吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 603-613.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230447
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
利用出租车时序数据识别城市功能区
- 长安大学 运输工程学院,西安 710064
Identifying urban functional structures using time-series taxi data
Shu-hong MA( ),Jun-jie ZHANG,Xi-fang CHEN,Guo-mei LIAO
),Jun-jie ZHANG,Xi-fang CHEN,Guo-mei LIAO
- College of Transportation Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
摘要:
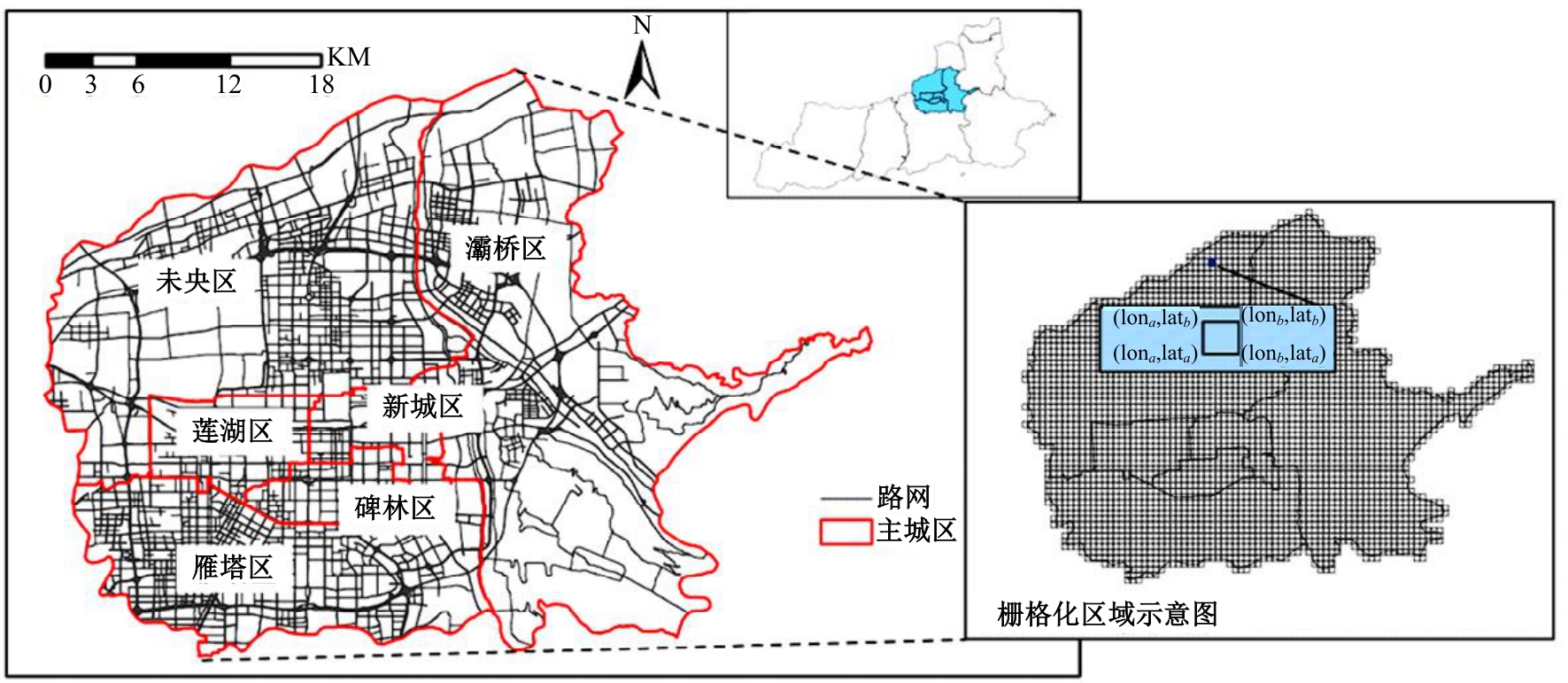
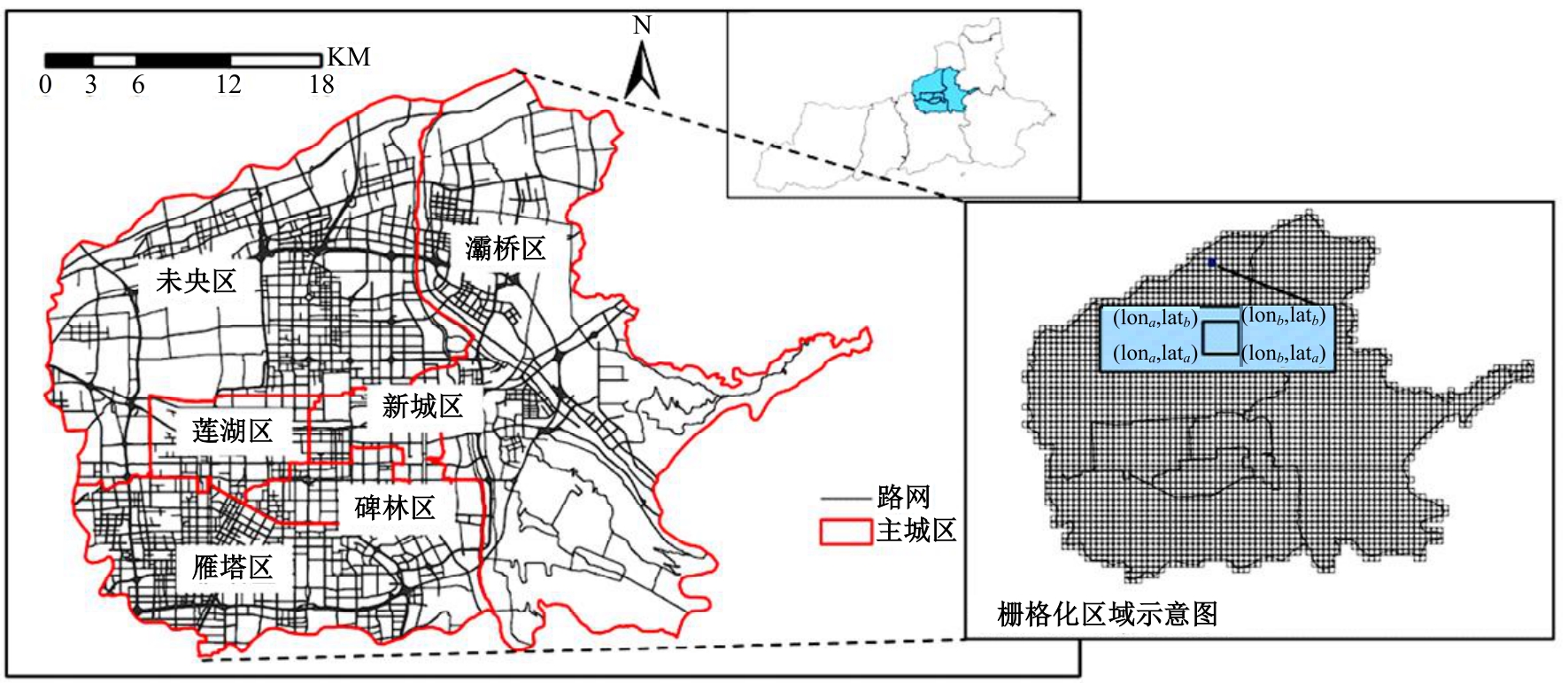
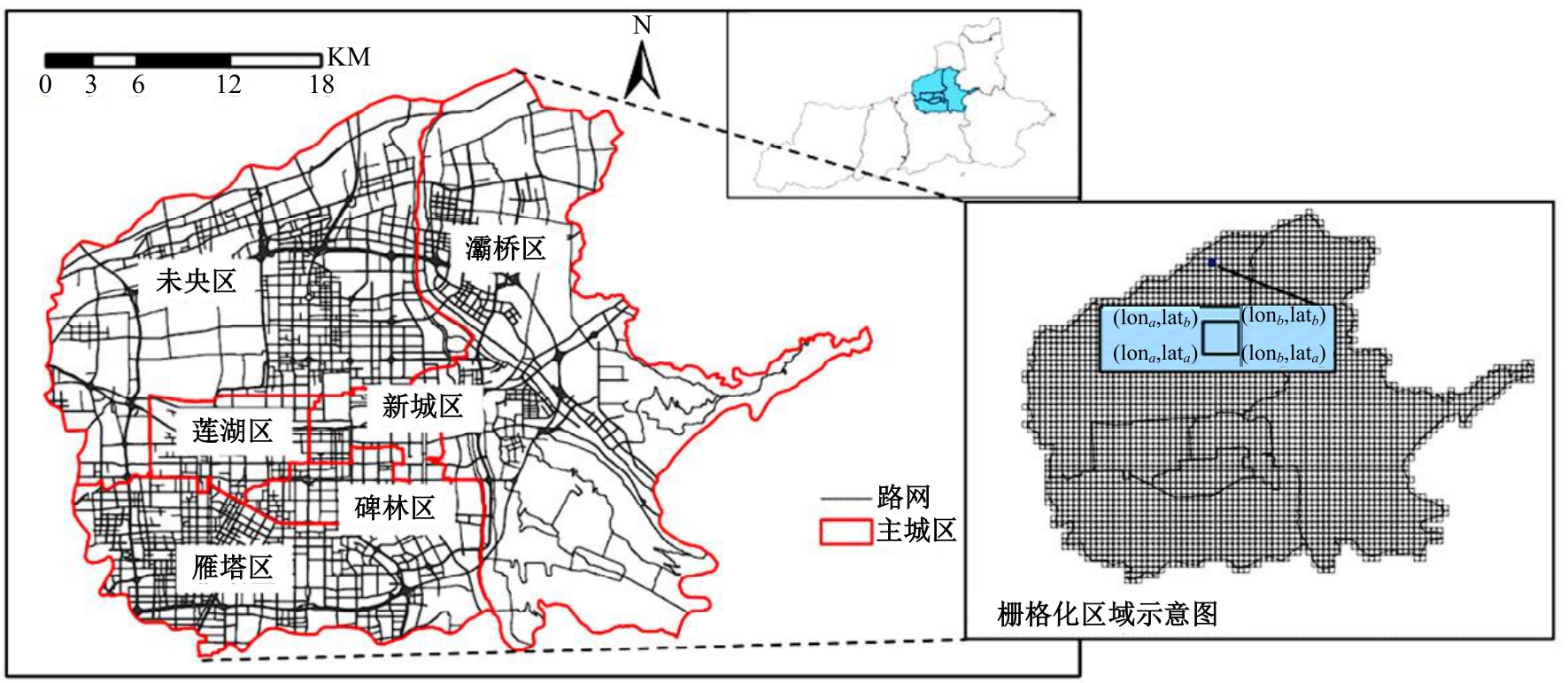
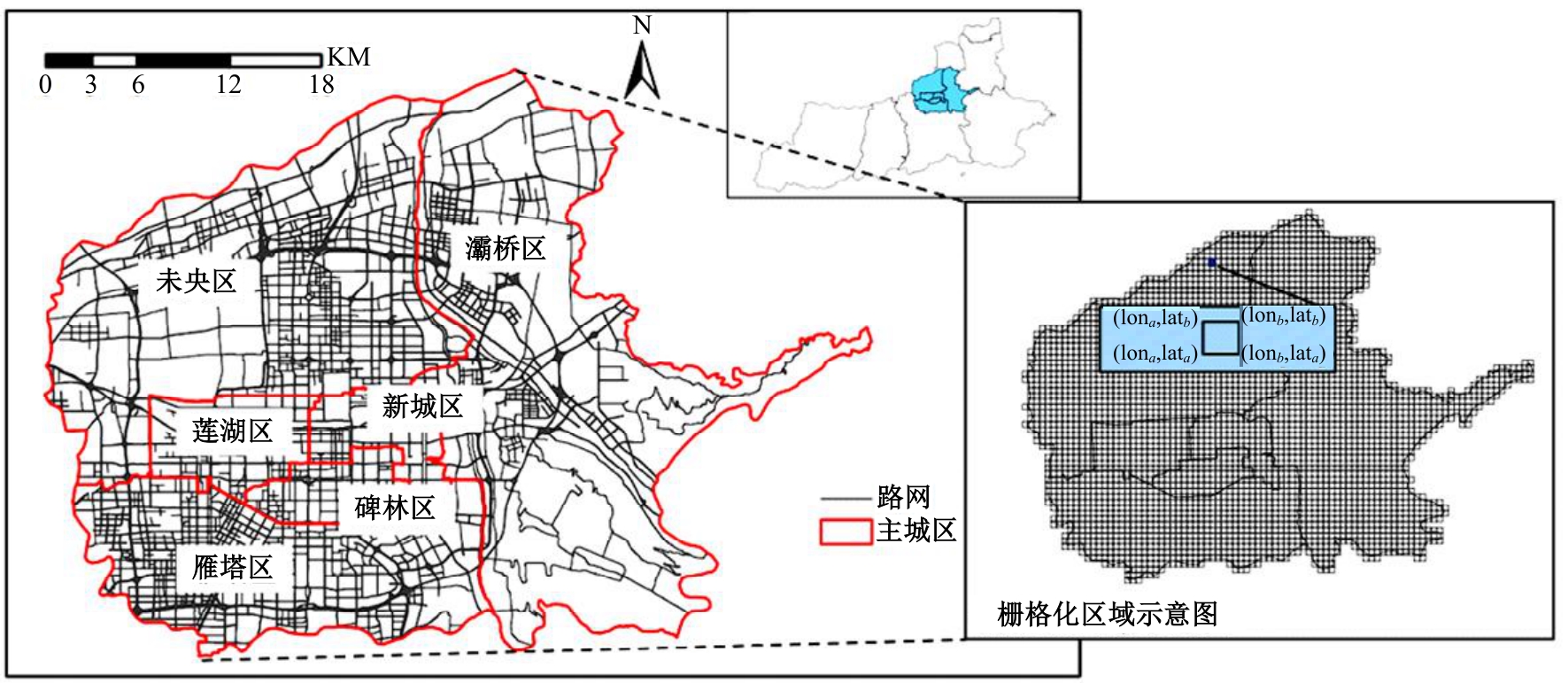
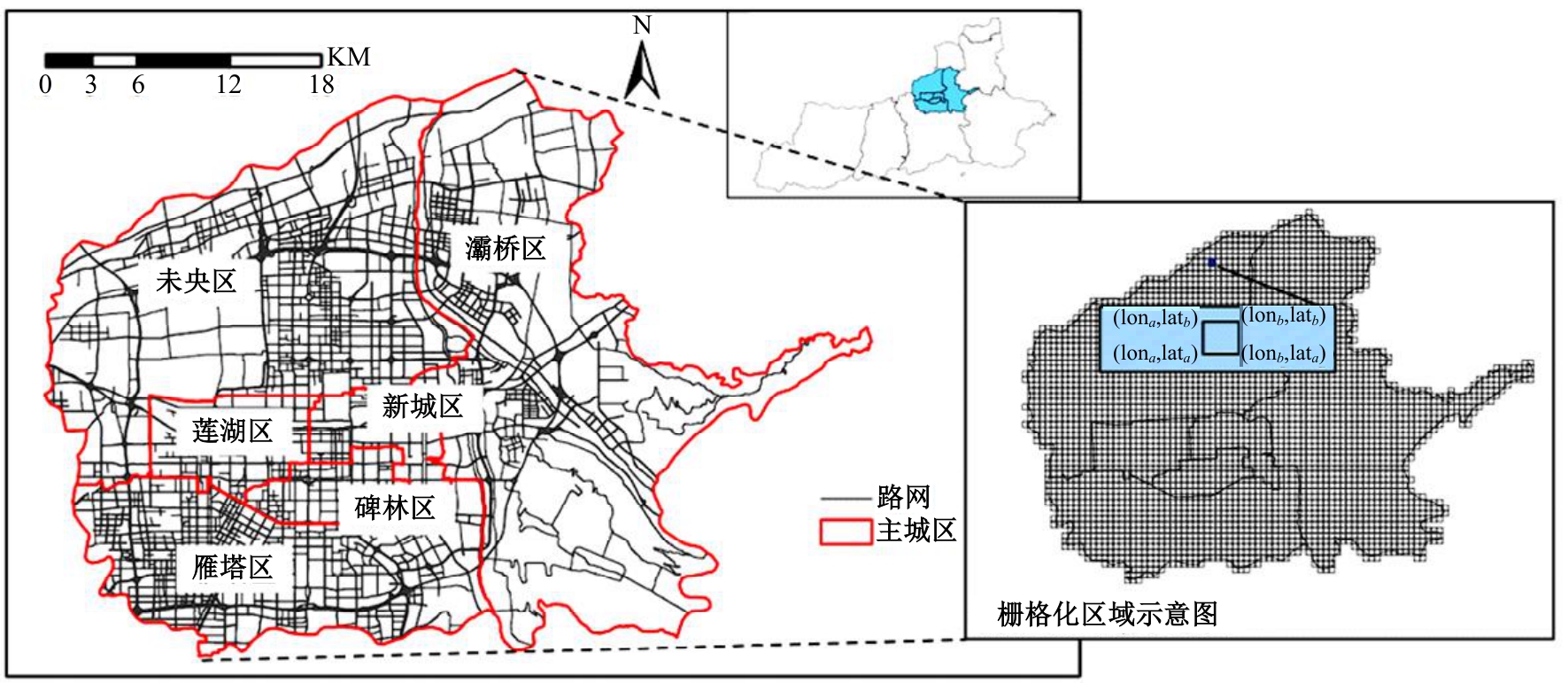
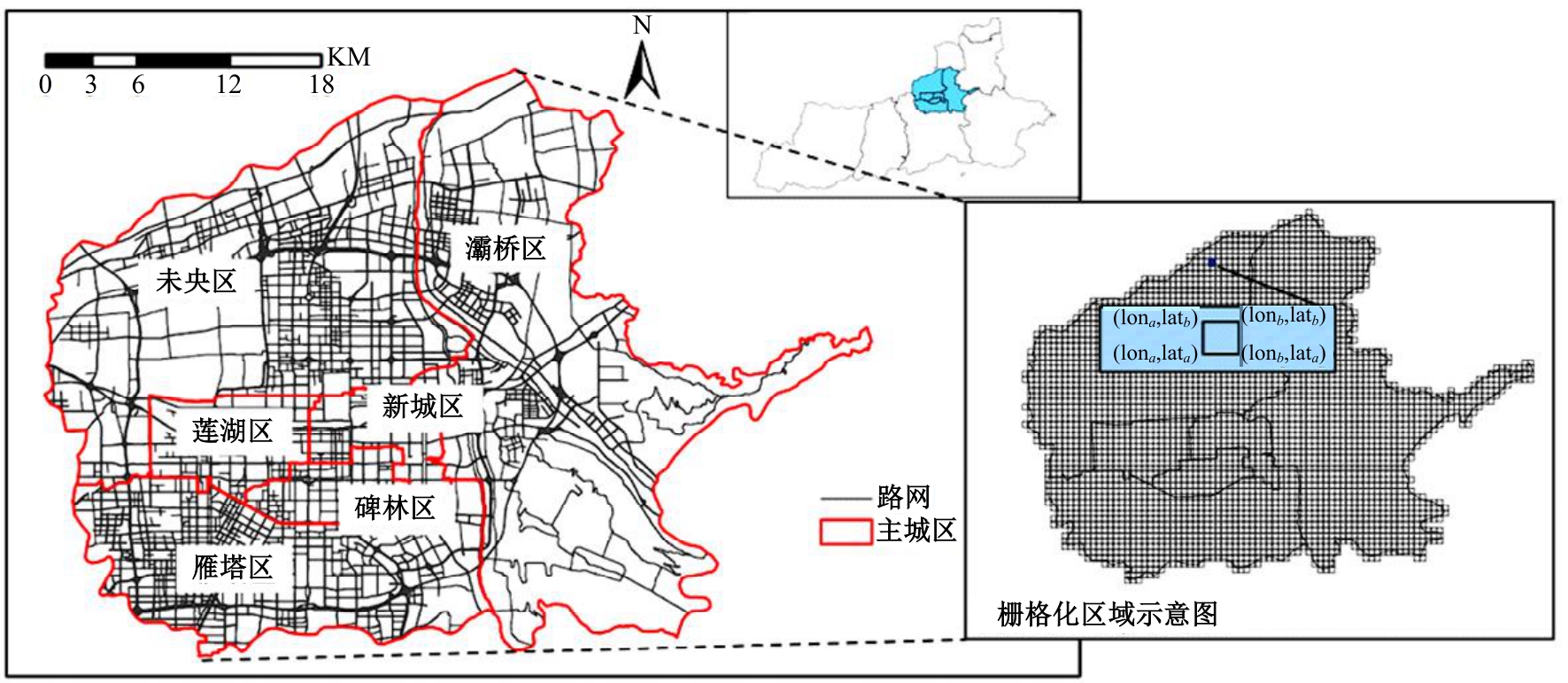
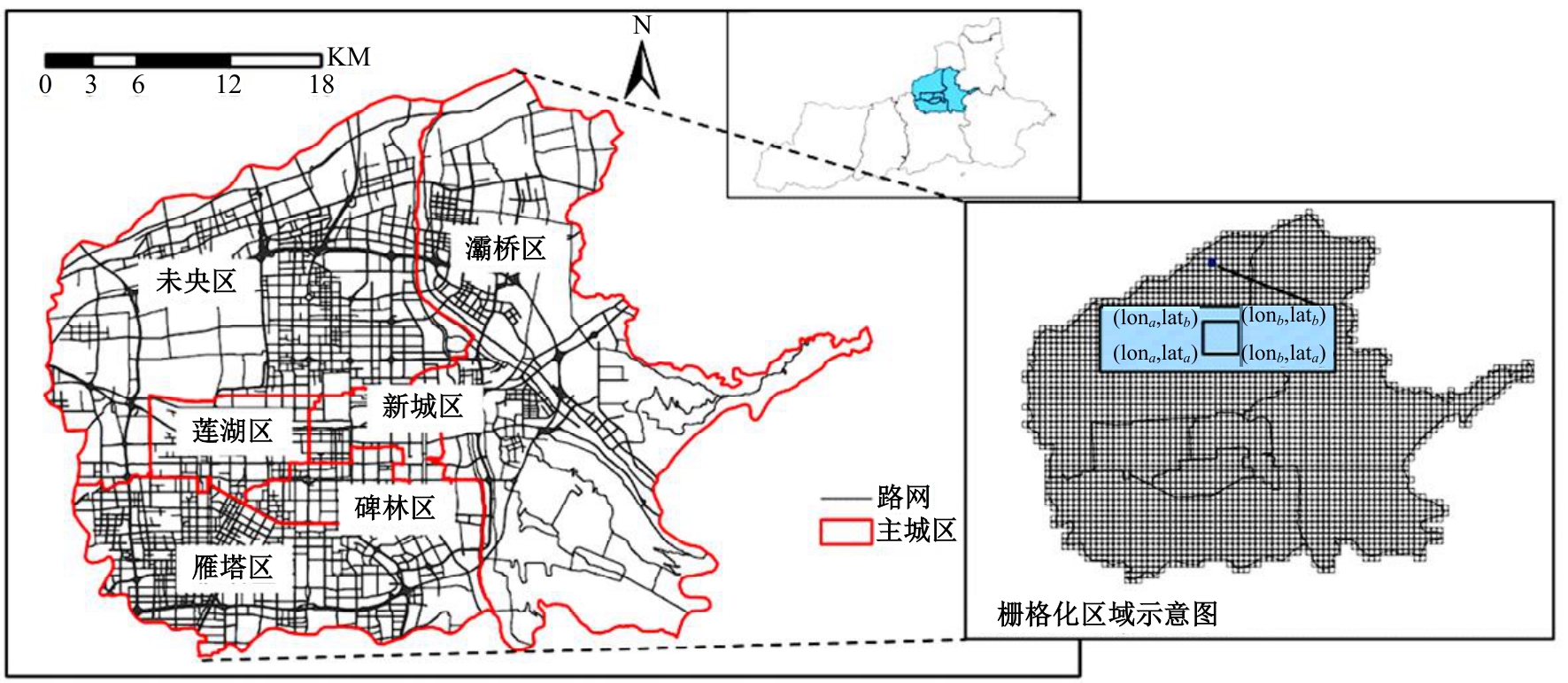
针对传统功能区识别方法缺乏对居民这一城市空间活动主体的动态表征,基于出租车轨迹与POI数据,提出了城市地块功能属性识别方法。首先,分别构造一类出发和到达时序向量;然后,利用改进的动态时间规整和聚类算法对居民出行模式进行聚类划分;最后,结合居民的出行曲线特征、POI密度、富集指数对地块功能属性进行识别。以西安市为例,讨论不同区域内居民在工作日与休息日的出发和到达模式特征,识别城市内不同地块的功能属性,结果表明:不同出发模式和到达模式曲线在早高峰、午高峰、晚高峰、夜间、凌晨展现出不同波峰,对应地块在空间分布中呈现一定圈层结构,并表现出各自的功能倾向,利用居民出发-到达模式特征和POI信息对地块功能属性的识别具有互补作用,其功能属性呈现出“职-住-休”三元结构发展,也侧面反映不同属性功能区与人群活动的时空变化规律。研究结果对规划部门重新分配交通资源、优化城市空间结构具有借鉴作用。
