吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (12): 3601-3613.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230164
深度神经网络模型并行自适应计算任务调度方法
- 兰州交通大学 电子与信息工程学院,兰州 730070
Adaptive scheduling of computing tasks for deep neural network model parallelism
Tao JU( ),Shuai LIU,Jiu-yuan HUO,Xue-jun ZHANG
),Shuai LIU,Jiu-yuan HUO,Xue-jun ZHANG
- School of Electronic and Information Engineering,Lanzhou Jiaotong University,Lanzhou 730070,China
摘要:
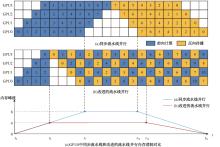
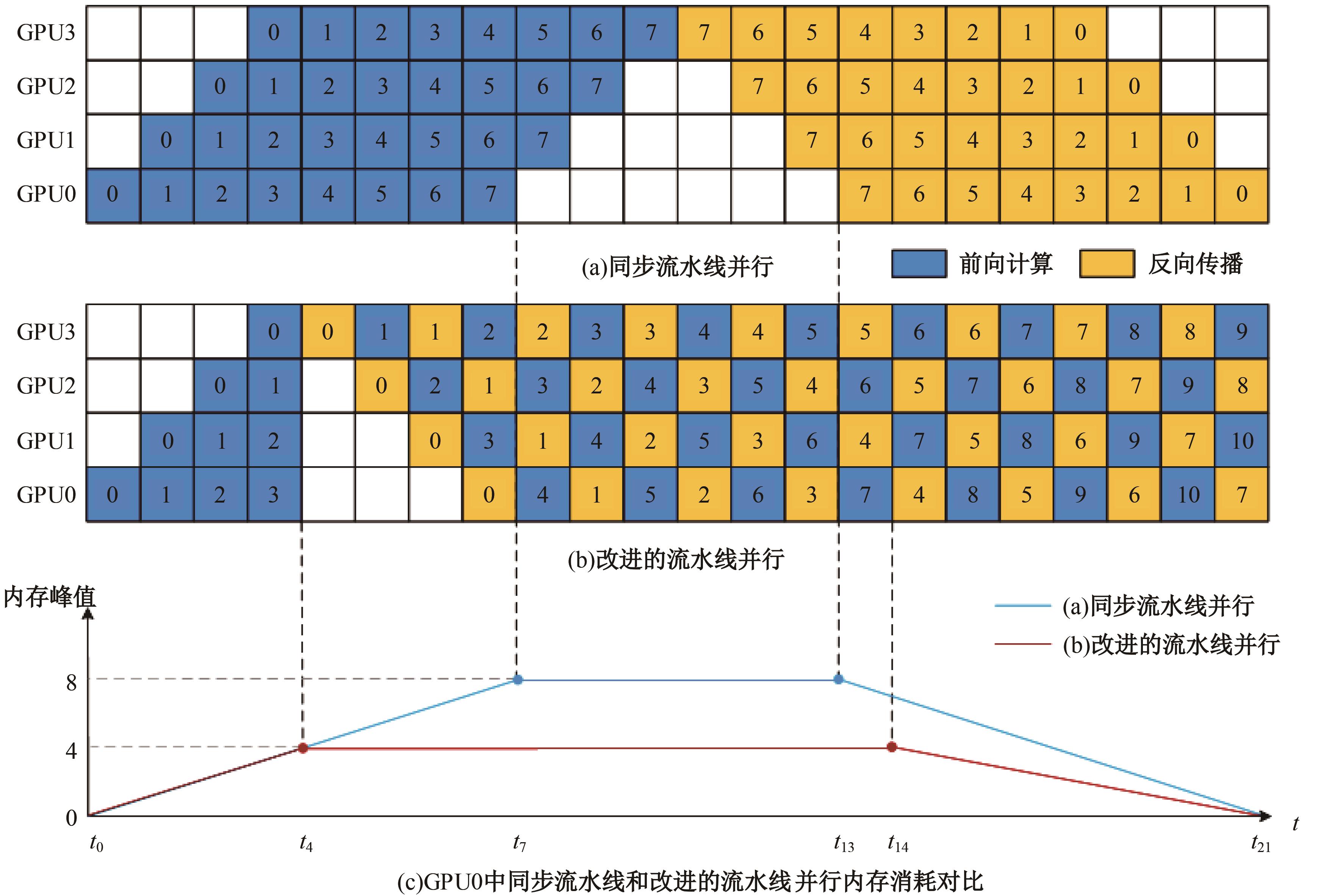
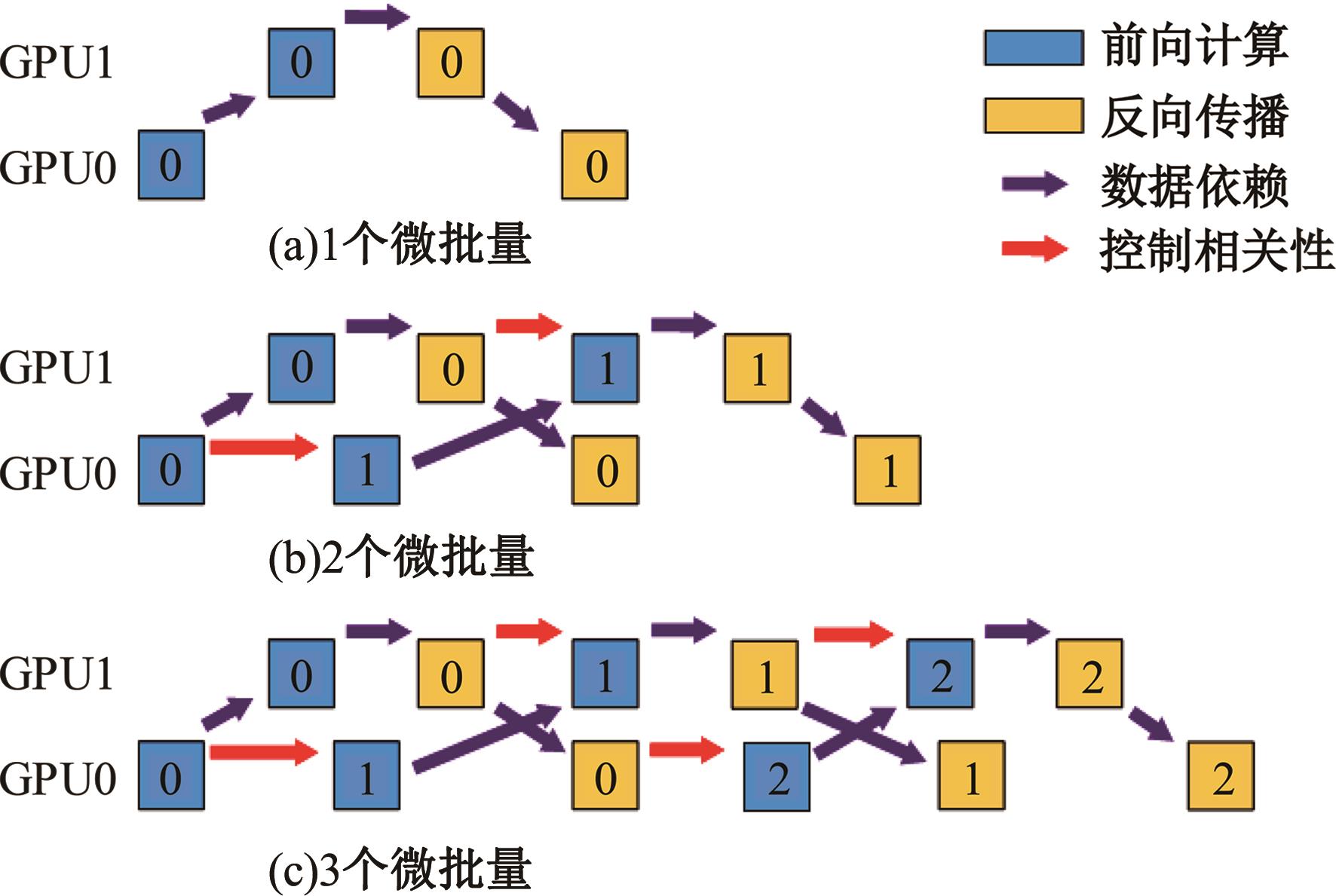
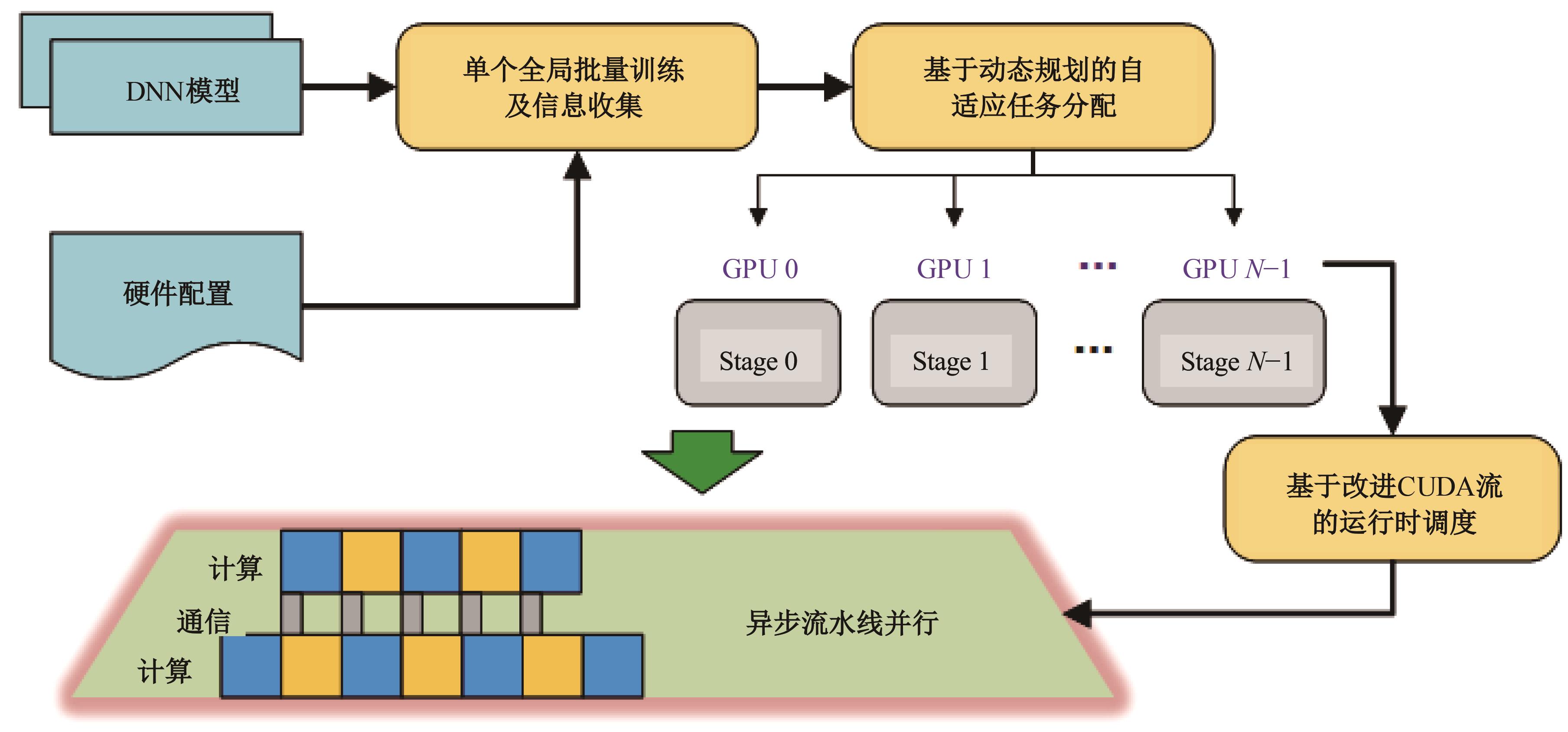
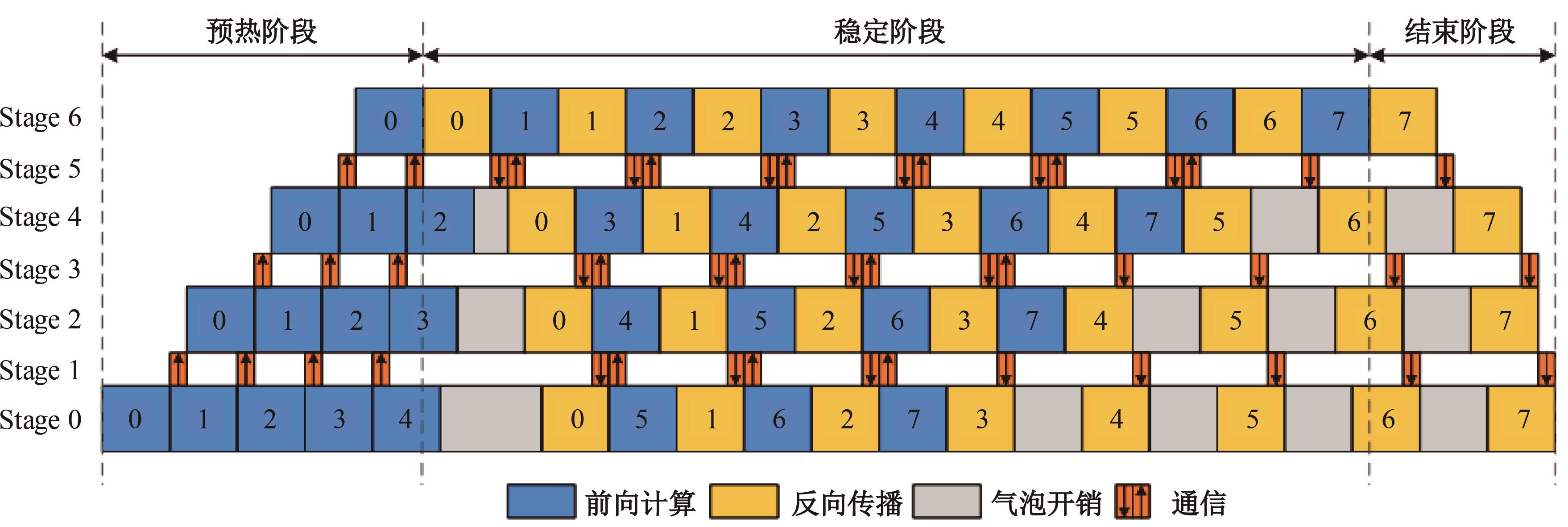
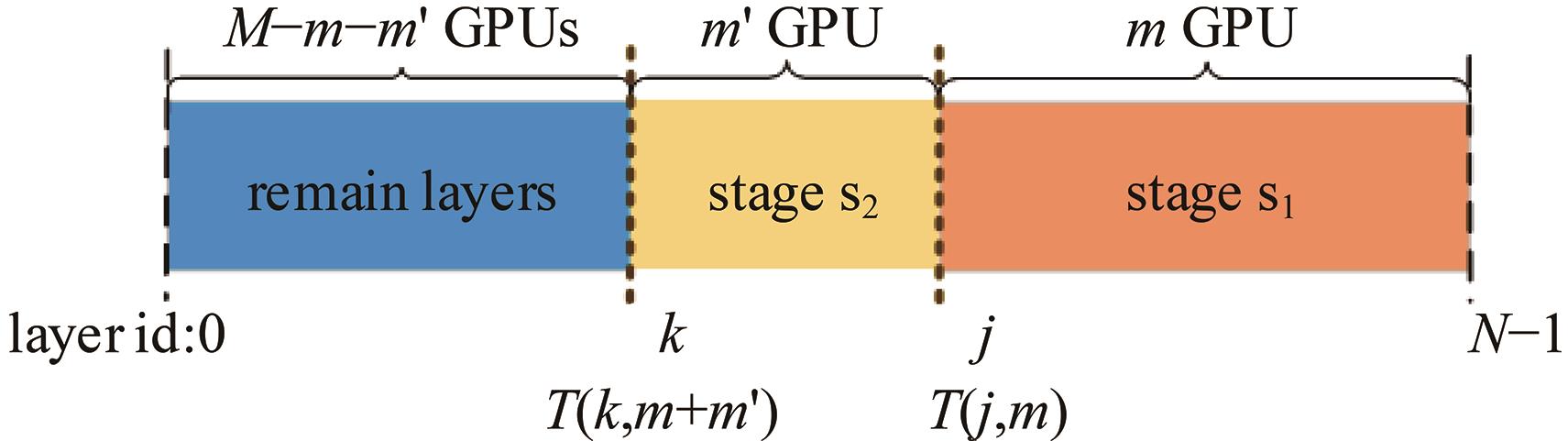
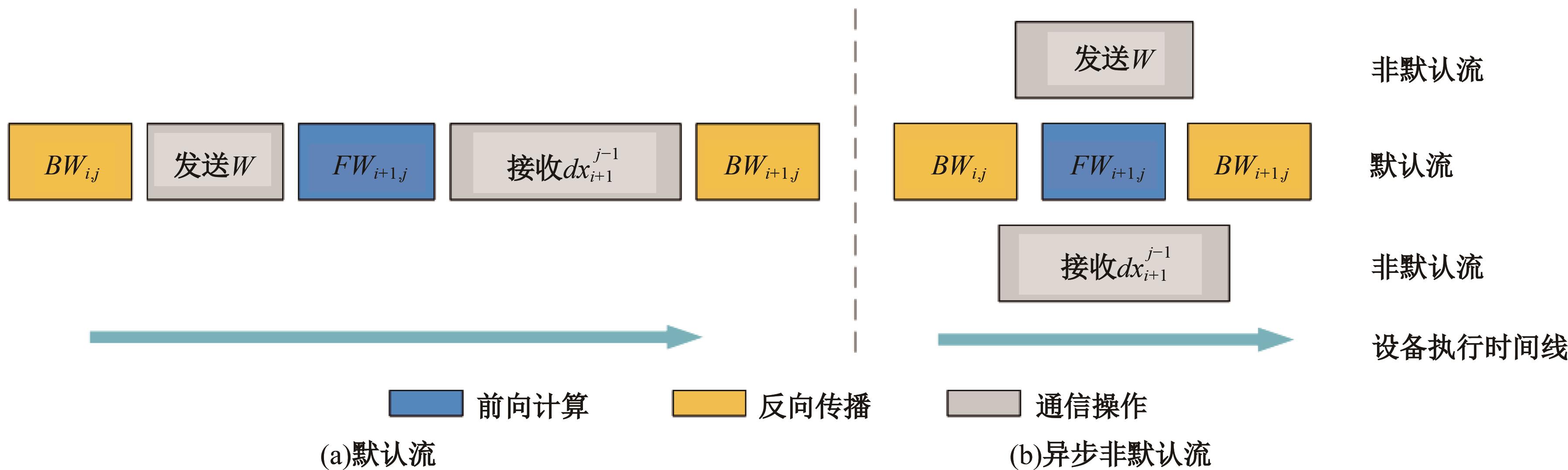
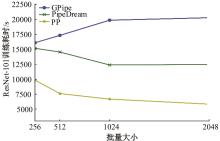
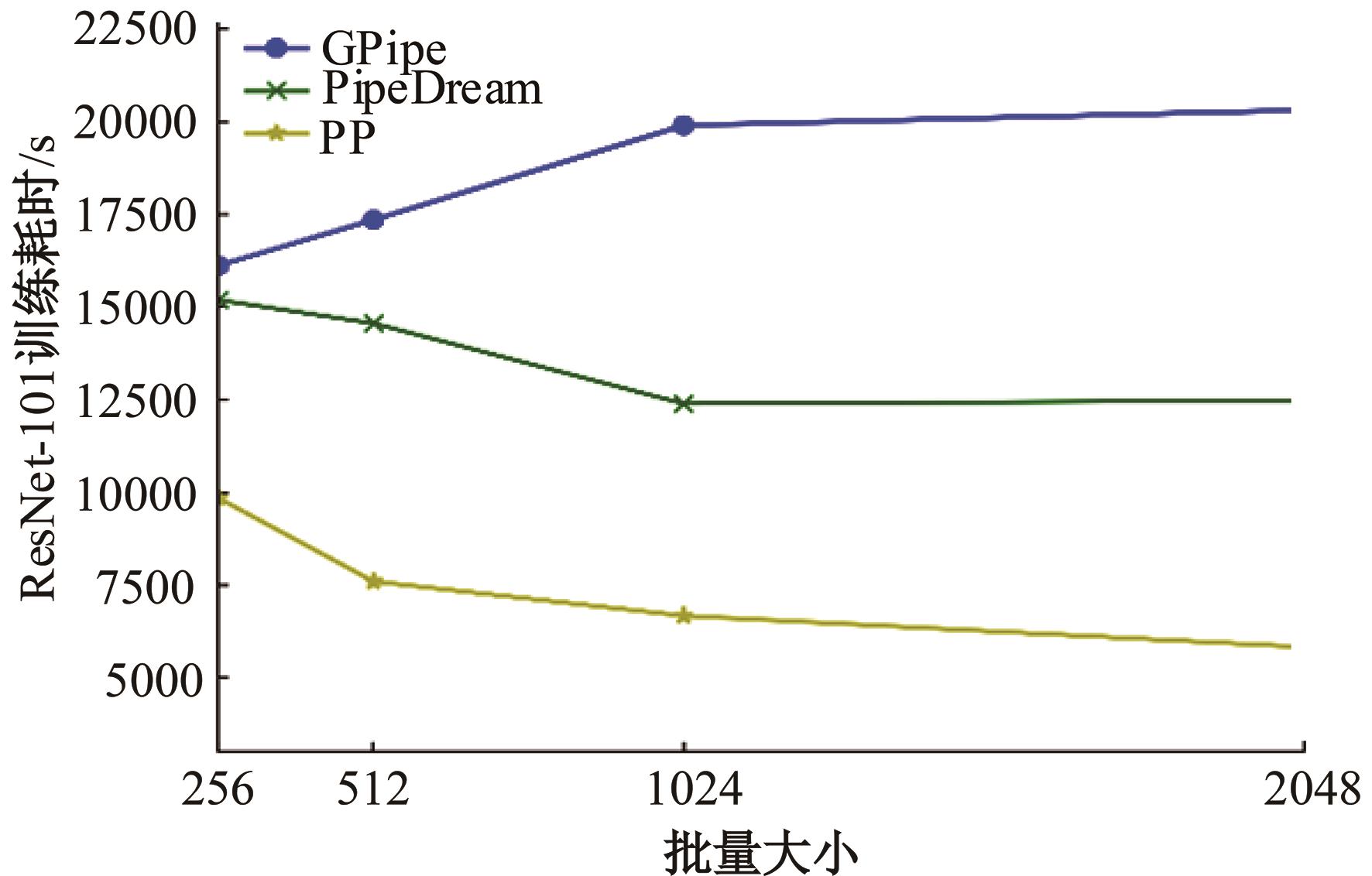
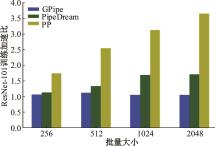
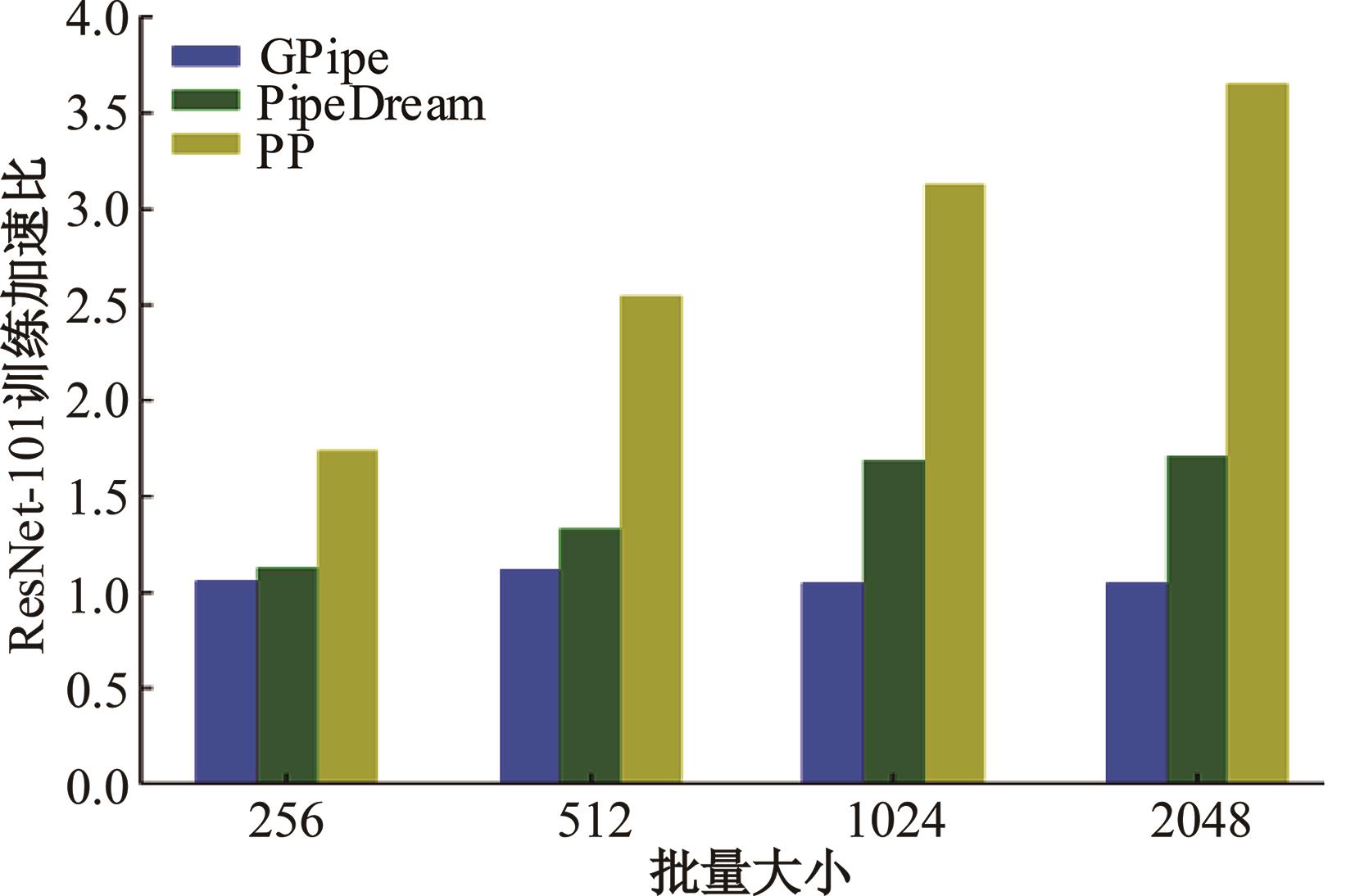
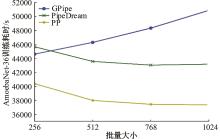
