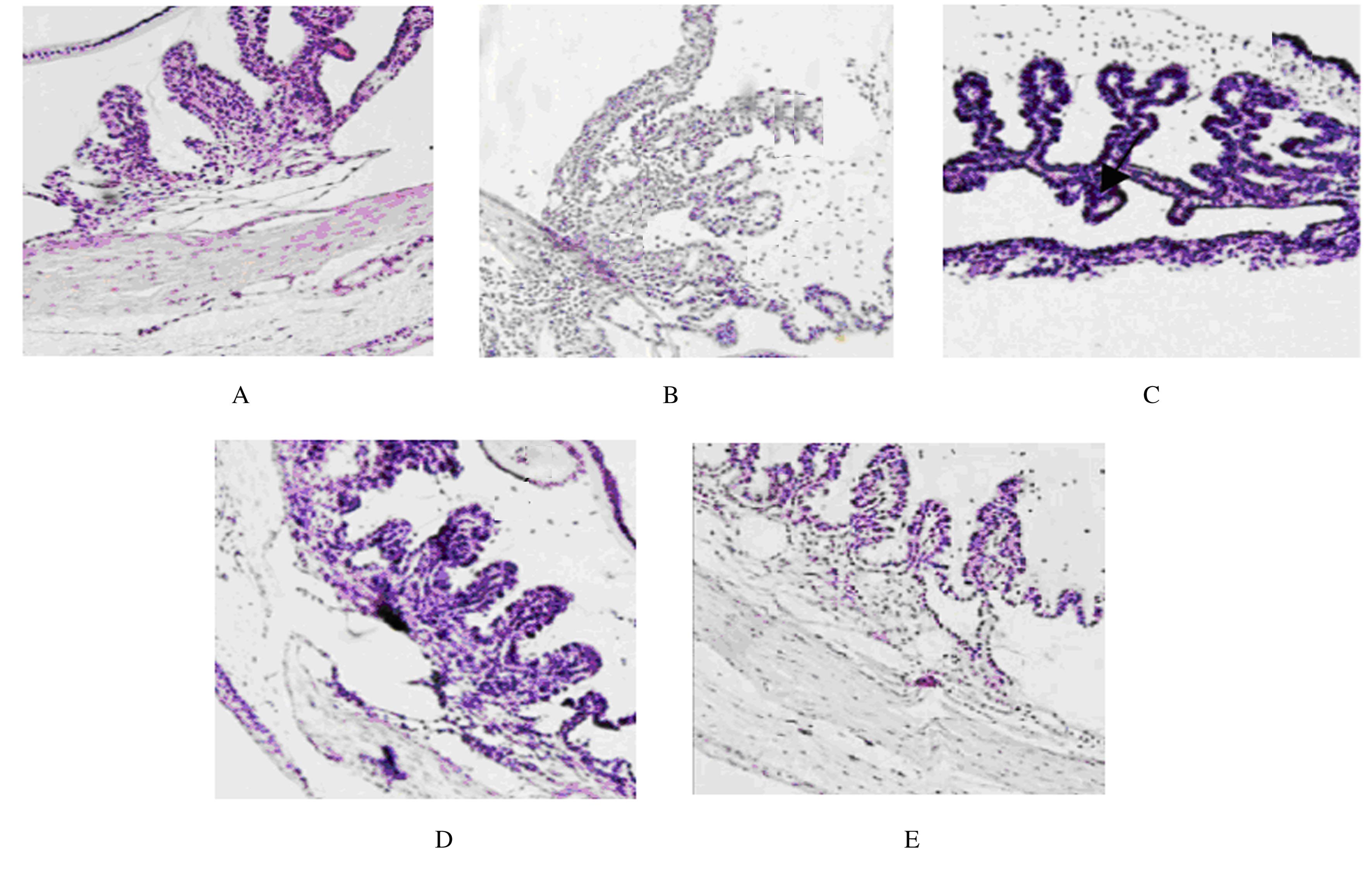
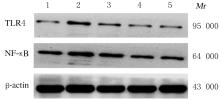
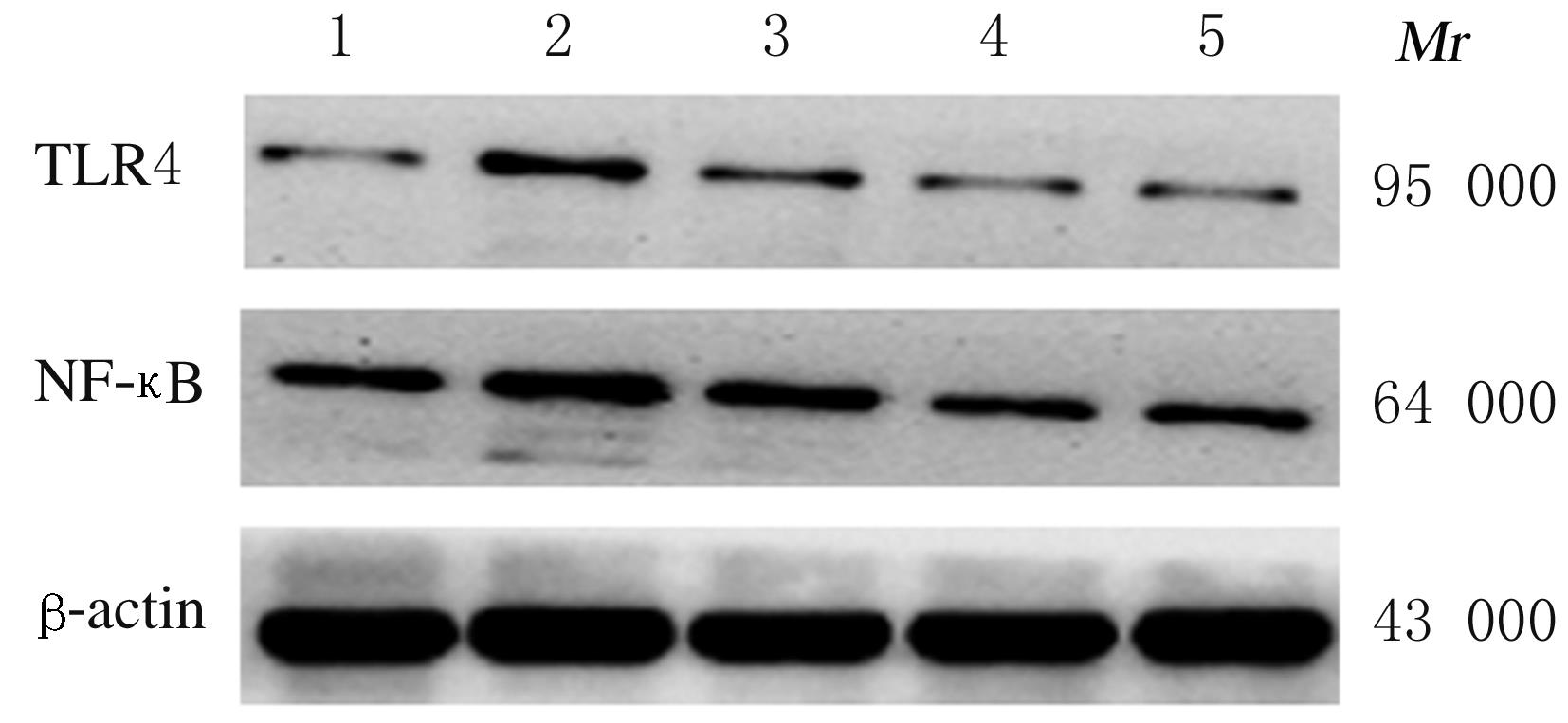
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 978-983.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210422
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Anti-inflammatory effect of honeysuckle extract on acute anterior uveitis mice induced by LPS and its mechanism
Kangning LI,Zhiling SONG,Lilong JIA,Miao CHU( ),Chaohui XIONG
),Chaohui XIONG
- Department of Ophthalmology,the First Hospital of Hebei Medical University,Shijiazhuang 050031,China
-
Received:2020-12-16Online:2021-07-28Published:2021-07-22 -
Contact:Miao CHU E-mail:kangkangba2828@163.com
CLC Number:
- R773.9
Cite this article
Kangning LI,Zhiling SONG,Lilong JIA,Miao CHU,Chaohui XIONG. Anti-inflammatory effect of honeysuckle extract on acute anterior uveitis mice induced by LPS and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 978-983.
