Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1055-1061.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240420
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of extraction orthodontic treatment on upper airway and surrounding tissue in adult patients with skeletal class Ⅱhigh angle malocclusion
Yu CHEN1,2,Huan JIANG1,Min HU1( )
)
- 1.Department of Orthodontics,Stomatology Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.Department of Stomatology,First Affiliated Hospital,Naval Medical University,Shanghai 200433,China
-
Received:2023-10-01Online:2024-07-28Published:2024-08-01 -
Contact:Min HU E-mail:humin@jlu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R783.5
Cite this article
Yu CHEN, Huan JIANG, Min HU. Effect of extraction orthodontic treatment on upper airway and surrounding tissue in adult patients with skeletal class Ⅱhigh angle malocclusion[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1055-1061.
share this article
Tab.1
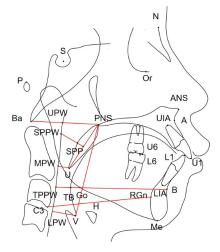
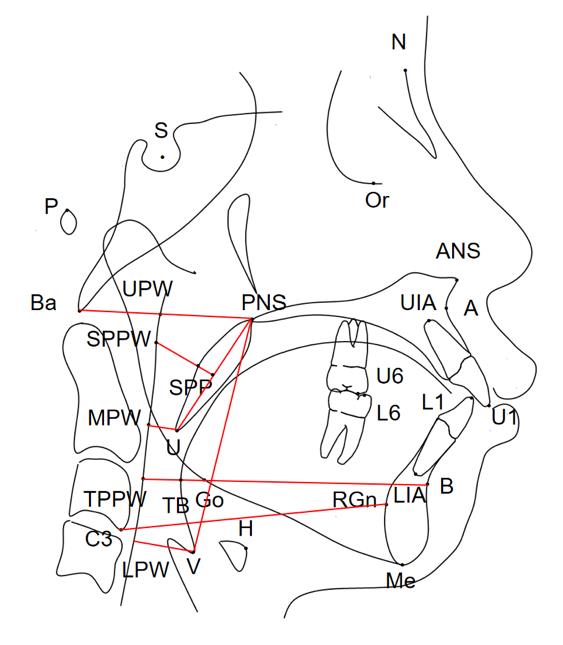
Measurement indicators of upper airway of patients in extration group before and after orthodontic treatment (n=30, xˉ±s,l/mm)"
| Group | PNS-Ba | PNS-UPW | SPP-SPPW | U-MPW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before orthodontic treatment | 43.25±3.79 | 25.94±3.39 | 11.31±2.83 | 10.63±3.24 |
| After orthodontic treatment | 42.04±3.29 | 25.87±2.97 | 11.18±3.69 | 9.60±3.04 |
| P | 0.068 | 0.843 | 0.795 | 0.023 |
| Group | TB-TPPW | V-LPW | C3-RGn | PNS-V |
| Before orthodontic treatment | 10.82±2.61 | 13.98±3.70 | 65.83±6.04 | 59.74±4.98 |
| After orthodontic treatment | 10.30±3.47 | 12.69±4.64 | 64.90±6.40 | 60.62±5.78 |
| P | 0.198 | 0.010 | 0.357 | 0.242 |
Tab.2
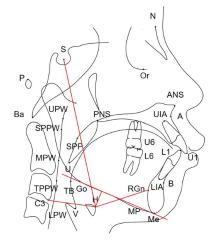
Measurement indicators of hoyid bone position of patients in extraction group before and after orthodontic treatment (n=30, xˉ±s,l/mm)"
| Group | Hy-MP | Hy-S | Hy-C3 | Hy-RGn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before orthodontic treatment | 9.62±4.14 | 99.50±6.63 | 33.87±3.78 | 33.79±4.60 |
| After orthodontic treatment | 10.45±4.49 | 101.07±7.09 | 33.50±4.10 | 33.06±5.30 |
| P | 0.125 | 0.053 | 0.305 | 0.405 |
Tab.3
Dental and maxillofacial measurement indicators of patients in extraction group before and after orthodontic treatment (n=30, xˉ±s, θ/°)"
| Group | SNA | SNB | ANB | OP-SN | MP-SN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before orthodontic treatment | 82.43±3.43 | 75.90±2.90 | 6.55±1.40 | 21.23±3.55 | 40.64±3.51 | |||
| After orthodontic treatment | 82.02±3.11 | 75.76±2.84 | 6.26±1.90 | 22.95±3.78 | 40.19±4.93 | |||
| P | 0.205 | 0.617 | 0.250 | 0.007 | 0.461 | |||
