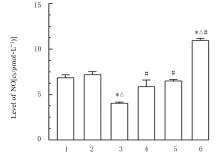
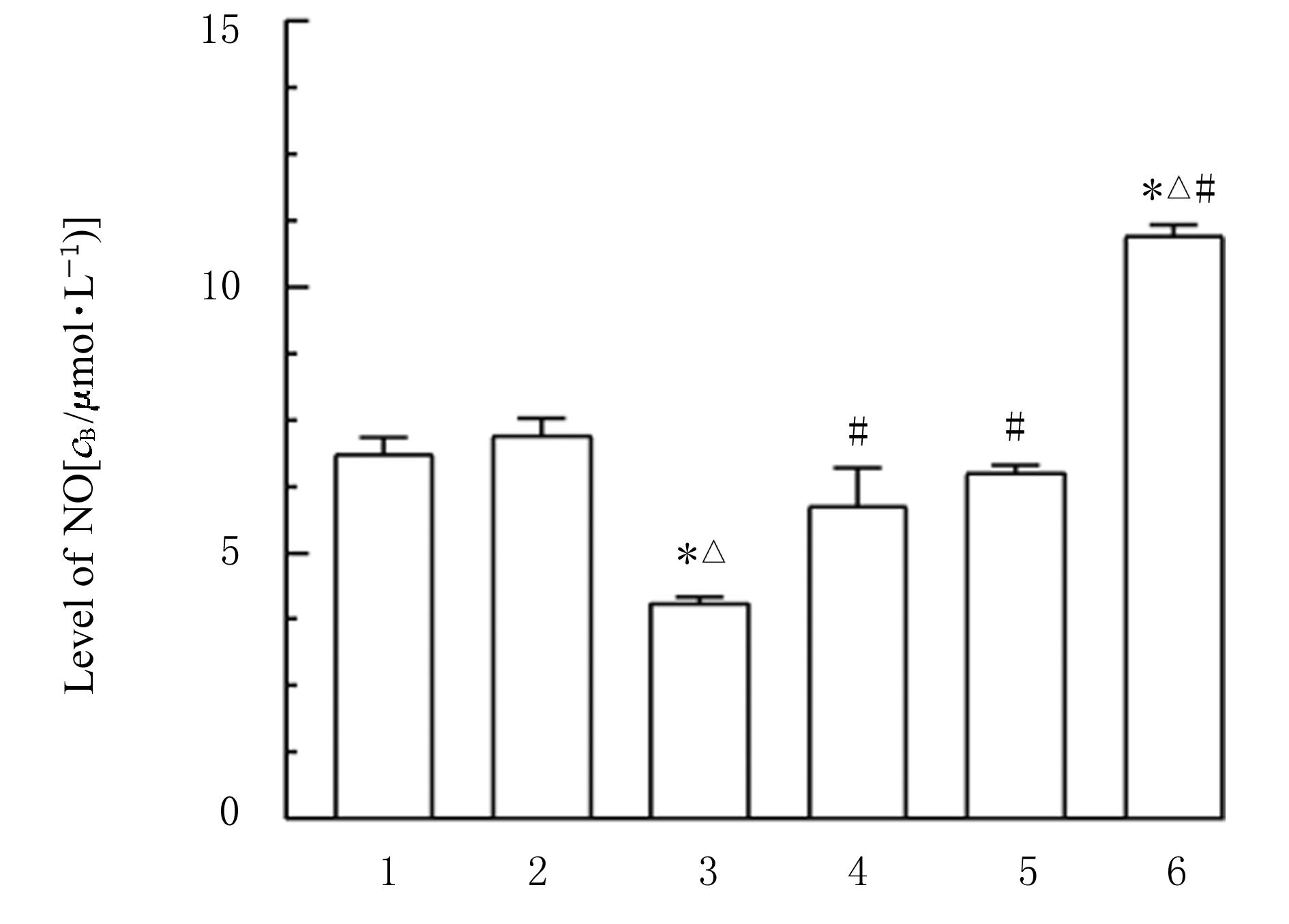
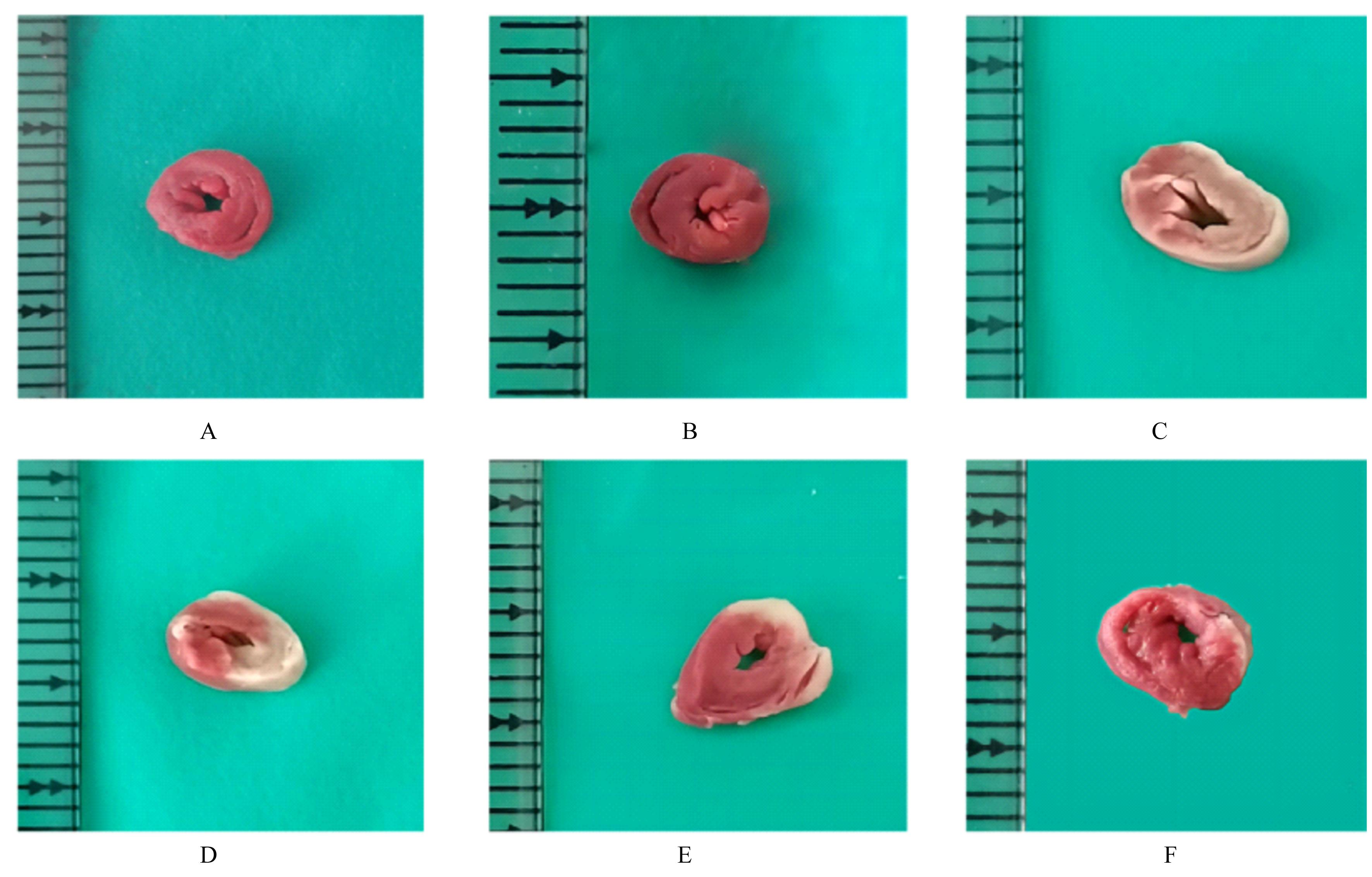
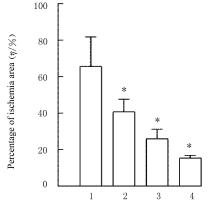
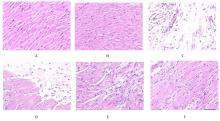
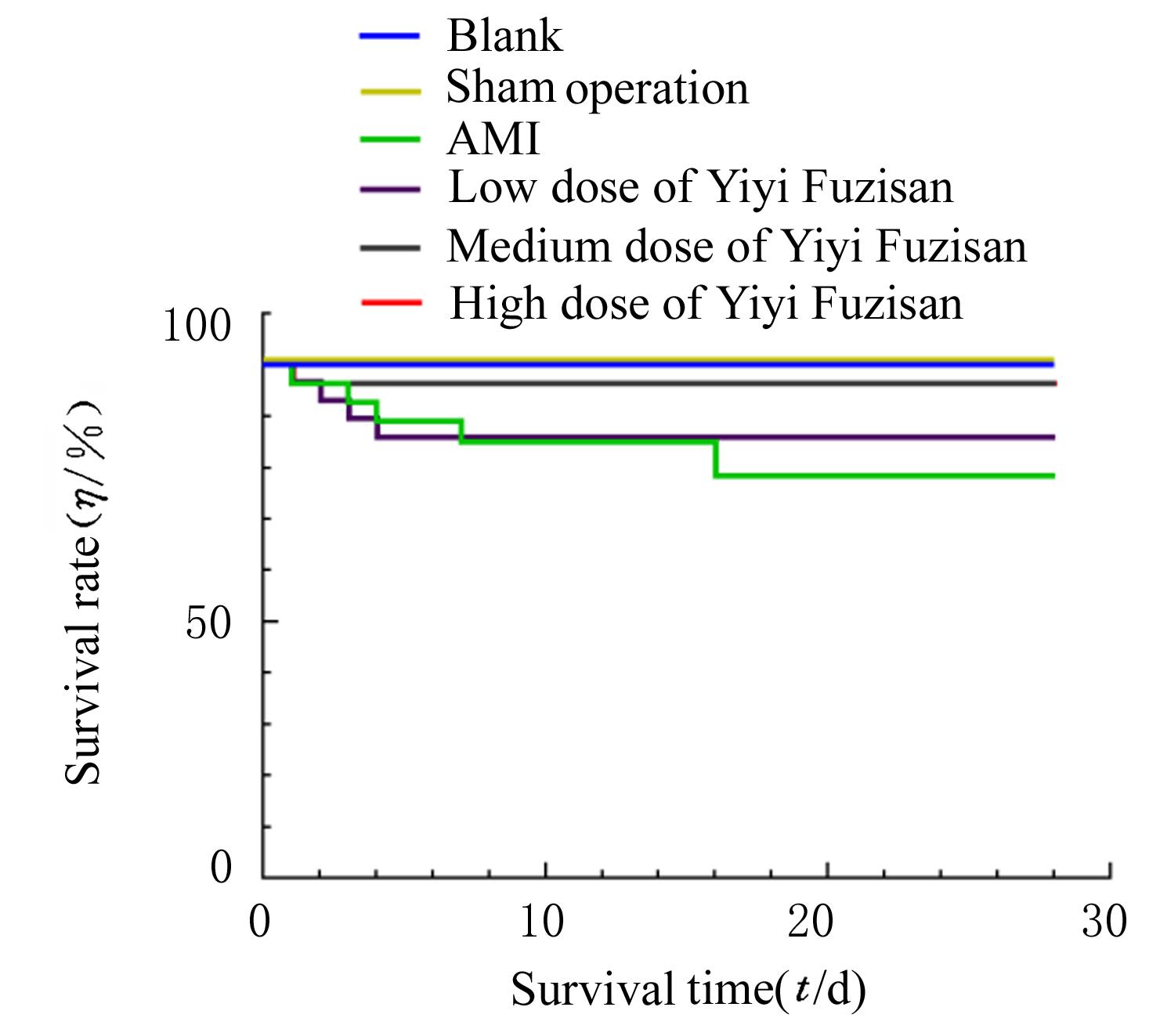
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 580-589.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230305