share this article
Tab.1
Expression levels of TLR4 and NF-κB mRNA and proteins in eye tissue of mice in various groups"
| Group | TLR4 | NF-κB | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA | Protein | mRNA | Protein | |
| Control | 1.00±0.02 | 0.12±0.02 | 1.00±0.03 | 0.31±0.01 |
Model Honeysuckle | 1.74±0.07* | 0.54±0.03* | 2.17±0.09* | 0.78±0.04* |
| Low dose | 1.59±0.08△ | 0.39±0.04△ | 1.68±0.05△ | 0.60±0.04△ |
| Medium dose | 1.26±0.09△# | 0.22±0.02△# | 1.60±0.07△# | 0.41±0.03△# |
| High dose | 1.20±0.07△#○ | 0.16±0.02△#○ | 1.31±0.05△#○ | 0.33±0.03△#○ |
Tab.2
Levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in eye tissue of mice in various groups [n=5,x±s,ρβ/(μg·L-1)]"
| Group | TNF-α | IL-6 | IL-10 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 45.33±6.72 | 26.32±3.21 | 55.60±6.41 |
Model Honeysuckle | 168.24±12.35* | 230.23±12.41* | 138.45±10.21* |
| Low dose | 102.31±10.20△ | 130.50±10.25△ | 96.31±8.74△ |
| Medium dose | 76.41±8.99△# | 67.09±5.49△# | 79.54±8.20△# |
| High dose | 59.70±8.02△#○ | 39.21±4.84△#○ | 62.11±7.66△#○ |
| 1 | GHITĂ A C, ILIE L, GHITĂ A M. The effects of inflammation and anti-inflammatory treatment on corneal endothelium in acute anterior uveitis[J]. Rom J Ophthalmol, 2019, 63(2): 161-165. |
| 2 | YU S, MAO C, YU J Y, et al. A study of the key genes and inflammatory signaling pathways involved in HLA-B27-associated acute anterior uveitis families[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2018, 42(1): 259-269. |
| 3 | 何 唯, 黄旭东. 内毒素诱导的葡萄膜炎动物模型相关研究进展[J]. 青岛医药卫生, 2017, 49(2): 135-138. |
| 4 | 樊俐慧, 吉红玉, 兰雨泽, 等. 金银花量效关系及其临床应用[J]. 吉林中医药, 2019, 39(5): 597-600. |
| 5 | 石艳宾, 李文静. 响应面优化金银花绿原酸提取工艺及抗氧化作用研究[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2019, 40(21): 152-158. |
| 6 | 李建军, 任美玲, 尚星晨, 等. 共水蒸馏法提取金银花挥发油及其成分分析[J].河南农业科学,2017,46(12):144-148. |
| 7 | ZHAO Y, DOU D, GUO Y, et al. Comparison of the trace elements and active components of lonicera japonica flos and lonicera flos using ICP-MS and HPLC-PDA[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2018, 183(2): 379-388. |
| 8 | KIM S J, KIM J S, CHOI H S, et al. HS-23, a Lonicera japonica extract, reverses sepsis-induced immunosuppression by inhibiting lymphocyte apoptosis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2015, 171: 231-239. |
| 9 | 杨 娟, 于晓涛, 郭丽娜, 等. 金银花抗肺癌作用机制的网络药理学研究[J]. 药物评价研究, 2020, 43(2): 213-220. |
| 10 | ZHANG T, LIU H, BAI X, et al. Fractionation and antioxidant activities of the water-soluble polysaccharides from Lonicera japonica Thunb[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2020, 151: 1058-1066. |
| 11 | 崔晓燕. 金银花提取物的抗炎免疫作用研究[J]. 中国药业, 2011, 20(23): 8-9. |
| 12 | 白 雪. 金银花提取物对化合物48/80,组胺及P物质诱导小鼠瘙痒模型的作用[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2015, 53(53): 46-49. |
| 13 | 王燕云, 张栋彦, 耿园园, 等. 血管生成素对脂多糖诱导的急性葡萄膜炎小鼠的抗炎作用[J]. 眼科新进展, 2020, 40(10): 933-935. |
| 14 | 余 奇, 许 迅. 实验性自身免疫性葡萄膜炎模型的研究进展[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2013,33(10):1411-1414. |
| 15 | 李 上, 卢 弘. LPS-TOLL样受体-4在急性前葡萄膜炎发病机制中的研究进展[J].眼科新进展,2009,29(9): 709-712. |
| 16 | SONG G X, HUANG J X, DENG Y L, et al. The expression of calprotectin and factors in TLR4/NF-κB/MyD88 pathway in patients with idiopathic acute anterior uveitis[J]. Ocular Immunol Inflamm, 2019, 27(7): 1144-1148. |
| 17 | 李 上, 卢 弘, 胡小凤, 等. TLR4-MyD88在大鼠急性前葡萄膜炎虹膜中的表达[J].眼科研究,2010,19(2): 97-102. |
| 18 | KAUPPINEN A, SUURONEN T, OJALA J, et al. Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders[J]. Cell Signal, 2013, 25(10): 1939-1948. |
| 19 | 张晓龙, 王 婧, 许卓再, 等. 大黄多糖对内毒素诱导急性前葡萄膜炎TLR4/NF-κB传导通路干预作用的实验研究[J]. 眼科, 2013, 22(2): 134-140. |
| 20 | RHODUS N L, CHENG B, MYERS S, et al. The feasibility of monitoring NF-κB associated cytokines: TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-6, and IL-8 in whole saliva for the malignant transformation of oral lichen planus[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2005, 44(2): 77-82. |