中图分类号:
- U491.12
| 1 | 杨喜平, 方志祥, 尹凌. 城市空间结构要素与人群聚散稳定性的关联性探索[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2018, 20(6): 791-798. |
| Yang Xi-ping, Fang Zhi-xiang, Yin Ling. Exploring the relationship between urban spatial structure and the stability of human convergence-divergence[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2018, 20(6): 791-798. | |
| 2 | Xiao J Y, Shen Y J, Ge J F, et al. Evaluating urban expansion and land use change in Shijiazhuang, China, by using GIS and remote sensing[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2006, 75(1): 69-80. |
| 3 | 贾斐雪, 闫金凤, 王甜. 大数据构建的赋分评价模型与功能区识别研究[J]. 测绘科学, 2021, 46(8): 172-178. |
| Jia Fei-xue, Yan Jin-feng, Wang Tian. Research on scoring evaluation model and functional regions identification constructed by big data[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(8):172-178. | |
| 4 | 禹文豪, 艾廷华, 杨敏, 等. 利用核密度与空间自相关进行城市设施兴趣点分布热点探测[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2016, 41(2): 221-227. |
| Yu Wen-hao, Ai Ting-hua, Yang Min, et al. Detecting "hot spots" of facility pois based on kernel density estimation and spatial autocorrelation technique[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2016, 41(2): 221-227. | |
| 5 | 高旭, 桂志鹏, 隆玺, 等. KDSG-DBSCAN:一种基于K-D Tree和Spark GraphX的高性能DBSCAN算法[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2017, 33(6): 1-7. |
| Gao Xu, Gui Zhi-peng, Long Xi, et al. KDSG-DBSCAN: a high performance DBSCAN algorithm based on K-D Tree and Spark GraphX[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2017, 33(6): 1-7. | |
| 6 | Zhen Q, Liu X T, Fei T, et al. Identification of urban functional areas by coupling satellite images and taxi GPS trajectories[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(15): No.12152449. |
| 7 | 于翔. 基于城市公交刷卡数据和兴趣点的城市功能区识别研究——以北京市为例[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学公共管理学院, 2014. |
