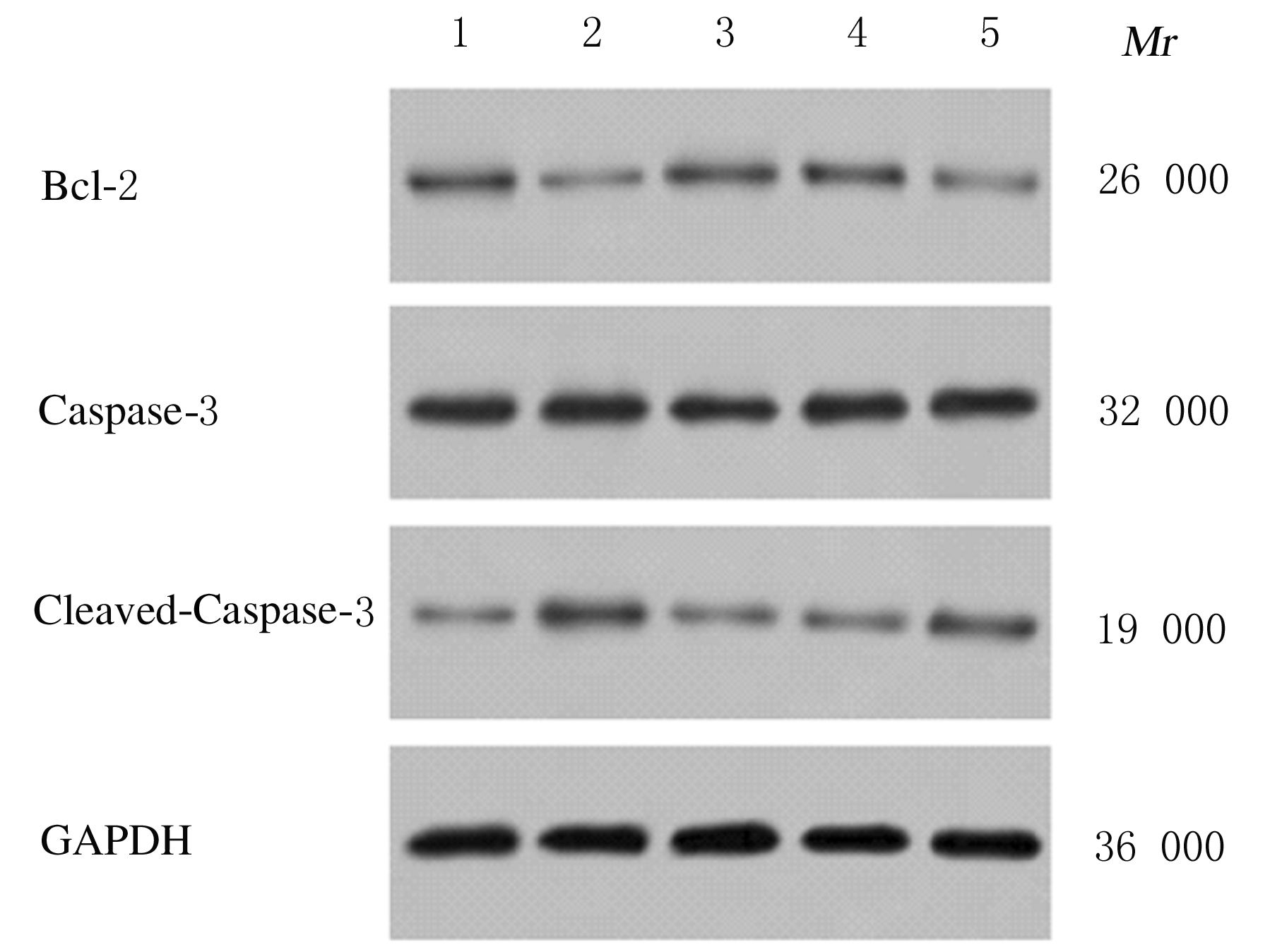
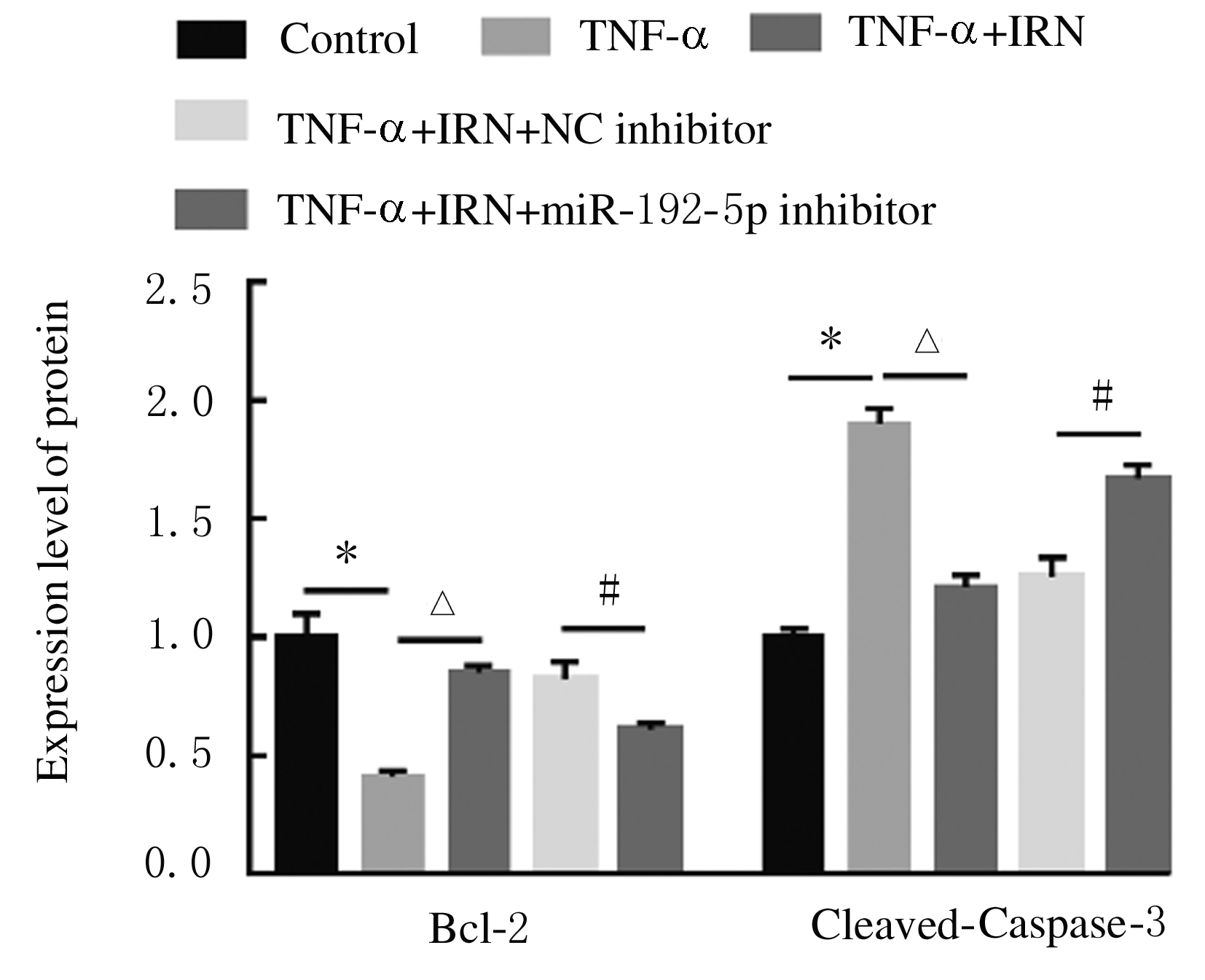
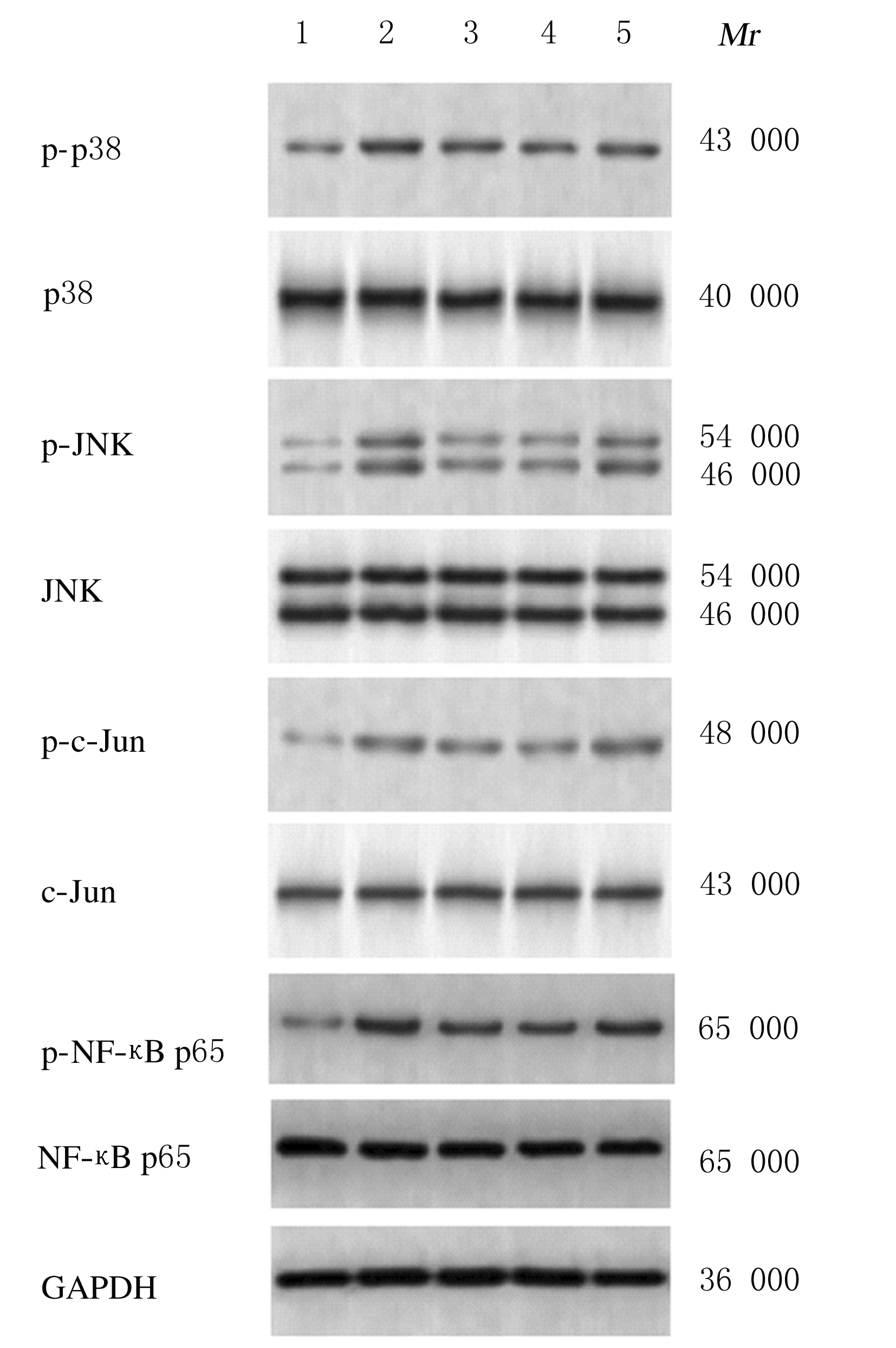
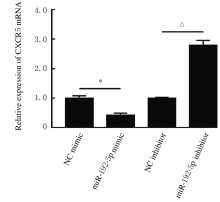
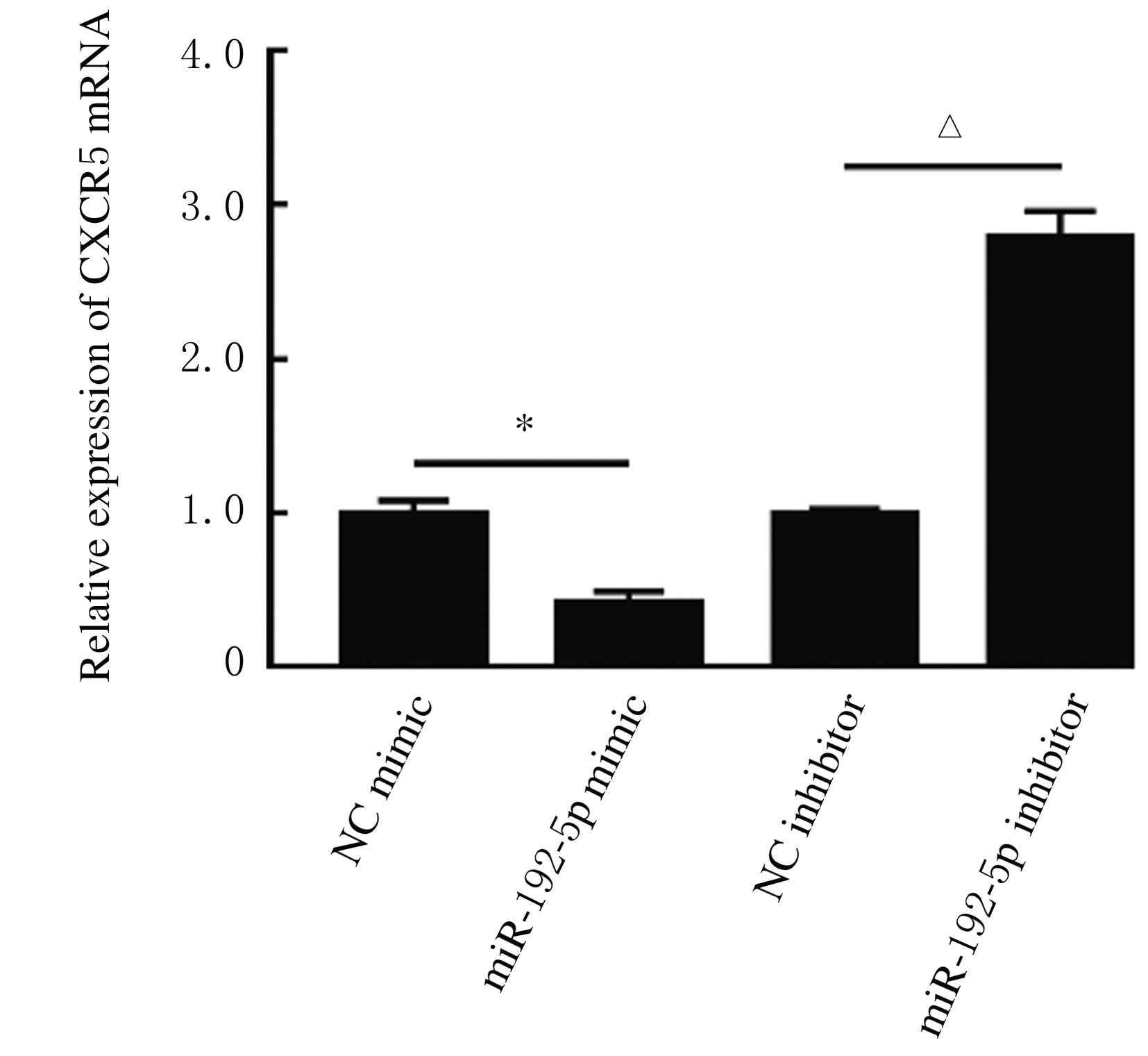
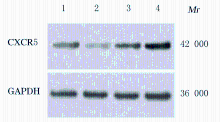