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
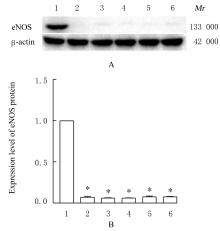
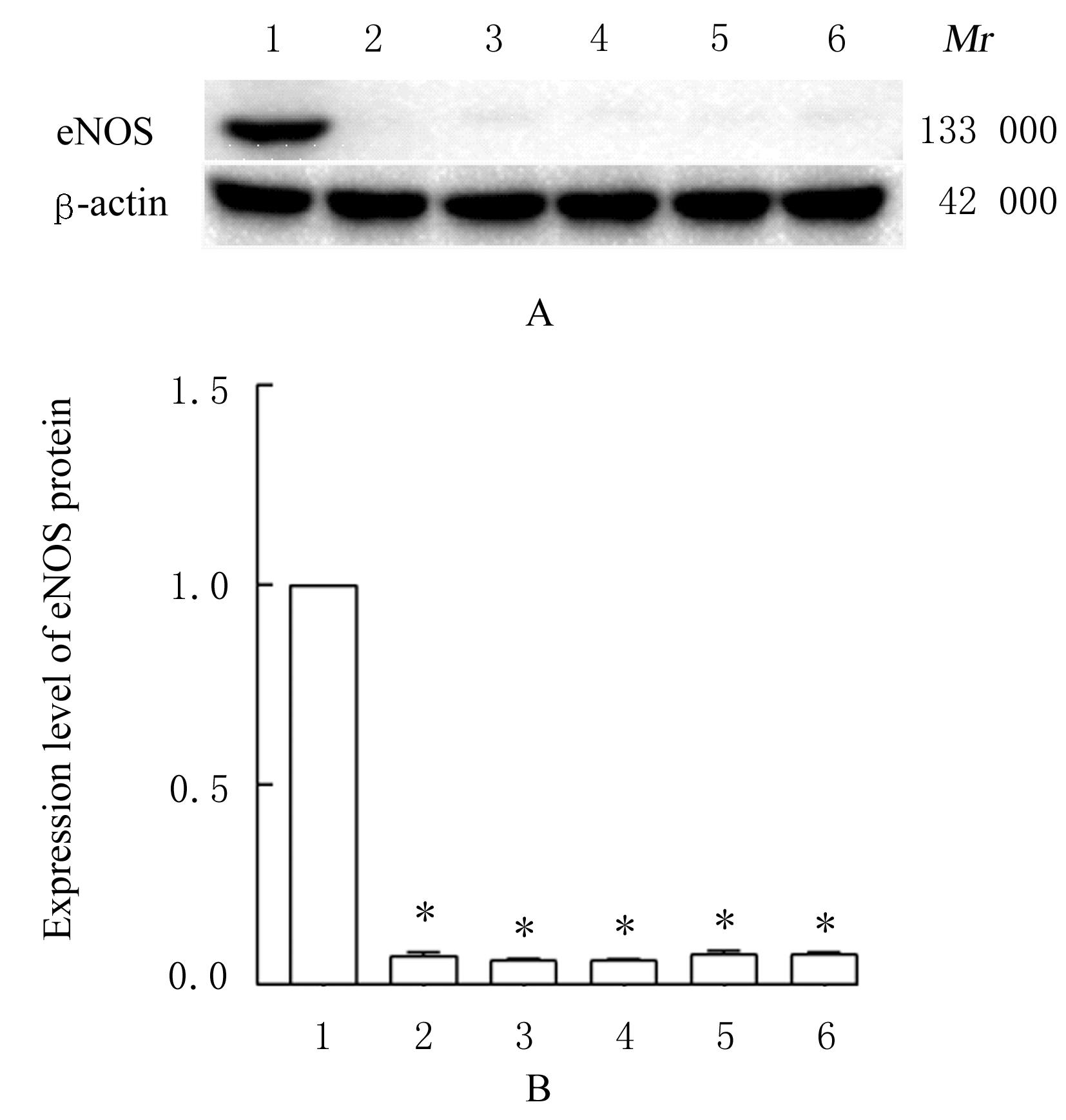
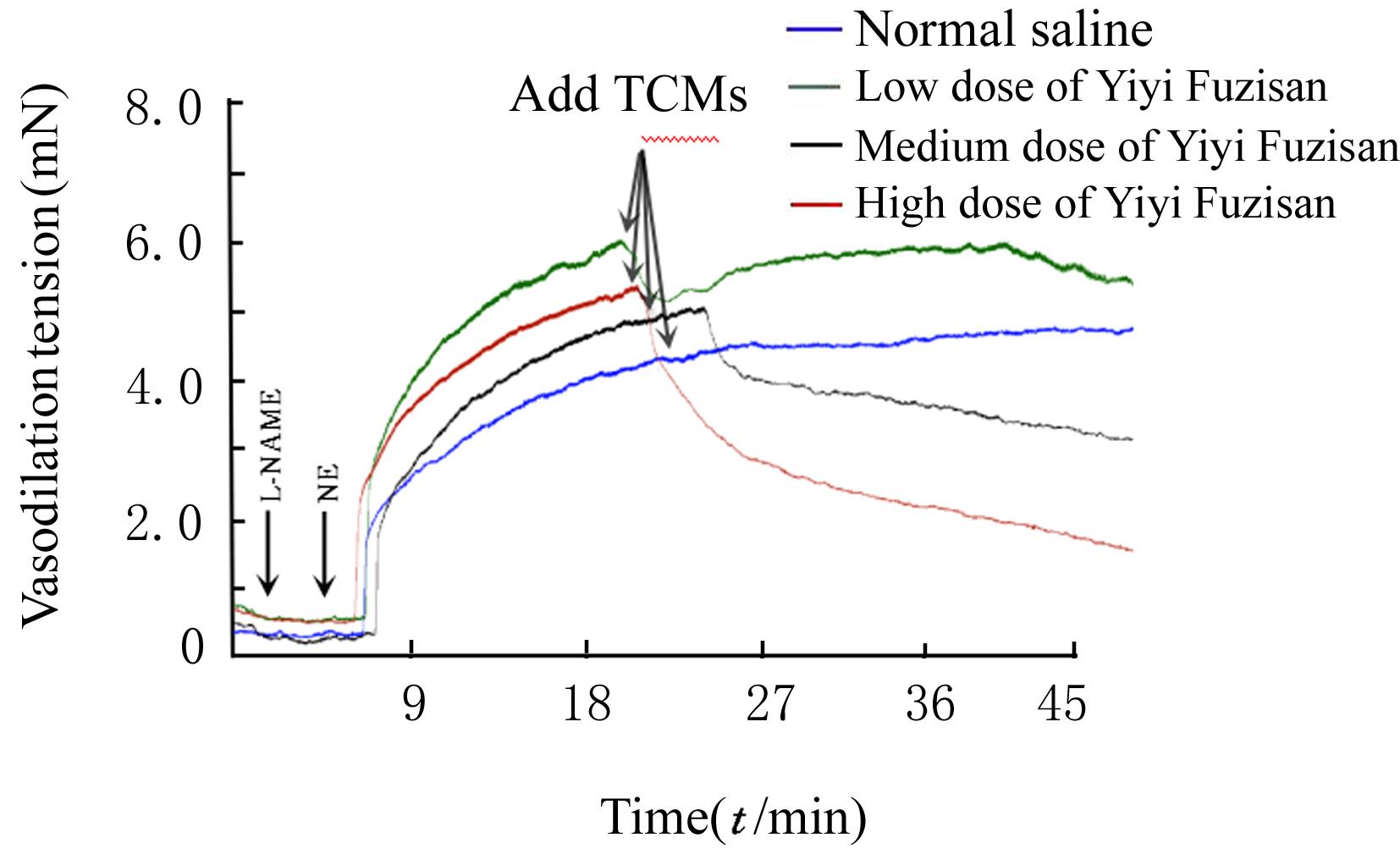
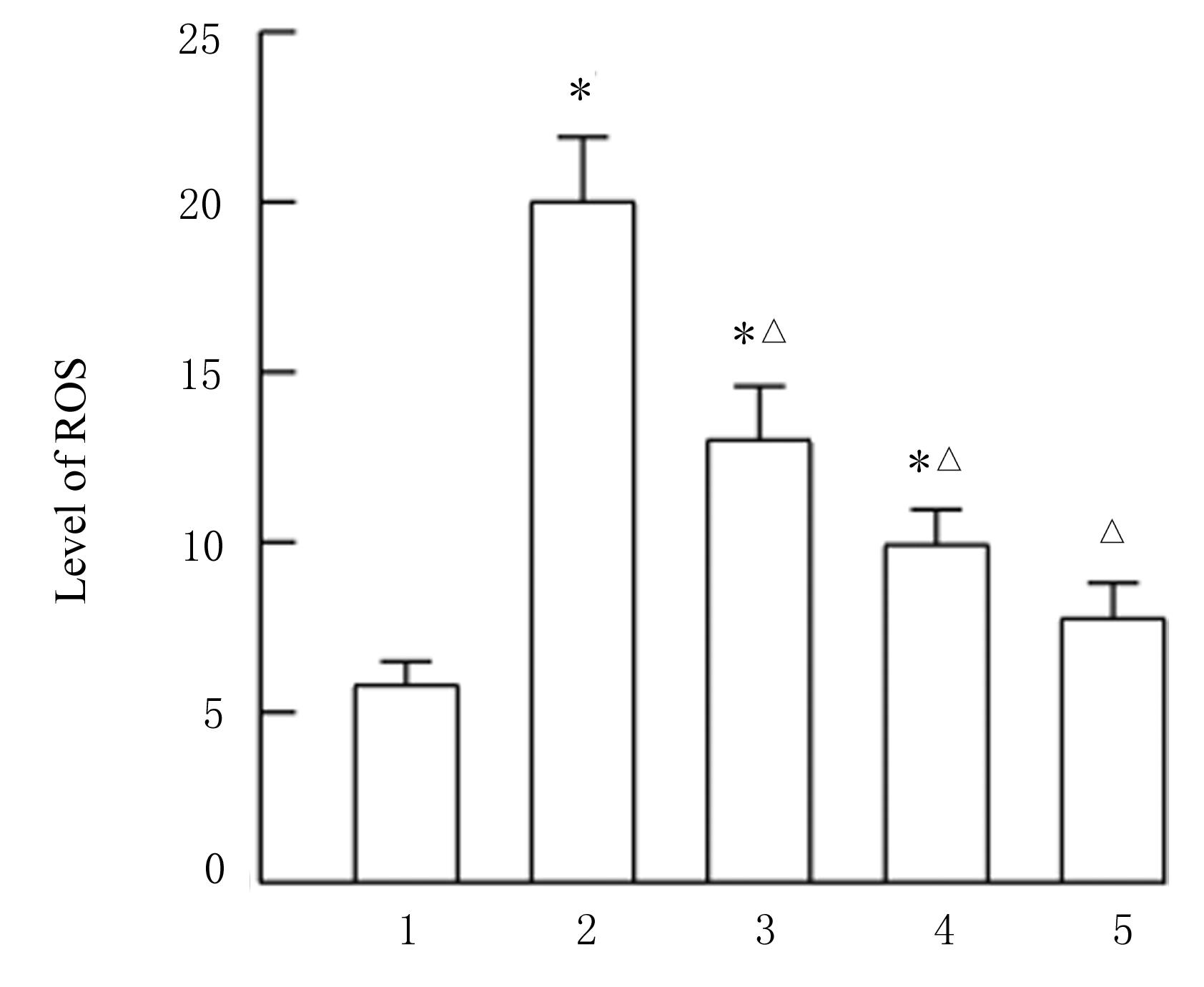
Protective effect of Yiyi Fuzisan on myocardium ischemia and vascular endothelial function injury in mice and its mechanism
Chang LI1,2,Zishan MA1,2,Shanmei HUANG1,2,Bangqiao YIN2,Zhifan CHEN1,2,Sha NIE1,2,Ziqian ZHANG3,Li LI3,Ying LIU1( ),Yaoping TANG2,4(
),Yaoping TANG2,4( )
)
- 1.Graduate School, Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
2.Affiliated Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, China
3.Center of Scientific Research, Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
4.Key Laboratory of Translational Medicine for Treating High-Incidence Infectious Diseases with Integrative Medicine, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning 530200, China
-
Received:2022-07-10Online:2023-05-28Published:2023-06-20 -
Contact:Ying LIU,Yaoping TANG E-mail:xdtly001@126.com;tangyp2014@gxtcmu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R541
Cite this article
Chang LI,Zishan MA,Shanmei HUANG,Bangqiao YIN,Zhifan CHEN,Sha NIE,Ziqian ZHANG,Li LI,Ying LIU,Yaoping TANG. Protective effect of Yiyi Fuzisan on myocardium ischemia and vascular endothelial function injury in mice and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 580-589.