| Yu Xiang. Discovering zones of different functions using bus smart card data and points of interest: a case study of Beijing[D]. Hangzhou: College of Public Administration, Zhejiang University, 2014. | |
| 8 | 杨振山, 苏锦华, 杨航, 等. 基于多源数据的城市功能区精细化研究——以北京为例[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(2): 477-494. |
| Yang Zhen-shan, Su Jin-hua, Yang Hang, et al. Exploring urban functional areas based on multi-source data: a case study of Beijing[J]. Geographical Research, 2021, 40(2): 477-494. | |
| 9 | 孙士杰, 孙群, 陆川伟, 等. 基于出租车上下客数据的城市功能区提取方法[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2019, 36(6): 637-642. |
| Sun Shi-jie, Sun Qun, Lu Chuan-wei, et al. Urban functional areas extraction method based on taxi origin and destination data[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2019, 36(6): 637-642. | |
| 10 | 刘菊, 许珺, 蔡玲, 等. 基于出租车用户出行的功能区识别[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2018, 20(11): 1550-1561. |
| Liu Ju, Xu Jun, Cai Ling, et al. Identifying functional regions based on the spatio-temporal pattern of taxi trajectories[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2018, 20(11): 1550-1561. | |
| 11 | 姚尧, 张亚涛, 关庆锋, 等. 使用时序出租车轨迹识别多层次城市功能结构[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2019, 44(6): 875-884. |
| Yao Yao, Zhang Ya-tao, Guan Qing-feng, et al. Sensing multi-level urban functional structures by using time series taxi trajectory data[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(6): 875-884. | |
| 12 | Pan G, Qi G, Wu Z, et al. Land-use classification using taxi GPS traces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(1): 113-123. |
| 13 | 李俊奎. 时间序列相似性问题研究[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学计算机科学与技术学院, 2008. |
| Li Jun-kui. Research on time series sequence similarity[D]. Wuhan:College of Computer Science and Technology of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2008. | |
| 14 | 王文璇, 朱晓东, 吴兵. 基于动态时间弯曲距离的快速路入口匝道周围路径分级方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(3): 970-979. |
| Wang Wen-xuan, Zhu Xiao-dong, Wu Bing. Utilizing dynamic time warping distance in classification of routes around expressway on-ramp[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(3): 970-979. | |
