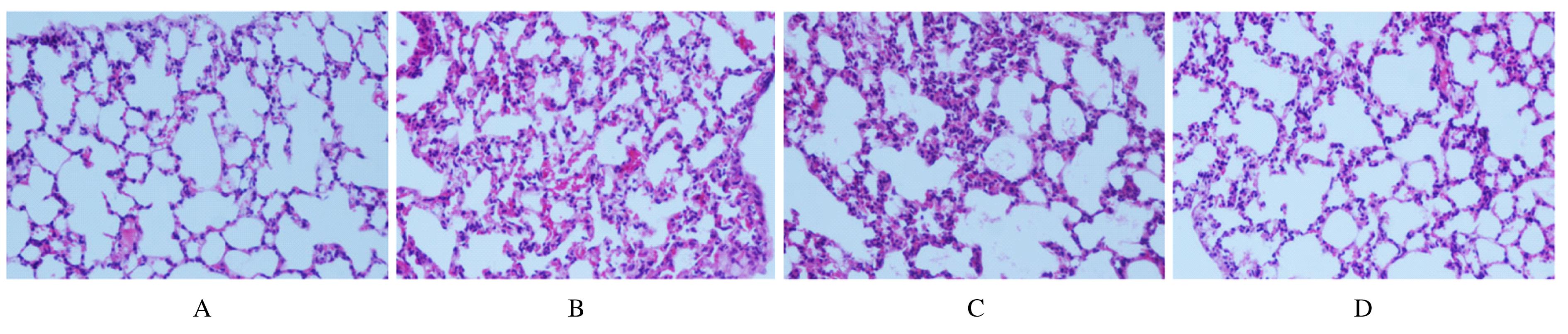
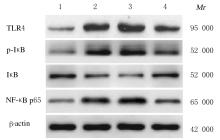
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 104-110.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220113
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulatory effect of miRNA-27a on immune function in experimental pulmonary tuberculosis rats and its mechanism
Na HAN1,Fanping LIU1,Yanqing TIAN1,Zhiqing ZHENG1,Weiming LANG1,Qian WANG1,Yatao LIU1,Jianguang ZHU2( )
)
- 1.Department of Tuberculosis,Affiliated Hospital,Hebei University,Baoding 071000,China
2.Department of Otolaryngology,No. 82 Military Hospital of PLA,Baoding 071000,China
-
Received:2021-05-24Online:2022-01-28Published:2022-01-17 -
Contact:Jianguang ZHU E-mail:zxfj6098@163.com
CLC Number:
- R-332
Cite this article
Na HAN,Fanping LIU,Yanqing TIAN,Zhiqing ZHENG,Weiming LANG,Qian WANG,Yatao LIU,Jianguang ZHU. Regulatory effect of miRNA-27a on immune function in experimental pulmonary tuberculosis rats and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 104-110.
share this article
Tab.2
Expression levels of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway related proteins in lung tissue of rats in various groups"
| Group | TLR4 | p-IκB | IκB | NF-κB p65 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.12±0.03 | 0.05±0.01 | 0.58±0.02 | 0.11±0.06 |
| Model | 0.74±0.08* | 0.83±0.04* | 0.18±0.02* | 0.67±0.02* |
| Agomir-NC | 0.77±0.06 | 0.85±0.03 | 0.15±0.01 | 0.71±0.02 |
| Agomir | 0.43±0.04△ | 0.28±0.02△ | 0.61±0.03△ | 0.32±0.03△ |
| 1 | 刘希芳, 马改霞, 干 杰, 等. 肺结核患者生存质量量表应用现状及建议[J]. 中国防痨杂志, 2020, 42(3): 200-203. |
| 2 | 郑惠文, 赵雁林. 中国结核病耐药监测现状与监测体系建设[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2015, 35(8): 647-650. |
| 3 | 陈瑞华, 谢 婷, 田 冰, 等. 板蓝根多糖通过TLR4-NF-κB通路对结核大鼠肺部炎症影响的机制研究[J]. 海南医学院学报, 2019, 25(16): 1215-1218, 1223. |
| 4 | NIU W Y, SUN B, LI M Y, et al. TLR-4/microRNA-125a/NF-κB signaling modulates the immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection[J]. Cell Cycle, 2018, 17(15): 1931-1945. |
| 5 | 王 琴, 付 宇, 王 平. 沉默miRNA-16对肺结核模型小鼠免疫功能的调控作用及其机制研究[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2020, 30(4): 86-91. |
| 6 | LV Y N, OU-YANG A J, FU L S. MicroRNA-27a negatively modulates the inflammatory response in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglia by targeting TLR4 and IRAK4[J].Cell Mol Neurobiol,2017,37(2):195-210. |
| 7 | JU M, LIU B, HE H, et al. MicroRNA-27a alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis through modulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway[J].Cell Cycle,2018,17(16): 2001-2018. |
| 8 | 陈振宇, 缪利娅, 朱银超. 槲皮素对实验性肺结核病小鼠TLR4、TRAF6、IL-1β表达影响的研究[J]. 新中医, 2019, 51(10): 8-13. |
| 9 | 冀小波, 毛敏杰, 黄晓庆, 等. 重症肺结核合并肺曲霉菌病患者免疫水平回顾性分析[J]. 浙江中西医结合杂志, 2020, 30(7): 553-555. |
| 10 | 刘 婷, 向延根, 范任华, 等. 肺结核病人细胞因子的研究进展[J]. 实用预防医学, 2016, 23(7): 894-897. |
| 11 | TARASHI S, BADI S A, MOSHIRI A, et al. The inter-talk between Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the epigenetic mechanisms[J]. Epigenomics, 2020, 12(5): 455-469. |
| 12 | 林 砺, 张舒林, 郭晓奎. 外泌体来源的miRNA在肺结核中的研究进展[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2020, 15(3): 371-374. |
| 13 | LIU F, CHEN J, WANG P, et al. MicroRNA-27a controls the intracellular survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by regulating calcium-associated autophagy[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 4295. |
| 14 | ORLANDO V, MANNA M PLA, GOLETTI D, et al. Human CD4 T-cells with a naive phenotype produce multiple cytokines during mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and correlate with active disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 1119. |
| 15 | LIN P L, FLYNN J L. CD8 T cells and Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2015, 37(3): 239-249. |
| 16 | 徐麒麟, 康 波, 姜冬梅, 等. 亚精胺对鼠免疫器官指数及炎症因子表达的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2017, 29(2): 200-205. |
| 17 | 闫慧明, 安 燕, 张 雪, 等. 双氢青蒿素对类风湿关节炎患者外周血单个核细胞TLR/MyD88信号通路的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(14): 1780-1784. |
| 18 | 徐 敏, 王凤仪, 赵党生, 等. 芍药汤对湿热内蕴型溃疡性结肠炎大鼠TLR4, NF-κB p65和IL-6表达的调控作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020, 26(14): 53-58. |
| 19 | 杨柳柳, 刘小虹, 詹少锋, 等. 肺康颗粒通过TLR4/NF-κB信号通路干预COPD大鼠炎症的相关机制[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2018, 29(6): 687-692. |
