Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1109-1115.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240425
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
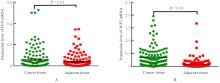
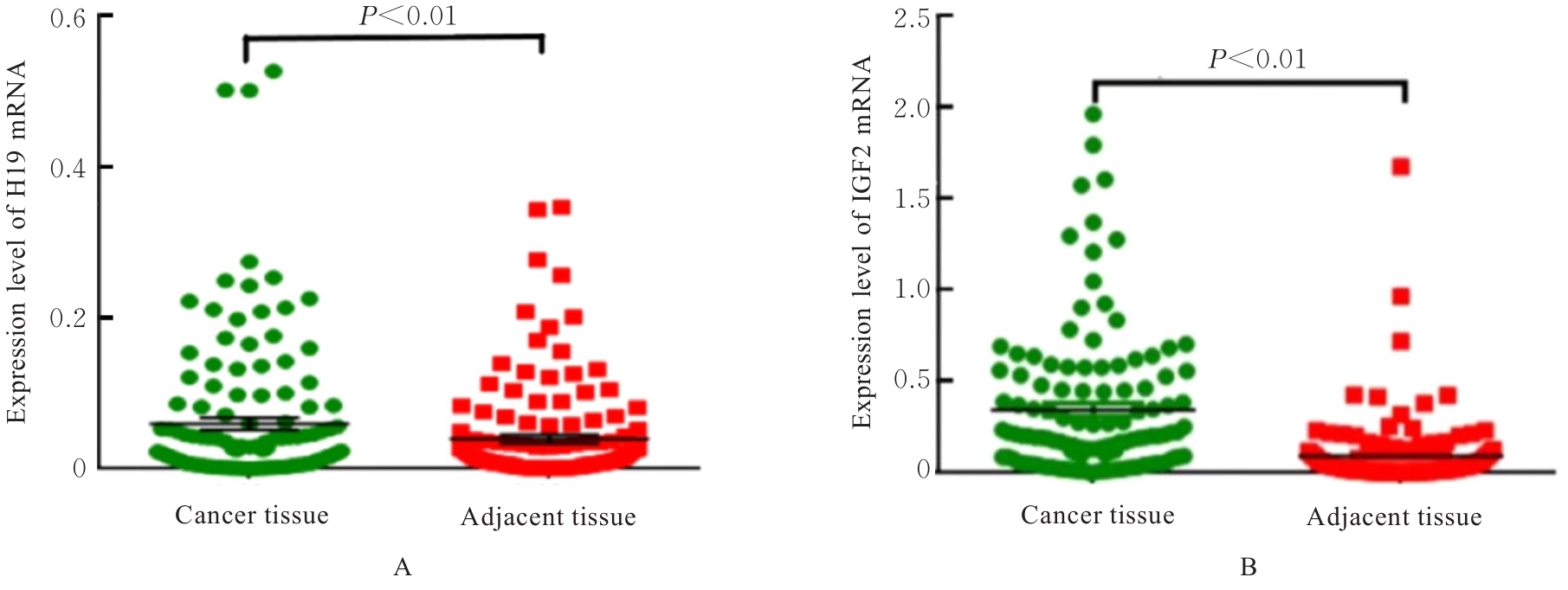
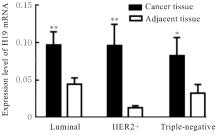
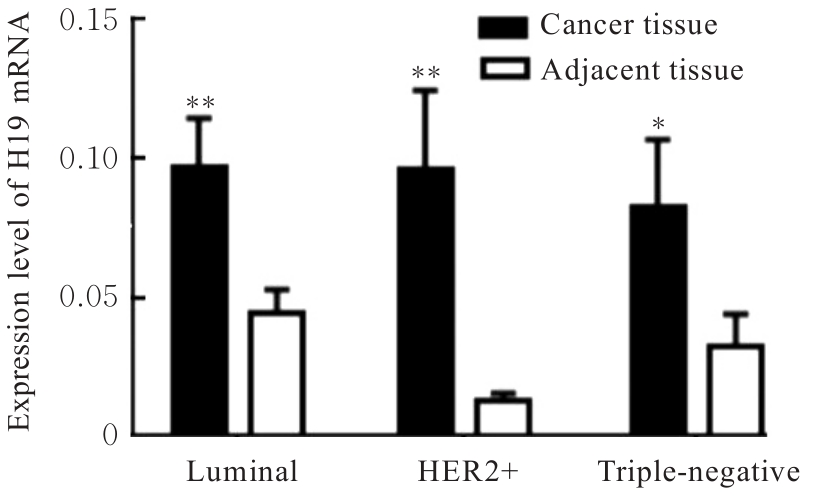
Expression levels and imprinting status of lncRNA H19 and IGF2 genes in breast cancer tissue
Xue WEI1,Xue WEN2,Xiao XIE1,Yueyuan WANG1,Dan HUANG1,Ming YANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Breast Surgery,General Surgery Center,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.Key Laboratory of Organ Regeneration and Transplantation,Ministry of Education,Cancer Center,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130061,China
-
Received:2023-08-16Online:2024-07-28Published:2024-08-01 -
Contact:Ming YANG E-mail:yangming@jlu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R737.9
Cite this article
Xue WEI,Xue WEN,Xiao XIE,Yueyuan WANG,Dan HUANG,Ming YANG. Expression levels and imprinting status of lncRNA H19 and IGF2 genes in breast cancer tissue[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1109-1115.