| 15 | 邸少宁, 朱杰, 郑加柱, 等. 出租车轨迹数据的南京人群出行模式挖掘[J]. 测绘科学, 2021, 46(1): 203-212. |
| Di Shao-ning, Zhu Jie, Zheng Jia-zhu, et al. Movement pattern mining of Nanjing residents based on taxi trajectory data[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(1): 203-212. | |
| 16 | 闫学东, 郭浩楠, 李永昌, 等. 基于顺风车数据和聚类方法的都市圈区域划分与层级结构研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息, 2021, 21(4): 30-39. |
| Yan Xue-dong, Guo Hao-nan, Li Yong-chang,et al. Regional division and hierarchical structure of metropolitan area based on carpooling data and clustering method[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21(4): 30-39. | |
| 17 | Dunn J C. A fuzzy relative of the ISODATA process and its use in detecting compact well-separated clusters[J]. Journal of Cybernetics, 1973, 3(3): 32-57. |
| 18 | Verburg P H, Nijs T C D, Eck J R V, et al. A method to analyze neighborhood characteristics of land use pattern[J]. Computers Environment and Urban Systems, 2004, 28(6): 667-690. |
| 19 | 程静, 刘家骏, 高勇. 基于时间序列聚类方法分析北京出租车出行量的时空特征[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2016, 18(9): 1227-1239. |
| Cheng Jing, Liu Jia-jun, Gao Yong. Analyzing the spatio-temporal characteristics of Beijing's OD trip volume based on time series clustering method[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2016, 18(9): 1227-1239. |
| [1] | 高天洋,胡大伟,姜瑞森,吴雪,刘慧甜. 基于模块化车辆的区域灵活接驳公交线路优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 537-545. |
| [2] | 李昱燃,汪飞,朱才华,韩飞,李岩. 污染天气居民通勤模式选择影响因素的链式效用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 577-590. |
| [3] | 徐慧智,蒋时森,王秀青,陈爽. 基于深度学习的车载图像车辆目标检测和测距[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 185-197. |
| [4] | 郑长江,陶童统,陈志超. 基于流量可调重分配的级联失效模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2441-2450. |
| [5] | 温晓岳,钱国敏,孔桦桦,缪月洁,王殿海. TrafficPro:一种针对城市信控路网的路段速度预测框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2214-2222. |
| [6] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,严丽平. 基于随机充电需求的充电桩优化双层模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2238-2244. |
