Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 111-121.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220114
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
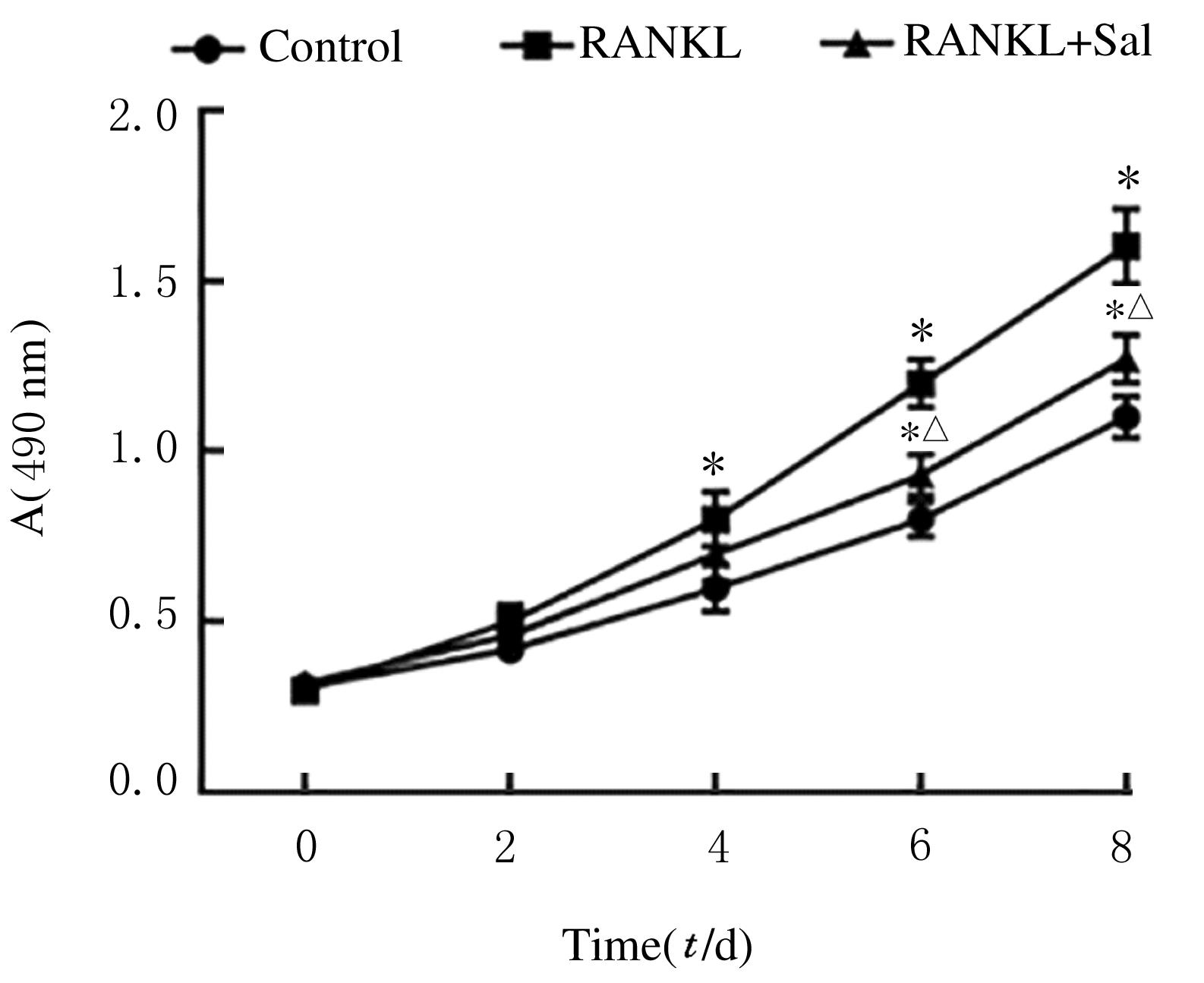
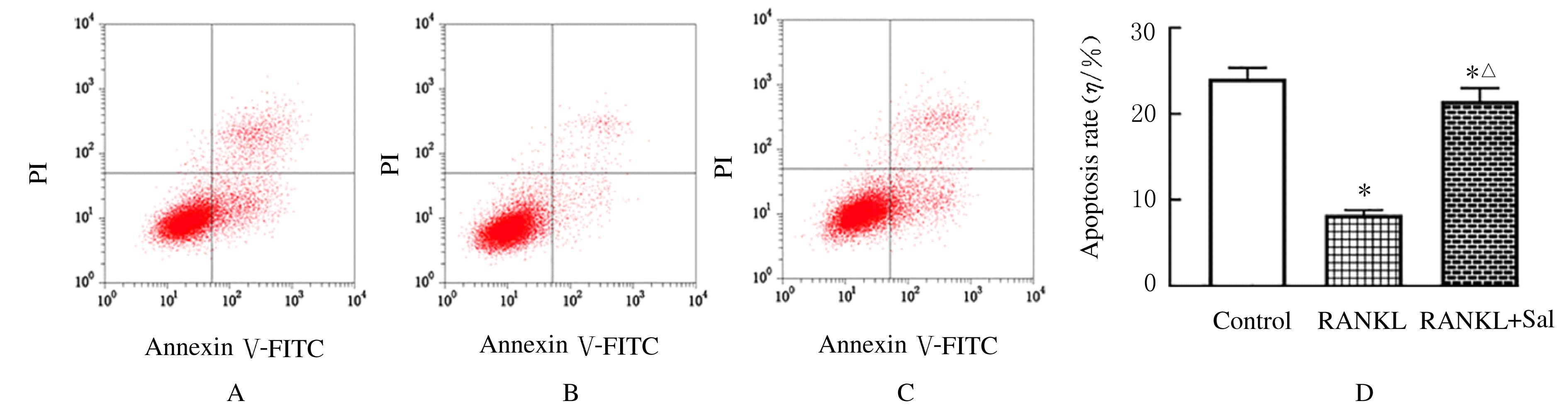
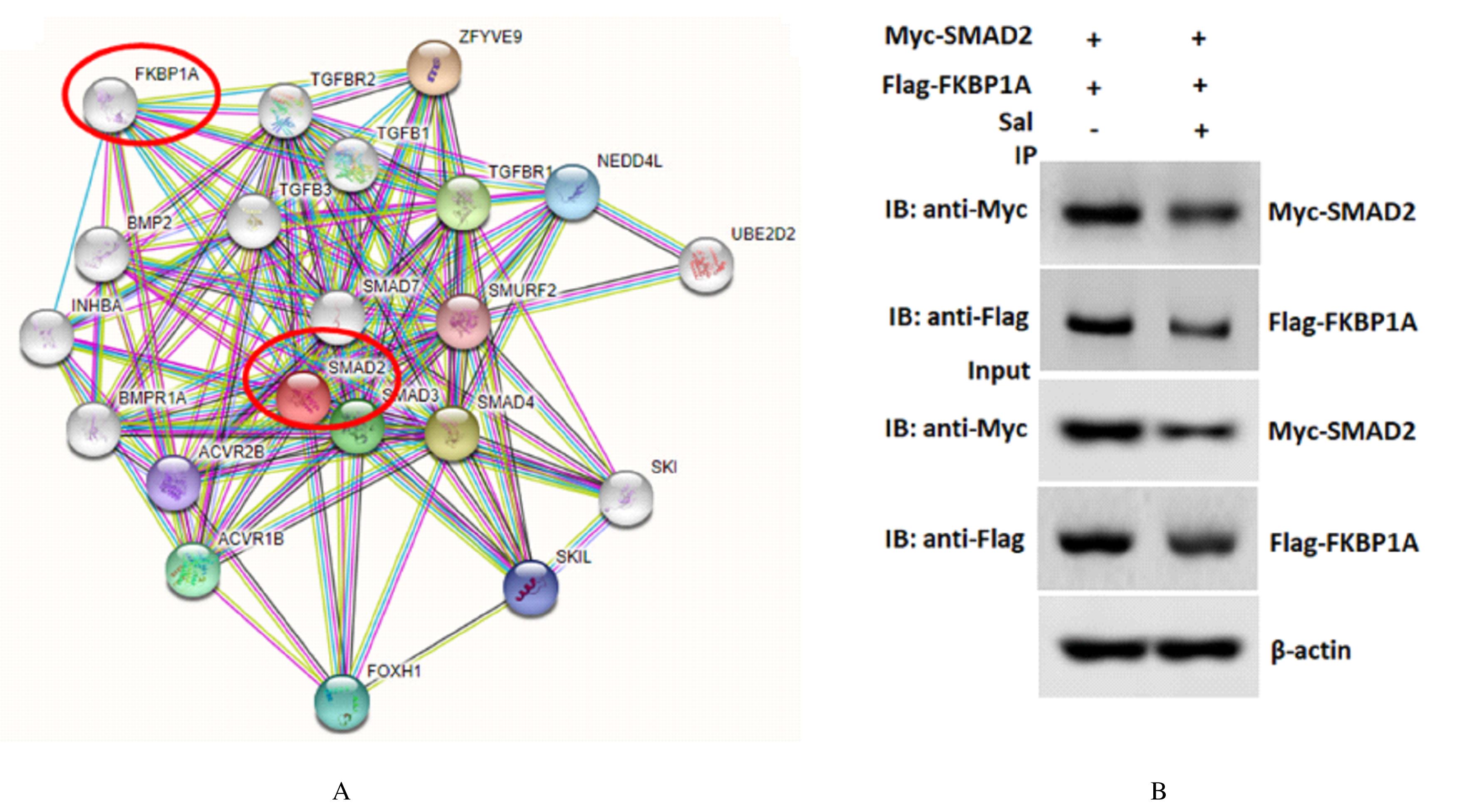
