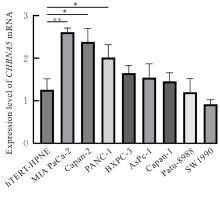
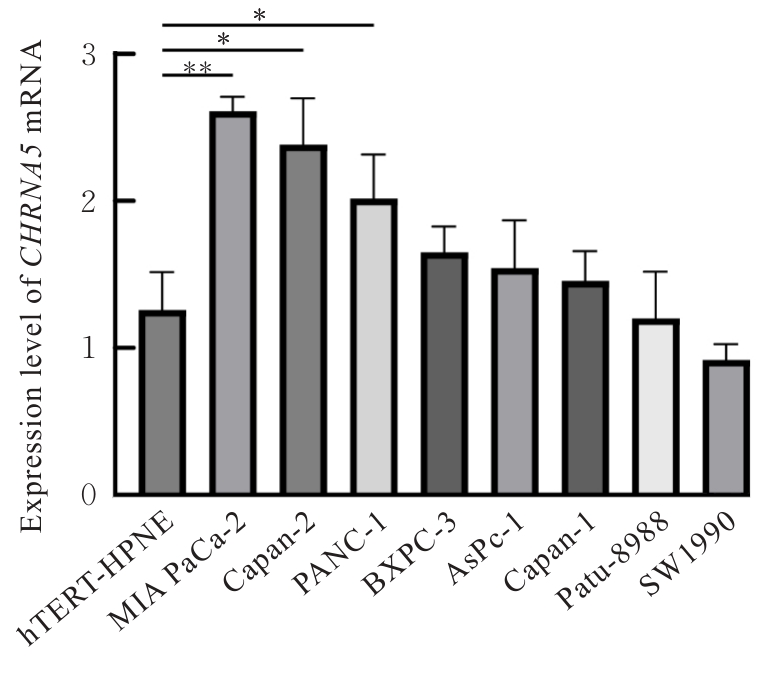
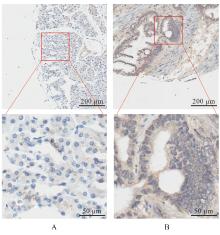
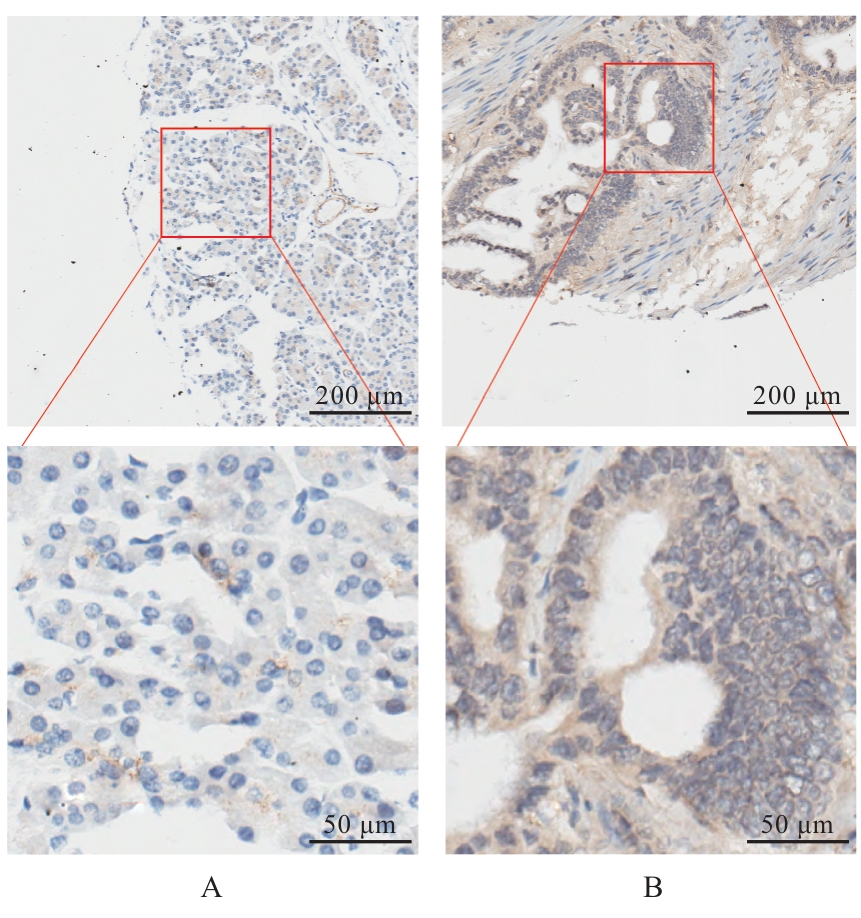
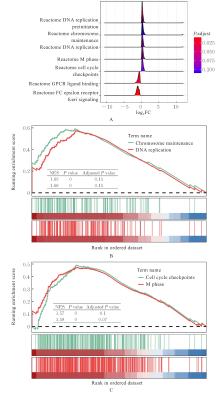
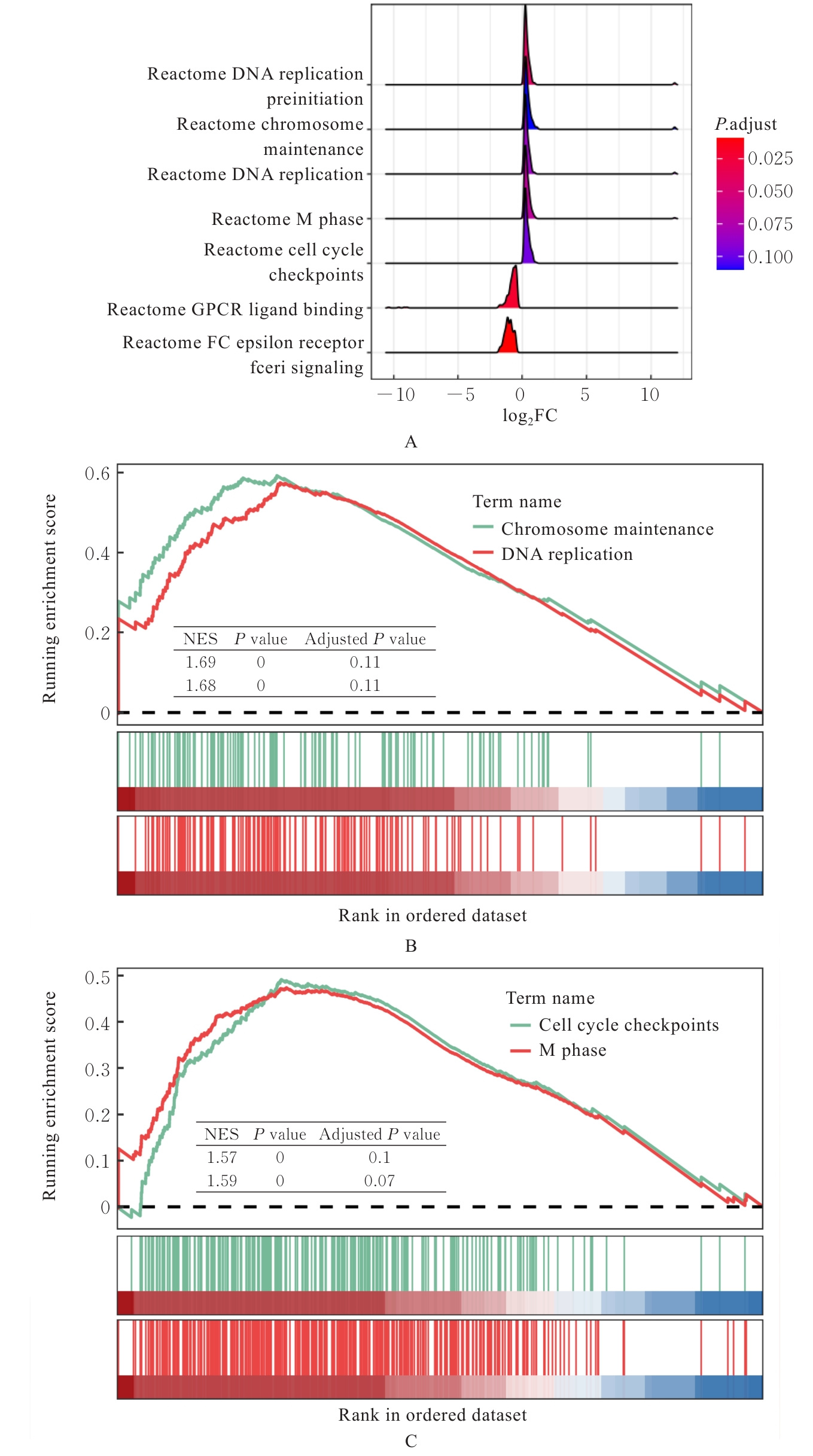
