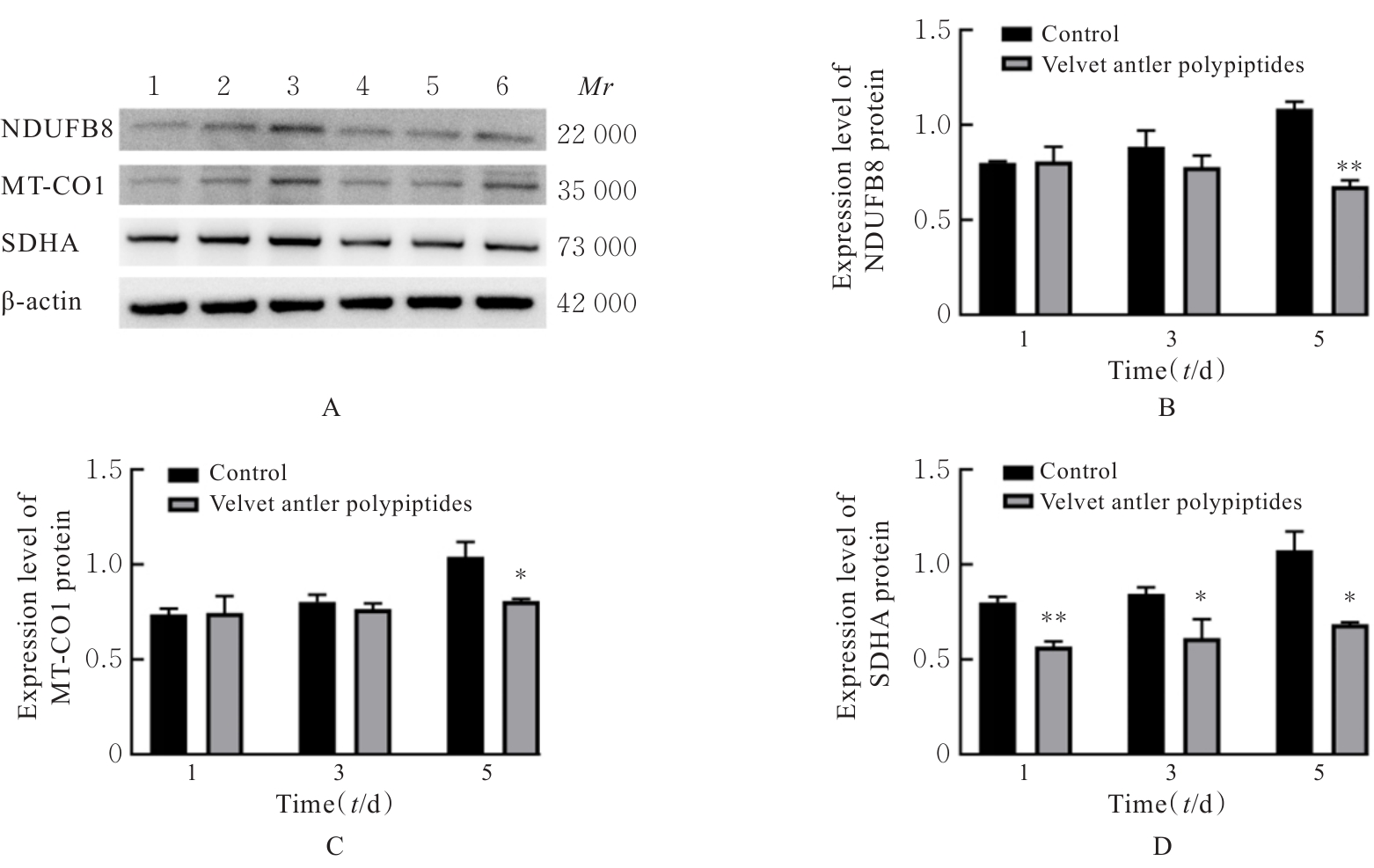
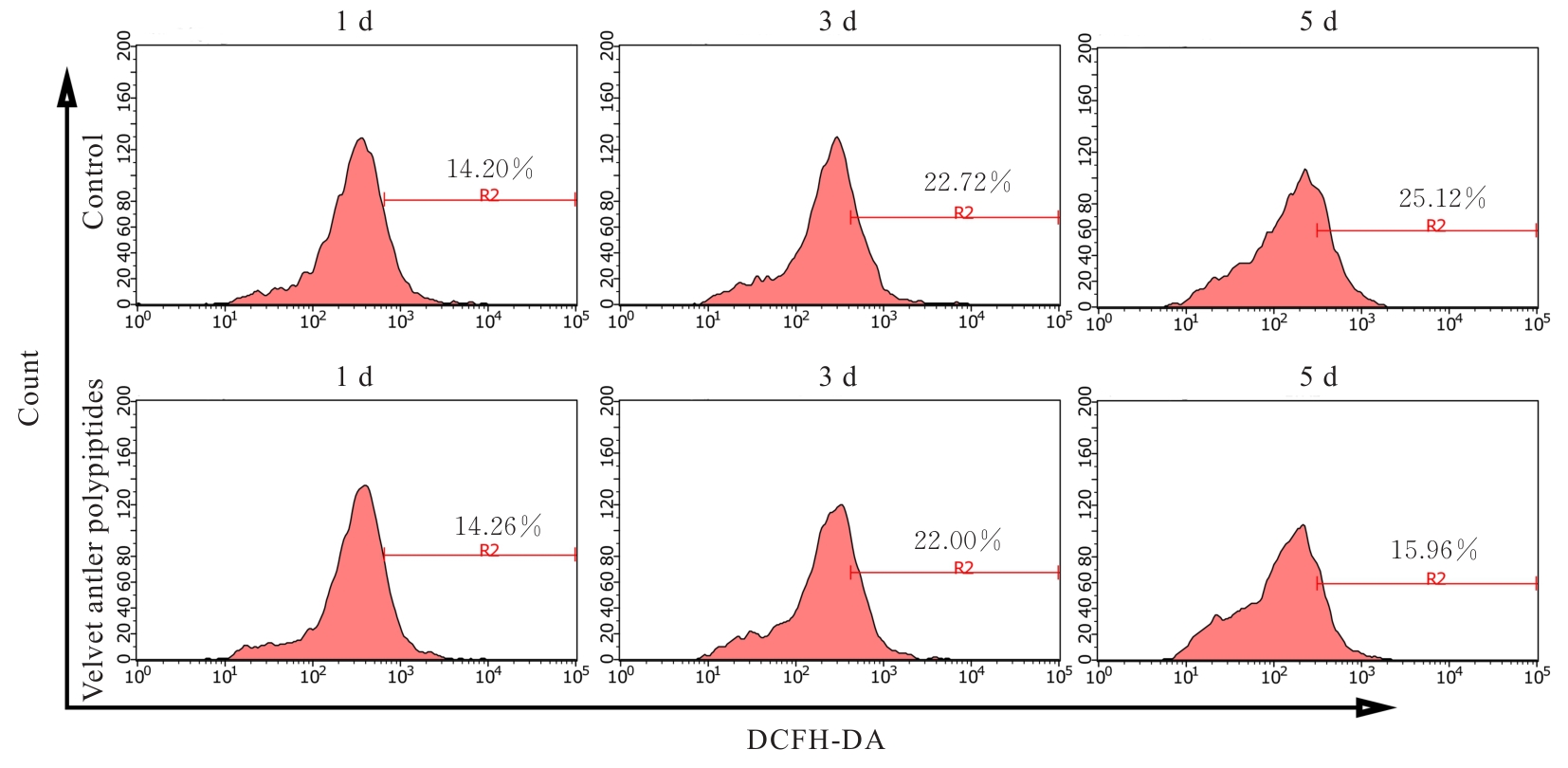
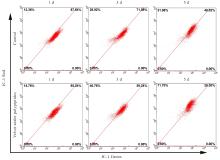
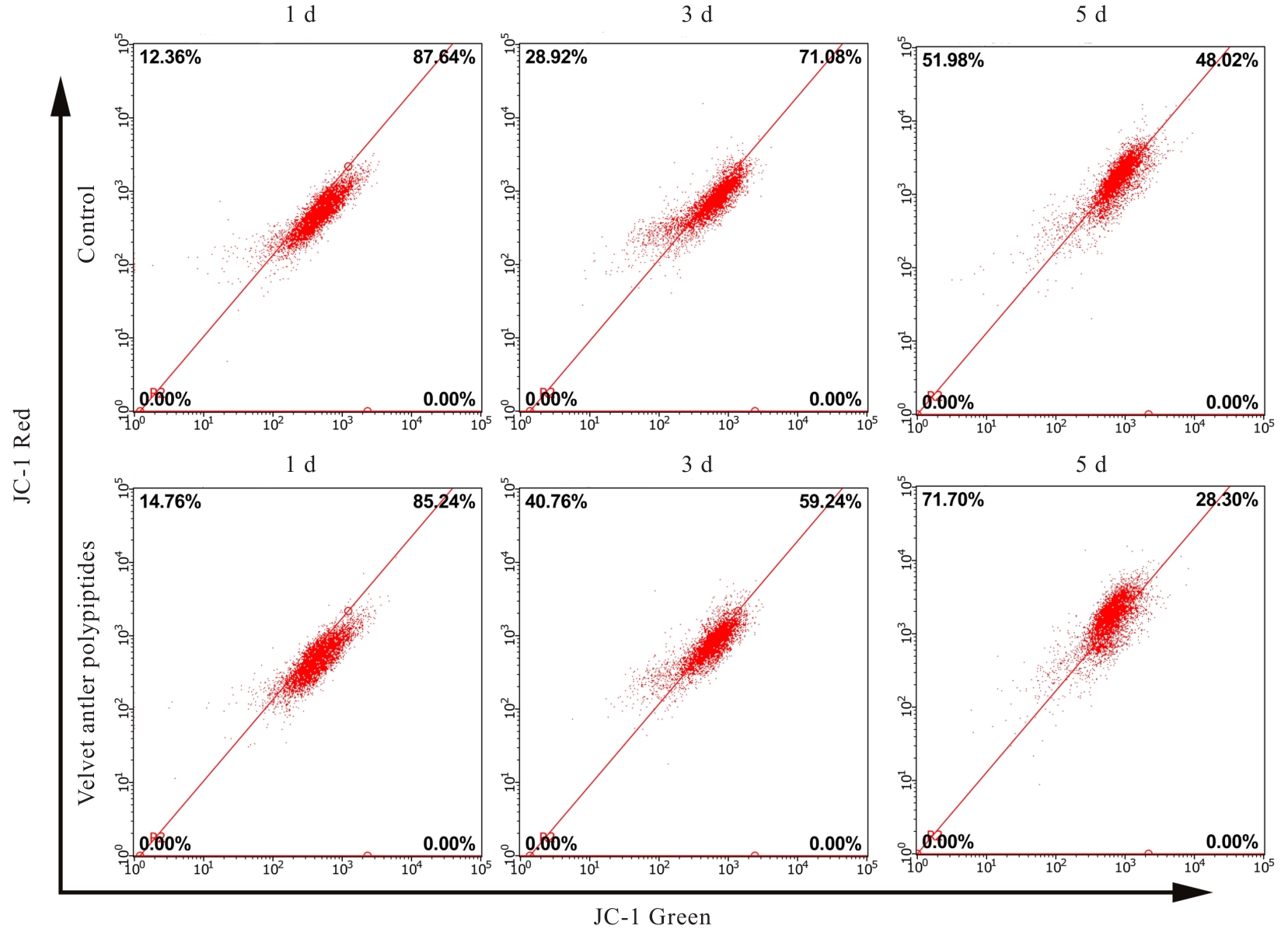
