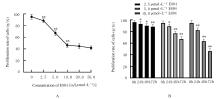
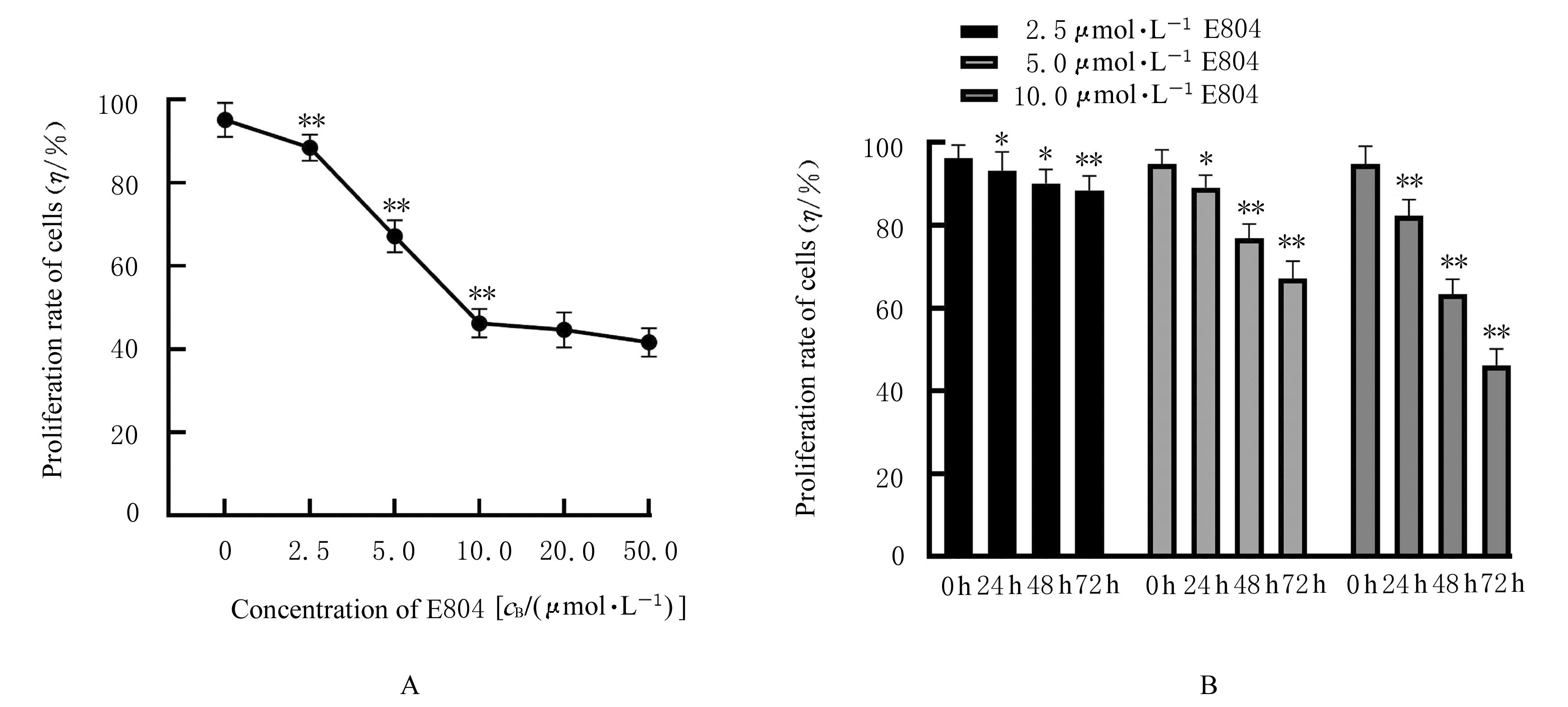