share this article
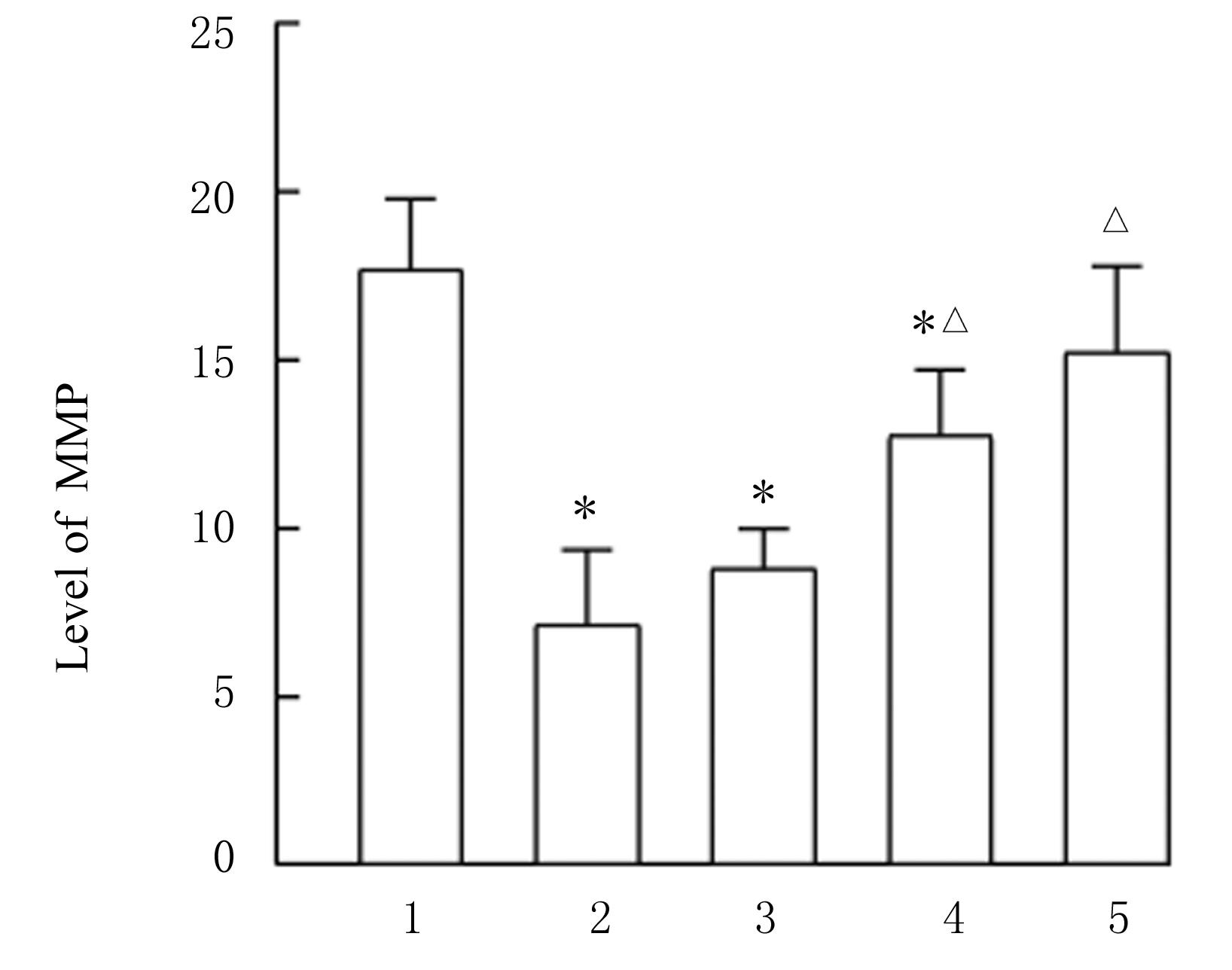
| 1 | HE X, LIU J K, ZANG W J. Mitochondrial homeostasis and redox status in cardiovascular diseases: protective role of the vagal system[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 178: 369-379. |
| 2 | ABOLHALAJ M, AMOLI M M, AMIRI P. eNOS gene variant in patients with coronary artery disease[J]. J Biomark, 2013, 2013: 403783. |
| 3 | LUBRANO V, PINGITORE A, TRAGHELLA I,et al. Emerging biomarkers of oxidative stress in acute and stable coronary artery disease: levels and determinants[J]. Antioxidants (Basel),2019,8(5): 115. |
| 4 | TOUSOULIS D, KAMPOLI A M, TENTOLOURIS C,et al. The role of nitric oxide on endothelial function[J]. Curr Vasc Pharmacol, 2012, 10(1): 4-18. |
| 5 | 李静静, 高海娟, 董 盛. 雷根平重用薏苡附子散加味治疗疑难病验案3则[J]. 江苏中医药, 2020, 52(11):65-67. |
| 6 | 王秀玲. 薏苡附子散加减治疗冠心病不稳定型心绞痛(阳气虚衰型)的临床观察[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江中医药大学,2018. |
| 7 | 杨 韬, 钟小雪, 何庆勇. 何庆勇副教授应用薏苡附子散治疗胸痹心痛的思想初探[J]. 中国中医急症, 2016, 25(5): 821-822, 825. |
| 8 | 王庆昌. 薏苡附子散加味治疗胸痹62例[J]. 国医论坛, 1993, 8(6): 17. |
| 9 | 王博龙. 基于生物信息技术的薏苡附子散网络药理学研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2019, 30(5): 564-570. |
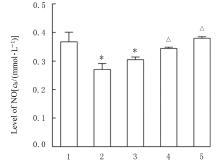
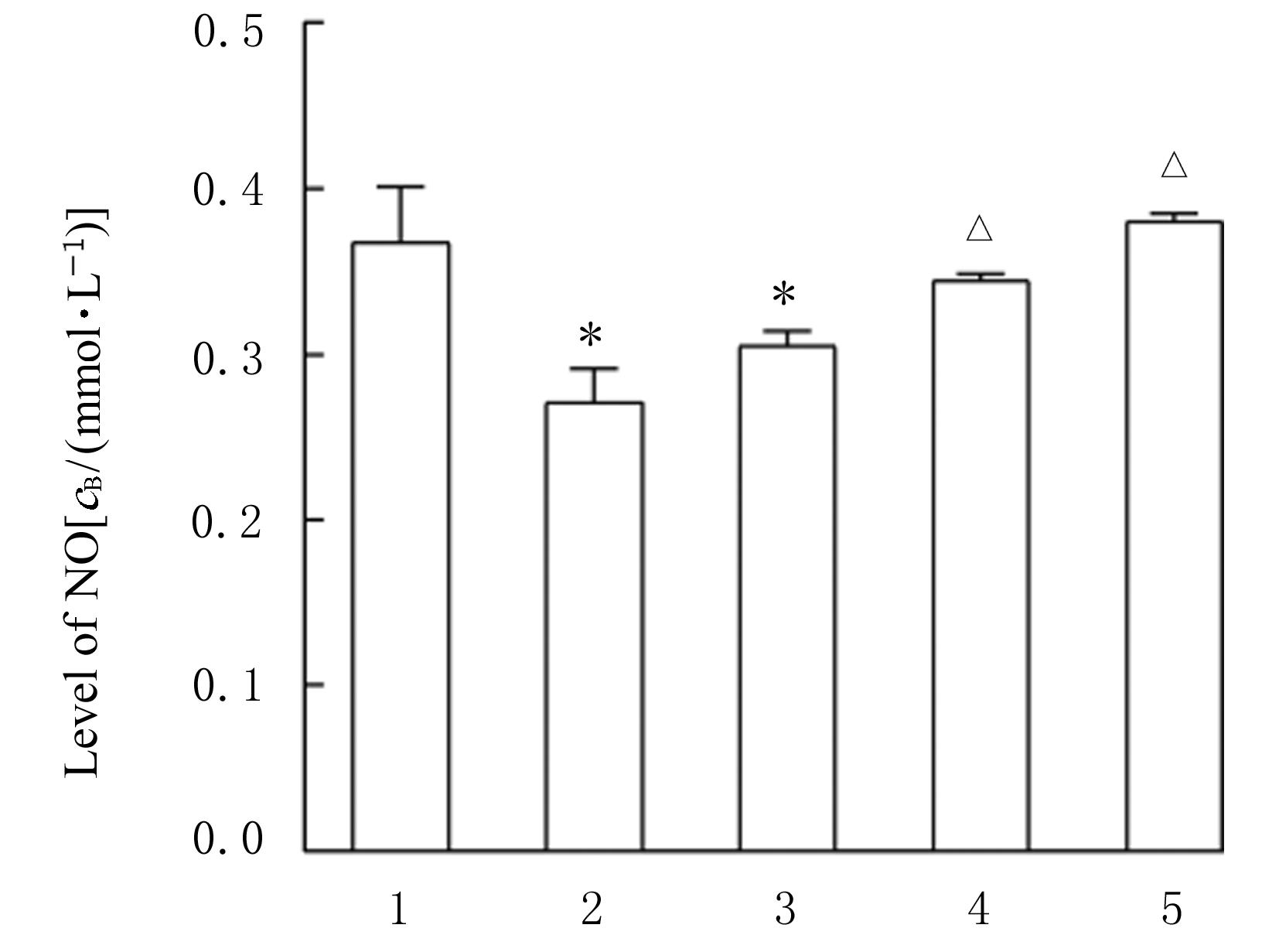
| 10 | 黄汕梅, 郭玉洪, 赵洋洋, 等. 基于NO3: NO2: NO通道探索白酒在瓜蒌薤白白酒汤保护小鼠缺血心肌中的佐使作用[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2021, 23(4): 23-27. |
| 11 | LIU G Q, PLACE A T, CHEN Z L, et al. ICAM-1-activated Src and eNOS signaling increase endothelial cell surface PECAM-1 adhesivity and neutrophil transmigration[J]. Blood, 2012, 120(9): 1942-1952. |
| 12 | TANG Y P, GARG H, GENG Y J, et al. Nitric oxide bioactivity of traditional Chinese medicines used for cardiovascular indications[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2009, 47(6): 835-840. |
| 13 | 郭玉洪, 唐耀平, 赵洋洋, 等. 瓜蒌薤白白酒汤通过NO3: NO2: NO途径保护小鼠缺血心肌的实验研究[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2022, 49(1): 202-207. |
| 14 | 李晓凯, 顾 坤, 梁慕文, 等. 薏苡仁化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(21): 5645-5657. |
| 15 | 唐 梅, 赵立春, 徐 敏, 等. 附子化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J]. 广西植物, 2017, 37(12): 1614-1627. |
| 16 | LUNDBERG J O, WEITZBERG E, GLADWIN M T. The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics[J].Nat Rev Drug Discov,2008,7(2):156-167. |
| 17 | CYR A R, HUCKABY L V, SHIVA S S, et al. Nitric oxide and endothelial dysfunction[J]. Crit Care Clin, 2020, 36(2): 307-321. |
| 18 | KUMAR G, DEY S K, KUNDU S.Functional implications of vascular endothelium in regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthesis to control blood pressure and cardiac functions[J]. Life Sci,2020,259:118377. |