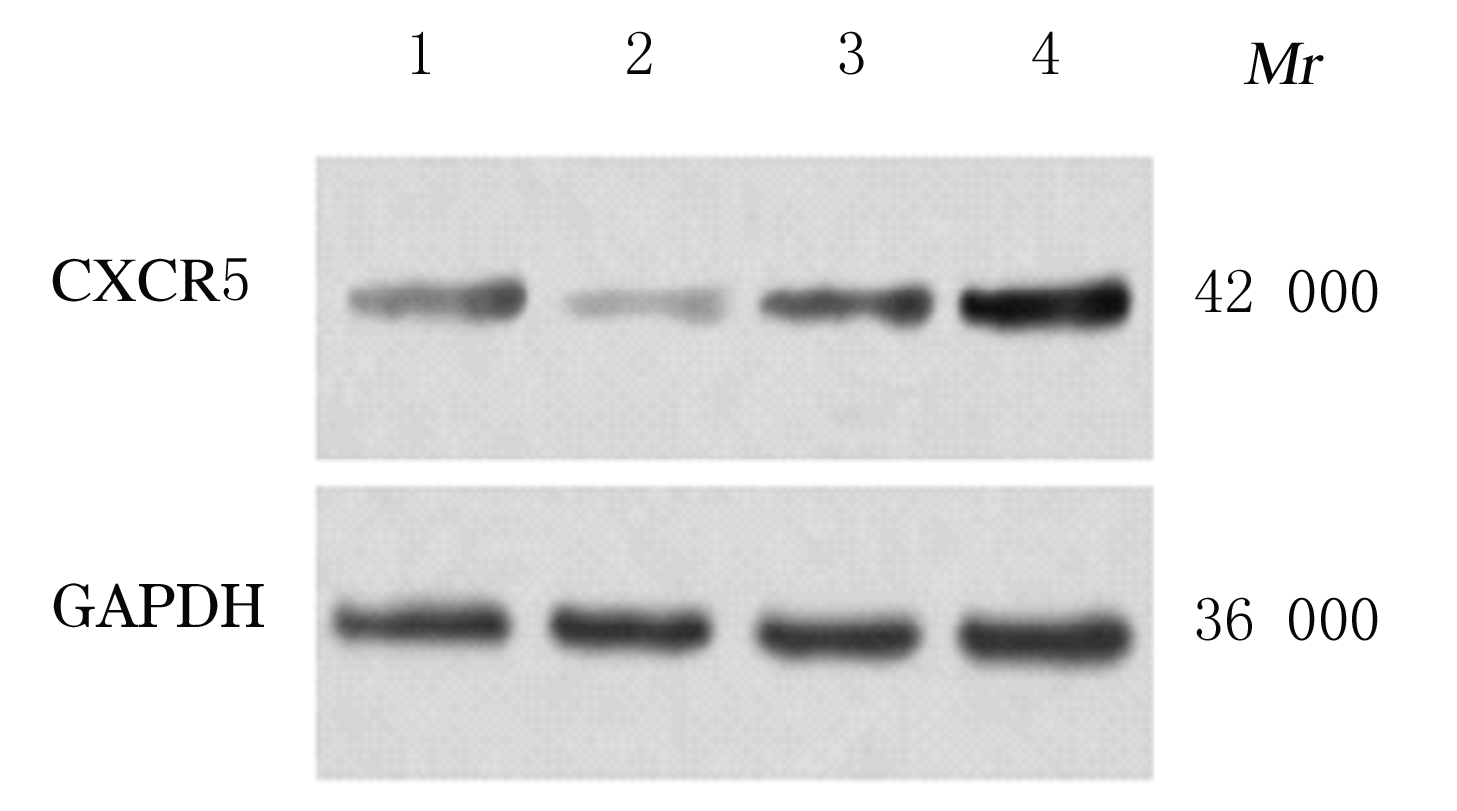
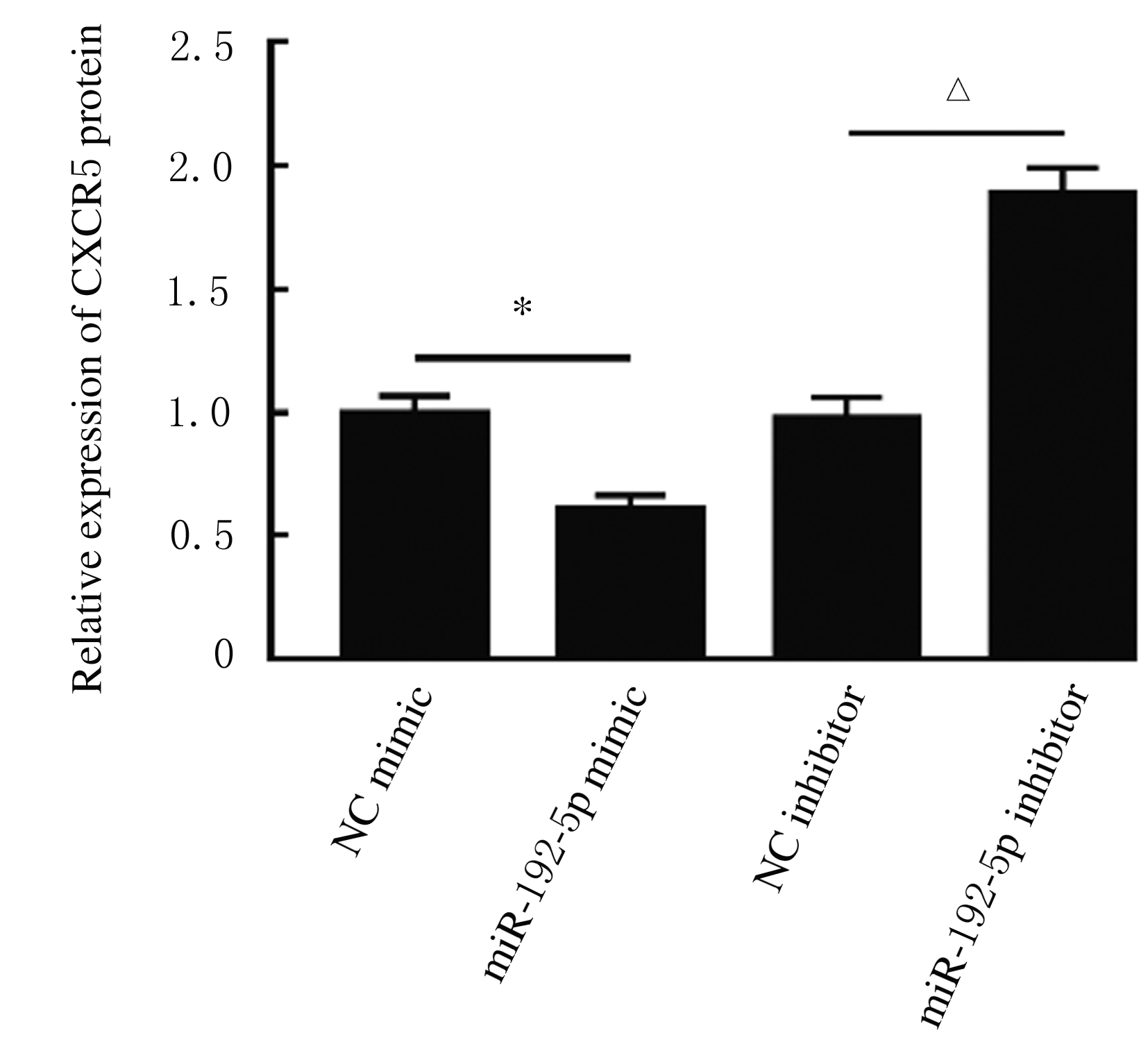
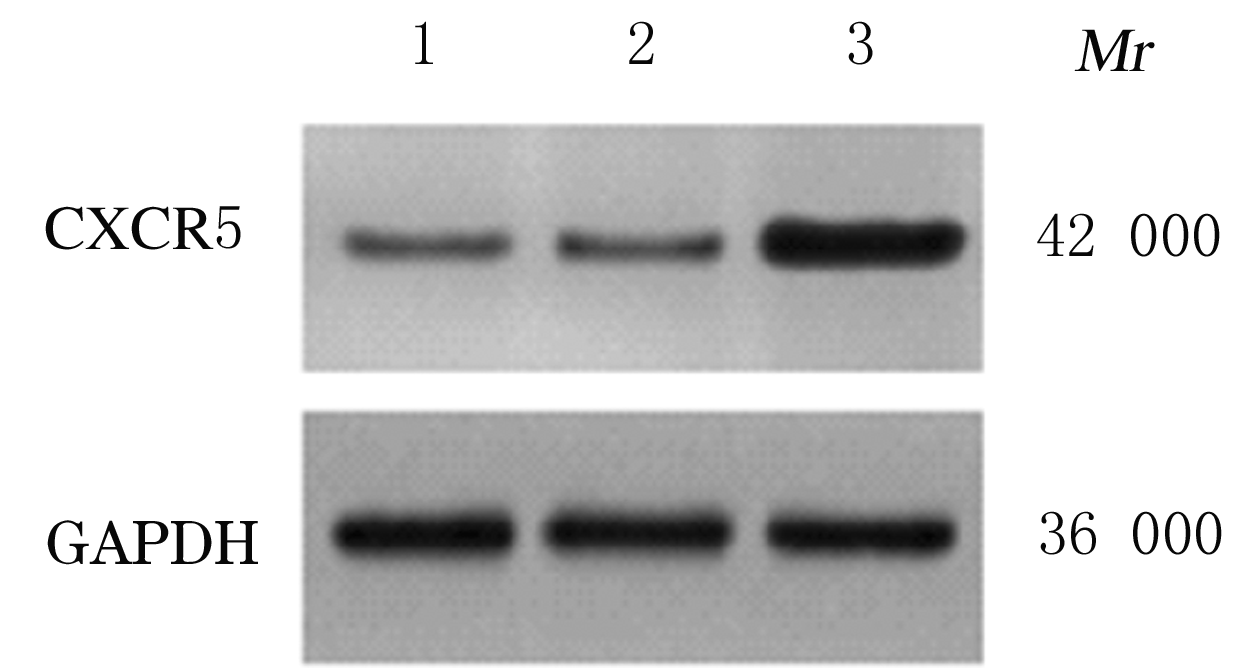
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (3): 595-607.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210308