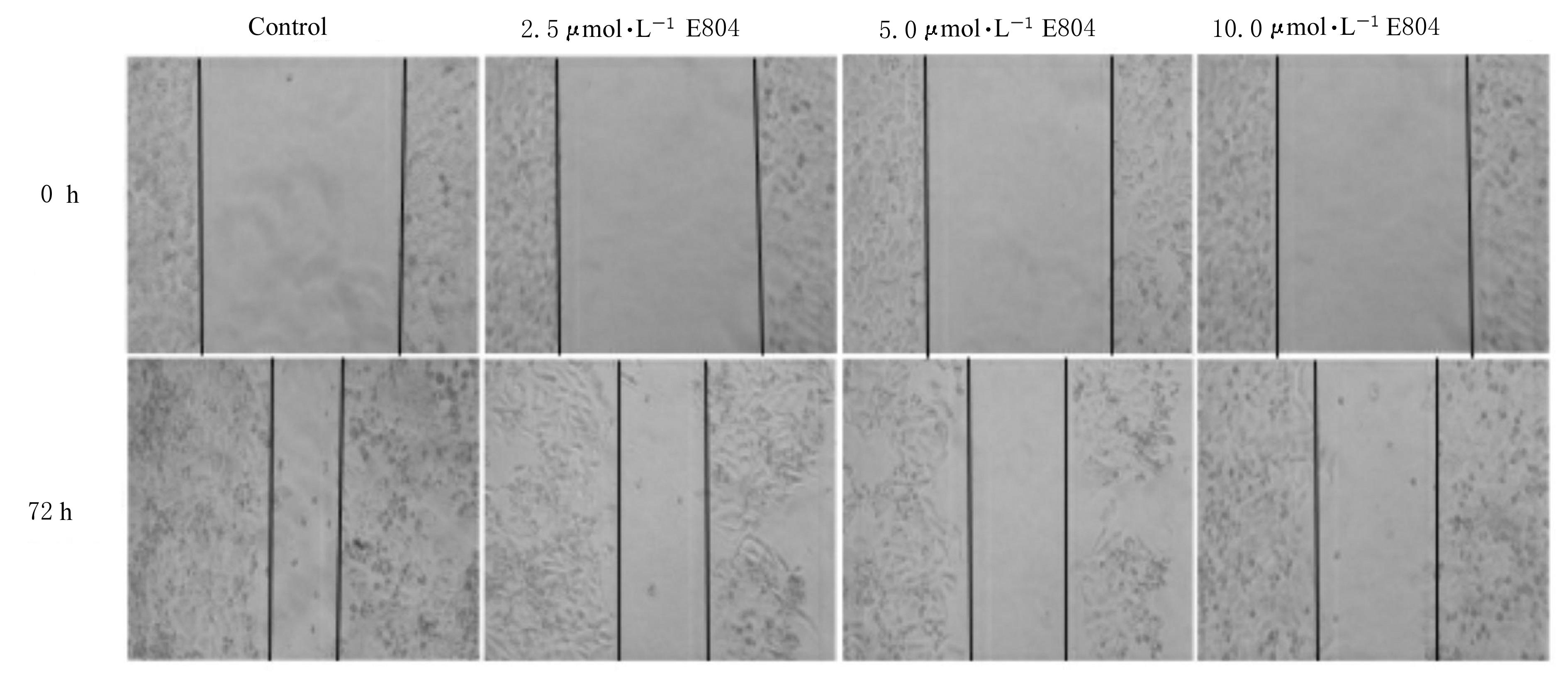
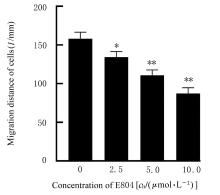
