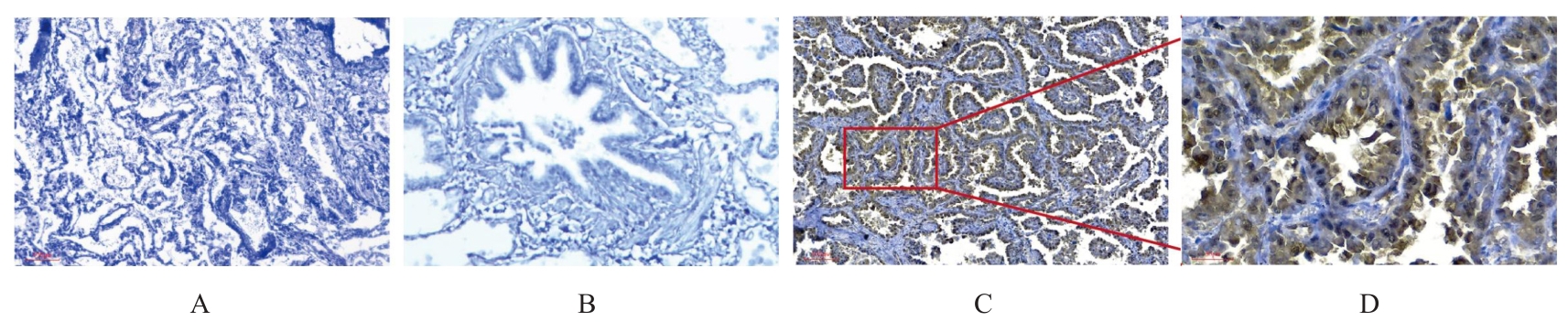
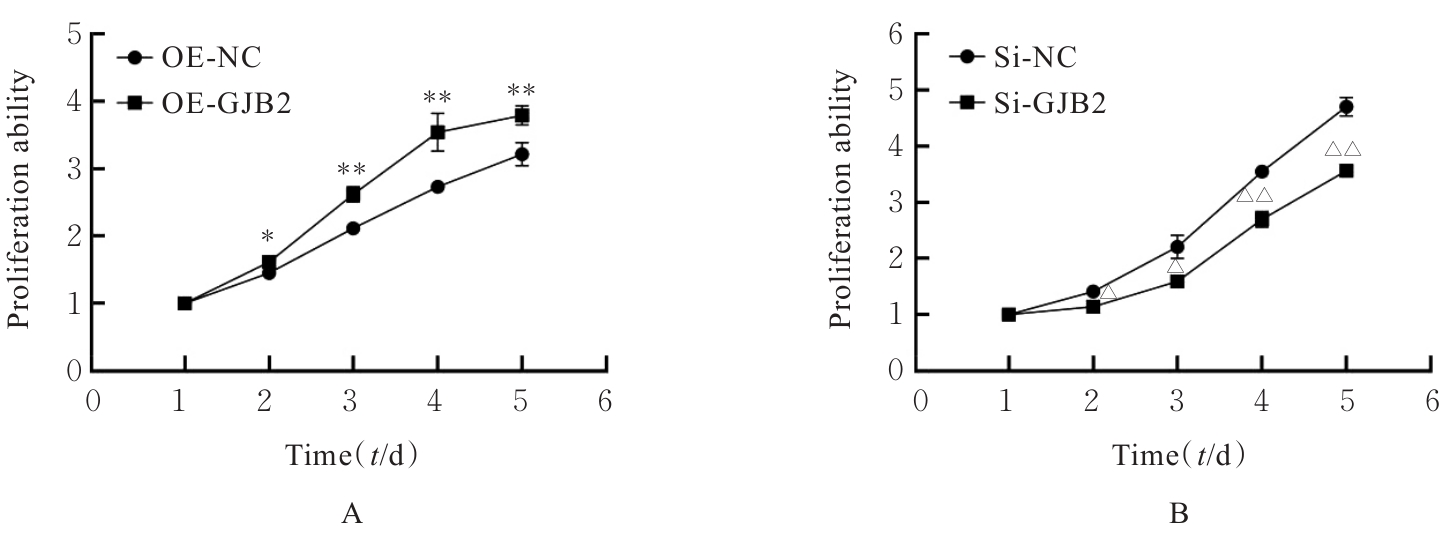
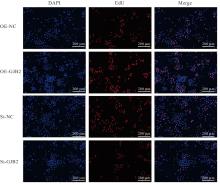
| [1] |
Xingxiang WANG,Ying ZHAO,Qiaotong REN,Hefei WANG,Gang PU,Chun LI.
