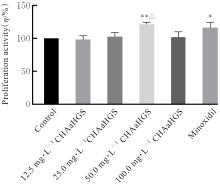
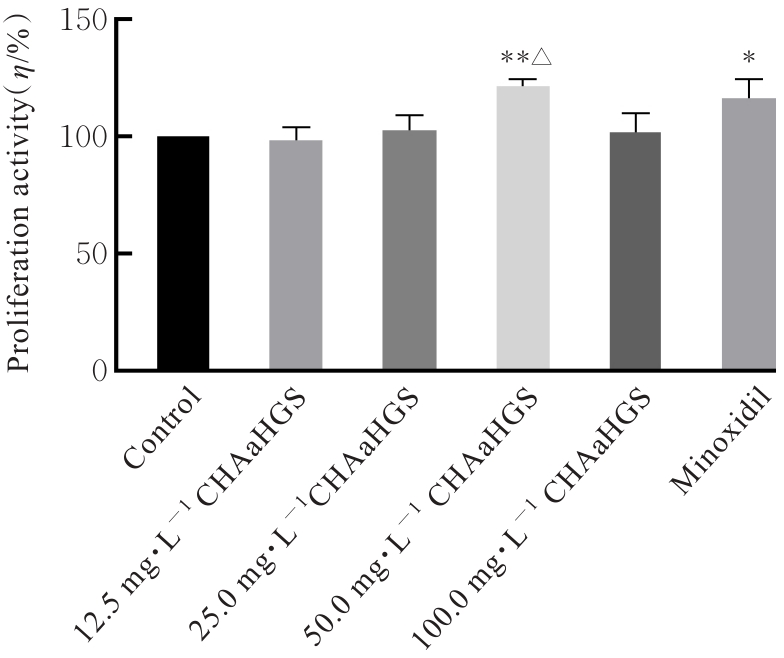
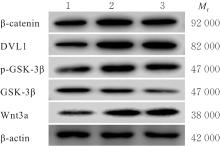
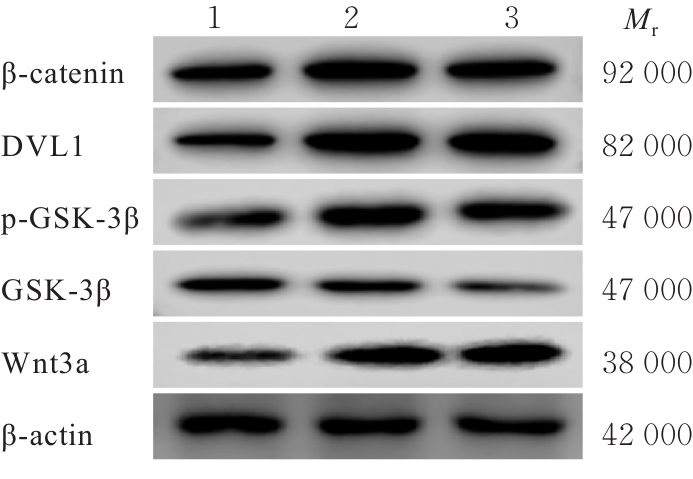
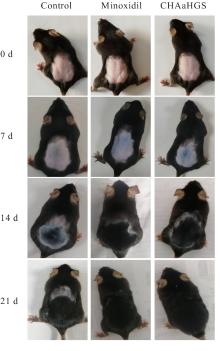
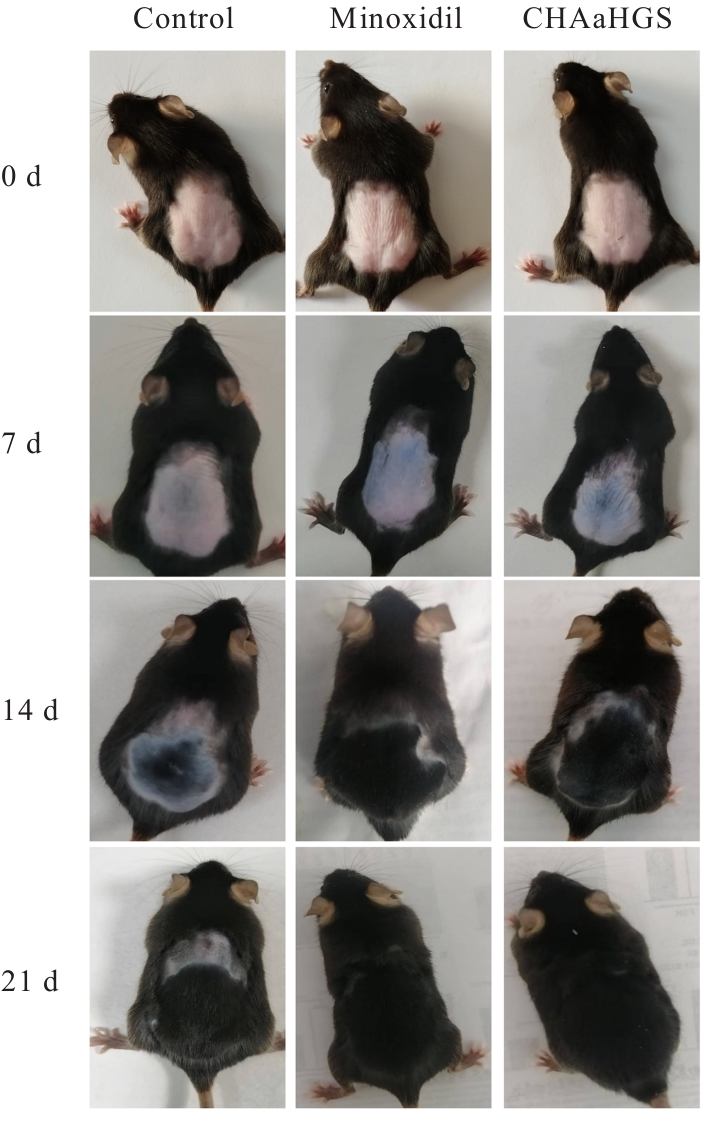
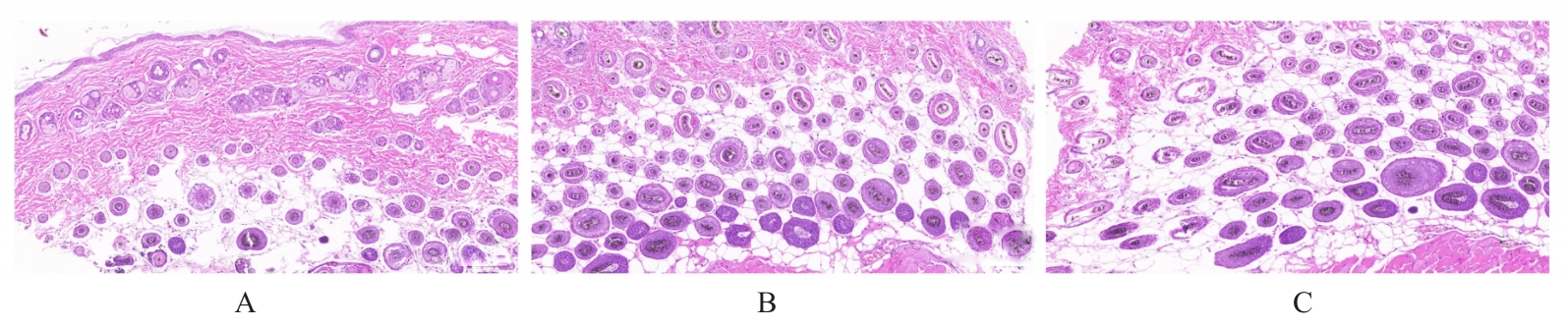
| [1] |
NESTOR M S, ABLON G, GADE A, et al. Treatment options for androgenetic alopecia: efficacy, side effects, compliance, financial considerations, and ethics[J]. J Cosmet Dermatol, 2021, 20(12): 3759-3781.
|
| [2] |
WU S Q, KOU X H, NIU Y J, et al. Progress on the mechanism of natural products alleviating androgenetic alopecia[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2024, 264: 116022.
|
| [3] |
吴 巍, 张 颖, 张 美, 等. 雄激素性脱发的药物研究进展[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志, 2022, 33(5): 308-311.
|
| [4] |
SHEN Y L, LI X Q, PAN R R, et al. Medicinal plants for the treatment of hair loss and the suggested mechanisms[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2018, 24(26): 3090-3100.
|
| [5] |
房 敏, 李泉洋, 杜丽东, 等. 当归及其复方防治脱发的研究进展[J]. 中国医药导刊, 2022, 24(11): 1113-1118.
|
| [6] |
ABELAN U S, DE OLIVEIRA A C, CACOCI É S P, et al. Potential use of essential oils in cosmetic and dermatological hair products: a review[J]. J Cosmet Dermatol, 2022, 21(4): 1407-1418.
|
| [7] |
PARK S, LEE J. Modulation of hair growth promoting effect by natural products[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13(12): 2163.
|
| [8] |
SHIN J Y, CHOI Y H, KIM J, et al. Polygonum multiflorum extract support hair growth by elongating anagen phase and abrogating the effect of androgen in cultured human dermal papilla cells[J]. BMC Complement Med Ther, 2020, 20(1): 144.