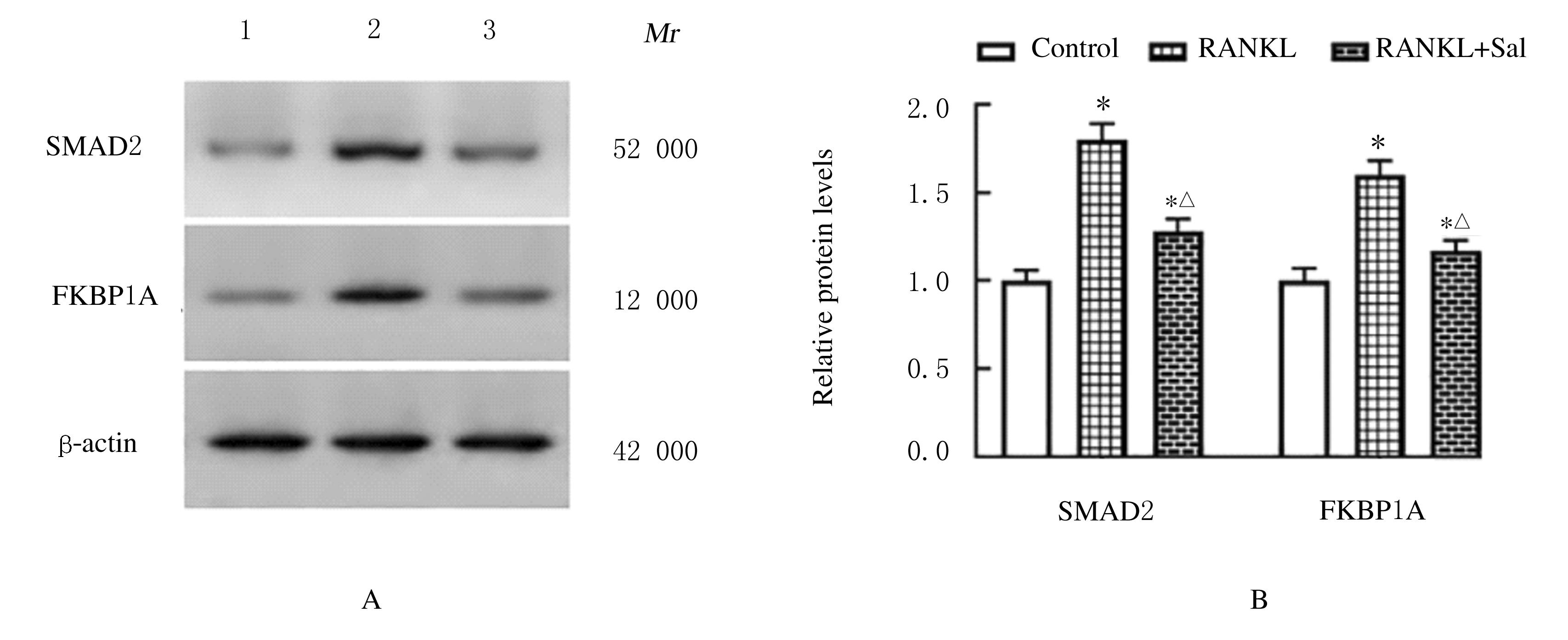
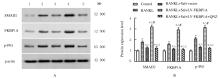
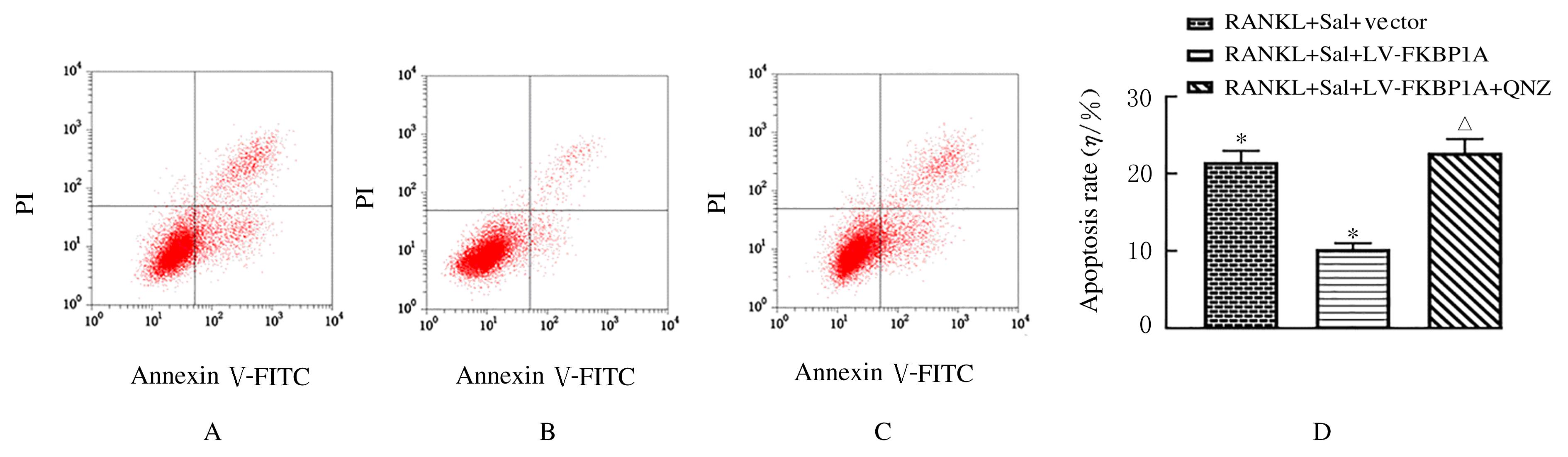
Effects of salvianolate on osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption in osteoporotic rats by regulating SMAD2/FKBP1A/NF-κB axis
Yunfeng MA1,Xiaofei HAN2
- 1.Department of Osteopathy,Second Affiliated Hospital,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450002,Henan
2.Department of Rheumatology,Second Affiliated Hospital,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450002,Henan
-
Received:2021-04-29Online:2022-01-28Published:2022-01-17
CLC Number:
- R274.9
Cite this article
Yunfeng MA,Xiaofei HAN. Effects of salvianolate on osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption in osteoporotic rats by regulating SMAD2/FKBP1A/NF-κB axis[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 111-121.
