吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (8): 2393-2400.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231159
• 农业工程·仿生工程 • 上一篇
模拟火壤结壳及其力学性能试验
党兆龙1( ),邹猛2,宋家锋2,陈百超1,申彦2,齐迎春2(
),邹猛2,宋家锋2,陈百超1,申彦2,齐迎春2( )
)
- 1.北京空间飞行器总体设计部,北京 100094
2.吉林大学 工程仿生教育部重点实验室,长春 130022
Experimental on mechanical properties of simulated Mars soil crust and its crusting
Zhao-long DANG1( ),Meng ZOU2,Jia-feng SONG2,Bai-chao CHEN1,Yan SHEN2,Ying-chun QI2(
),Meng ZOU2,Jia-feng SONG2,Bai-chao CHEN1,Yan SHEN2,Ying-chun QI2( )
)
- 1.Institute of Spacecraft System Engineering,CAST,Beijing 100094,China
2.Key Lab. for Bionics Engineering of Education Ministry,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
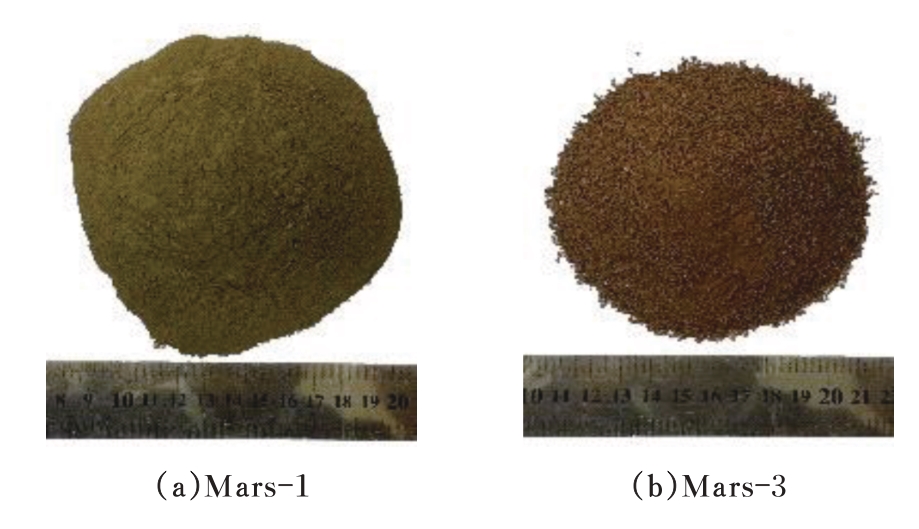
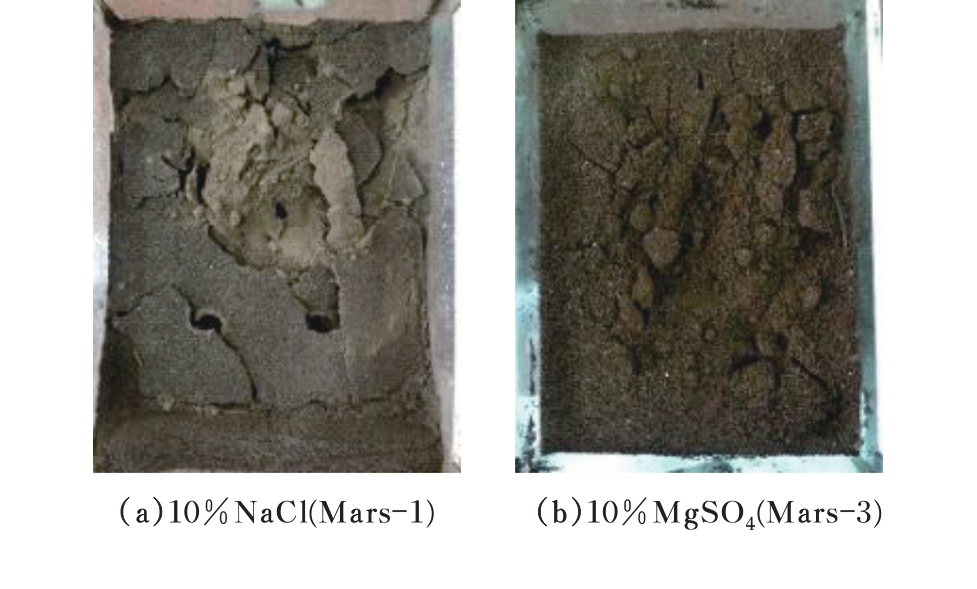
