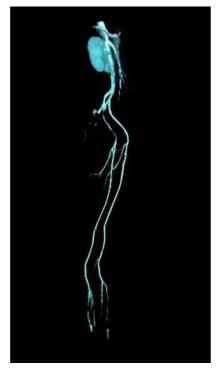
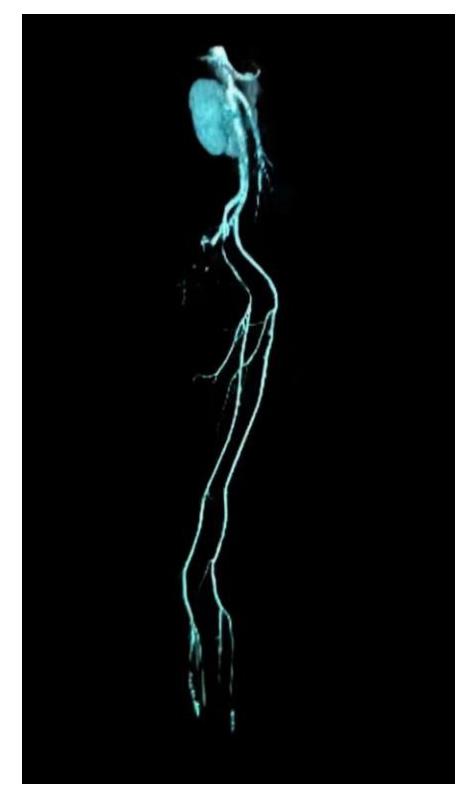
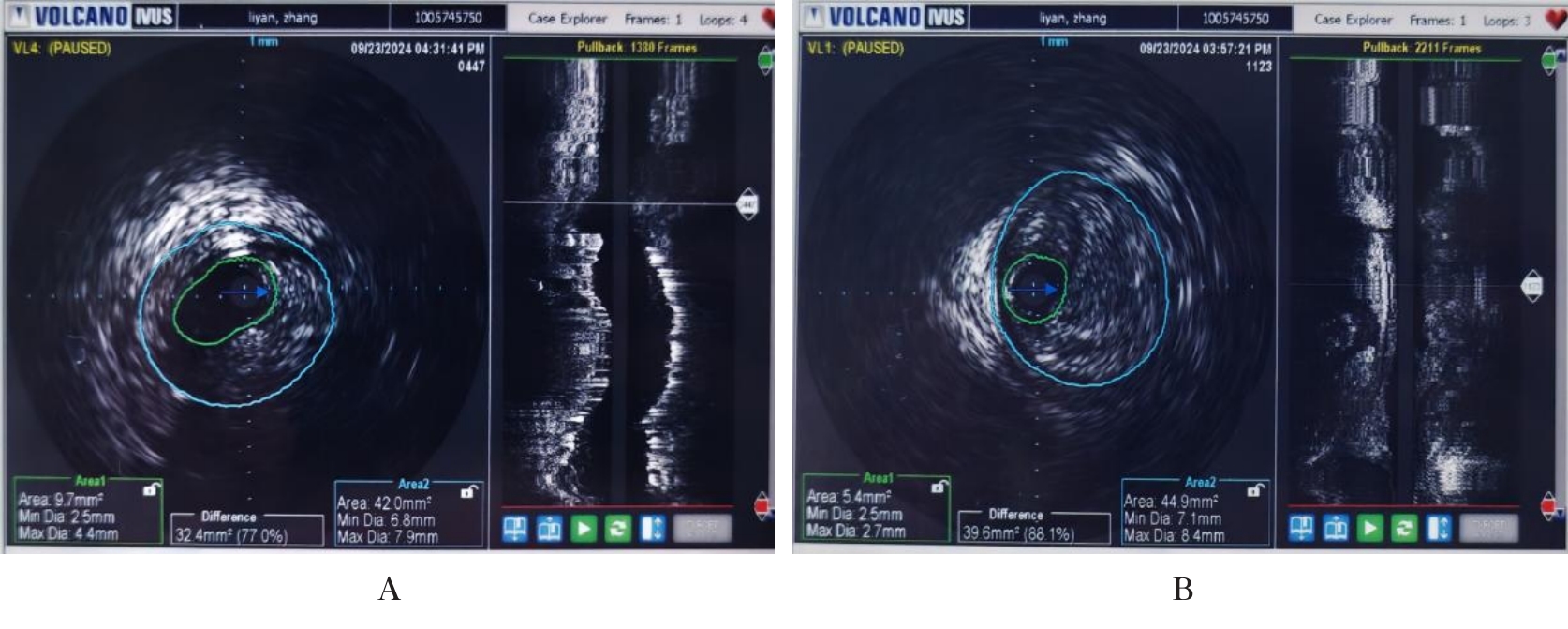
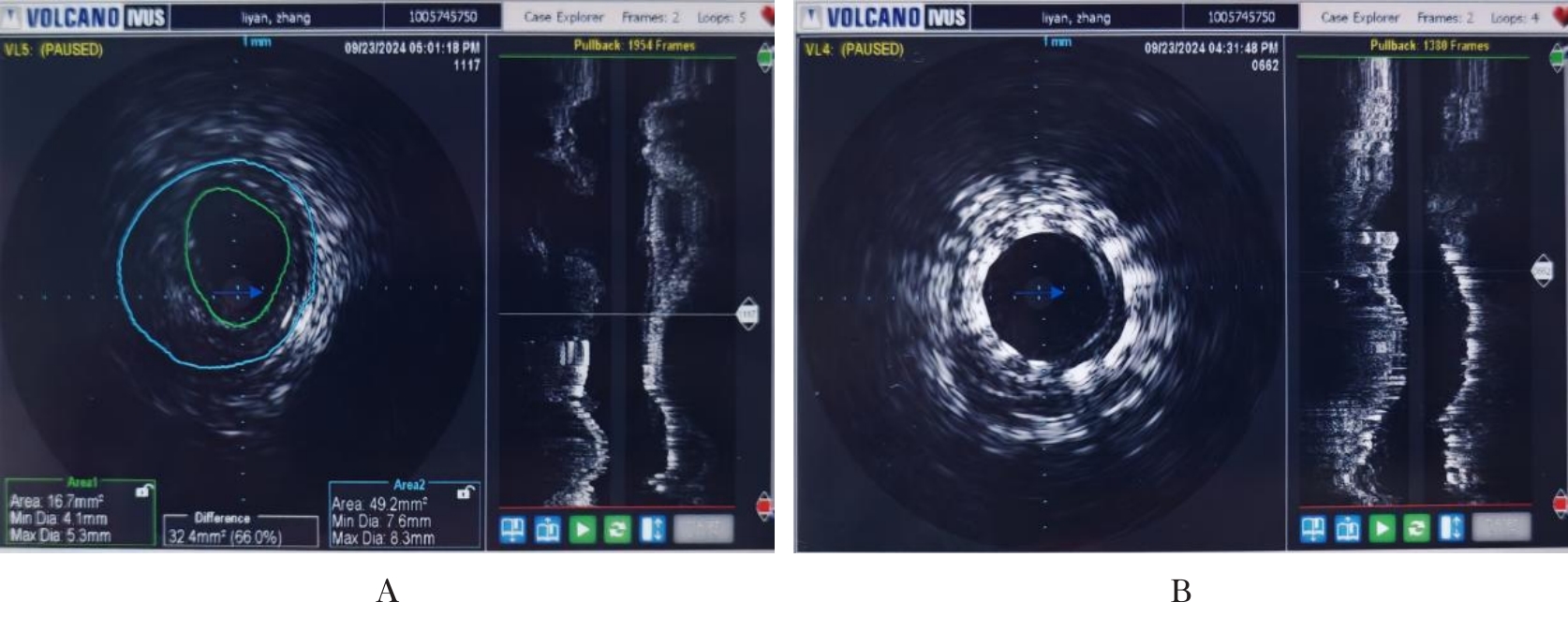
| [1] |
中华医学会外科学分会血管外科学组. 下肢动脉硬化闭塞症诊治指南[J]. 中华医学杂志,2015,95(24):1883-1896.
|
| [2] |
NORDANSTIG J, BEHRENDT C A, BAUMGARTNER I, et al. Editor’s choice: European society for vascular surgery (ESVS) 2024 clinical practice guidelines on the management of asymptomatic lower limb peripheral arterial disease and intermittent claudication[J]. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg, 2024, 67(1): 9-96.
|
| [3] |
ALI Z A, KARIMI GALOUGAHI K, MAEHARA A, et al. Outcomes of optical coherence tomography compared with intravascular ultrasound and with angiography to guide coronary stent implantation: one-year results from the ILUMIEN Ⅲ: OPTIMIZE PCI trial[J]. EuroIntervention, 2021, 16(13): 1085-1091.
|
| [4] |
ALLAN R B, PUCKRIDGE P J, SPARK J I, et al. The impact of intravascular ultrasound on femoropopliteal artery endovascular interventions: a randomized controlled trial[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2022, 15(5): 536-546.
|
| [5] |
ADOU C, MAGNE J, GAZERE N, et al. Global epidemiology of lower extremity artery disease in the 21st century (2000-21): a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Prev Cardiol, 2024, 31(7): 803-811.
|
| [6] |
SCHLAGER O. A global burden in cardiovascular medicine of the 21st century: lower extremity artery disease[J]. Eur J Prev Cardiol, 2024, 31(7): 801-802.
|
| [7] |
刘明波, 何新叶, 杨晓红, 等. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2023》概要(心血管疾病流行及介入诊疗状况)[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2024, 32(10): 541-550.
|
| [8] |
LAWALL H, HUPPERT P, ESPINOLA-KLEIN C, et al. The diagnosis and treatment of peripheral arterial vascular disease[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2016, 113(43): 729-736.