Promotive effect of M2 macrophages on epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells by regulating NF-κB signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 642-652.
|
| [2] |
Donghui LIU,Yunzhe CI,Chunyan WANG,Wenyi MA.
Effect of miR-199a-5p on expression of Caveolin-1, cell migration and apoptosis in glioma U251 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 663-671.
|
| [3] |
Shuyan SUN,Huakun ZHANG,Ziru ZHOU,Feng LI,Xiaobin CUI.
Expression of CRNN protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue and influence of its overexpression in biological behavior of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Eca9706 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 275-283.
|
| [4] |
Mengyun LU,Yucheng HAN,Yihong HU,Minhui HE,Yanqun ZHANG,Xianqiong ZOU.
Effects of glycolipid transfer protein on proliferation, migration,and invasion of pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 284-295.
|
| [5] |
Jing DENG,Xuan WANG,Changyu SHI,Siqi YANG,Qinling ZOU,Ming JIN.
Effect of securinine on proliferation and apoptosis of human colon cancer SW620 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 307-316.
|
| [6] |
Ying YANG,Liang ZHAO,Yong YOU,Qian XU,Zhenjun YANG.
Influence of 17β-estradiol in proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neural stem cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 317-324.
|
| [7] |
Yan WANG,Zouyu ZHAO,Panpan YU,Ping YANG.
Expression of I kappa B kinase-interacting protein in cervical cancer tissue and its effect on proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 341-351.
|
| [8] |
Yaqi ZHANG,Jing MI,Jingrong YANG,Xinming LI,Li LI.
Effect of up-regulation of miR-31 expression on osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells through Wnt-β/catenin signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 412-419.
|
| [9] |
Pengli WU,Fengyu LI,Bo LIU,Yang LYU.
Effect of silencing DDX39A gene on proliferation, migration and invasion of esophageal cancer TE-1 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 115-123.
|
| [10] |
Mengmeng ZHAO,Yalu WANG,Yuxiang XU,Kaige YANG,Yuwen CAO,Wenhu ZHOU,Jing FEI,Wen WANG,Chenghua LUO,Jianming HU.
Effects of hydrogen sulfide synthase CBS and CSE on malignant biological behaviour of breast cancer cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 34-43.
|
| [11] |
Lu YANG,Jiacai FU,Fengjin LI,Ling QI.
Inhibitory effect of schisandrin on migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 44-50.
|
| [12] |
Fang ZHAO,Zhenling LI,Lihua PIAO,Longzhe HAN,Yinji CUI,Chunji QUAN,Xuemei JIN.
Effect of Yes-associated proteins on biological behaviors of human cervical cancer SiHa cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 68-75.
|
| [13] |
Xin WANG,Jierui ZHAO,Yumiao GUO,Shutong CHEN,Zonghao HOU,Ruowen ZHANG.
Effect of silencing CD147 gene on proliferation, migration, invasion, and inducing apoptosis of prostate cancer cells inhibited by curcumin
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1572-1586.
|
| [14] |
Bin ZHAO,Jinye YANG,Zhiyao LI,Chengwei BI,Libo YANG,Zhiyu SHI,Xin LI,Jianpeng ZHANG,Yuanlong SHI,Yong YANG,Guoying ZHANG.
Inhibitory effect of miR-30c-5p on proliferation, migration, and invasion of prostate cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1632-1643.
|
| [15] |
Jing LOU,Lei ZHAO,Yanjie ZHU,Shuaiqiang YUAN,Fei WANG,Hangzhou ZHANG,Jiaojiao XU,Xiaoke YU,Liufa HOU.
Effect of Fuzheng Ruanjian Anticancer Formula on malignant biological behaviors of hepatocellulars carcinoma HepG2 cells by regulating Akt/MDM2/P53 signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1654-1663.
|
 )
)