|
| [9] |
高合意, 雷登凤, 程树军, 等. 当归提取物对毛发生长作用的体外与体内研究[J]. 日用化学工业, 2020, 50(12): 867-874.
|
| [10] |
TRUONG V L, JEONG W S. Hair growth-promoting mechanisms of red ginseng extract through stimulating dermal papilla cell proliferation and enhancing skin health[J]. Prev Nutr Food Sci, 2021, 26(3): 275-284.
|
| [11] |
王 任, 袁 婷, 周 雯, 等. 桑柏生发方对毛发再生过程中VEGF等细胞因子的影响[J]. 中医药导报, 2016, 22(15): 24-27.
|
| [12] |
张 敏, 黄 蓉, 段亚君, 等. 霍山石斛通过激活自噬和抑制凋亡促进脱发模型小鼠生发作用[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 45(6): 844-848.
|
| [13] |
吴久阳, 曾衍生, 何海鸥, 等. 中草药提取液在防脱生发洗发水中的应用[J]. 精细与专用化学品, 2016, 24(10): 41-44.
|
| [14] |
赵海婷, 郑 琴, 章德林, 等. 中药及其活性成分防脱生发的研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2022, 53(22): 7254-7263.
|
| [15] |
KINOSHITA-ISE M, FUKUYAMA M, OHYAMA M. Recent advances in understanding of the etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of hair loss diseases[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(9): 3259.
|
| [16] |
YUAN A R, BIAN Q, GAO J Q. Current advances in stem cell-based therapies for hair regeneration[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2020, 881: 173197.
|
| [17] |
冯 骥, 张志英, 谢 君, 等. 武汉市人群雄激素性脱发情况及影响因素调查[J]. 武汉大学学报(医学版), 2023, 44(1): 65-69.
|
| [18] |
LIN X Y, ZHU L, HE J. Morphogenesis, growth cycle and molecular regulation of hair follicles[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 899095.
|
| [19] |
姜晓勇, 王德辉. 人毛乳头细胞的生物学特性研究[J]. 福建医药杂志, 2013, 35(1): 51-55.
|
| [20] |
王晓杰, 殷文浩. 红光对人毛乳头细胞增殖和分泌细胞因子的影响[J]. 中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2021, 35(9): 983-986.
|
| [21] |
张 欣, 朱 艳, 陈小艳. 祛湿健发汤联合米诺地尔治疗脾虚湿滞型脂溢性脱发的效果及对IGF-Ⅰ、HGF、TGF-β2水平的影响[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2023, 8(24): 130-133.
|
| [22] |
JEONG G H, BOISVERT W A, XI M Z, et al. Effect of Miscanthus sinensis var. purpurascens flower extract on proliferation and molecular regulation in human dermal papilla cells and stressed C57BL/6 mice[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2018, 24(8): 591-599.
|
| [23] |
KIM Y, LEE J M, JANG Y N, et al. Irisin promotes hair growth and hair cycle transition by activating the GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway[J]. Exp Dermatol, 2024, 33(8): e15155.
|
| [24] |
SHIN D W. The molecular mechanism of natural products activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway for improving hair loss[J]. Life, 2022, 12(11): 1856.
|
| [25] |
XUN Y, LI Z, TANG Y X, et al. Neuroglobin regulates Wnt/β-catenin and NFκB signaling pathway through Dvl1[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(7): 2133.
|
| [26] |
OH J W, KLOEPPER J, LANGAN E A, et al. A guide to studying human hair follicle cycling in vivo [J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2016, 136(1): 34-44.
|
| [27] |
ROH S S, KIM C D, LEE M H, et al. The hair growth promoting effect of Sophora flavescens extract and its molecular regulation[J]. J Dermatol Sci, 2002, 30(1): 43-49.
|
| [28] |
CECERSKA-HERYĆ E, GOSZKA M, SERWIN N, et al. Applications of the regenerative capacity of platelets in modern medicine[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2022, 64: 84-94.
|
| [29] |
COLIN-PIERRE C, BERTHÉLÉMY N, BELLOY N, et al. The glypican-1/HGF/C-met and glypican-1/VEGF/VEGFR2 ternary complexes regulate hair follicle angiogenesis[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 781172.
|
| [30] |
PARK H J, JIN G R, JUNG J H, et al. Hair growth promotion effect of Nelumbinis Semen extract with high antioxidant activity[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021: 6661373.
|
| [31] |
CASTRO A R, PORTINHA C, LOGARINHO E. The emergent power of human cellular vs mouse models in translational hair research[J]. Stem Cells Transl Med, 2022, 11(10): 1021-1028.
|
 ),Rui JIANG2(
),Rui JIANG2( )
)