|
| [9] |
GIMNICH O A, ZIL-E-ALI A, BRUNNER G. Imaging approaches to the diagnosis of vascular diseases[J]. Curr Atheroscler Rep, 2022, 24(2): 85-96.
|
| [10] |
MUKHERJEE D, WHITE C J. Role of IVUS imaging during arterial and venous lower extremity interventions: hype or meaningful benefits?[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2022, 15(15): 1579-1581.
|
| [11] |
袁 涛, 侯佳豪, 许诗卉, 等. 超声造影在血管疾病介入诊疗中的应用[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2024, 33(11): 1262-1266.
|
| [12] |
TUNG E T, YIM K H C, LI C L, et al. Optical coherence tomography in peripheral arterial disease: a systematic review[J]. Int J Clin Pract, 2021, 75(10): e14628.
|
| [13] |
KANG H R, JEONG J, BROCKOW K. Diagnosis and prevention of hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2022, 14(4): 348-360.
|
| [14] |
SECEMSKY E A, PARIKH S A, KOHI M, et al. Intravascular ultrasound guidance for lower extremity arterial and venous interventions[J]. EuroIntervention, 2022, 18(7): 598-608.
|
| [15] |
PESONEN L O, KNOL M C, SHELGIKAR C S, et al. Efficacy and utilization of intravascular ultrasound in office-based lower extremity endovascular interventions for peripheral arterial disease[J]. Vascular, 2024, 32(1): 57-64.
|
| [16] |
SHIMODA T, D’ORIA M, KUNO T, et al. Comparative effectiveness of intravascular ultrasound versus angiography in abdominal and thoracic endovascular aortic repair: systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2024, 223: 81-91.
|
| [17] |
BOM N, LANCÉE C T, VAN EGMOND F C. An ultrasonic intracardiac scanner[J]. Ultrasonics, 1972, 10(2): 72-76.
|
| [18] |
LOFFROY R, FALVO N, GALLAND C, et al. Intravascular ultrasound in the endovascular treatment of patients with peripheral arterial disease: current role and future perspectives[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2020, 7: 551861.
|
| [19] |
LI X B, GE Z, KAN J, et al. Intravascular ultrasound-guided versus angiography-guided percutaneous coronary intervention in acute coronary syndromes (IVUS-ACS): a two-stage, multicentre, randomised trial[J]. Lancet, 2024, 403(10439): 1855-1865.
|
| [20] |
刘 娴, 王颖东, 梁振洋, 等. 应用血管内超声评估经导管主动脉瓣置换术中冠状动脉阻塞风险12例回顾分析[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2024, 44(5): 409-414.
|
| [21] |
KUHARA A, KOGANEMARU M, TANOUE S, et al. Stent graft placement guided by intravascular ultrasound for subclavian artery dissecting aneurysm[J]. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol, 2022, 31(6): 969-972.
|
| [22] |
SECEMSKY E A, MOSARLA R C, ROSENFIELD K, et al. Appropriate use of intravascular ultrasound during arterial and venous lower extremity interventions[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2022, 15(15): 1558-1568.
|
| [23] |
MARULANDA K, GENOVESE E A. Adjunctive utilization of intravascular ultrasound in peripheral arterial disease treatment[J]. Ann Vasc Surg, 2024, 107: 195-207.
|
| [24] |
KUMAR A, SHARIFF M, MAJMUNDAR M, et al. Intravascular ultrasound during endovascular intervention for peripheral artery disease, by severity, location, device, and procedure[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2024, 225: 41-51.
|
| [25] |
DIVAKARAN S, PARIKH S A, HAWKINS B M, et al. Temporal trends, practice variation, and associated outcomes with IVUS use during peripheral arterial intervention[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2022, 15(20): 2080-2090.
|
| [26] |
TSUKAGOSHI J, SHIMODA T, YOKOYAMA Y, et al. The mid-term effect of intravascular ultrasound on endovascular interventions for lower extremity peripheral arterial disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2024, 79(4): 963-972.e11.
|
| [27] |
MORETTI F, RONDI M, OTTANI F. Zero-contrast IVUS-guided complex PCI in a patient with NSTE-ACS and severe renal impairment[J]. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv, 2023, 101(6): 1074-1080.
|
| [28] |
董 捷, 欧阳文斌, 李泽夫, 等. 超声引导下无造影剂经导管主动脉瓣置换术一例[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2023, 30(2): 320-324.
|
| [29] |
KAWASAKI D, FUJII K, FUKUNAGA M, et al. Preprocedural evaluation and endovascular treatment of iliofemoral artery disease without contrast media for patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency[J]. Circ J, 2011, 75(1): 179-184.
|
| [30] |
佘守章, 吴新民, 于布为, 等. 临床麻醉监测快捷指南[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2012, 28(7): 698-699.
|
 ),Dahai LIU(
),Dahai LIU( )
)