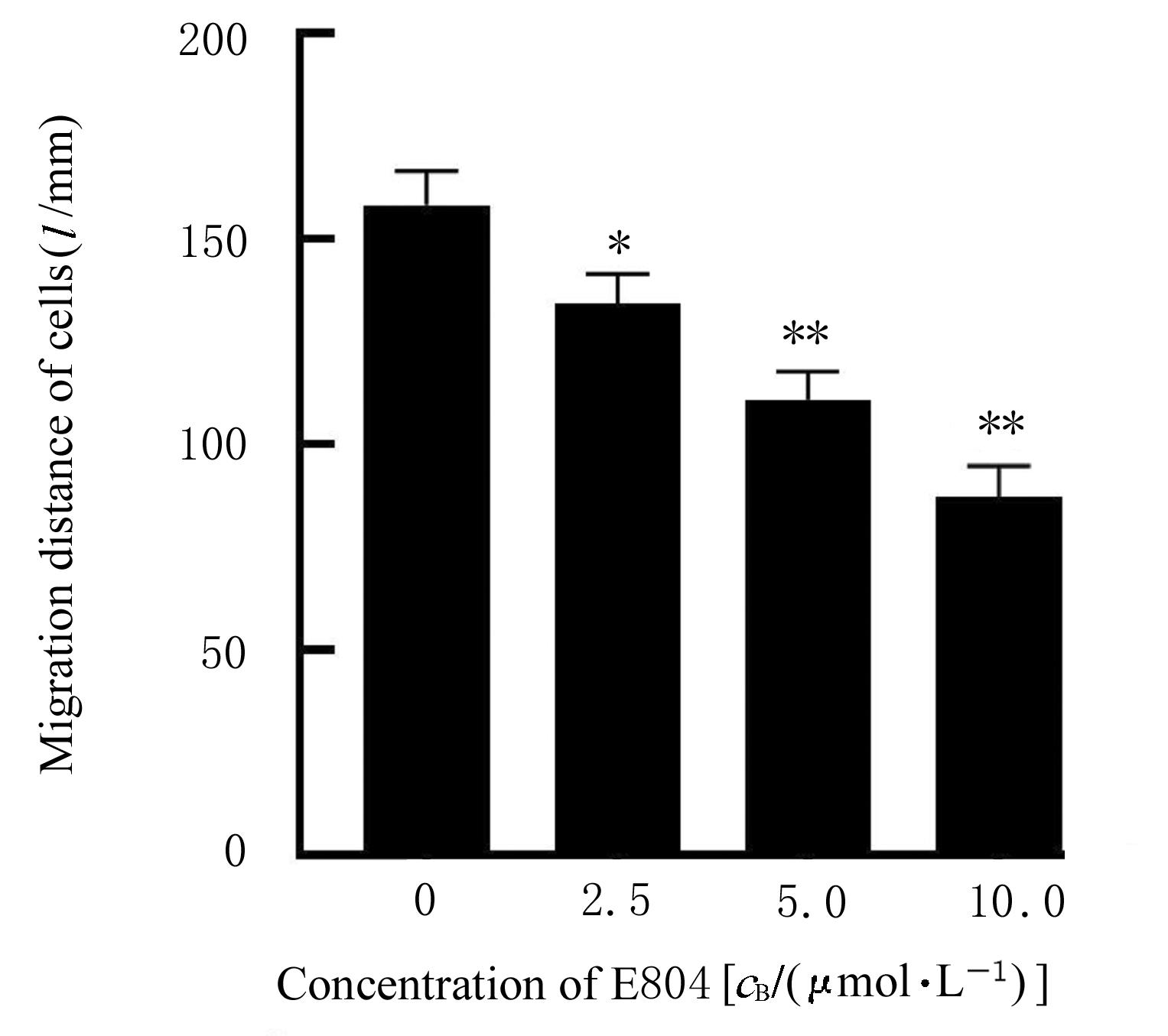
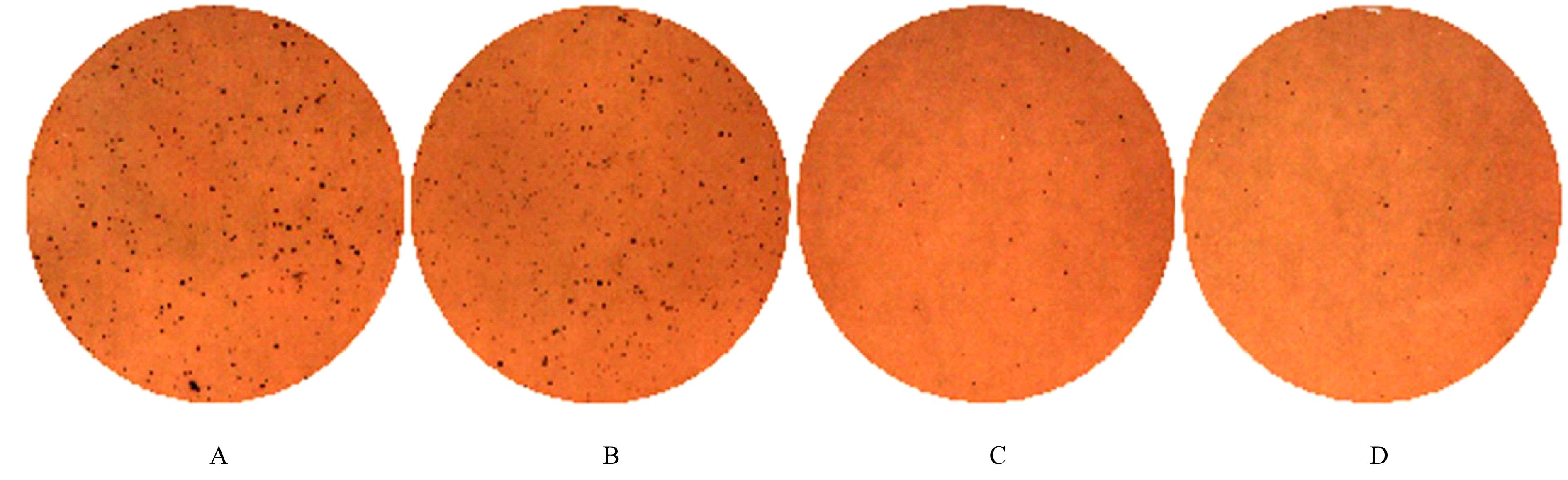