| Group | MP-FH | U1-SN | L1-MP | U1-L1 | ||||
| Before orthodontic treatment | 31.99±2.82 | 106.07±7.33 | 97.95±5.50 | 115.32±11.08 | ||||
| After orthodontic treatment | 31.69±4.33 | 98.52±6.51 | 92.75±7.08 | 128.53±9.41 | ||||
| P | 0.616 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
Tab.4
Measurement indicators of upper airway of patients in non-extration group before and after orthodontic treatment (n=30, xˉ±s, l/mm)"
| Group | PNS-Ba | PNS-UPW | SPP-SPPW | U-MPW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before orthodontic treatment | 41.33±3.01 | 24.49±2.74 | 11.17±2.30 | 9.10±2.43 |
| After orthodontic treatment | 41.12±3.06 | 24.60±2.59 | 10.35±3.54 | 8.65±2.75 |
| P | 0.607 | 0.789 | 0.205 | 0.410 |
| Group | TB-TPPW | V-LPW | C3-RGn | PNS-V |
| Before orthodontic treatment | 9.57±2.48 | 12.03±3.73 | 62.60±5.09 | 62.29±5.73 |
| After orthodontic treatment | 9.35±2.62 | 12.33±3.25 | 63.18±5.41 | 62.15±6.21 |
| P | 0.558 | 0.656 | 0.485 | 0.881 |
Tab.5
Measurement indicators of hoyid bone position of patients in non-extraction group before and after orthodontic treatment (n=30, xˉ±s, l/mm)"
| Group | Hy-MP | Hy-S | Hy-C3 | Hy-RGn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before orthodontic treatment | 13.88±4.22 | 105.10±8.38 | 32.26±3.93 | 32.30±4.85 |
| After orthodontic treatment | 13.12±3.85 | 105.48±10.63 | 32.17±3.94 | 33.16±4.75 |
| P | 0.234 | 0.709 | 0.787 | 0.218 |
Tab.6
Dental and maxilloficial measurement indicators of patients in non-extraction group before and after orthodontic treatment (n=30, xˉ±s, θ/°)"
| Group | SNA | SNB | ANB | OP-SN | MP-SN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before orthodontic treatment | 82.42±3.86 | 75.43±3.32 | 7.00±1.62 | 20.66±3.44 | 39.52±1.76 | |||
| After orthodontic treatment | 82.40±4.21 | 75.94±3.79 | 6.45±1.59 | 22.61±3.86 | 39.09±2.65 | |||
| P | 0.939 | 0.073 | 0.033 | 0.002 | 0.225 | |||
| Group | MP-FH | U1-SN | L1-MP | U1-L1 | ||||
| Before orthodontic treatment | 31.18±2.46 | 103.19±8.36 | 94.04±6.23 | 123.25±11.02 | ||||
| After orthodontic treatment | 30.86±2.94 | 103.16±5.37 | 99.22±7.24 | 118.52±8.19 | ||||
| P | 0.322 | 0.080 | 0.002 | 0.080 | ||||
| 1 | JIANG Y Y. Correlation between hyoid bone position and airway dimensions in Chinese adolescents by cone beam computed tomography analysis[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2016, 45(7): 914-921. |
| 2 | CDDS AUVENSHINE R, JDMD PETTIT N. The hyoid bone: an overview[J]. Cranio, 2020,38(1): 6-14. |
| 3 |
王志会, 贾 莹, 丁 琪. 不同垂直骨面型骨性Ⅲ类错 颅-舌骨的平面投影关系[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2021, 39(3): 282-285. 颅-舌骨的平面投影关系[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2021, 39(3): 282-285.