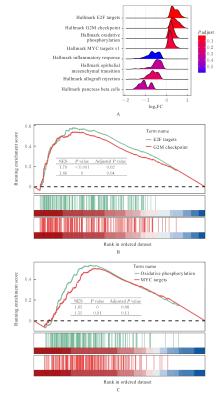
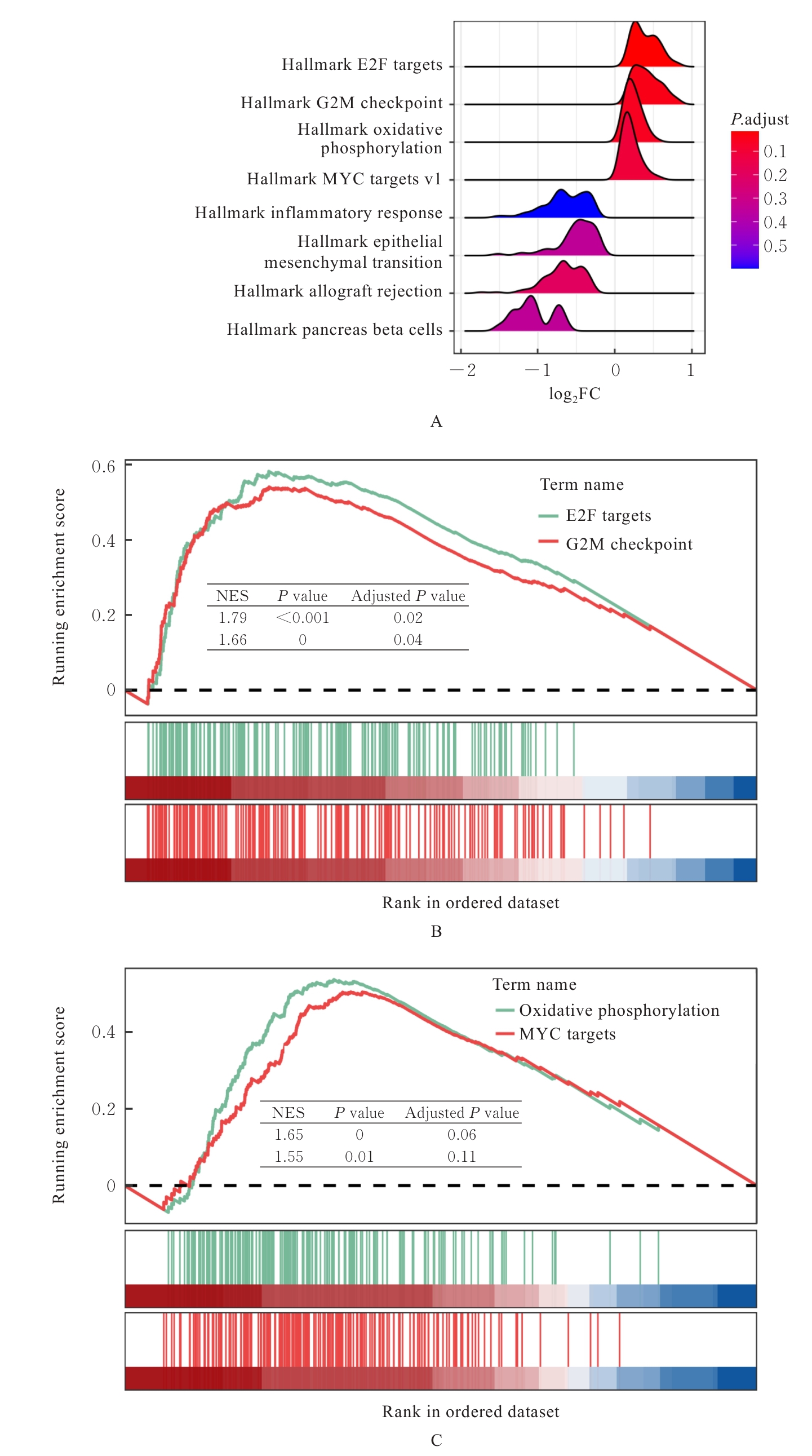
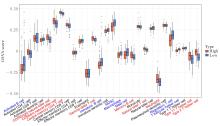
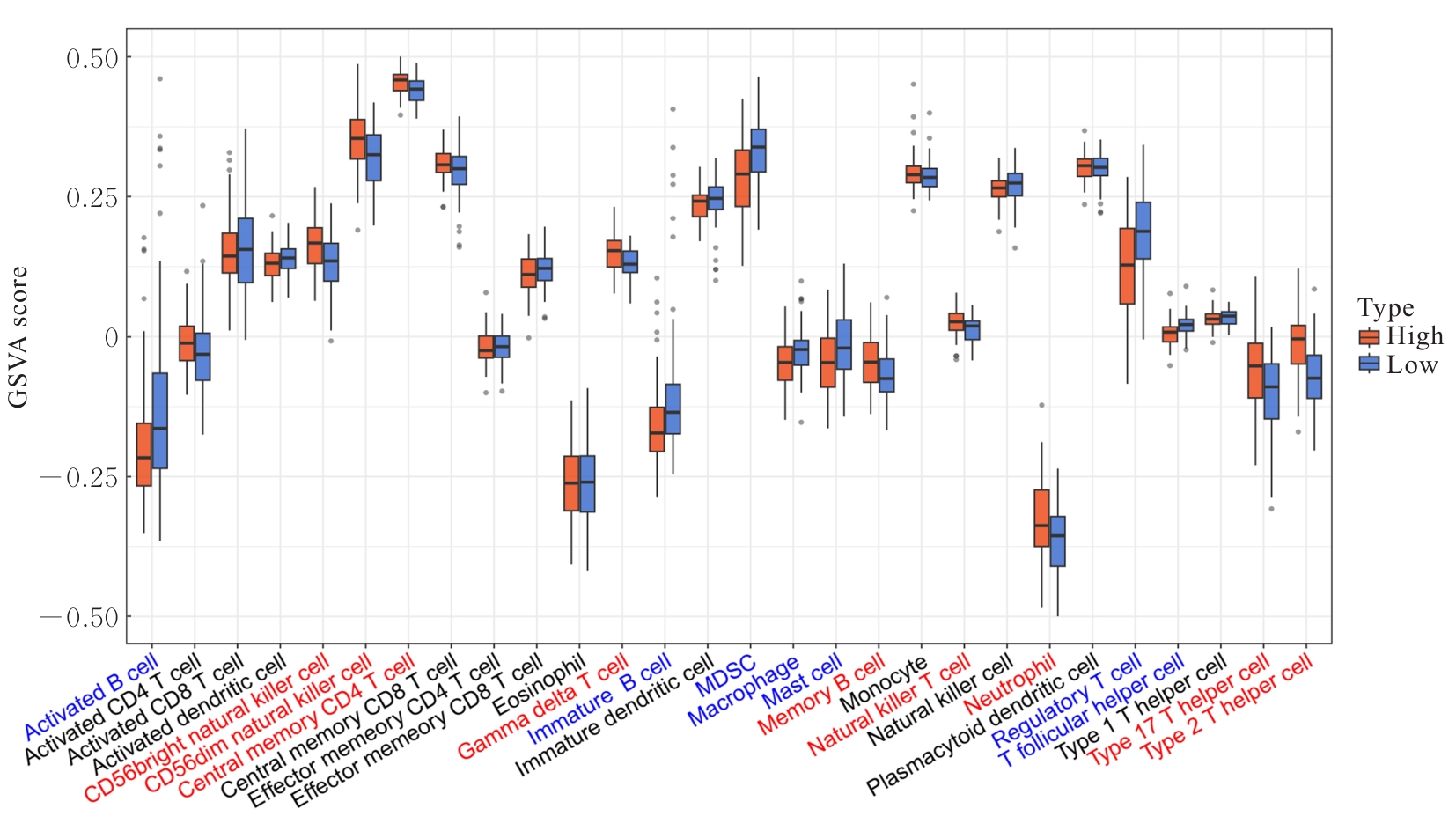
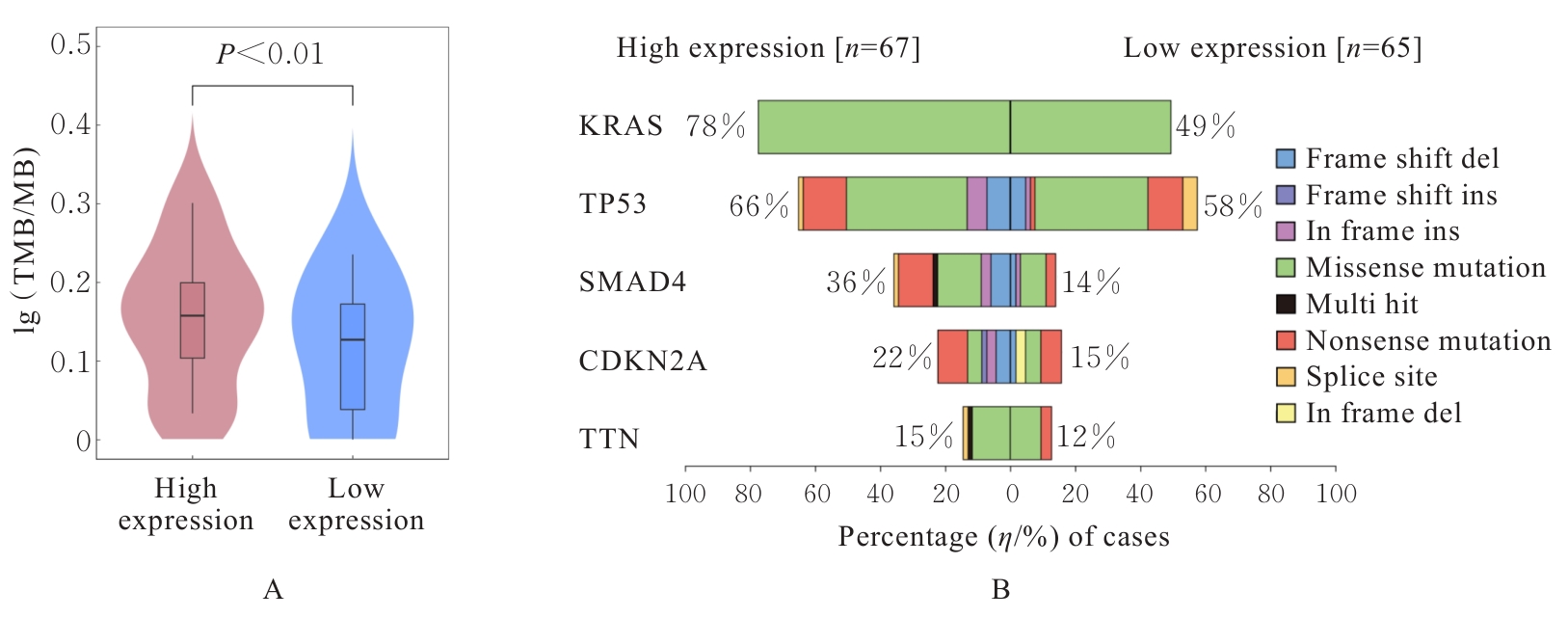
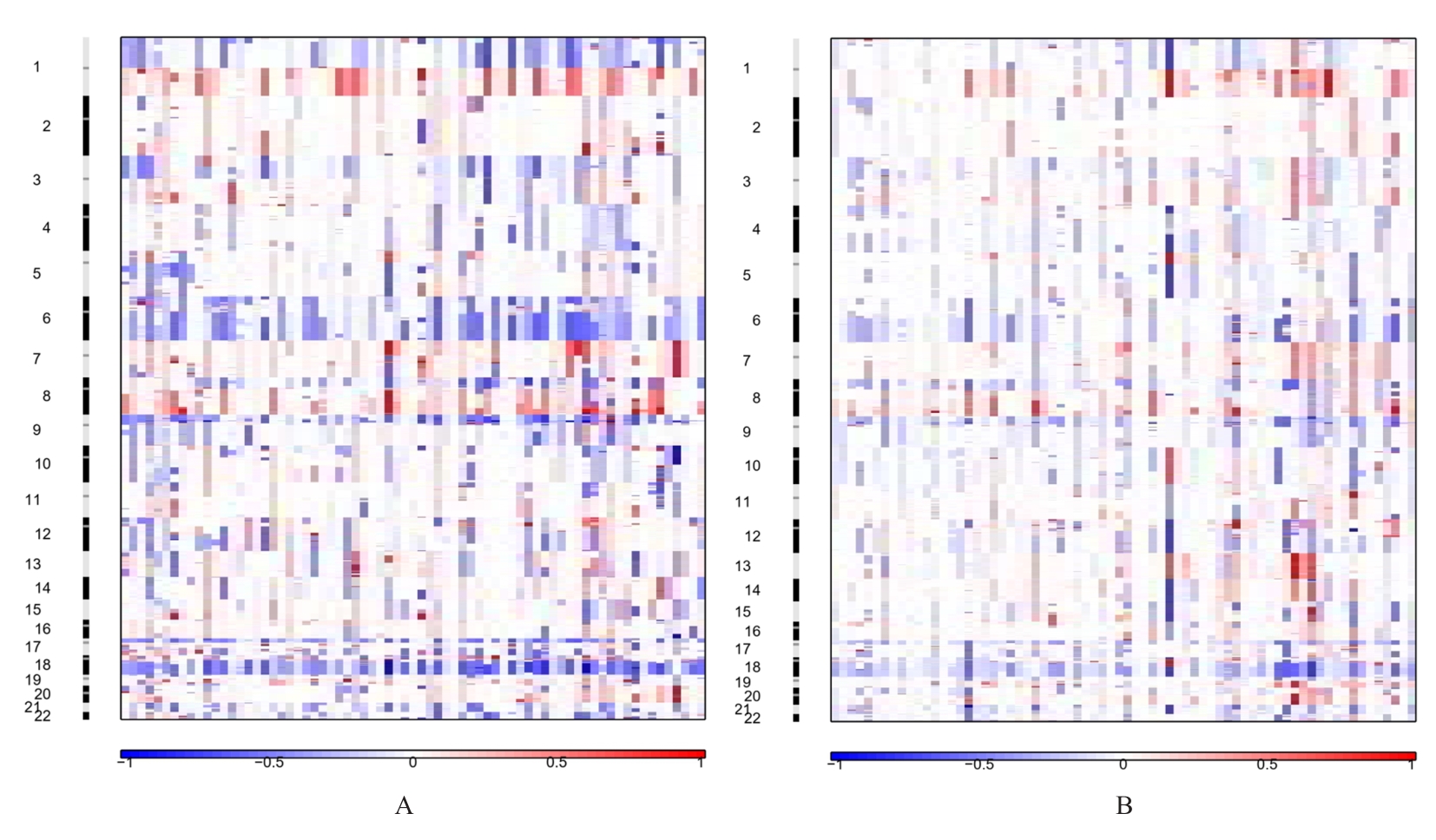