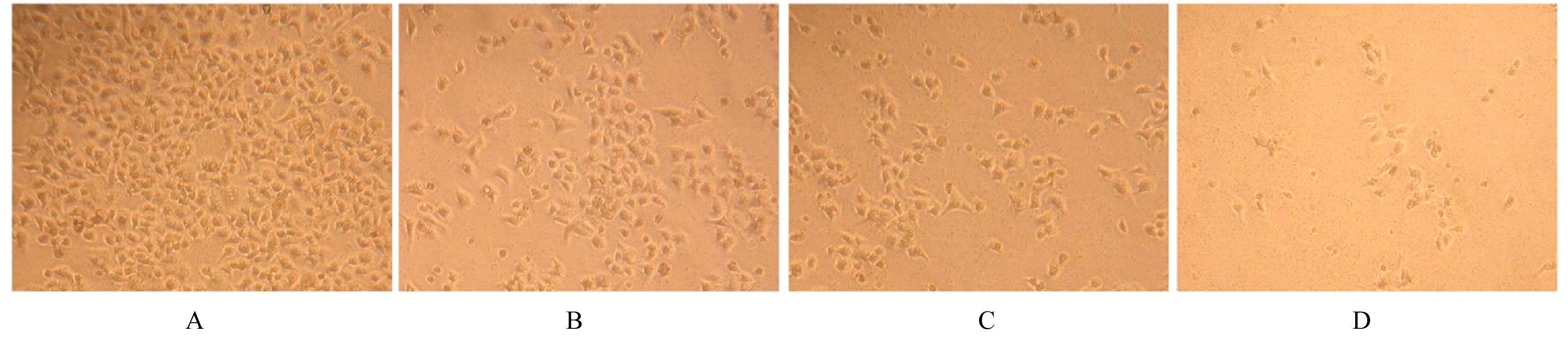
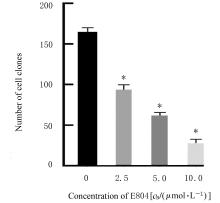