| 21 | ZUSSO M, LUNARDI V, FRANCESCHINI D, et al. Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin attenuate microglia inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-kB pathway[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2019, 16(1): 148. |
| 22 | 邓 珍, 吴一峰, 姜 蕾, 等. 苦参碱眼液调控TLR4/NF-κB通路影响实验性葡萄膜炎家兔相关细胞因子的表达[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(4): 568-572. |
| [1] | Shuwei QIAO,Baosheng LI,Xiaoyu LI,Zixuan WANG,Birong LI,Bo DONG,Weiyan MENG. Expression levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4 in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts under inflammation and their significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 922-928. |
| [2] | Zhaowei WANG,Yanan LYU,Zheng HU,Yongguang YANG. Construction of LDLR gene knockout immunodeficient mouse model and its phenotypic analysis based on CRISPR/cas9 technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 271-276. |
| [3] | Manying WANG,Baoyu FU,Xiaohao XU,Xiangzhu LI,Hong CHEN,Liwei SUN,Daqing ZHAO. Anti-fatigue effect of ginseng adventitious root protein in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 18-25. |
| [4] | Xue BAI,Lu YU,Wenqiang YANG,Xin HE,Xinsheng YANG,Jing YANG. Inhibitory effect of carnosine on LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine release in astrocytes and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 330-337. |
| [5] | YANG Jiping, FEI Lin, CHAI Xuejun, GOU Xingchun. Inhibitory effect of MyD88 inhibitory peptide on polarization of BV2 microglial cells induced by LPS and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 899-904. |
| [6] | LIU Lanqing, LI Ruilin, ZHOU Xiaomin, MENG Jun. Dynamic expression and localization of CDC14B in each cell cycle of mouse one-cell fertilized eggs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 675-679. |
| [7] | WANG Xinxin, LI Sijia, GUAN Hongquan, HOU Diandong. Induction effect of DNCB on atopic dermatitis BALB/c mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 439-443. |
| [8] | LIN Jiuhan, TIAN Lin, ZHANG Nana, DONG Ying, LYU Hang, WANG Dan, QU Meng, ZHANG Yong, SUN Liankun, YU Chunyan, LIU Xi. Inhibitory effect of mitochondrial dynamics changes on growth of transplanted melanoma in APP/PS1 mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 476-481. |
| [9] | CHEN Zhouhua, GONG Hui, FENG Lei, XIAO Yujie, HUANG Lizhong. Induction of LPS on epithelial mesenchymal transition in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and its effect on β-catenin expression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 309-315. |
| [10] | ZHANG Chenhao, LI Yao, LI Zhengyi, LUO Xiaofeng. Protective effect of procyanidine B1 on LPS-induced injury of mouse macrophages RAW264.7 and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1243-1247. |
| [11] | LIANG Xiaobo, WU Dehong, WANG Xing, ZHANG Yun, WANG Xiaoyun, LI Guoping. Evaluation on mouse models of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease induced by intranasal instillation of cigarette smoke extract and lipopolysaccharide [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1454-1458. |
| [12] | YANG Yun, MA Xixing, WANG Dahu, ZHANG Huanhuan, MA Yaohui, REN Cuimin, LIU Qiang. Influence of tanshinone Ⅱ A on expressins of Cosmc and AOPP in kidney tissue of allergic purpura nephritis mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 867-871. |
| [13] | ZHOU Haixia, HOU Lijian, WANG Zhengming, TIAN Yu, HAN Liang, LI Mifu. Inhibitory effect of HOXA4 on transplantationglioma of nude mice through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 474-478. |
| [14] | ZOU Jun, CHEN Bing, FANG Minghui, HU Zheng. Establishment and identification of humanized mouse models with human immune system and allogeneic human melanoma growth [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 718-724. |
| [15] | ZHANG Jing, ZHAO Yan, CAI Enbo, ZHU Hongyan, LI Pingya, LIU Jinping. Anti-tumor activity of sesquiterpenoids from ginseng in S180tumor-bearing mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 280-285. |