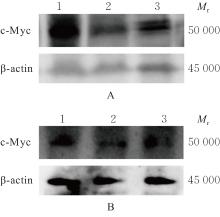
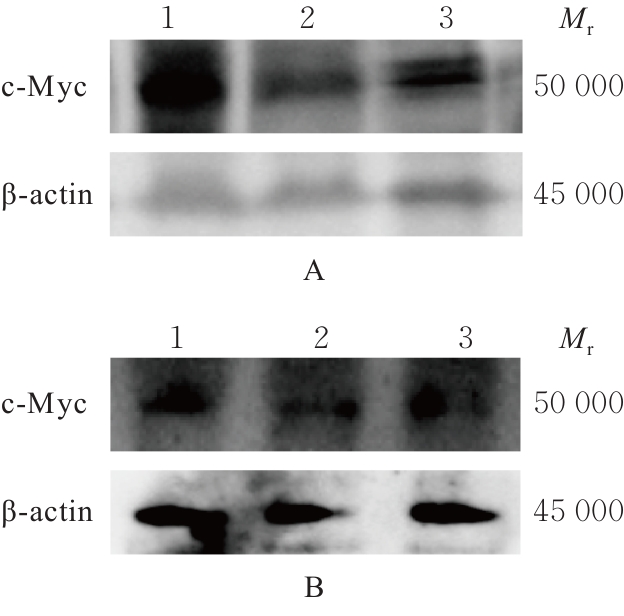
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1518-1531.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250608
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles
Effect of CHRNA5 in occurrence and development of pancreas cancer and its mechanism
Dayou DAI,Zhigang ZHANG( ),Hui LI(
),Hui LI( )
)
- State Key Laboratory of Systems Medicine for Cancer,Shanghai Cancer Institute,Renji Hospital,School of Medicine,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200240,China
-
Received:2024-12-30Accepted:2025-02-06Online:2025-11-28Published:2025-12-15 -
Contact:Zhigang ZHANG,Hui LI E-mail:zzhang@shsci.org;huili@shsci.org
CLC Number:
- R735.9
Cite this article
Dayou DAI,Zhigang ZHANG,Hui LI. Effect of CHRNA5 in occurrence and development of pancreas cancer and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(6): 1518-1531.
