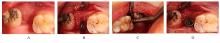
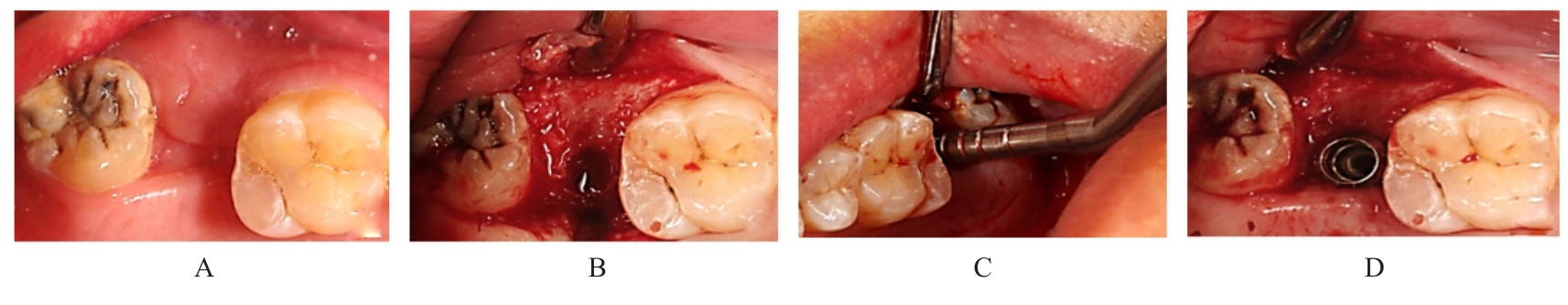
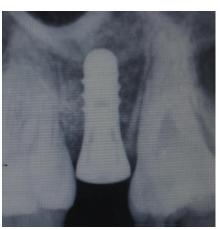
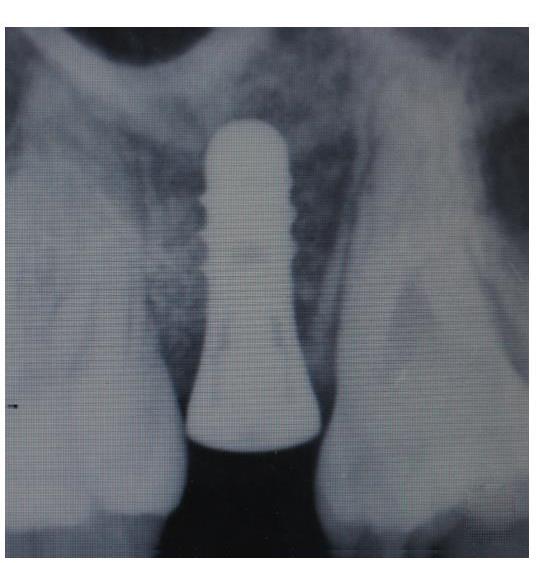
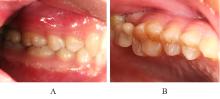
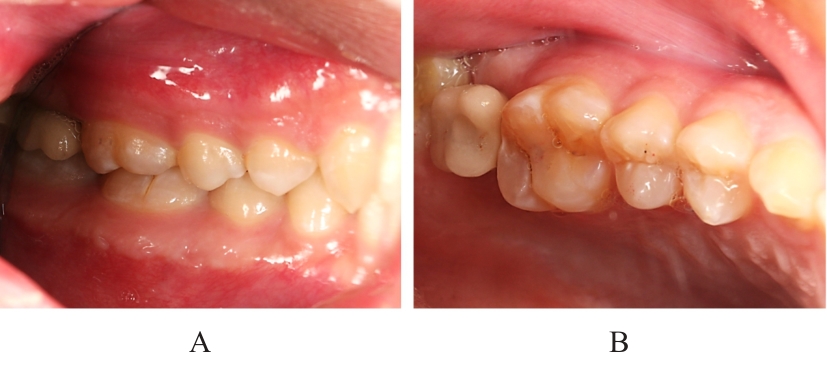
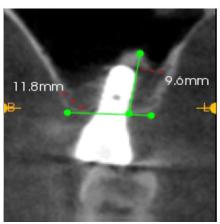
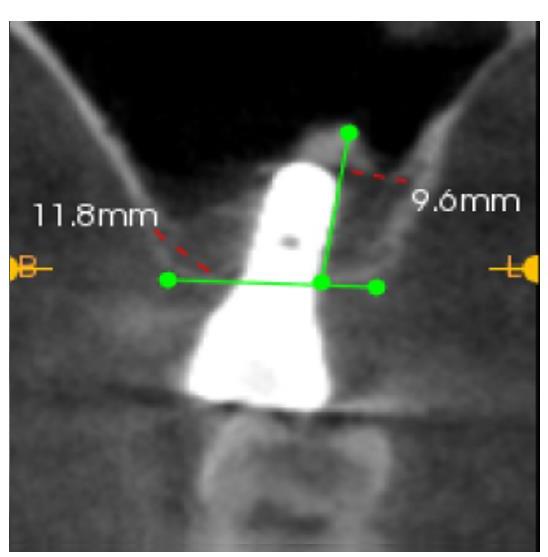
| [1] |
HARLOS M M, SILVA T B DA, MONTAGNER P G, et al. Histomorphometric evaluation of different graft associations for maxillary sinus elevation in wide antral cavities: a randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2022, 26(8): 1-9.
|
| [2] |
AFRASHTEHFAR K I, KATSOULIS J, KOKA S, et al. Single versus splinted short implants at sinus augmented sites: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2021, 122(3): 303-310.