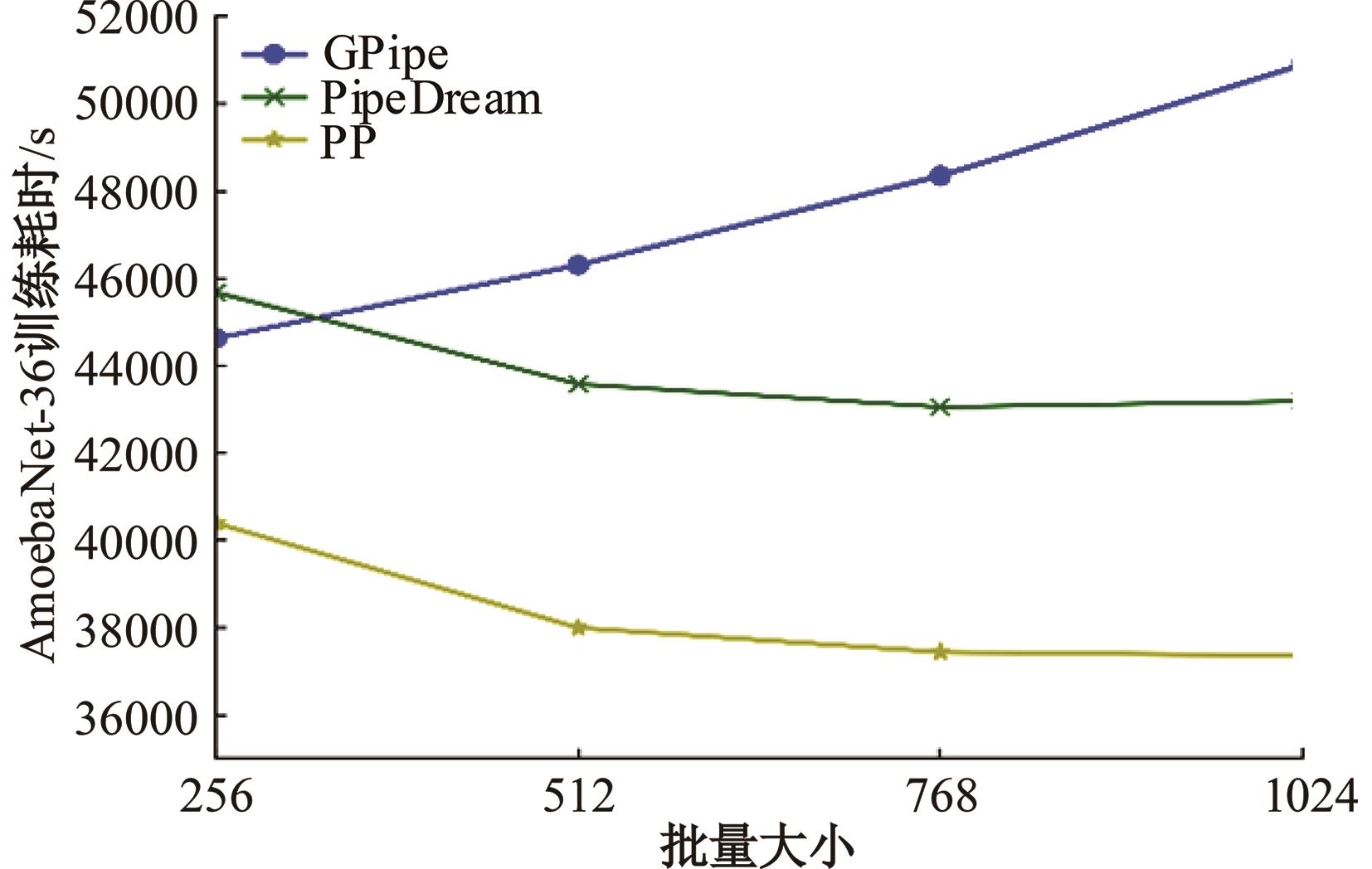
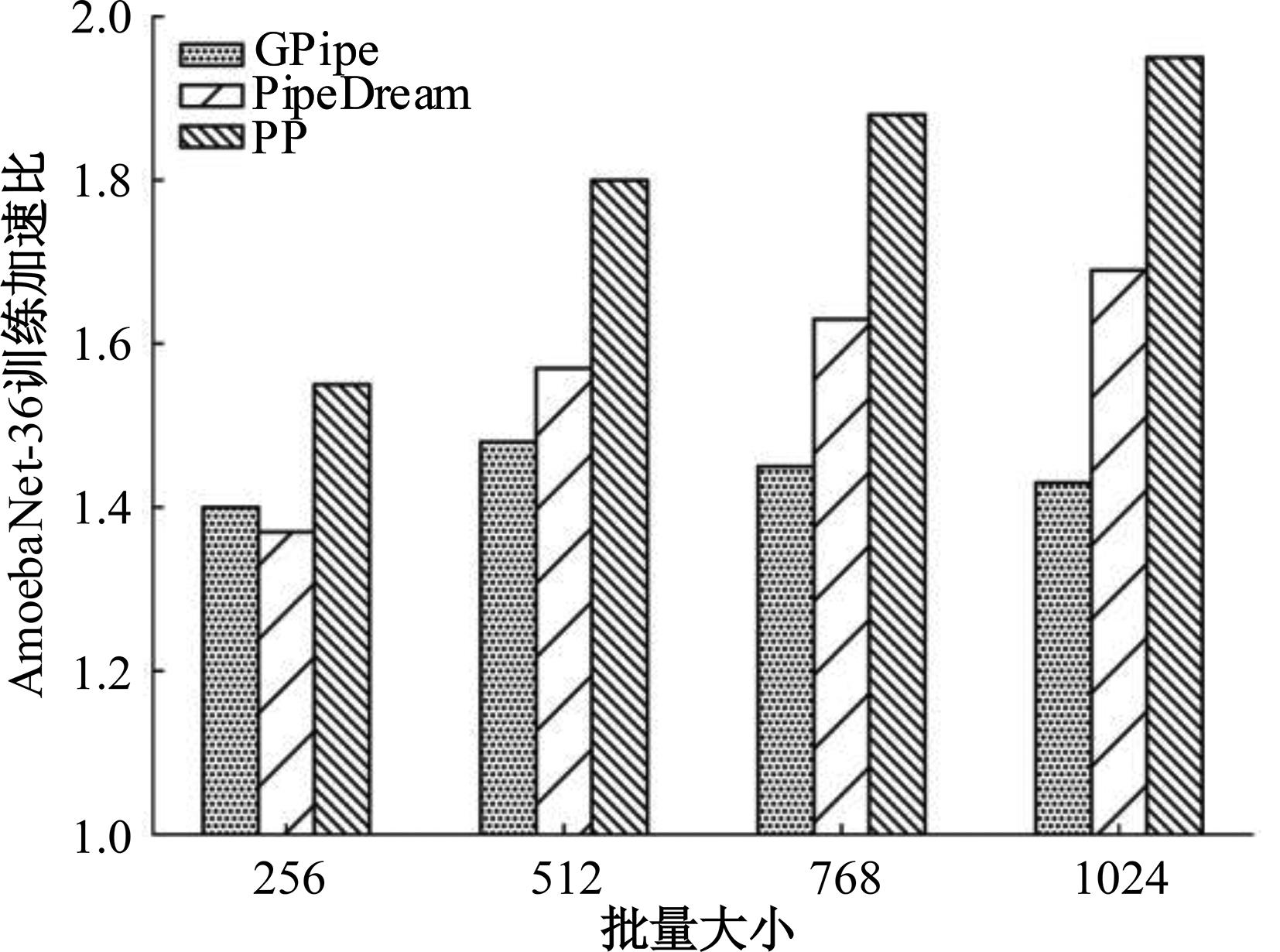
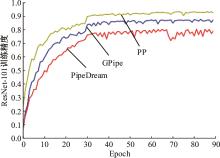
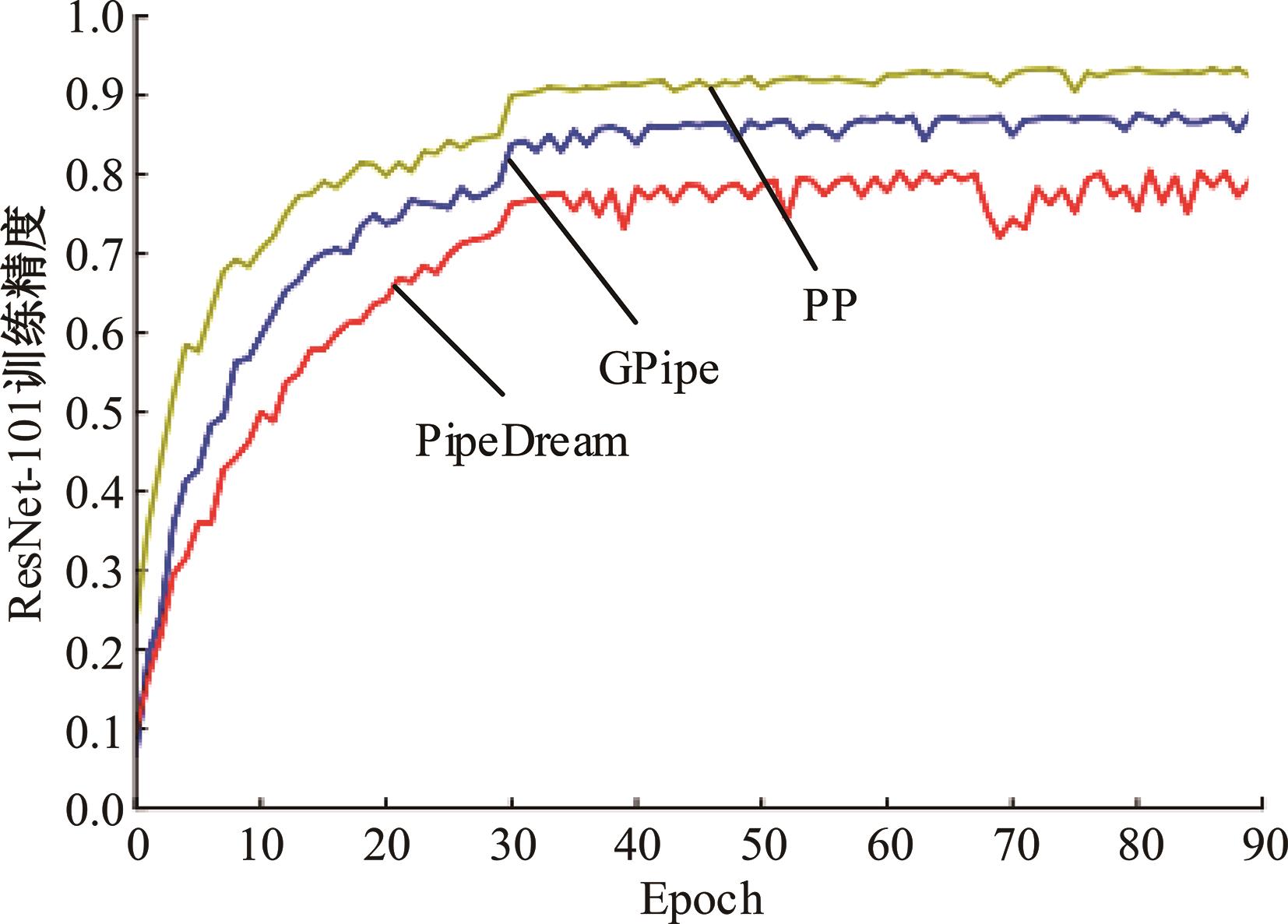
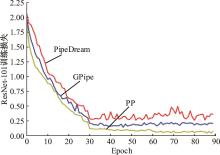
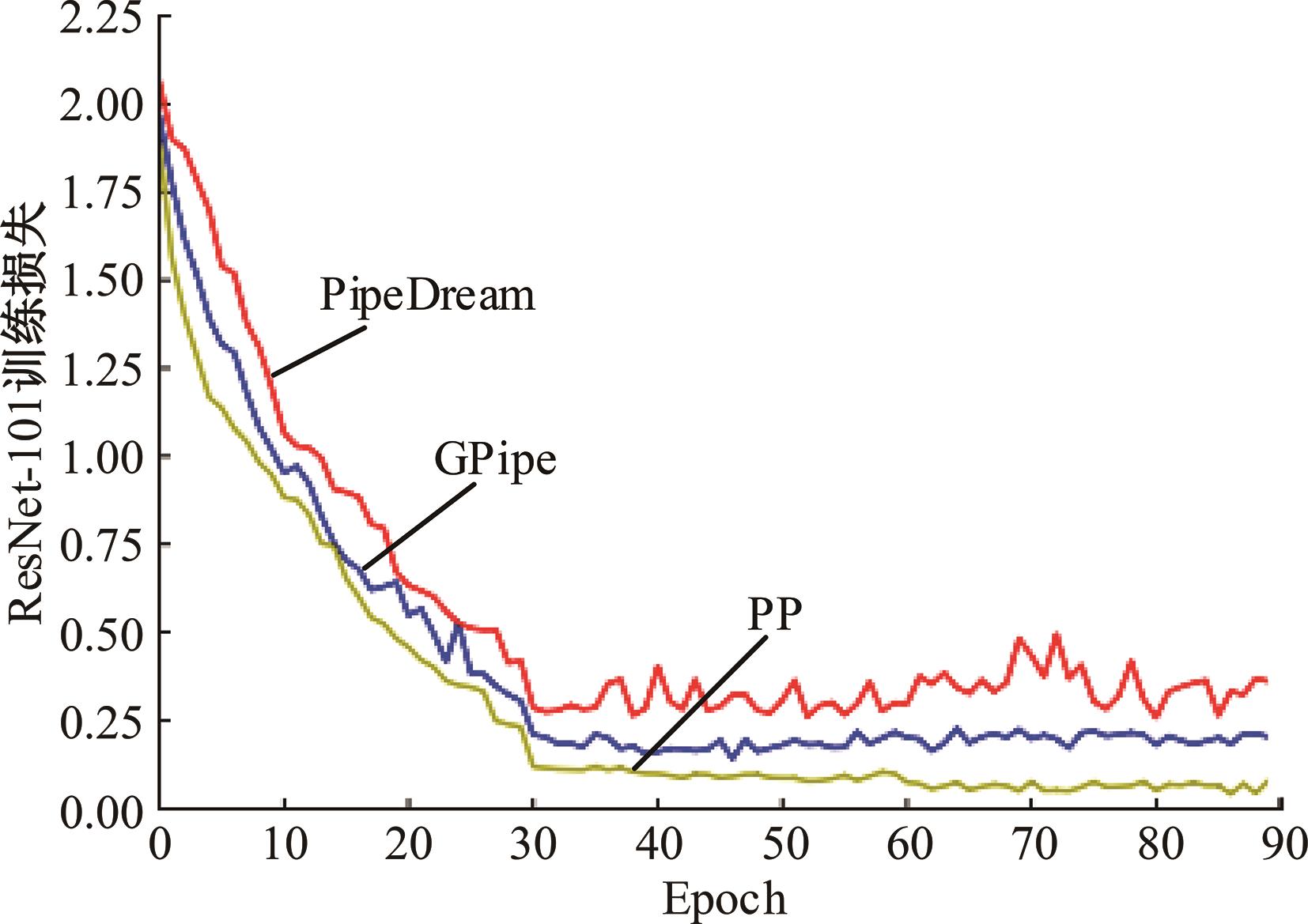
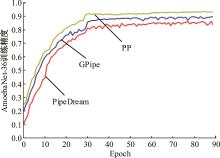
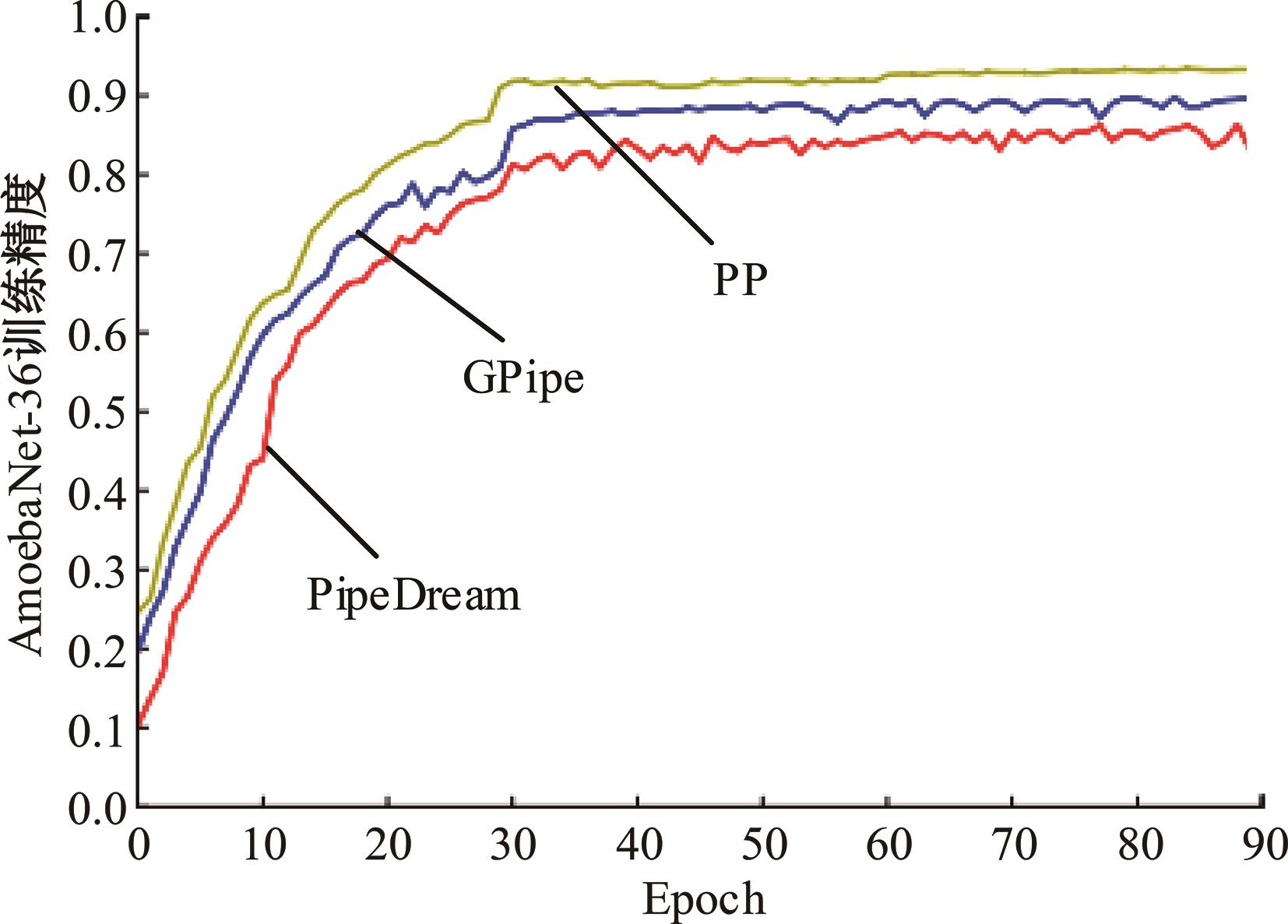
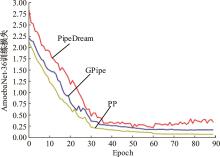
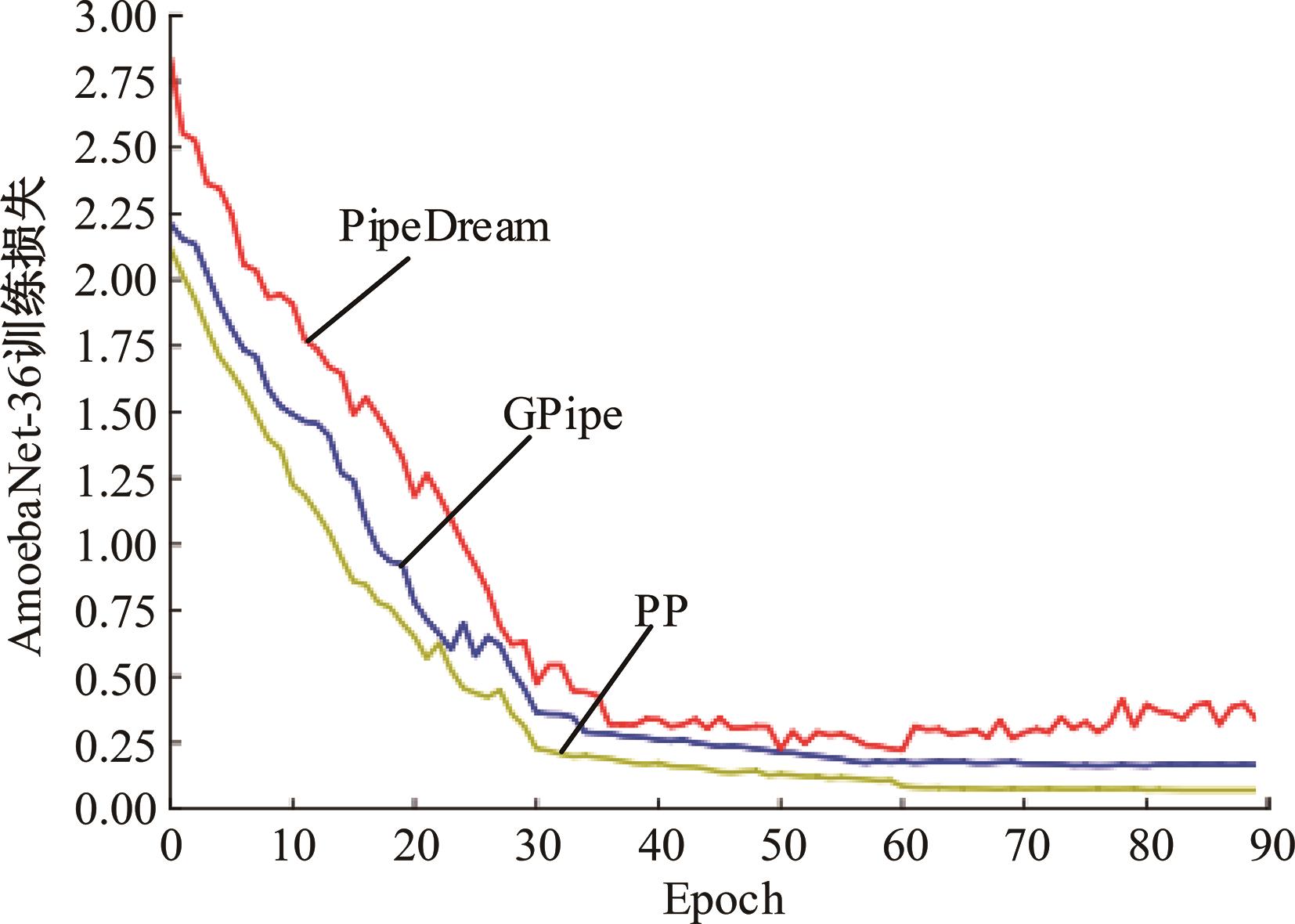
针对大规模深度神经网络模型并行面临的内存消耗大、设备利用率低、训练时间长、模型难以收敛的问题,提出了一种面向深度神经网络模型并行的计算任务自适应调度方法。通过建立模型并行计算任务的多迭代异步并行管理机制,控制微批量单元具体调度过程,实现模型合理分区和计算资源合理分配,解决异步迭代时产生的梯度延迟更新问题;基于拓扑感知设计计算资源的分配机制,实现模型训练任务和计算资源的合理匹配;设计计算资源和模型任务的运行时调度策略,实现深度学习模型训练过程中计算与通信重叠的最大化,提高计算资源利用率。实验结果表明:与已有的模型并行方法相比,本文方法可以充分利用各GPU计算资源,在保证模型训练精度的同时,可以将大规模深度神经网络模型训练速度平均提高2.8倍。
中图分类号:
- TP311
| 1 | 朱泓睿, 元国军, 姚成吉, 等. 分布式深度学习训练网络综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2021, 58(1): 98-115. |
| Zhu Hong-rui, Yuan Guo-jun, Yao Cheng-ji, et al. Survey on network of distributed deep learning training[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2021, 58(1): 98-115. | |