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
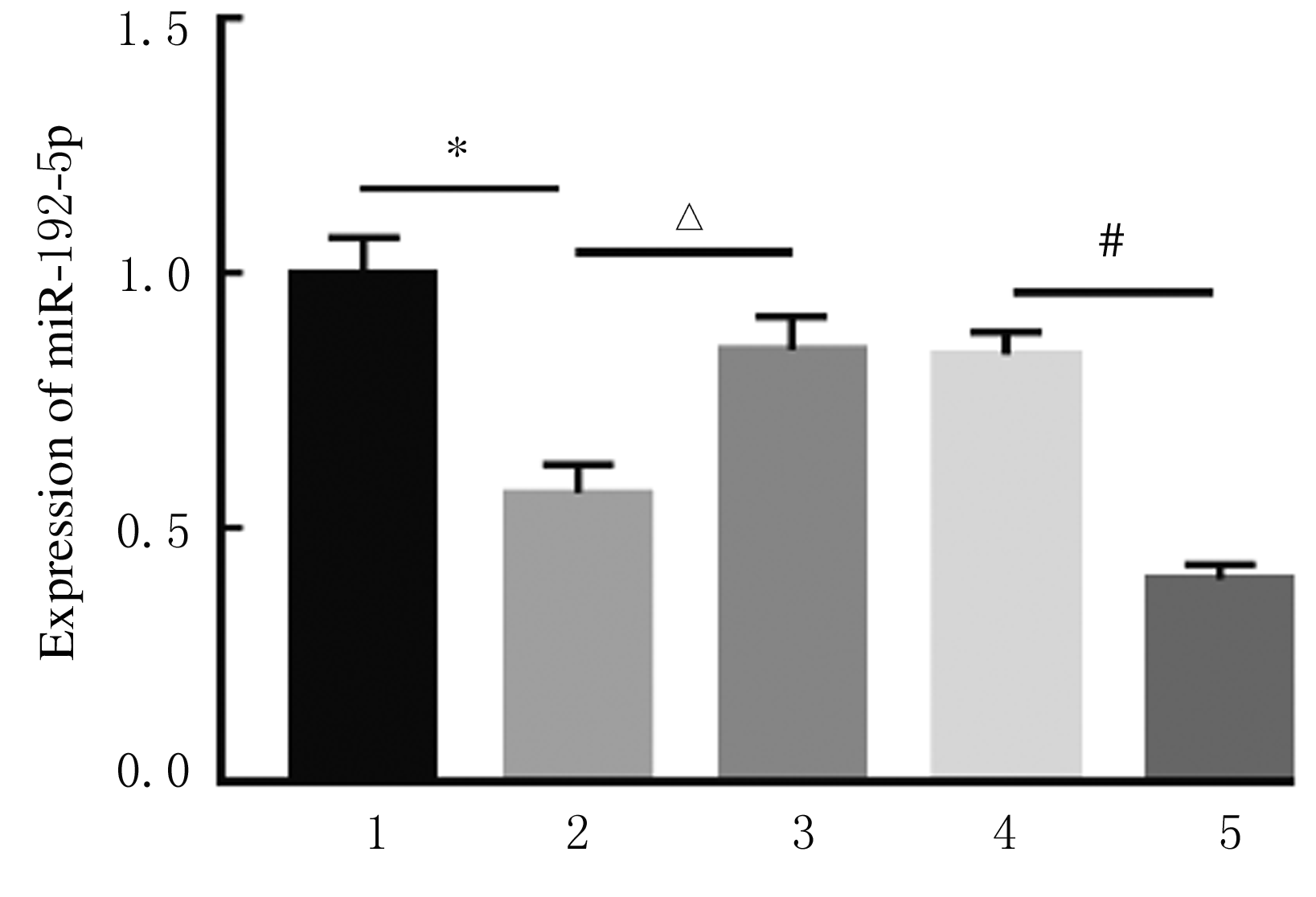
Effect of isorhynchophylline on apoptosis and release of inflammatory factors in human bronchial epithelial cells induced by TNF-α via up-regulating miR-192-5p and its mechanism
Congling HOU( ),Xiaofan LU,Xiaoting LEI,Bin LI,Runyang ZHAO
),Xiaofan LU,Xiaoting LEI,Bin LI,Runyang ZHAO
- Department of Pulmonary Diseases,Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450002,China
-
Received:2020-10-19Online:2021-05-28Published:2021-05-28 -
Contact:Congling HOU E-mail:xbhhyper@sina.com
CLC Number:
- Q71
Cite this article
Congling HOU, Xiaofan LU, Xiaoting LEI, Bin LI, Runyang ZHAO. Effect of isorhynchophylline on apoptosis and release of inflammatory factors in human bronchial epithelial cells induced by TNF-α via up-regulating miR-192-5p and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 595-607.