|
| [3] |
辛禧瑞, 蔡 青, 汪汉池, 等. 上颌后牙游离端应用倾斜种植的研究进展[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(1): 86-89.
|
| [4] |
CHEN J Y, TAO B X, YU X B, et al. Accuracy of zygomatic implant placement using task-autonomous robotic system or dynamic navigation: an in vitro study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2025, 36(2): 178-190.
|
| [5] |
FARINA R, FRANZINI C, TROMBELLI L, et al. Minimal invasiveness in the transcrestal elevation of the maxillary sinus floor: a systematic review[J]. Periodontol 2000, 2023, 91(1): 145-166.
|
| [6] |
TATUM H JR. Maxillary and sinus implant reconstructions[J]. Dent Clin North Am, 1986, 30(2): 207-229.
|
| [7] |
TASCHIERI S, LOLATO A, TESTORI T, et al. Short dental implants as compared to maxillary sinus augmentation procedure for the rehabilitation of edentulous posterior maxilla: Three-year results of a randomized clinical study[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2018, 20(1): 9-20.
|
| [8] |
ALVES N, TORRES-VILLAR C, CEBALLOS F, et al. Frequency, location, and diameter of the anastomosis between the posterior superior alveolar artery and the infraorbital artery in imaging studies: systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Surg Radiol Anat, 2023, 45(4): 431-443.
|
| [9] |
SUMMERS R B. A new concept in maxillary implant surgery: the osteotome technique[J]. Compendium, 1994, 15(2): 152.
|
| [10] |
CĂLIN C, PETRE A, DRAFTA S. Osteotome-mediated sinus floor elevation: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2014, 29(3): 558-576.
|
| [11] |
YE M F, LIU W J, CHENG S L, et al. Outcomes of implants placed after osteotome sinus floor elevation without bone grafts: a systematic review and meta-analysis of single-arm studies[J]. Int J Implant Dent, 2021, 7(1): 72.
|
| [12] |
TROMBELLI L, FRANCESCHETTI G, TRISI P, et al. Incremental, transcrestal sinus floor elevation with a minimally invasive technique in the rehabilitation of severe maxillary atrophy. Clinical and histological findings from a proof-of-concept case series[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2015, 73(5): 861-888.
|
| [13] |
陈 浚, 徐光宙. 上颌窦底提升技术的研究现状[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2023, 21(3): 291-300.
|
| [14] |
WANG J, SUN Y, LIU Y P, et al. Effects of platelet-rich fibrin on osteogenic differentiation of Schneiderian membrane derived mesenchymal stem cells and bone formation in maxillary sinus[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2022, 20(1): 88.
|
| [15] |
WENG Y T, WANG H C, WU D, et al. A novel lineage of osteoprogenitor cells with dual epithelial and mesenchymal properties govern maxillofacial bone homeostasis and regeneration after MSFL[J]. Cell Res, 2022, 32(9): 814-830.
|
| [16] |
SHARANAPPA M, DESHMUKH G S, VADVADGI V H. Simplified sinus floor augmentation: an economical approach using a modified balloon technique[J]. Cureus, 2024, 16(7): e65346.
|
| [17] |
BRUSCHI G B, BRUSCHI E, PAPETTI L. Flapless localised management of sinus floor (LMSF) for trans-crestal sinus floor augmentation and simultaneous implant placement. A retrospective non-randomized study: 5-year of follow-up[J]. Heliyon, 2021, 7(9): e07927.
|
| [18] |
KADKHODAZADEH M, MOSCOWCHI A, ZAMANI Z, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of a novel transalveolar sinus floor elevation technique[J]. J Maxillofac Oral Surg, 2022, 21(2): 548-556.
|
| [19] |
CHEN S, BUSER D, WISMEIJER D. 国际口腔种植学会口腔种植临床指南(第5卷): 上颌窦底提升的临床程序[M]. 宿玉成, 译. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2012.
|
| [20] |
PICHOTANO E C, DE MOLON R S, DE SOUZA R V, et al. Evaluation of L-PRF combined with deproteinized bovine bone mineral for early implant placement after maxillary sinus augmentation: a randomized clinical trial[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2019, 21(2): 253-262.
|
| [21] |
YU J, ZHAO W, LU J Y, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin as a scaffold in combination with either deciduous or permanent dental pulp cells for bone tissue engineering[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2016, 9(8): 15177-15184.
|
| [22] |
CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, SIMONPIERI A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part Ⅳ: clinical effects on tissue healing[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2006, 101(3): e56-60.
|
| [23] |
CHO Y S, HWANG K G, JUN S H, et al. Radiologic comparative analysis between saline and platelet-rich fibrin filling after hydraulic transcrestal sinus lifting without adjunctive bone graft: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2020, 31(11): 1087-1093.
|
| [24] |
ORTEGA-MEJIA H, ESTRUGO-DEVESA A, SAKA-HERRÁN C, et al. Platelet-rich plasma in maxillary sinus augmentation: systematic review[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(3): 622.
|
| [25] |
STARCH-JENSEN T, BRUUN N H, SPIN-NETO R. Endo-sinus bone gain following osteotome-mediated sinus floor elevation with Bio-Oss Collagen compared with no grafting material: a one-year single-blind randomized controlled trial[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2023, 52(11): 1205-1215.
|
| [26] |
GUILLOU E, LERHE B, GEMMI T, et al. Simultaneous sinus elevation and immediate implant placement without biomaterial: a technical note[J]. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2024, 125(2): 101677.
|
| [27] |
TESTORI T, TAVELLI L, SCAINI R, et al. How to avoid intraoperative and postoperative complications in maxillary sinus elevation[J]. Periodontol 2000, 2023, 92(1): 299-328.
|
 )
)