| 2 | 巨涛, 赵宇阳, 刘帅, 等. 面向图片识别的深度学习模型并行优化方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2023(1): 141-151. |
| Ju Tao, Zhao Yu-yang, Liu Shuai, et al. A parallel optimization method of deep learning model for image recognition[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2023(1):141-151. | |
| 3 | Real E, Aggarwal A, Huang Y P, et al. Regularized evolution for image classifier architecture search[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, USA, 2019: 4780-4789. |
| 4 | Zoph B, Vasudevan V, Shlens J, et al. Learning transferable architectures for scalable image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8697-8710. |
| 5 | Devlin J, Chang M W, Lee K, et al. Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[DB/OL]. [2023-02-15]. |
| 6 | Brown T, Mann B, Ryder N, et al. Language models are few-shot learners[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 1877-1901. |
| 7 | Li M, Andersen D G, Park J W, et al. Scaling distributed machine learning with the parameter server[C]∥Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Big Data Science and Computing,Stanford, USA, 2014: 583-598. |
| 8 | 朱虎明, 李佩, 焦李成, 等. 深度神经网络并行化研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(8): 1861-1881. |
| Zhu Hu-ming, Li Pei, Jiao Li-cheng, et al. Review of parallel deep neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(8): 1861-1881. | |
| 9 | 巨涛, 刘帅, 王志强, 等. 深度神经网络模型任务切分及并行优化方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(9): 2739-2752. |
| Ju Tao, Liu Shuai, Wang Zhi-qiang, et al. Task segmentation and parallel optimization of DNN model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(9): 2739-2752. | |
| 10 | Shoeybi M, Patwary M, Puri R, et al. Megatron-lm: training multi-billion parameter language models using model parallelism[DB/OL].[2023-02-15]. |