share this article
| 1 | TIAN L, YANG R, WEI L, et al. Prevalence of osteoporosis and related lifestyle and metabolic factors of postmenopausal women and elderly men: a cross-sectional study in Gansu Province, Northwestern of China[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2017, 96(43): e8294. |
| 2 | WANG N, AGRAWAL A, JØRGENSEN N R, et al. P2X7 receptor regulates osteoclast function and bone loss in a mouse model of osteoporosis[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 3507. |
| 3 | DONG P, HU H, GUAN X, et al. Cost-consequence analysis of salvianolate injection for the treatment of coronary heart disease[J]. Chin Med, 2018, 13: 28. |
| 4 | ZHANG D, WU J R, LIU S, et al. Salvianolate injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine, 2016, 95(51): e5692. |
| 5 | LIU Y, CUI Y, ZHANG X, et al. Effects of salvianolate on bone metabolism in glucocorticoid-treated lupus-prone B6.MRL-Fas (lpr) /J mice[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2016, 10: 2535-2546. |
| 6 | KIM B J, HWANG J Y, HAN B G, et al. Association of SMAD2 polymorphisms with bone mineral density in postmenopausal Korean women[J]. Osteoporos Int, 2011, 22(8): 2273-2282. |
| 7 | OMATA Y, NAKAMURA S, KOYAMA T, et al. Identification of Nedd9 as a TGF-β-Smad2/3 target gene involved in RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by comprehensive analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(6): e0157992. |
| 8 | QIU H L, LIU W, LAN T H, et al. Salvianolate reduces atrial fibrillation through suppressing atrial interstitial fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad2/3 and TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathways in post-MI rats[J]. Phytomedicine, 2018, 51: 255-265. |
| 9 | SONG G A, KIM H J, WOO K M, et al. Molecular consequences of the ACVR1(R206H) mutation of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva[J]. J Biol Chem, 2010, 285(29): 22542-22553. |
| 10 | LI C H, XU L L, JIAN L L, et al. Stattic inhibits RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis by suppressing activation of STAT3 and NF-κB pathways[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2018, 58: 136-144. |
| 11 | OMI M, KAARTINEN V, MISHINA Y. Activin A receptor type 1-mediated BMP signaling regulates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via canonical SMAD-signaling pathway[J].J Biol Chem,2019,294(47): 17818-17836. |
| 12 | WANG Y, DING H, WANG X, et al. Associated factors for osteoporosis and fracture in Chinese elderly[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 5580-5588. |
| 13 | CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions[J]. Connect Tissue Res, 2018, 59(2): 99-107. |
| 14 | ASTLEFORD K, CAMPBELL E, NORTON A, et al. Epigenetic regulators involved in osteoclast differentiation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(19): 7080. |
| 15 | SOYSA N S, ALLES N. Positive and negative regulators of osteoclast apoptosis[J]. Bone Rep, 2019, 11: 100225. |
| 16 | JIN Y X, WU P, MAO Y F, et al. Chinese herbal medicine for osteoporosis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. J Clin Densitom, 2017, 20(4): 516-525. |
| 17 | QIAO J, LIU A, LIU J, et al. Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) alleviates the decreased activity induced by prednisolone acetate on osteoblasts by up-regulation of bone formation and differentiation genes[J].Food Funct, 2019, 10(9): 6184-6192. |
| 18 | CUI L, LI T, LIU Y, et al. Salvianolic acid B prevents bone loss in prednisone-treated rats through stimulation of osteogenesis and bone marrow angiogenesis[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(4): e34647. |
| 19 | JUNRUI P, BINGYUN L, YANHUI G, et al. Relationship between fluoride exposure and osteoclast markers during RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation[J]. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol, 2016, 46: 241-245. |
| 20 | ALOTAIBI M K, KITASE Y, SHULER C F. Smad2 overexpression induces alveolar bone loss and up regulates TNF-α, and RANKL[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2016, 71: 38-45. |
| 21 | CHEN H, ZHANG W, SUN X, et al. Fkbp1a controls ventricular myocardium trabeculation and compaction by regulating endocardial Notch1 activity[J]. Development, 2013, 140(9): 1946-1957. |
