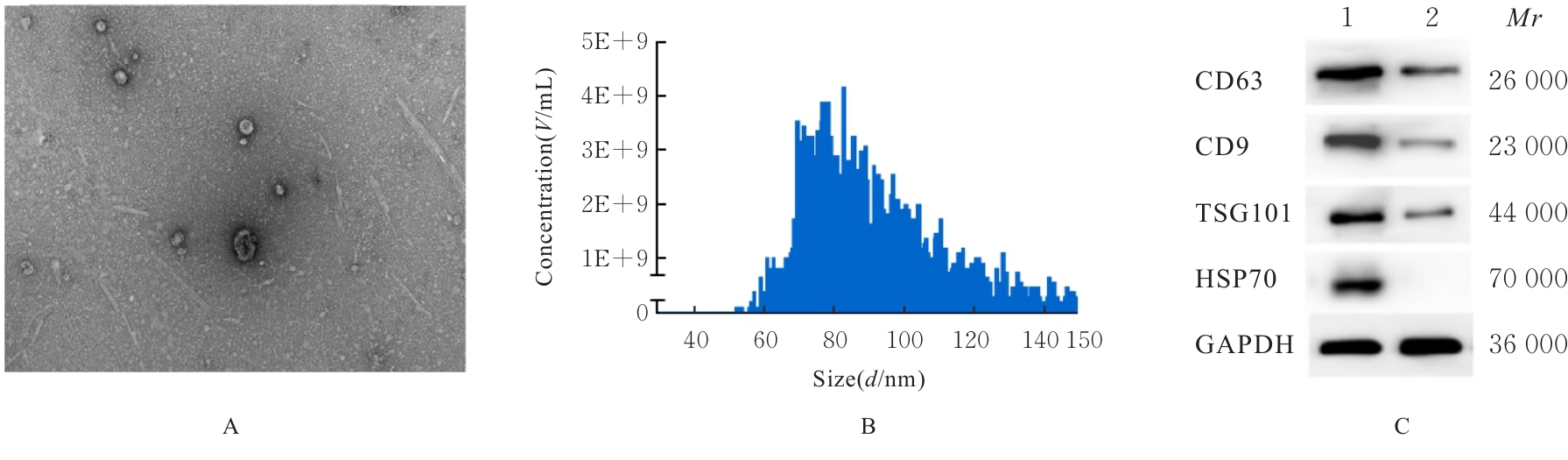
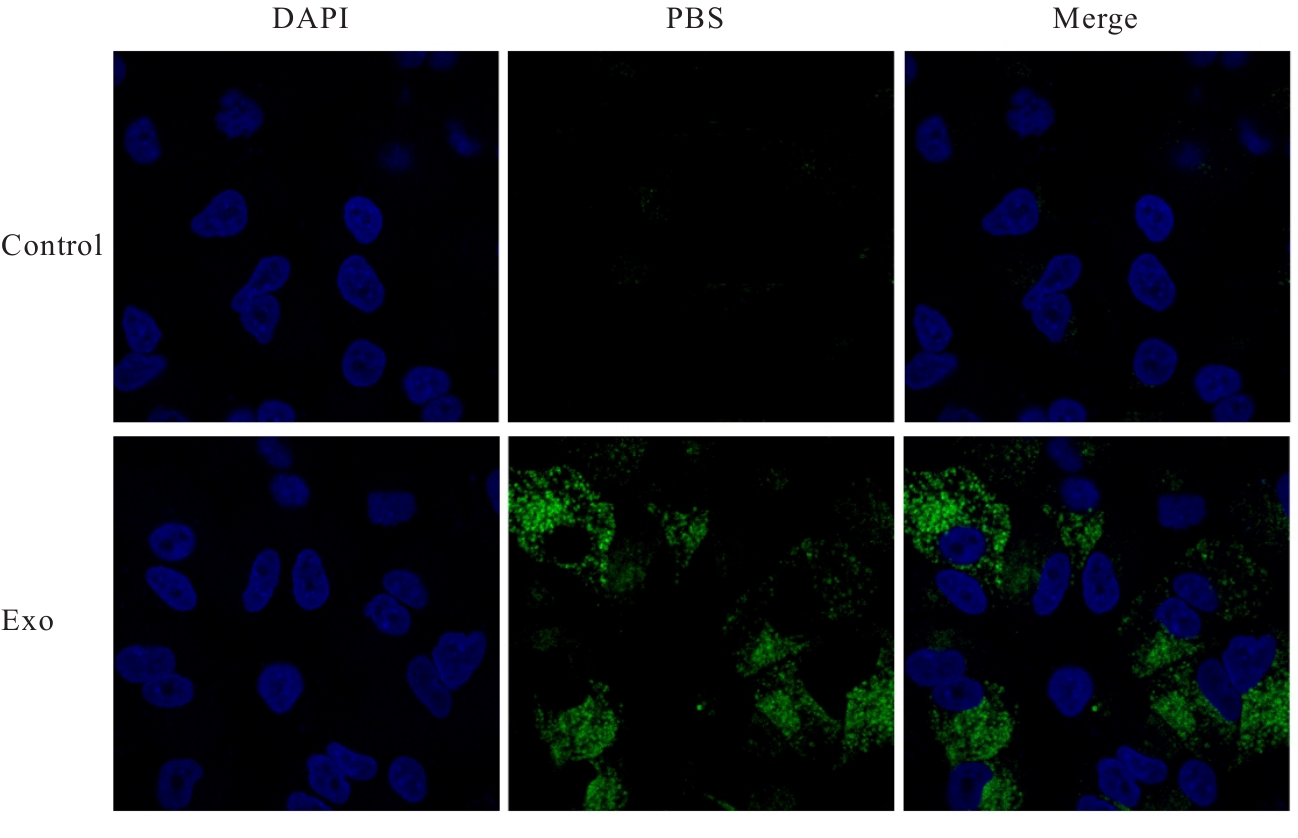
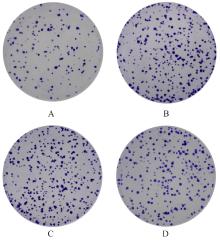
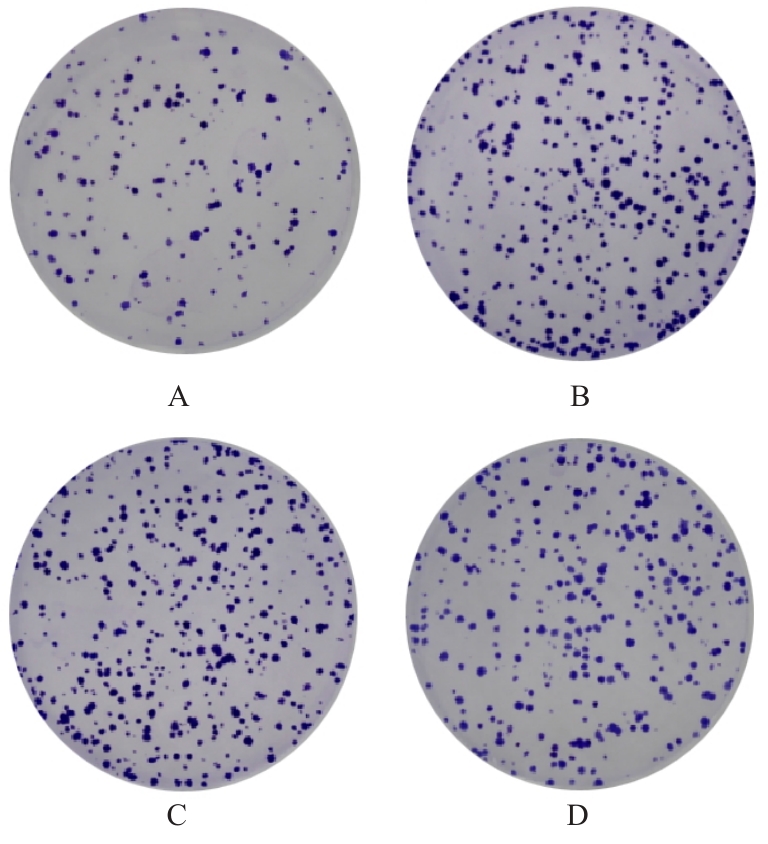