| 19 | CALABRISO N, GNONI A, STANCA E, et al. Hydroxytyrosol ameliorates endothelial function under inflammatory conditions by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018, 2018: 9086947. |
| 20 | WANG D P, KANG K, SUN J, et al. URB597 and andrographolide improve brain microvascular endothelial cell permeability and apoptosis by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation associated with activation of Nrf2 signaling in oxygen-glucose deprivation[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 4139330. |
| 21 | 武兵兵, 马礼科, 刘秀珠, 等.中药通过AMPK途径对糖尿病致内皮功能障碍的保护作用及机制[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2022, 38(3):225-230. |
| 22 | YAO H, XIE Q, HE Q M, et al. Pretreatment with panaxatriol saponin attenuates mitochondrial apoptosis and oxidative stress to facilitate treatment of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via the regulation of Keap1/Nrf2 activity[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022,2022: 9626703. |
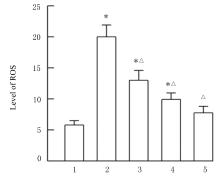
| 23 | YI C L, SONG M J, SUN L F, et al. Asiatic acid alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting the ROS-mediated mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 3267450. |
| 24 | WANG Y M, LI X K, GU K, et al. Study on the potential mechanism of the active components in YiYiFuZi Powder in homotherapy for hetropathy of coronary heart disease and rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Front Chem, 2022, 10: 926950. |
| [1] | Desheng HUANG,Yanan ZHAO,Yun CHEN,Yiyao SUN,Weilin QIN,Moujie LIU,Juhua XIE. Improvement effect of metformin on hypertrophy of H9C2 cardiomyocytes and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 675-681. |
| [2] | Jun ZHU,Nan ZHOU,Deming LI. Improvement effect of propofol postconditioning on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 46-54. |
| [3] | Dan GUO,Xu WEN,Danni WU,Qinyu WANG,Shanshan LIU,Duochun JI,Like WANG,Dan WANG,Ying DONG,Chunyan YU. Characteristics of antioxidant capacity of muscle tissue in aging sarcopenia mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1209-1215. |
| [4] | Yuan LIAO,Kaiju WANG,Haoyan LI,Huiping CHEN,Xuanyi LI,Yong HUANG. Improvement effects of neuropeptide PACAP27 on cyclophosphamide-induced testicular injury in rats by inhibiting mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1266-1275. |