| 22 | PING Y, LOU F, YANG X, et al. Up-regulation of Notch1 inhibits proliferation and differentiation of osteoclast in vitro [J]. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2016, 34(2): 121-124. |
| [1] | Xuanchen LIU,Xiaoying TIE,Yulin LIU, WangNing. Effect of polygonum multiflorum extract on osteoporosis and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in agravic mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1386-1396. |
| [2] | . Primary hyperparathyrodism combined with papillary thyroid carcinoma and moderate anemia: A case report and literature reviewHAN Hui1,YU Tingting2,WANG Yechi3,HONG Shiping1,WANG Peisong1,MENG Wei1,BI Ming4(1.Department of Thyroid Surgery, First Hospital, Jilin University,Changchun 130021, China; 2. Department of Otolaryngology and Head-Neck Surgery,First Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China; 3. Department of Pathology, First Hospital,Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China;4. Department of General Dentistry, Stomatology Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China) [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1287-1291. |
| [3] | Xining LI,Wei WENG,Zheyuan SHEN,Xiaojie DOU,Jikang MIN. Therapeutic effect of estradiol combined with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on postmenopausal osteoporosis in rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 857-864. |
| [4] | Tianjiao MAO,Duo SUN,Xing GAO,Wei WEI,Xiheng LI,Kexin JIANG,Qiu JIANG,Jiang LI. [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 896-903. |
| [5] | Qian MAO, Cuicui CHEN, Huankun LIANG, Penge LIU, Shuhai ZHONG, Laiqing LI. Establishment and evaluation of a double?labeled time? resolved immunofluorescence analysis method for detecting levels of β?CTX and N?MID [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 770-776. |
| [6] | SUN Jingchun, JIN Hui, YANG Wenqi, XU Hui. Effect of total flavonids of Rhizomadrynariae on sclerostin expression in bone tissue of osteoporosis rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 911-916. |
| [7] | XU Dongliang, PENG Zhaohui, XIONG Meicai. Promotion effect of curcumin on implant osseointegration in osteoporosis rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 877-881. |
| [8] | LIU Shaowei, JIANG Huan, WANG Xiaolong, LI Menghong, CHEN Yu, TANG Zhongyuan, HU Min. Preparation and application of rabbit anti-osteoclastic protein tyrosine phosphatase polyclonal antibody [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(03): 661-666. |
| [9] | LI Xining, CHEN Xiaochun, ZHU Yunfei, CAO Jingnan, ZOU Yiting, DU Xiao, WANG Qichun. Effect of PERK signaling pathway on osteoblast differentiation of female rats with experimental postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 260-264. |
| [10] | WANG Junmei, SUN Qinyue, WU Zhe, LI Tong, LI Jing. Effects of Ginkgo Bitoba extract on differentiation and bone resorption ofosteoclasts and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(06): 1130-1136. |
| [11] | WANG Sihan, JIANG Huan, YU Hang, LIU Shaowei, LI Menghong, WANG Liuyi, YANG Junxing, HU Min. Effects of ursolic acid at different concentrations on proliferation and differentiation of osteoclasts and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(02): 236-240. |
| [12] | ZHU Tongtong, HUANG Liandi, LI Junwei, ZHAO Benzheng, JIANG Mengyang, LI Na, ZHAO Fan. Protective effect of icariin on osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(05): 915-919. |
| [13] | YAO Jindan, HAN Guanghong, HU Min. Effects of IL-17 on expressions of MMP-9 in osteoclasts and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(03): 462-466. |
| [14] | LIU Juanjuan, LI Peng, DONG Wei, FENG Xiaojie, WEN Liming, SUN Hong, QI Mengchun. Effects of zoledronate on gene expressions of calmodulin- dependent kinase Ⅱ and Ⅳ in osteoclast differentiation [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(01): 19-23. |
| [15] | ZHU Yun, WANG Zhengyu, YANG Xiaozhong, MA Tao, CHEN Tingmei, ZHANG Jian. Construction of recombinant adenovirus of mouse MafB gene and its effect on osteoclast differentiation [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(01): 32-38. |
|