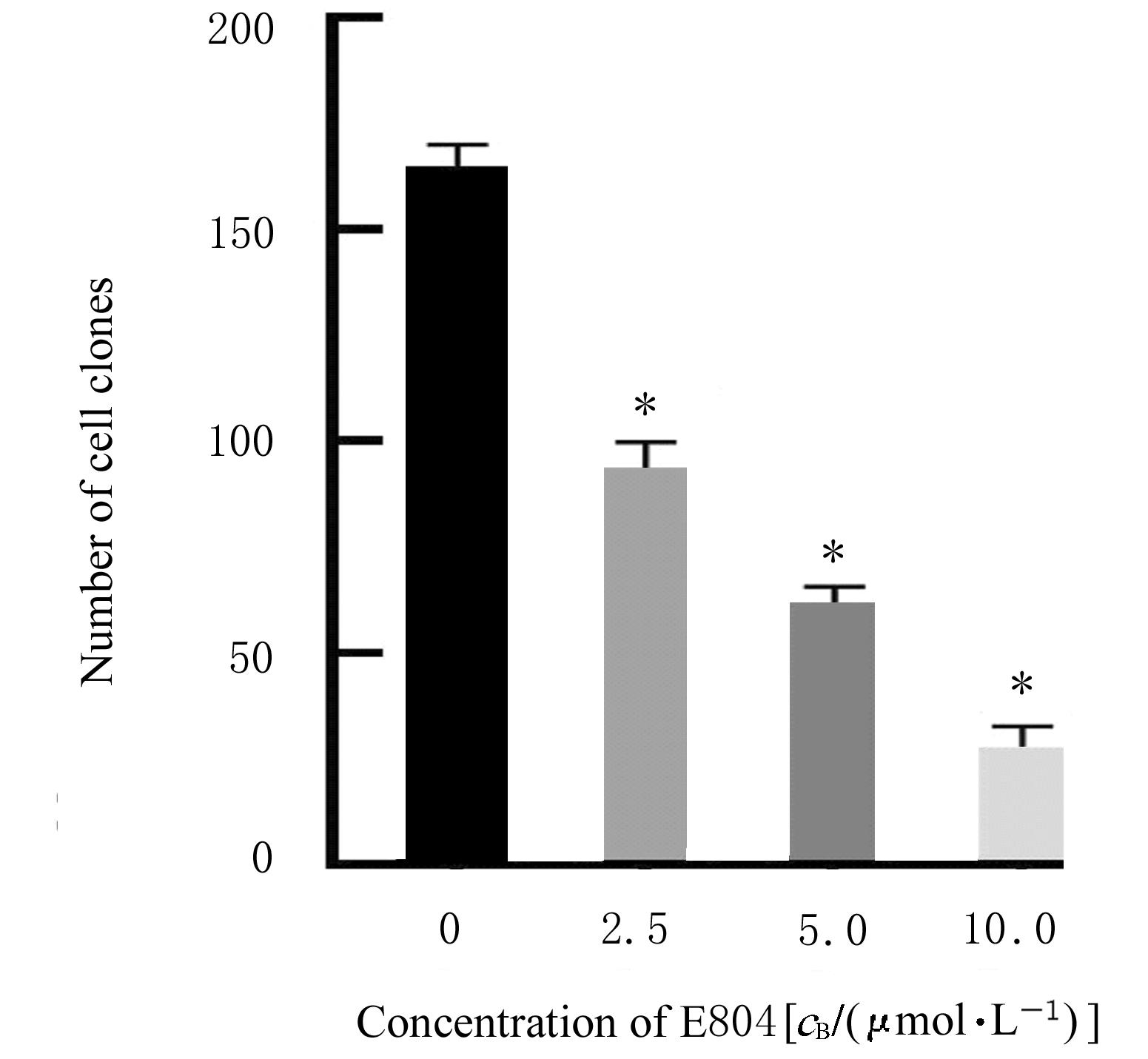
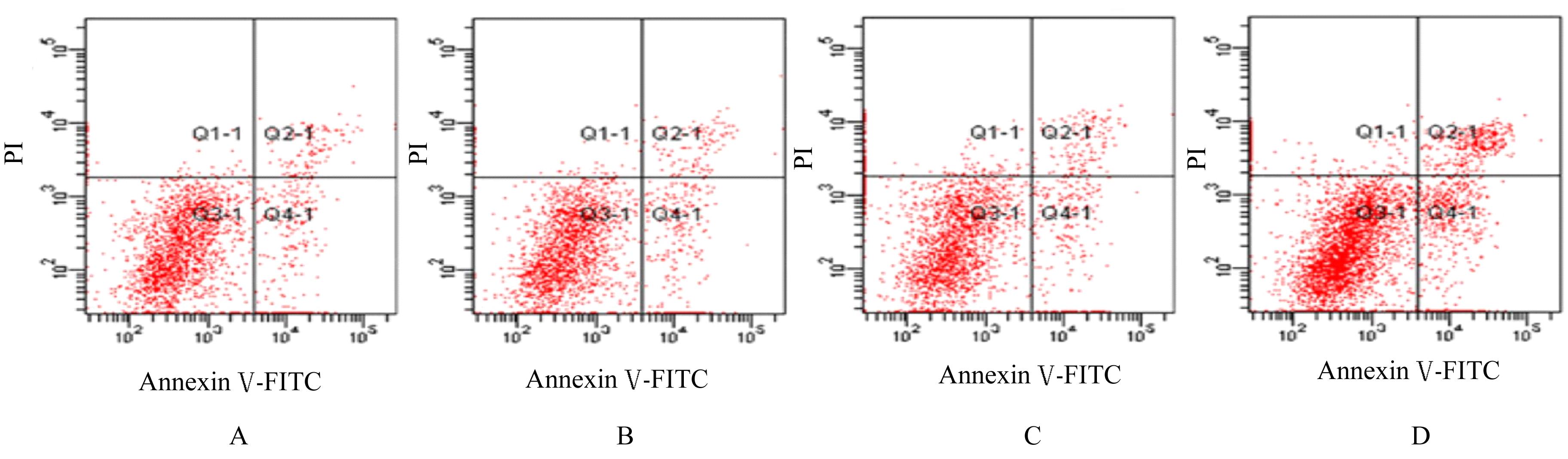