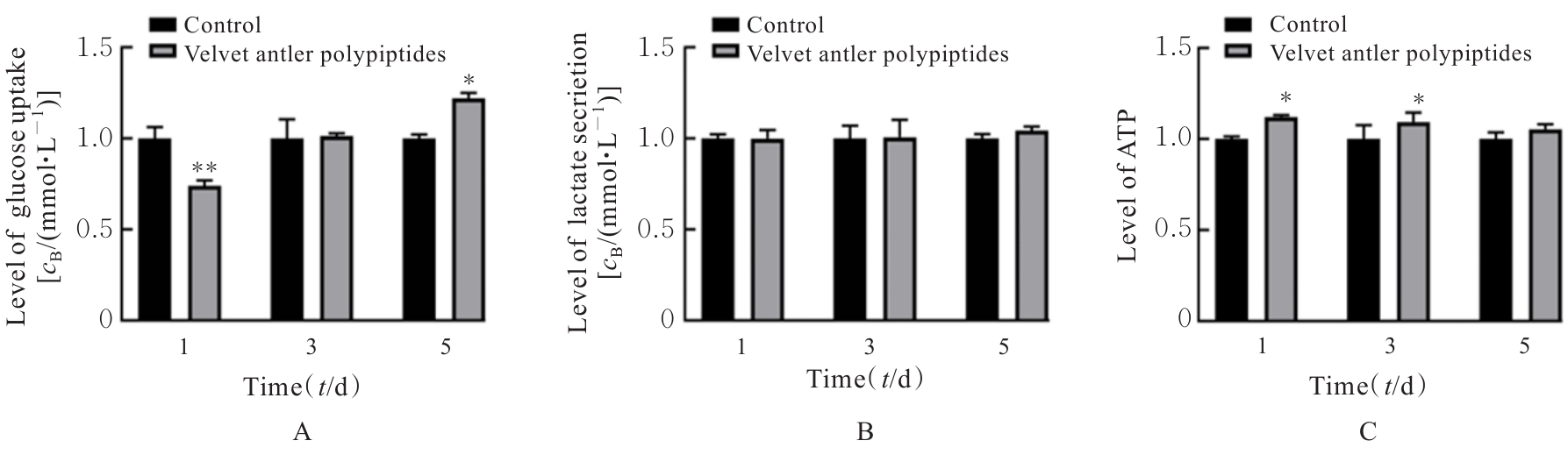
Protective effect of Velvet antler polypeptide pretreatment on myocardial H9c2 cell injury induced by TBHP through regulating TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway with miR-133a
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 369-376.
|