share this article
Tab.1
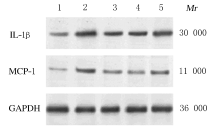
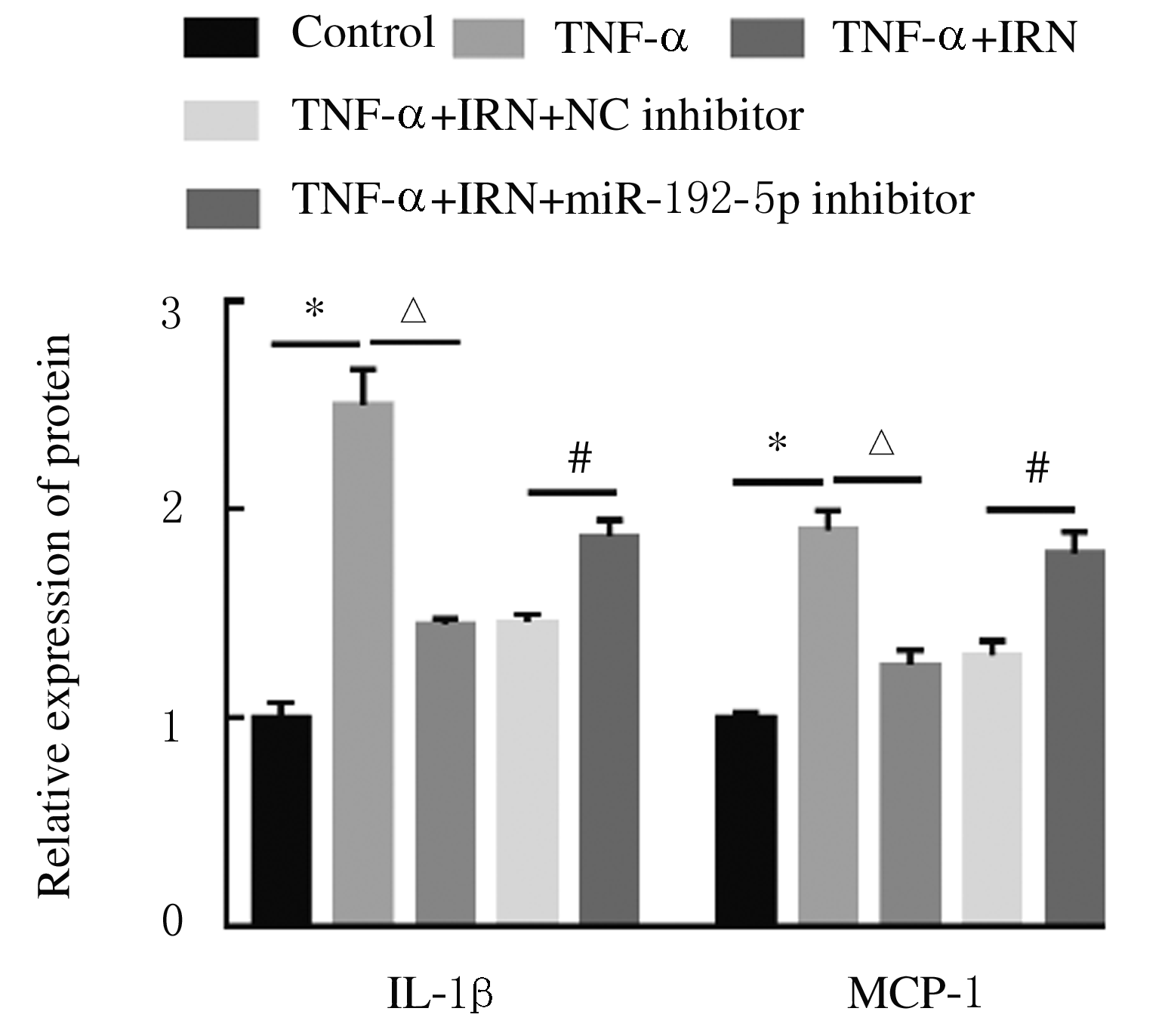
Levels of IL-1β and MCP-1 in supernatant of 16HBE cells in various groups detected by ELISA method [n=3,x±s,ρB/(ng·L-1)]"
| Group | IL-1β | MCP-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 48.21±3.24 | 65.34±5.11 |
| TNF-α | 510.40±19.32* | 482.80±24.87* |
| TNF-α+IRN | 173.20±13.90△ | 125.60±15.32△ |
| TNF-α+IRN+NC inhibitor | 171.91±10.81 | 127.35±12.20 |
| TNF-α+IRN+ miR-192-5p inhibitor | 365.62±18.53# | 299.58±24.21# |
Tab.2
Ratios of p-p38/-p38, p-JNK/JNK, p-c-Jun/c-Jun, and p-NF-κB p65/NF-κB p65 in 16HBE cells in various groups"
| Group | p-p38/p38 | p-JNK/JNK | p-c-Jun/c-Jun | p?NF?κB p65/ NF?κB p65 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.00±0.09 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.06 | 1.00±0.06 |
| TNF-α | 3.51±0.15* | 2.64±0.10* | 2.23±0.08* | 2.41±0.18* |
| TNF-α+IRN | 2.38±0.12△ | 1.59±0.16△ | 1.24±0.03△ | 1.54±0.14△ |
| TNF-α+IRN+NC inhibitor | 2.35±0.07 | 1.65±0.11 | 1.21±0.06 | 1.49±0.09 |
| TNF-α+IRN+ miR-192-5p inhibitor | 3.14±0.07# | 2.29±0.06# | 1.56±0.09# | 1.97±0.02# |
Tab.3
Levels of IL-1β and MCP-1 in supernatant of 16HBE cells in various groups detected by ELISA method [n=3,x±s,ρB/(ng·L-1)]"
| Group | IL-1β | MCP-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 52.17±3.53 | 70.68±5.08 |
| TNF-α | 497.15±14.89* | 511.57±27.24* |
| TNF-α+IRN | 154.32±13.24△ | 182.11±15.68△ |
| TNF-α+IRN+pcDNA3.1 | 150.62±11.35 | 179.00±12.28 |
| TNF-α+IRN+ pcDNA3.1 CXCR5 | 267.35±16.55# | 290.85±24.49# |
|
| [1] | Jing HUANG,Ming DING,Xiaoli ZHU,Pingsheng CHEN,Shuhua HAN. Pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma complicated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 196-202. |
| [2] | LIANG Xiaobo, WU Dehong, WANG Xing, ZHANG Yun, WANG Xiaoyun, LI Guoping. Evaluation on mouse models of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease induced by intranasal instillation of cigarette smoke extract and lipopolysaccharide [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1454-1458. |
| [3] | REN Fangping, JIANG Yanwen. Application of N-acetylcysteine inhalation in treatment of elderly patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1141-1145. |
| [4] | HOU Hailong, TANG Ying, QU Xinglong, HUA Shucheng. Clinical effect of dexmedetomidine combined with non-invasive positive pressure ventilation in treatment of patients with AECOPD complicated with pulmonary encephalopathy and evaluation on its safety [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(05): 1014-1019. |