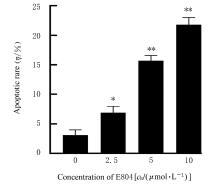
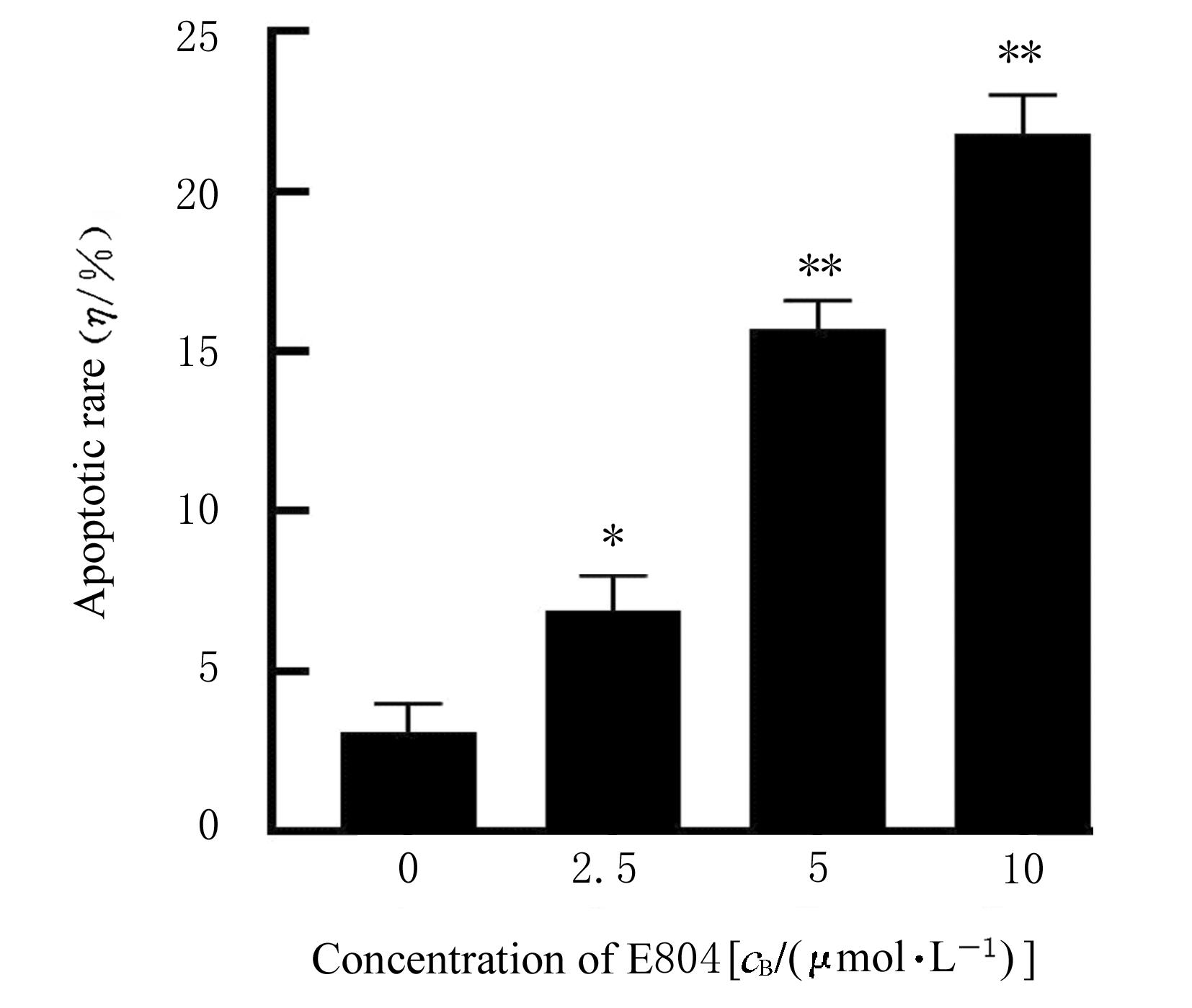
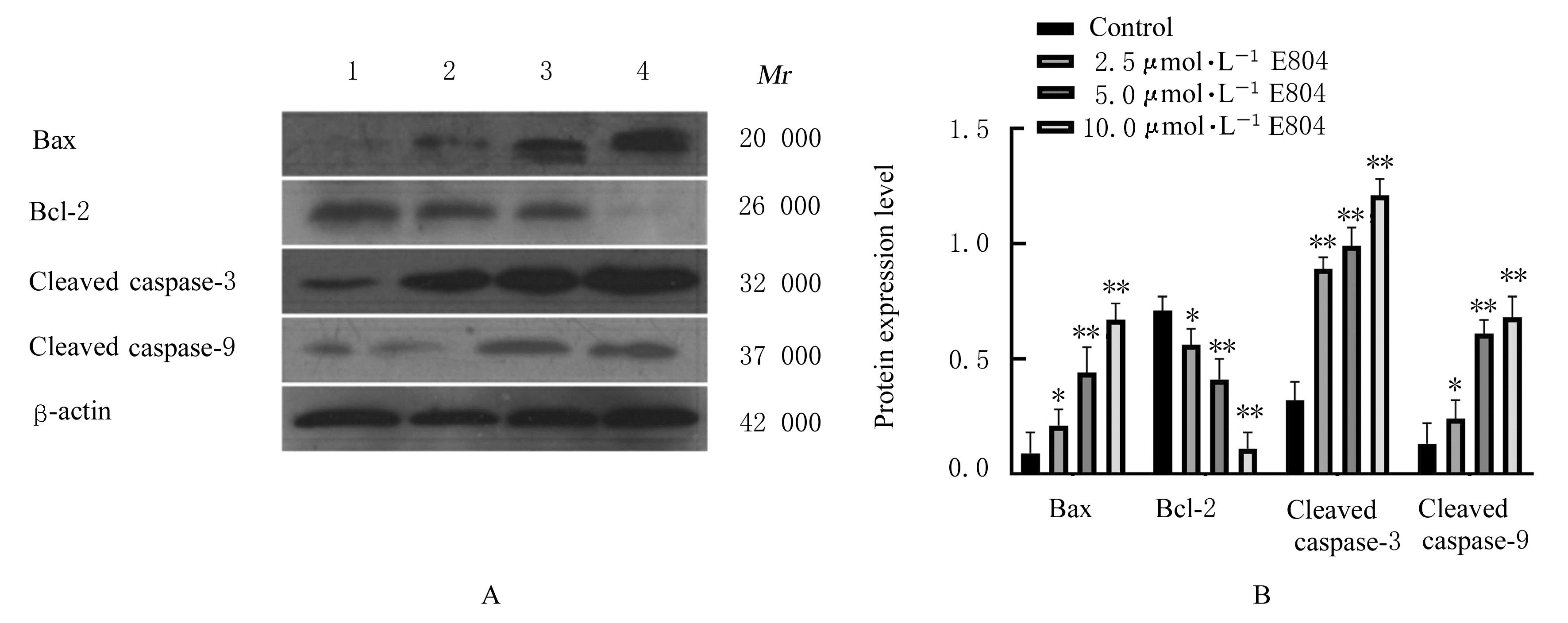
| [1] |
Bingbing WU,Aiping ZHANG,Xinke ZHAO,Yingdong LI,Kai LIU.