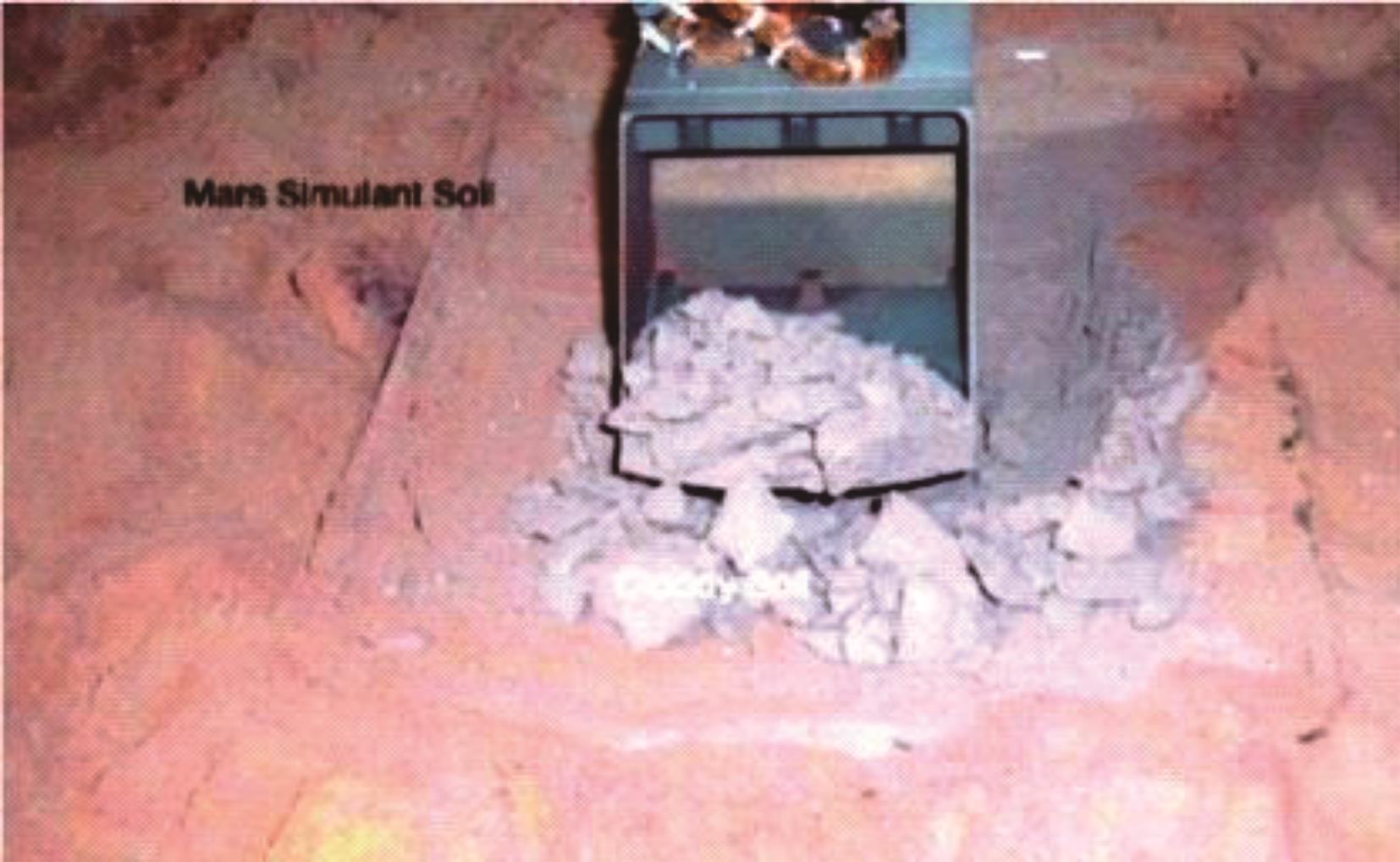
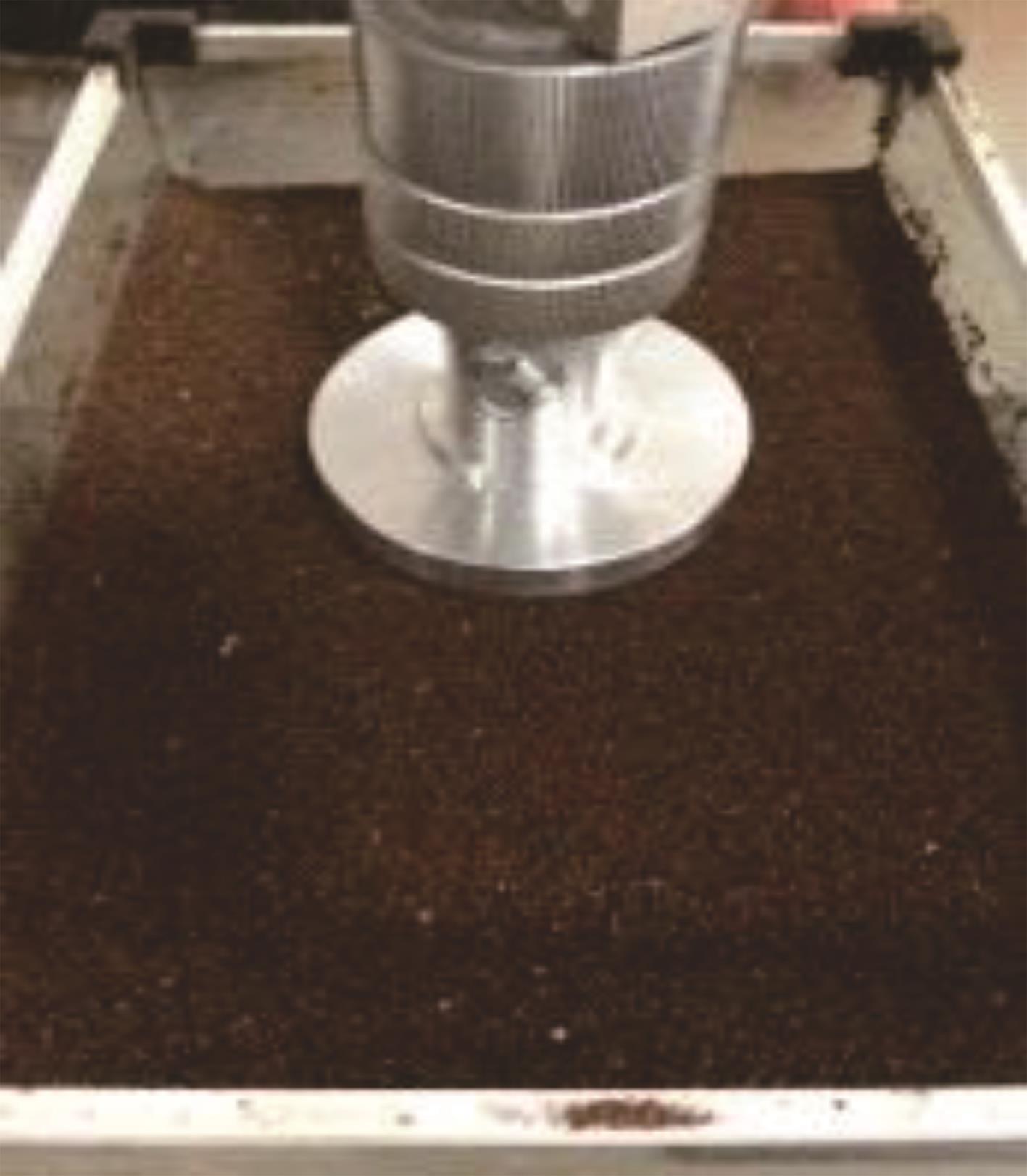
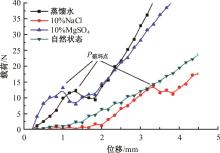
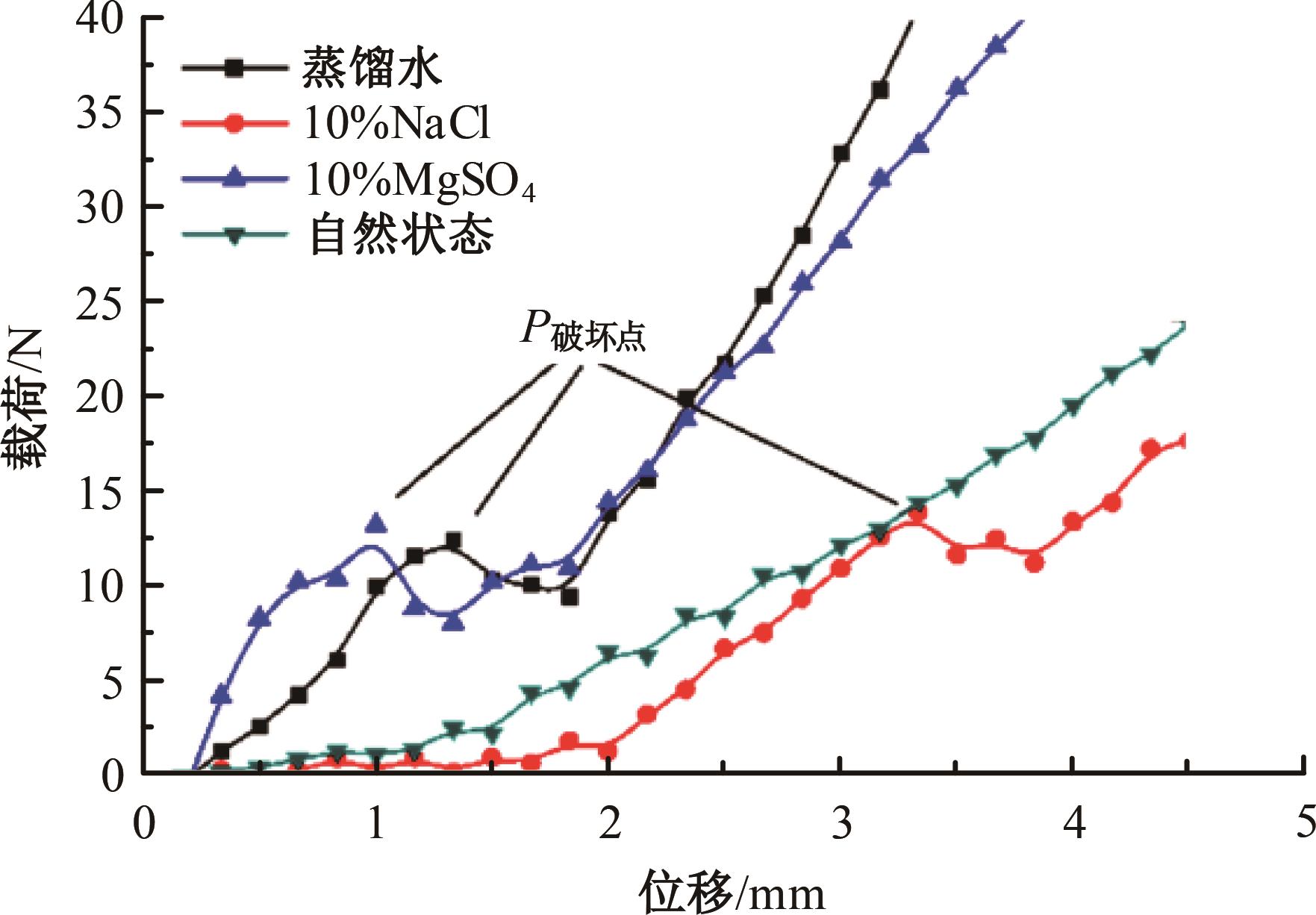