|
| 4 |
董浩鑫, 徐文华, 马众辉, 等. 不同垂直骨面型骨性Ⅲ类错 畸形患者正畸掩饰性治疗后上气道形态和舌骨位置的变化[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022,57(6): 816-821. 畸形患者正畸掩饰性治疗后上气道形态和舌骨位置的变化[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022,57(6): 816-821.
|
| 5 | 毛渤淳, 田雅婧, 文艺峰, 等. 基于三维可形变模型的骨性Ⅱ类高角患者正畸前后面型分析[J]. 中华口腔正畸学杂志, 2022, 29(3): 127-131. |
| 6 | SIVAKUMAR A, AZHARUDDIN M, SIVAKUMAR I, et al. Assessment of hyoid bone position among different skeletal patterns[J]. Orthod Waves, 2017, 76(4): 221-225. |
| 7 | CHAN J, EDMAN J C, KOLTAI P J. Obstructive sleep apnea in children[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2004,69(5): 1147-1154. |
| 8 | CHIANG C C, JEFFRES M N, MILLER A, et al. Three-dimensional airway evaluation in 387 subjects from one university orthodontic clinic using cone beam computed tomography[J]. Angle Orthod, 2012, 82(6): 985-992. |
| 9 | IWASAKI T, PAPAGEORGIOU S N, YAMASAKI Y,et al. Nasal ventilation and rapid maxillary expansion (RME):a randomized trial[J].Eur J Orthod,2021,43(3): 283-292. |
| 10 | VENEZIA P, NUCCI L, MOSCHITTO S, et al. Short-term and long-term changes of nasal soft tissue after rapid maxillary expansion (RME) with tooth-borne and bone-borne devices. A CBCT retrospective study[J]. Diagnostics, 2022, 12(4): 875. |
| 11 | 温伟生, 胡 敏, 柳春明, 等. 不同体位下软腭位置与腭后气道的相关性研究[J]. 军医进修学院学报, 2001, 22(1): 57-59. |
| 12 | HUANG T W, CHENG P W. Microdebrider-assisted extended uvulopalatoplasty: an effective and safe technique for selected patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome[J]. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2008, 134(2): 141-145. |
| 13 | 何权瀛. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停的主要危险因素及其发病机制[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2019, 18(6): 610-612. |
| 14 | CHEN Y, HONG L, WANG C L, et al. Effect of large incisor retraction on upper airway morphology in adult bimaxillary protrusion patients[J]. Angle Orthod, 2012, 82(6): 964-970. |
| 15 | WANG Q Z, JIA P Z, ANDERSON N K, et al. Changes of pharyngeal airway size and hyoid bone position following orthodontic treatment of Class Ⅰbimaxillary protrusion[J]. Angle Orthod, 2012, 82(1): 115-121. |
| 16 | BATTAGEL J M, JOHAL A, L’ESTRANGE P R, et al. Changes in airway and hyoid position in response to mandibular protrusion in subjects with obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA)[J]. Eur J Orthod,1999,21(4): 363-376. |
| 17 | RANA S S, KHARBANDA O P, AGARWAL B. Influence of tongue volume, oral cavity volume and their ratio on upper airway: a cone beam computed tomography study[J]. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res, 2020, 10(2): 110-117. |
| 18 | GUIMARÃES C H Jr, HENRIQUES J F, JANSON G,et al. Prospective study of dentoskeletal changes in Class Ⅱ division malocclusion treatment with twin force bite corrector[J]. Angle Orthod, 2013, 83(2): 319-326. |
| 19 | COSTA E DDA, ROQUE-TORRES G D, BRASIL D M,et al. Correlation between the position of hyoid bone and subregions of the pharyngeal airway space in lateral cephalometry and cone beam computed tomography[J]. Angle Orthod, 2017, 87(5): 688-695. |