share this article
Tab. 3
Polymorphismsof H19 and IGF2 genes in breast cancer patients with different molecular types"
| Group | n | H19/IGF2 homozygous | H19/IGF2 heterozygous | H19 homozygous /IGF2 heterozygous | H19 heterozygous /IGF2 homozygous |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luminal | 86 | 33 (38.4) | 19 (22.1) | 15 (17.4) | 19 (22.1) |
| HER2+ | 14 | 6 (42.9) | 6 (42.9) | 1 (7.1) | 1 (7.1) |
| Triple-negative | 17 | 6 (35.3) | 7 (41.2) | 3 (17.6) | 1 (5.9) |
| 1 | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| 2 | BREAST CANCER ASSOCIATION CONSORTIUM, MAVADDAT N, DORLING L, et al. Pathology of tumors associated with pathogenic germline variants in 9 breast cancer susceptibility genes[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2022, 8(3): e216744. |
| 3 | TUCCI V, ISLES A R, KELSEY G, et al. Genomic imprinting and rhysiological processes in mammals[J]. Cell, 2019, 176(5): 952-965. |
| 4 | WANG J, SUN J Y, YANG F. The role of long non-coding RNA H19 in breast cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 19(1): 7-16. |
| 5 | LIVINGSTONE C. IGF2 and cancer[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2013, 20(6): R321-R339. |
| 6 | PEPERSTRAETE E, LECERF C, COLLETTE J, et al. Enhancement of breast cancer cell aggressiveness by lncRNA H19 and its mir-675 derivative: insight into shared and different actions[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(7): 1730. |
| 7 | CHAO W, D’AMORE P A. IGF2: epigenetic regulation and role in development and disease[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2008, 19(2): 111-120. |
| 8 | RATAJCZAK M Z. IGF2-H19, an imprinted tandem gene, is an important regulator of embryonic development, a guardian of proliferation of adult pluripotent stem cells, a regulator of longevity, and a ‘passkey’ to cancerogenesis[J]. Folia Histochem Cytobiol, 2012, 50(2): 171-179. |
| 9 | GAILHOUSTE L, LIEW L C, YASUKAWA K, et al. MEG3-derived miR-493-5p overcomes the oncogenic feature of IGF2-miR-483 loss of imprinting in hepatic cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(8): 553. |
| 10 | WANG Y, ZHOU P H, LI P, et al. Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates proliferation and doxorubicin resistance in MCF-7 cells by targeting PARP1[J]. Bioengineered, 2020, 11(1): 536-546. |
| 11 | WEI Y G, LIU Z Y, FANG J H. H19 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate human epidermal growth factor receptor expression by sequestering let-7c in gastric cancer[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 17(2): 2600-2606. |
| 12 | ZHOU W, YE X L, XU J, et al. The lncRNA H19 mediates breast cancer cell plasticity during EMT and MET plasticity by differentially sponging miR-200b/c and let-7b[J]. Sci Signal, 2017, 10(483): eaak9557. |
| 13 | LIU Y, SHARMA S, WATABE K. Roles of lncRNA in breast cancer[J]. Front Biosci, 2015, 7(1): 94-108. |
| 14 | SUN H, WANG G, PENG Y, et al. H19 lncRNA mediates 17β-estradiol-induced cell proliferation in MCF-7 breast cancer cells[J]. Oncol Rep, 2015, 33(6): 3045-3052. |
| 15 | BASAK P, CHATTERJEE S, WEGER S, et al. Estrogen regulates luminal progenitor cell differentiation through H19 gene expression[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2015, 22(4): 505-517. |
| 16 | BERTEAUX N, LOTTIN S, MONTÉ D, et al. H19 mRNA-like noncoding RNA promotes breast cancer cell proliferation through positive control by E2F1[J]. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(33): 29625-29636. |
| 17 | YU H, ROHAN T. Role of the insulin-like growth factor family in cancer development and progression[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2000, 92(18): 1472-1489. |
| 18 | EL-BADRY O M, HELMAN L J, CHATTEN J, et al. Insulin-like growth factor Ⅱ-mediated proliferation of human neuroblastoma[J]. J Clin Invest, 1991, 87(2): 648-657. |
| 19 | HEFFELFINGER S C, MILLER M A, YASSIN R, et al. Angiogenic growth factors in preinvasive breast disease[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 1999, 5(10): 2867-2876. |
| 20 | GUI Y R, AGUILAR-MAHECHA A, KRZEMIEN U, et al. Metastatic breast carcinoma-associated fibroblasts have enhanced protumorigenic properties related to increased IGF2 expression[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 25(23): 7229-7242. |