Protective effect of ultra-filtration extract from Angelica Sinensis Radix and Hedysari Radix on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury induced by X-ray and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1139-1147.
|
| [2] |
Hongxia SUN,Chunxu LIU,Xuejun AN,Guanghua CUI,Jingyu WANG,Shuangxi TONG,Xiaoqiu YANG.
Effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide on proliferation and apoptosis of human bladder cancer T24 cells and its mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1216-1222.
|
| [3] |
Yuan LIAO,Kaiju WANG,Haoyan LI,Huiping CHEN,Xuanyi LI,Yong HUANG.
Improvement effects of neuropeptide PACAP27 on cyclophosphamide-induced testicular injury in rats by inhibiting mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1266-1275.
|
| [4] |
Qingxu LANG,Xueshuang NIU,Kaiwen YANG,Ren ZHANG,Siteng WANG, ZUMIRETIGULI·Wumaier,Zhenqi WANG.
Effects of sodium butyrate combined with ionizing radiation on apoptosis of lung cancer A549 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 915-921.
|
| [5] |
Guanhu LI,Qingxu LANG,Chunyan LIU,Qin LIU,Mengrou GENG,Xiaoqian LI,Zhenqi WANG.
Inhibitory effect of valproic acid combined with X-ray irradiation on proliferation of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 622-629.
|
| [6] |
Qiuting CAO,Jingchun HAN,Xiaofei ZHANG.
Effect of silencing helicase BLM gene on chemotherapy sensitivity of irinotecan in colorectal cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 657-667.
|
| [7] |
Cuilan LIU,Fengai HU,Jing LIU,Dan WANG,Changyun QIU,Dunjiang LIU,Di ZHAO.
Effect of adiponectin receptor agonist AdiopRon on biological behaviors of glioma cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 702-710.
|
| [8] |
Ming xing YANG,Wen DONG,Ji LI.
Inductive effect of peiminine on apoptosis of lung cancer A549 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 711-717.
|
| [9] |
Ming LI,Qiuting WANG,Shan CHEN,Huifang SHI.
Improvement effect of p38 MAPK inhibitor on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease injury in mice through inhibiting cell pyrotosis mediated by NLRP3 pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 744-754.
|
| [10] |
Suxian CHEN,Zehui GU,Yangfei MA,Qi TAN,Qi LI,Yadi WANG.
Promotion effect of rutin on apoptosis of human colon cancer SW480 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 356-363.
|
| [11] |
Zhihui ZHAO,Xianghua BAI,Jinling HE,Weiqin DUAN,Min LIU,Shengmao ZHANG.
Inhibitory effect of sufentanil on apoptosis of myocardial cells in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 364-373.
|
| [12] |
Guangsong XU,Haibing JIANG,Jing PAN,Guoqing LI.
Inhibitory effects of betulinic acid on migration and invasion of gastric cancer MGC-803 cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 122-128.
|
| [13] |
Wenxiong SUN,Pu LI.
Expression of SOCS3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its effect on autophagy and apoptosis of OCI-LY7 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 172-179.
|
| [14] |
Leihua CUI,Yubo HOU,Chang SU,Minghe LI,Xin NIE.
Effect of N-acetylcysteine on apoptosis of MC3T3-E1 cells induced by nicotine and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 26-32.
|
| [15] |
Yu ZHU,Jingjing WANG,Fang WU.
Expression of miR-150-5p in kidney tissue of diabetic nephropathy model mice and its effect on MPC5 mouse podocyte injury and mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 44-51.
|
 )
)