| 11 | Lepikhin D, Lee H J, Xu Y H, et al. Gshard: scaling giant models with conditional computation and automatic sharding[DB/OL].[2023-02-15]. |
| 12 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30: 6000-6010. |
| 13 | Geng J K, Li D, Wang S. Elasticpipe: an efficient and dynamic model-parallel solution to dnn training[C]∥Proceedings of the 10th Workshop on Scientific Cloud Computing, Phoenix AZ, USA, 2019:5-9. |
| 14 | Rasley J, Rajbhandari S, Ruwase O, et al. Deepspeed: system optimizations enable training deep learning models with over 100 billion parameters[C]∥Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Virtual Event, USA, 2020: 3505-3506. |
| 15 | Huang Y P, Cheng Y L, Bapna A, et al. GPipe: efficient training of giant neural networks using pipeline parallelism[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2019, 32: 103-112. |
| 16 | Shazeer N, Cheng Y L, Parmar N, et al. Mesh-tensorflow: deep learning for supercomputers[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2018, 31: 10435-10444. |
| 17 | Kim C, Lee H, Jeong M, et al. torchgpipe: on-the-fly pipeline parallelism for training giant models[DB/OL].[2023-2-15]. |
| 18 | Narayanan D, Phanishayee A, Shi K, et al. Memory-efficient pipeline-parallel DNN training[C]∥Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 2021: 7937-7947. |
| 19 | Fan S Q, Rong Y, Meng C, et al. DAPPLE: a pipelined data parallel approach for training large models[C]∥Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGPLAN Symposium on Principles and Practice of Parallel Programming, Virtual Event, Republic of Korea, 2021: 431-445. |
| 20 | Jangda A, Huang J, Liu G D, et al. Breaking the computation and communication abstraction barrier in distributed machine learning workloads[C]∥Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2022: 402-416. |
| 21 | Guan L, Yin W T, Li D S, et al. XPipe: efficient pipeline model parallelism for multi-GPU DNN training[DB/OL].[2023-02-15]. |