| [7] | 曲大义,刘浩敏,杨子奕,戴守晨. 基于车路协同的交通瓶颈路段车流动态分配机制及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2187-2196. |
| [8] | 陈桂珍,程慧婷,朱才华,李昱燃,李岩. 考虑驾驶员生理信息的城市交叉口风险评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1277-1284. |
| [9] | 赵晓华,刘畅,亓航,欧居尚,姚莹,郭淼,杨海益. 高速公路交通事故影响因素及异质性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 987-995. |
| [10] | 杨秀建,贾晓寒,张生斌. 考虑汽车队列动态特性的混合交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 947-958. |
| [11] | 范博松,邵春福. 城市轨道交通突发事件风险等级判别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [12] | 郑长江,胡欢,杜牧青. 考虑枢纽失效的多式联运快递网络结构设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2304-2311. |
| [13] | 王殿海,胡佑薇,蔡正义,曾佳棋,姚文彬. 基于BPR函数的城市道路间断流动态路阻模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1951-1961. |
| [14] | 李艳波,柳柏松,姚博彬,陈俊硕,渠开发,武奇生,曹洁宁. 考虑路网随机特性的高速公路换电站选址[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1364-1371. |
| [15] | 胡莹,邵春福,王书灵,蒋熙,孙海瑞. 基于共享单车骑行轨迹的骑行质量识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1040-1046. |
|
||