| [5] | Qingxu LANG,Xueshuang NIU,Kaiwen YANG,Ren ZHANG,Siteng WANG, ZUMIRETIGULI·Wumaier,Zhenqi WANG. Effects of sodium butyrate combined with ionizing radiation on apoptosis of lung cancer A549 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 915-921. |
| [6] | Minmin DAI,Ying CHANG,Na XU,Yan WANG,Meng XU,Wenyue XU,Jiawang MA,Wensen LIU,Zhengai CHEN. Improvement effect of Rubus root polysaccharide on pancreatic mitochondrial function in type 2 diabetic mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 938-945. |
| [7] | Dan MAO,Zhishuang LI,Jiaxin CHENG,Ping HOU. Effect of Shenxianshengmai Oral Liquid on ROS expression in mice with sick sinus syndrome and its regulation on HCN4 ion channel [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1353-1361. |
| [8] | Lu LU,Dongming LI,Xueguo WANG,Dan SONG,Taicheng WANG,Hongyan ZHAO,Xiaoyong WU. Effect of chloroquine on gemcitabine-resistant cells by affecting autophagy and mitochondrial function of pancreatic cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 926-933. |
| [9] | Xu ZHANG,Naimeng LIU,Jiaoyan MA,Nan LIN,Mindan SUN. Effect of mitochondrial fission/fussion protein expression imbalance in pathological changes of kidney tissue in IgA nephropathy mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 284-291. |
| [10] | Fei LIU,Shuo LIANG,Yuexuan WANG,Lijing QIN,Wei GUO,Zhicheng WANG. Effect of low dose ionizing radiation on hippocampal neurons in STZ-induced diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 1-7. |
| [11] | Haiying ZHANG,Wenxin ZHANG,Wenjing ZHAO,Wei LI. Induction effect of gallic acid on apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG-2 cells through regulating mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 125-132. |
| [12] | Chen JI,Wenjuan ZHANG,Ning GUAN,Xiuqiu GAO,Linyuan WANG. Effect of M1 macrophages on immune status in chronic periodontitis model mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1137-1142. |
| [13] | LIN Jiuhan, TIAN Lin, ZHANG Nana, DONG Ying, LYU Hang, WANG Dan, QU Meng, ZHANG Yong, SUN Liankun, YU Chunyan, LIU Xi. Inhibitory effect of mitochondrial dynamics changes on growth of transplanted melanoma in APP/PS1 mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 476-481. |
| [14] | CAI Rujia, GUAN Ning, LIU Yizhen, GAO Xiuqiu, WANG Linyuan. Expressions of M1 macrophage-related factors in gingiva tissue of patients with severe chronic periodontitis and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 372-376. |
| [15] | LOU Tingting, HUANG Qingxia, LI Xiangyan, ZHAO Daqing. Protective effect of ginseng extract on cardiomyocyte injury induced by palmitic acidand its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1248-1255. |