share this article
| [1] | REBECCA L S, KIMBERLY D, NIKITA S W, et al. Cancer statistics, 2023[J] . CA Cancer J Clin, 2023, 73(1): 17-48. |
| [2] | MIZRAHI J D, SURANA R, VALLE J W, et al. Pancreatic cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10242): 2008-2020. |
| [3] | SHERMAN M H, BEATTY G L. Tumor microenvironment in pancreatic cancer pathogenesis and therapeutic resistance[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2023, 18: 123-148. |
| [4] | CHY Y, MILLY M, ALBERT D, et al. Temporal changes in cause of death among adolescents and adults in six countries in eastern and southern Africa in 1995-2019: a multi-country surveillance study of verbal autopsy data[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2024, 12(8): e1278-e1287. |
| [5] | JIANG S H, Hu L P, WANG Xet al. Neurotransmitters: emerging targets in cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39(3): 503-515. |
| [6] | LUTGENDORF S K, SOOD A K, ANTONI M H, Host factors and cancer progression : biobehavioral signaling pathways and interventions[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28(26): 4094-4099. |
| [7] | YANG Y H, LIU J B, GUI Y, et al. Relationship between autophagy and perineural invasion, clinicopathological features, and prognosis in pancreatic cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(40): 7232-7241. |
| [8] | SALOMAN J L, ALBERS K M, LI D J, et al. Ablation of sensory neurons in a genetic model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma slows initiation and progression of cancer[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2016, 113(11): 3078-3083. |
| [9] | WANG X B, ROUZANNA I, YE L H, et al. Phenotype screens of murine pancreatic cancer identify a Tgf-α-Ccl2-paxillin axis driving human-like neural invasion[J]. J Clin Invest, 2023, 133(21): e166333. |
| [10] | KRAIS A M, HAUTEFEUILLE A H, CROS M P, et al. CHRNA5 as negative regulator of nicotine signaling in normal and cancer bronchial cells: effects on motility, migration and p63 expression[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2011, 32(9): 1388-1395. |
| [11] | WALTERS I B, BURACK L H, RCOVENet al T. Suberythemogenic narrow-band UVB is markedly more effective than conventional UVB in treatment of psoriasis vulgaris[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 1999, 40(6): 893-900. |
| [12] | MENTER A, KORMAN N J, ELMENTS C A, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 4. Guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with traditional systemic agents[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2009, 61(3): 451-85. |
| [13] | MENTER A, FELDMAN S R, WEINSTEIN G D, et al. A randomized comparison of continuous vs. intermittent infliximab maintenance regimens over 1 year in the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2007, 56(1): 31.e1-31.e15. |
| [14] | KAUR-KNUDSEN D, BOJSEN S E, TYBJARG-HANSEN A, et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor polymorphism, smoking behavior, and tobacco-related cancer and lung and cardiovascular diseases: a cohort study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(21): 2875-2882. |
| [15] | EMOKE R, DE LEEUW J, BAERVELDT E Met al. Cellular and molecular effects of pulsed dye laser and local narrow-band UVB therapy in psoriasis[J]. Lasers Surg Med, 2010, 42(3): 201-210. |
| [16] | ZOU H L, CHEN Y, ZHU X P, et al. Spinosad blocks CHRNA5 mediated EGFR signaling pathway activation to inhibit lung adenocarcinoma proliferation[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 177: 117105. |
| [17] | FU Y, SHEN K Y, WANG H, et al. Alpha5 nicotine acetylcholine receptor subunit promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma metastasis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2024, 9(1): 63. |
| [18] | ZAHALKA A H, FRENETTE P S, Nerves in cancer [J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2020, 20(3): 143-157. |
| [19] | ZHANG Y, JIA Y F, LI P, et al. Reciprocal activation of α5-nAChR and STAT3 in nicotine-induced human lung cancer cell proliferation[J]. J Genet Genomics, 2017, 44(7): 355-362. |
| [20] | RUFFELL B, AFFARA N I, Coussens Lisa M, Differential macrophage programming in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Trends Immunol, 2012, 33(3): 119-126. |
| [21] | ZHANG W R, WANG M M, JI C H, et al. Macrophage polarization in the tumor microenvironment: Emerging roles and therapeutic potentials[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 177: 116930. |
| [22] | LAUMONT C M, BANVILLE A C, GILARDI M, et al. Tumour-infiltrating B cells: immunological mechanisms, clinical impact and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2022, 22(7): 414-430. |
| [23] | JIN L, Kim H S, SHI J Q, Neutrophil in the Pancreatic Tumor Microenvironment [J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(8): 1170. |