| [5] | WANG Xiaoyun, LAN Nan, TANG Hongmei, YUAN Xiefang, WANG Xing, LI Guoping. Effect of Lyn on expression of MUC5AC in human bronchial epithelial cells induced by house dust mite and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 211-215. |
| [6] | ZHANG Xueyang, MA Ji, MENG Guangping, WANG Qi, LI Wei, XU Yanling, ZHANG Jie, GAO Peng. Analysis on prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease based on pulmonary function screening in Changchun urban area of Jilin province [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(05): 1047-1052. |
| [7] | QI Huiqin, ZHANG Lianlian, XING Liping, SUN Luyao, LIU Ying, YU Zhenxiang. Changes of serum TGF-β and MMP-9 levels in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease after treated with ipratropium bromide combined with N-acety-L-cysteine and their clinical significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(04): 777-782. |
| [8] | LI Na, HE Ye, LI Minchao. Analysis on correlation between expression level of pressure-sensitive channel protein and airway remodeling in COPD patients [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(02): 277-282. |
| [9] | WANG Guoqiang, MU Jia, LI Yuan, YUAN Yuze, WANG Yubo, SONG Chenxue, XIE Jingshu, ZHENG Jingtong, WANG Fang. Influence of NLRP3,AIM2 and CASP1 genes in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(01): 130-133. |
| [10] | TANG Wenfang, LIU Rihui, YU Yaqin, LIU Jin, GAO Peng, WANG Ke. Prevalence of COPD among Chinese people aged 40 years and over from 2000 to 2014:A Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(05): 961-968. |
| [11] | WU Zhonglian, HUANG Xuekuan, LUO Yan, ZHANG Chaonan, JIANG Juan. Effects of BeiMuGuaLou powder on expression level of angiotensin Ⅱ in lung tissue of rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(03): 527-531. |
| [12] | CHEN Xin, LIU Te, WANG Shuyue, ZHANG Wenjing, XIE Jingfang, QIN Yuanming, QIAN Donghua, YE Lin. Effect of daily mean temperature on hospital admissions of patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(02): 389-392. |
| [13] | LI Fang, GUAN Wenxia, REN Fei, TONG Xuexia, SUN Yuning. Expressions of Sirt-1 and Hif-1α in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(02): 356-361. |
| [14] | ZHANG Wenjing, JING Hongyu, XU Hongbang, QIAN Donghua. Analysis on association between polymorphisms of IL-4-33C/T and IL-6-572C/G and susceptibility of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(01): 145-149. |
| [15] | XU Xiao-guang,JIANG Zhen-yu,DU Min-juan,YANG Ya-qin,JIANG Ying-chao. Evaluation on effectiveness of salmeterol/fluticasonepropionate combined with N-acetylcysteine in treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(04): 870-874. |
|
||