| 20 | WANG Y, WANG D, JIN Z. miR‑27a suppresses TLR4‑induced renal ischemia‑reperfusion injury[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 20(2): 967-976. |
| 21 | ZHANG P, LI L Q, ZHANG D, et al. Over-expressed miR-27a-3p inhibits inflammatory response to spinal cord injury by decreasing TLR4[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22(17): 5416-5423. |
| 22 | ZHU M M, WANG L, YANG D, et al. Wedelolactone alleviates doxorubicin-induced inflammation and oxidative stress damage of podocytes by IκK/IκB/NF-κB pathway[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 117: 109088. |
| [1] | Xin SHEN,Yang LIU,Hongyu CHEN,Jie ZHANG,Qingli CHENG,Guang YANG. Regulatory effect of high glucose on polarization of RAW264.7 macrophages via miR-125b in mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 847-857. |
| [2] | Song SU,Hongbo WANG,Yucong MA,Xin FANG,Junrong LIU,Hongmei QIAO. Kawasaki disease with inflammatory changes in parapharyngeal space:A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 228-233. |
| [3] | Mimi REN,Menghan GAO,Jing WANG,Jiamei LAI,Jinyu YU,Hang YUAN. Protective effect of 12/15-lipoxygenase gene knockout on kidney tissue of obesity-related glomerulopathy model mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1337-1346. |
| [4] | Liyan ZHU,Yaoming WANG,Zheng QIN,Huanhuan ZHAO,Zengying WANG,Xiuhong YANG. Improvement effect of angiotensin(1-7) on kidney injury induced by limb ischemia-reperfusion in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 834-841. |
| [5] | Xue LUAN, Guanghai YAN, Haibo LI, Bo ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Yuanyuan HUANG. Effect of salidroside on airway inflammation in mice with asthma and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 537-544. |
| [6] | Lijun YAN,Shengquan TONG,Jing LIU,Dongmei GAO,Nanfang CHEN,Jie HU. Therapeutic effect of total glucosides of paeony in model rats with rheumatoid arthritis by mediating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway and its mechanisim [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 390-396. |
| [7] | QIAO Liangwei, QU Qingshan, LI Ming. Effect of LncRNA-ATB on acute rejection of kidney transplanted rats by regulating miR-200c expression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 955-962. |
| [8] | ZHAO Liping, HUANG Shubing, ZHANG Boping, ZHOU Zhilan, JIA Xuebing, SUN Mengfei, QIAO Chenmeng, CHEN Xue, SHEN Yanqin, CUI Chun. Inhibitory effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus on intestinal inflammation after spinal cord injury in zebrafishes and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 680-686. |
| [9] | WANG Yazhou, HE Peng, WANG Danhong. Effects of montelukast on proliferation and apoptosis of airway smooth muscle cells in asthmatic rats by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 274-279. |
| [10] | WANG Tianyue, ZHOU Qianlan, SHANG Yunxiao. Effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on airway inflammation and Treg/Th17 immune balance of mice with obese asthma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 491-497. |
| [11] | WANG Shangning, WANG Sisi, TIAN Shuyan, LI Jialin, LIU Wei. Early changes of peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in patients with lung adenocarcinoma after single-port thoracoscopic lobectomy and their clinical significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 606-613. |
| [12] | WANG Xuemin, DENG Shurong, PENG Lingling, PAN Maohua, PAN Yuzheng. Dynamic changes of pulmonary morphology and mast cell activity in rats after tracheotomy and intubation and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 262-267. |
| [13] | YUAN Zhongzheng, LIU Yin, SHEN Yuqin, LIN Chongtao. Effect of periodontitis patient's own tissue nucleic acid on expression of NLRP3 mRNA in murine macrophages and its significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 23-27. |
| [14] | ZHAO Jing, LIU Jian, ZHANG Min, WU Shan, ZHAO Benzheng, CHEN Junyu, JIN Yanze. Immunotoxicity of herbicide atrazine and its effect on immune function of rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(06): 1163-1168. |
| [15] | RAN Qin, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Yun, QIU Yuhuan, YUAN Xiefang, WANG Xiaoyun, TANG Hongmei, WANG Xing, LI Guoping. Inhibitory effect of resveratrol on pulmonary inflammation in mice with neutrophilic asthma and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(05): 897-902. |
|