| [24] | SILVESTRE-ROIG C, KALAFATI L, CHAVAKIS T, Neutrophils are shaped by the tumor microenvironment : novel possibilities for targeting neutrophils in cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2024, 9(1): 77. |
| [25] | RENUMATHY D, ANJA, MAHAUAD-FERNANDEZ W D, et al. The MYC oncogene-the grand orchestrator of cancer growth and immune evasion [J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2022, 19(1): 23-36. |
| [26] | ARIANNA G, SARA T, GIORGIA G, et al. The FGF/FGFR/c-Myc axis as a promising therapeutic target in multiple myeloma [J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2024, 43(1): 294. |
| [27] | MCINTYRE C A, ADRIEN G, JIWOON P, et al. Distinct clinical outcomes and biological features of specific KRAS mutants in human pancreatic cancer [J]. Cancer Cell, 2024, 42(9): 1614-1629.e5. |
| [28] | MASUGI Y, TAKAMATSU M, TANAKA M, et al. Post-operative mortality and recurrence patterns in pancreatic cancer according to KRAS mutation and CDKN2A, p53, and SMAD4 expression[J]. J Pathol Clin Res, 2023, 9(5): 339-353. |
| [1] | Chao LIANG,Juanjuan DAI,Ning ZHOU,Dandan WANG,Jie ZHAO,Di AN,Yan WU. Effect of oridonin on cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of human nasopharynx carcinoma HONE-1 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 917-924. |
| [2] | Jiacai FU,Lingsha QING,Lu YANG,Meihui SONG,Xianying ZHANG,Xiaocui LIU,Fengjin LI,Ling QI. Inhibitory effect of Schisandrin B on proliferation of pancreatic cancer Pan02 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 638-646. |
| [3] | Zhongxin FENG,Mei LI. Effect of soluble CD40 ligand on biological behavior of THP-1 cells through long non-coding RNA linc00239 [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 88-96. |
| [4] | Lu FU, Yanjue YE, Jiangying LI, Ziyi TANG, Li YIN. Expressions of Sirtuins protein in testis tissue and GC-2 cells in male reproductive system damage model mice induced by bisphenol A and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1107-1116. |
| [5] | Naixu SHI,Miao HAO,Tianfu ZHANG,Kelin ZHAO,Ziyan HUANG,Chunyan LI,Xiaofeng WANG. Inhibitory effect of baicalein on proliferation of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma CAL27 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 985-993. |
| [6] | Haiyao PANG,Li HOU,Wenning HE,Jun MENG. Expression levels of serum and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase 3 in one-cell stage fertilized eggs at different cell cycles in mice and its subcellular localization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 884-889. |
| [7] | Hongyuan TIAN,Caiyun YIN,Li WANG,Peiyun HU,Chenyang ZHANG,Qiuyue LI,Qingzhao ZHENG,Yali QI,Fang FANG,Zhicheng WANG. Effects of hydroxyurea combined with radiation on cell cycle and apoptosis of cells after silencing ATRX [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 590-598. |
| [8] | Yun LIU,Linqi ZHU,Shihe SHAO. Effects of circular RNA hsa_circ_0009735 on epithelial mesenchymal transformation, cell cycle, and autophagy of gastric cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1498-1509. |
| [9] | Qiuting CAO,Jingchun HAN,Xiaofei ZHANG. Effect of silencing helicase BLM gene on chemotherapy sensitivity of irinotecan in colorectal cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 657-667. |
| [10] | Cuilan LIU,Fengai HU,Jing LIU,Dan WANG,Changyun QIU,Dunjiang LIU,Di ZHAO. Effect of adiponectin receptor agonist AdiopRon on biological behaviors of glioma cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 702-710. |
| [11] | Lijing QIN,Bing HAN,Zhongqi LI,Qi SUO,Zhen JIA,Hongli CUI,Weiqiang XU,Fang FANG,Zhicheng WANG. Effects of targeting-silenced ATRX on cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by radiation in cervical cancer HeLa cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 904-910. |
| [12] | Fei LIU,Shuo LIANG,Yuexuan WANG,Lijing QIN,Wei GUO,Zhicheng WANG. Effect of low dose ionizing radiation on hippocampal neurons in STZ-induced diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 1-7. |
| [13] | Lu LIU,Tianfu ZHANG,Xiaofeng WANG,Chenfei KONG. Regulatory effects of syndecan-1 on migration, invasion and cell cycle of tongue squamous cell carcinoma CAL27 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 59-65. |
| [14] | LIU Lanqing, LI Ruilin, ZHOU Xiaomin, MENG Jun. Dynamic expression and localization of CDC14B in each cell cycle of mouse one-cell fertilized eggs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 675-679. |
| [15] | ZHANG Chu, HAO Miao, WANG Huiyu, WANG Xiaofeng, ZHANG Tianfu. Effect of Oxaliplatin on proliferation and apoptosis of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma CAL27 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 233-239. |
|
||