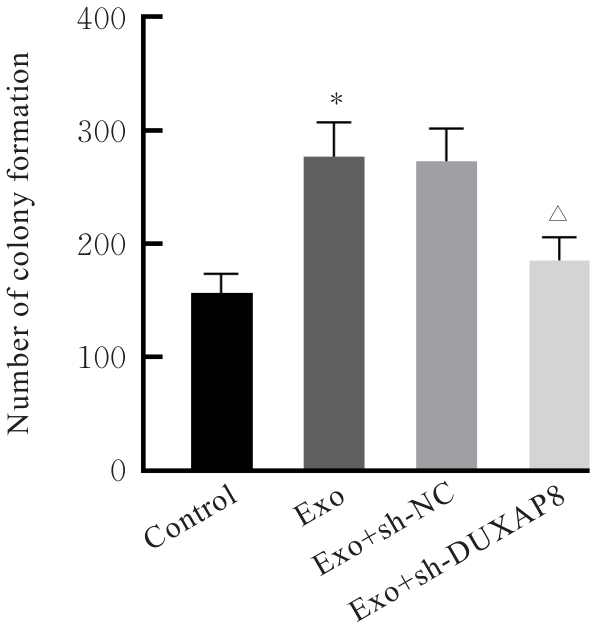
| [1] |
Yixuan GAO,Peng WANG,Silong ZHANG,Ruijuan GAO,Yingfang MA,Keke ZHANG,Dan FENG,Zongqi HUANG,Ketao MA,Li LI,Junqiang SI.