| 21 | MARTINO M D, FORZATI F, MARFELLA M, et al. HMGA1P7-pseudogene regulates H19 and Igf2 expression by a competitive endogenous RNA mechanism[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 37622. |
| 22 | BERTEAUX N, APTEL N, CATHALA G, et al. A novel H19 antisense RNA overexpressed in breast cancer contributes to paternal IGF2 expression[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2008, 28(22): 6731-6745. |
| [1] | Xiaomin FU,Jianling JIA,Yanhong DOU,Wenyong REN,Aiping SHI. Research progress in effect of intestinal flora on occurrence and development of breast cancer and its therapeutic application [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1182-1188. |
| [2] | Yuesheng ZHAO,Zubin LI,Haiou LIU,Kunlin TAO,Qihai ZHAO,Na LI. Inhibitory effect of silencing CDKL1 gene on proliferation and invasion of breast cancer MCF-7 cells by regulating PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1234-1242. |
| [3] | Changchun MU,Chunji QUAN,Quanjin JIN,Zhengri PIAO. Expression of thymosin beta4 in breast cancer tissue and its effect on migration and invasion of breast cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 890-895. |
| [4] | Xiuyan YU,Ting LI,Zhanjie CONG,Wenlong WANG,Xiaowei ZHANG,Xuefeng WU. Combined detection of hMAM, SBEM and CEACAM19 mRNA in peripheral blood of breast cancer patients and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 195-202. |
| [5] | Xiuyan YU,Chunying TIAN,Xiaowei ZHANG,Xuefeng WU. Clinical significances of serum levels of SBEM, hMAM and CEACAM19 in early diagnosis of breast cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1518-1525. |
| [6] | Yang YU,Sainan LIU,Yunkai LIU,Yong LI,Yichun QIAO,Yi CHENG. Bioinformatic analysis on expression characteristics of PRPS2 and its relationship with prognosis of breast cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1229-1236. |
| [7] | Pei GONG, Jingran LIU, Shimin ZHAO, Yuzhen WANG, Jiming XIE. Inhibitory effect of MCM10 silencing on proliferation of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 652-659. |
| [8] | Qing WANG,Siqi XIE,Kai ZHENG,Yiyin TANG,Hongwan LI,Hengyu ZHANG,Mingjian TAN,Lei PENG,Dequan LIU,Shicong TANG. Detection of serum vitamin-B levels in breast cancer patients receiving different chemotherapy regimens and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 724-730. |
| [9] | Haoxuan TANG,Nanfeng MENG,Meiling DU,Wei WANG,Tao HE. Inhibitory effect of new VEGF monoclonal antibody combined with all-trans retinoic acid on proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 344-351. |
| [10] | KONG Wencong, HE Wubin, SU Rongjian, JIA Daqi, GU Yanjiao, WANG Yue, DU Xiaoyuan. Inhibitory effect and apoptosisinduction of MST1R inhibitor BMS-777607 on proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 451-457. |
| [11] | ZHANG Lifang, CAI Lin, WANG Yunhua, ZHANG Keshi, WU Rina. Analysis on association between selenoprotein P polymorphism and risk of papillary thyriod carcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 383-388. |
| [12] | CHEN Zhouhua, GONG Hui, FENG Lei, XIAO Yujie, HUANG Lizhong. Induction of LPS on epithelial mesenchymal transition in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and its effect on β-catenin expression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 309-315. |
| [13] | ZHOU Chun, WANG Guanghua, ZHANG Bangzhu. Effects of miR-367 on proliferation, invasion and migration of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1353-1360. |
| [14] | YANG Zhuangqing, LU Mei, YANG Xiaojuan, WANG Chang'an, ZOU Jieya. Inhibitory effect of inhibiting TRIM24 gene expression on proliferation, apopotosis,invasion and migration of breast cancer MCF-7 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1379-1383. |
| [15] | YUE Yuan, XU Yinglian, WANG Jingjing, SUN Minying, ZHANG Zenan, ZHAO Xinyue, LI Zongpu, TAI Guixiang. Inhibitory effects of down-regulation of JNK enzymatic activity on growth of human prostate cancer cells, hepatocellular carcinoma cells and breast cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1046-1051. |