| 22 | Harlap A, Narayanan D, Phanishayee A, et al. Pipedream: fast and efficient pipeline parallel DNN training[DB/OL]. [2023-02-15]. |
| 23 | Zhao S X, Li F X, Chen X S, et al. vPipe: a virtualized acceleration system for achieving efficient and scalable pipeline parallel DNN training[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2021, 33(3): 489-506. |
| 24 | Athlur S, Saran N, Sivathanu M, et al. Varuna: scalable, low-cost training of massive deep learning models[C]∥Proceedings of the Seventeenth European Conference on Computer Systems, Rennes, France, 2022: 472-487. |
| 25 | Li S, Zhao Y L, Varma R, et al. Pytorch distributed: experiences on accelerating data parallel training[DB/OL]. [2023-02-15]. |
| 26 | He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 27 | Micikevicius P, Narang S, Alben J, et al. Mixed precision training[DB/OL].[2023-02-15]. |
| 28 | Rajbhandari S, Ruwase O, Rasley J, et al. Zero-infinity: breaking the gpu memory wall for extreme scale deep learning[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, St. Louis Missouri, USA, 2021: No.07857. |
| [1] | 兰凤崇,李继文,陈吉清. 面向动态场景复合深度学习与并行计算的DG-SLAM算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1437-1446. |
| [2] | 张笑东,夏筱筠,吕海峰,公绪超,廉梦佳. 大数据网络并行计算环境中生理数据流动态负载均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 247-254. |
| [3] | 许岩岩, 陈辉, 刘家驹, 袁金钊. CELL处理器并行实现立体匹配算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 952-958. |
| [4] | 宋康, 陈潇凯, 林逸. 动力总成悬置系统的稳健设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 692-699. |
| [5] | 韩成, 张超, 秦贵和, 薛耀红, 杨帆, 范静涛, 刘文静. 大型正交多幕投影系统光辐射补偿算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1266-1273. |
| [6] | 李军, 倪宏, 王玲芳, 陈君. 流媒体系统中基于请求迁移的任务调度算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 938-945. |
| [7] | 刘苗1,2,王珂1, 丛玉良1. 认知无线电中基于分派问题模型的优化PAPR算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(6): 1788-1792. |
|