Inhibitory effect of safranal on proliferation, migration and phenotypic transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells of rats induced by high glucose in vitro
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(4): 948-957.
|
| [2] |
Wenxuan LI,Minru ZONG.
Research progress in role of migration of Schwann cells in repairment of peripheral nerve injury
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(4): 1137-1144.
|
| [3] |
Fan WANG,Xin WEN,Yixuan WANG,Yuan WANG.
Effect of gap junction β2 on prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma and biological behavior of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 716-726.
|
| [4] |
DILIXIATI·Dilidaer,Lin JIA.
Improvement effect of exosomes derived from human adipose-derived stem cells and human dermal fibroblasts on ultraviolet-induced photoaging skin wrinkles in nude mice
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 621-631.
|
| [5] |
Yuling GU,Cui ZHENG,Yunxian TANG.
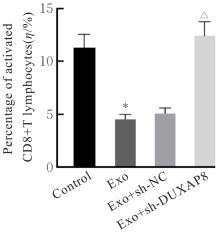
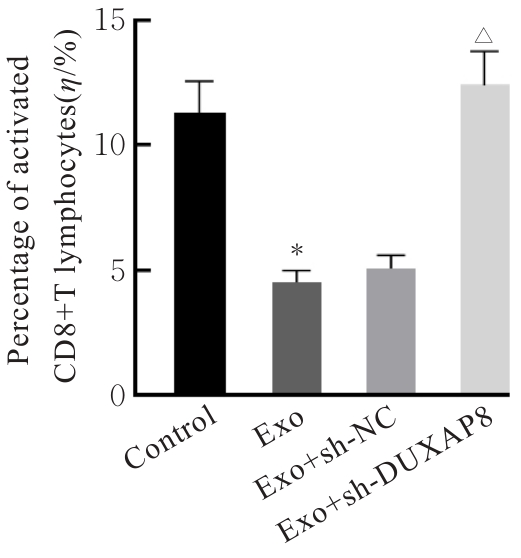
Inhibitory effect of silencing of circadian rhythm gene TIMELESS on immune escape of ovarian cancer SK-OV-3 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 653-662.
|
| [6] |
Yihui WANG,Qing ZHANG,Yingnan LI,Liping YE.
Effect of KIAA1522 on proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 727-739.
|
| [7] |
Shuyan SUN,Huakun ZHANG,Ziru ZHOU,Feng LI,Xiaobin CUI.
Expression of CRNN protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue and influence of its overexpression in biological behavior of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Eca9706 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 275-283.
|
| [8] |
Jing DENG,Xuan WANG,Changyu SHI,Siqi YANG,Qinling ZOU,Ming JIN.
Effect of securinine on proliferation and apoptosis of human colon cancer SW620 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 307-316.
|
| [9] |
Mengyun LU,Yucheng HAN,Yihong HU,Minhui HE,Yanqun ZHANG,Xianqiong ZOU.
Effects of glycolipid transfer protein on proliferation, migration,and invasion of pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 284-295.
|
| [10] |
Yan WANG,Zouyu ZHAO,Panpan YU,Ping YANG.
Expression of I kappa B kinase-interacting protein in cervical cancer tissue and its effect on proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 341-351.
|
| [11] |
Yaqi ZHANG,Jing MI,Jingrong YANG,Xinming LI,Li LI.
Effect of up-regulation of miR-31 expression on osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells through Wnt-β/catenin signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 412-419.
|
| [12] |
Ying YANG,Liang ZHAO,Yong YOU,Qian XU,Zhenjun YANG.
Influence of 17β-estradiol in proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neural stem cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 317-324.
|
| [13] |
Shuo ZHANG,Yunxiu XIA,Weiwei CHEN,Hongliang DONG,Bingjie CUI,Cuilan LIU,Zhiqiang LIU,Fei WANG,Jing DU.
Effect of over-expression of NR2F2 on biological behaviors of human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 58-67.
|
| [14] |
Fang ZHAO,Zhenling LI,Lihua PIAO,Longzhe HAN,Yinji CUI,Chunji QUAN,Xuemei JIN.
Effect of Yes-associated proteins on biological behaviors of human cervical cancer SiHa cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 68-75.
|
| [15] |
Mengmeng ZHAO,Yalu WANG,Yuxiang XU,Kaige YANG,Yuwen CAO,Wenhu ZHOU,Jing FEI,Wen WANG,Chenghua LUO,Jianming HU.
Effects of hydrogen sulfide synthase CBS and CSE on malignant biological behaviour of breast cancer cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 34-43.
|
 )
)