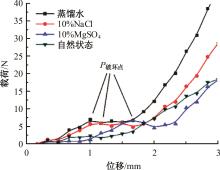
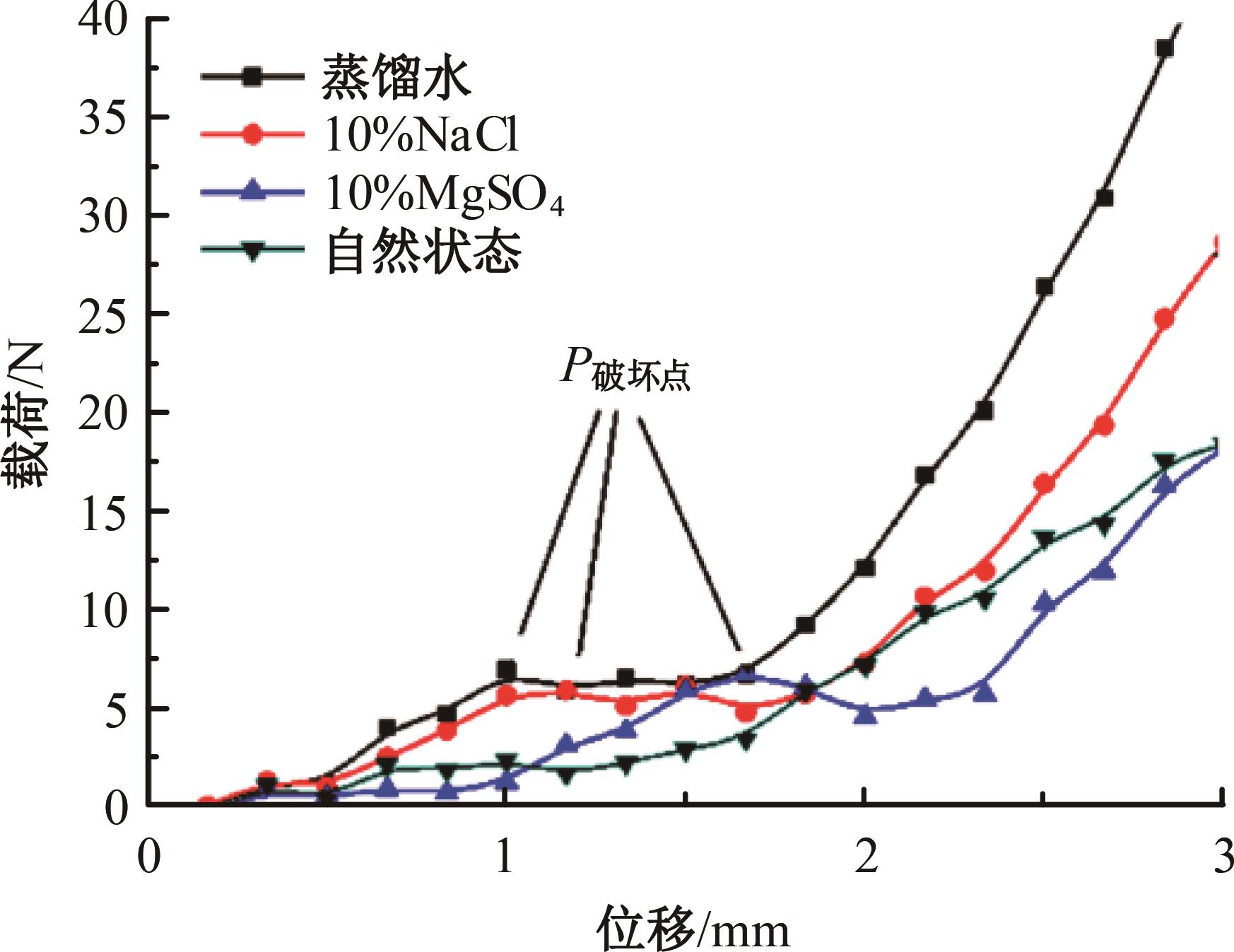
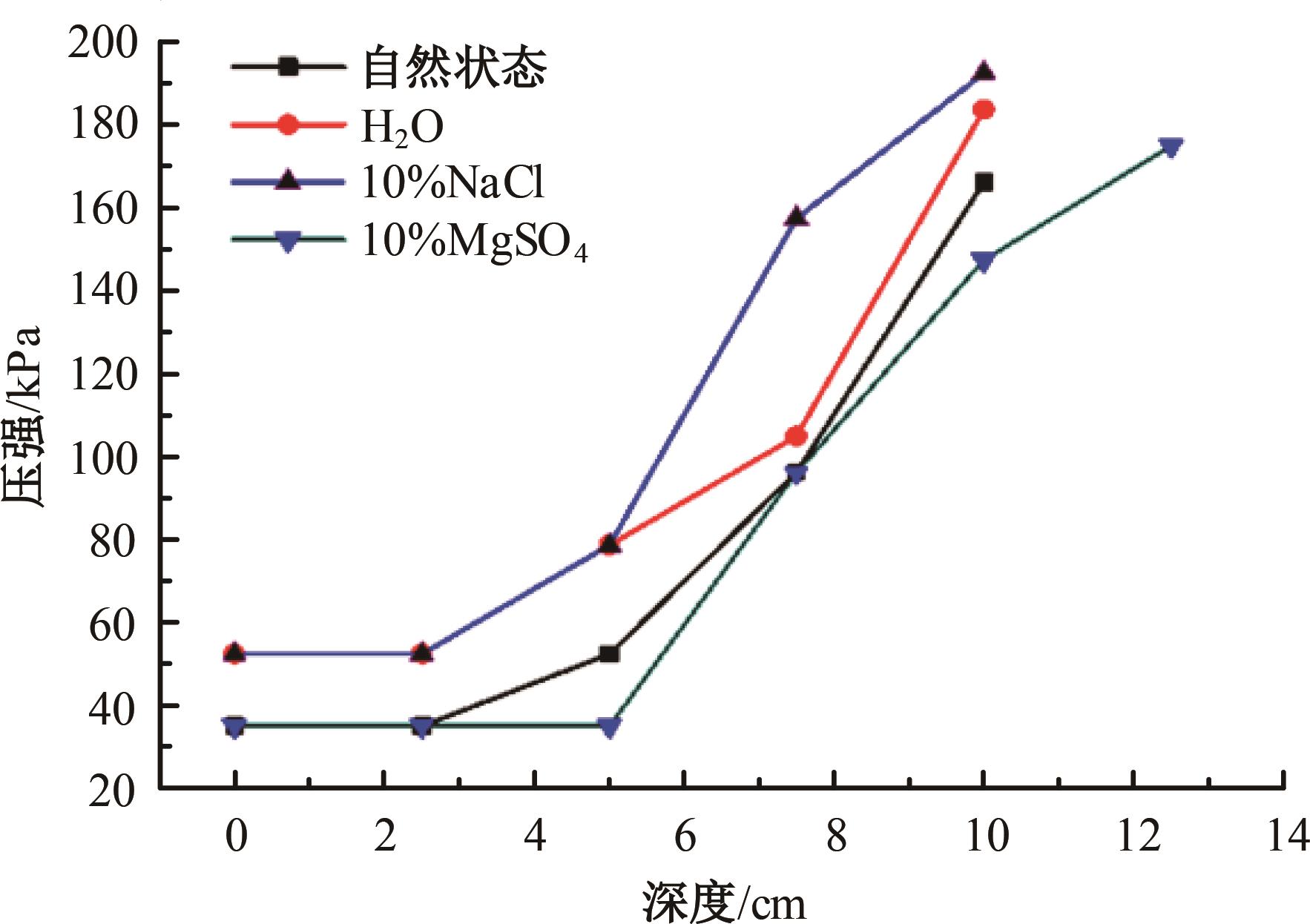
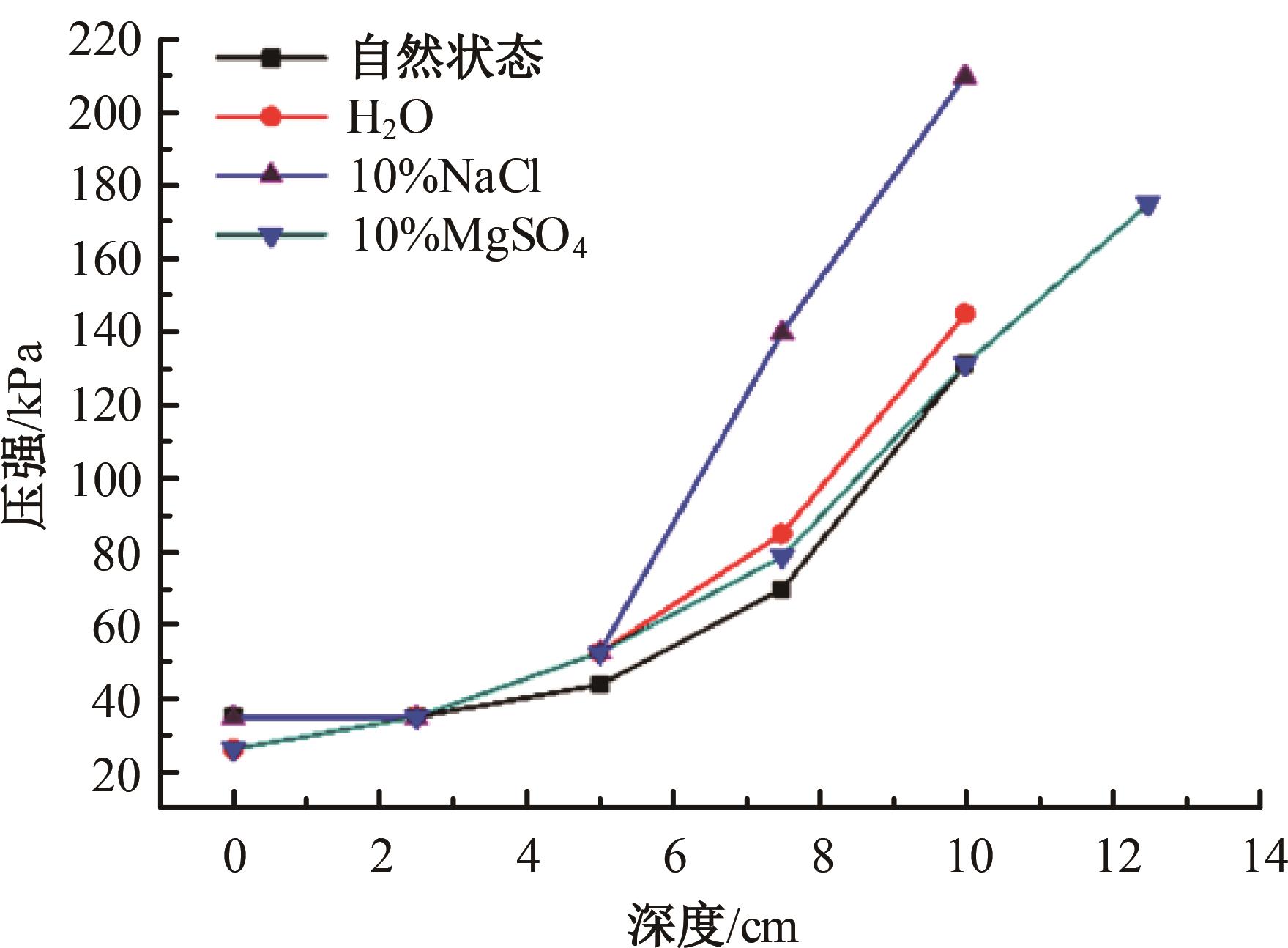
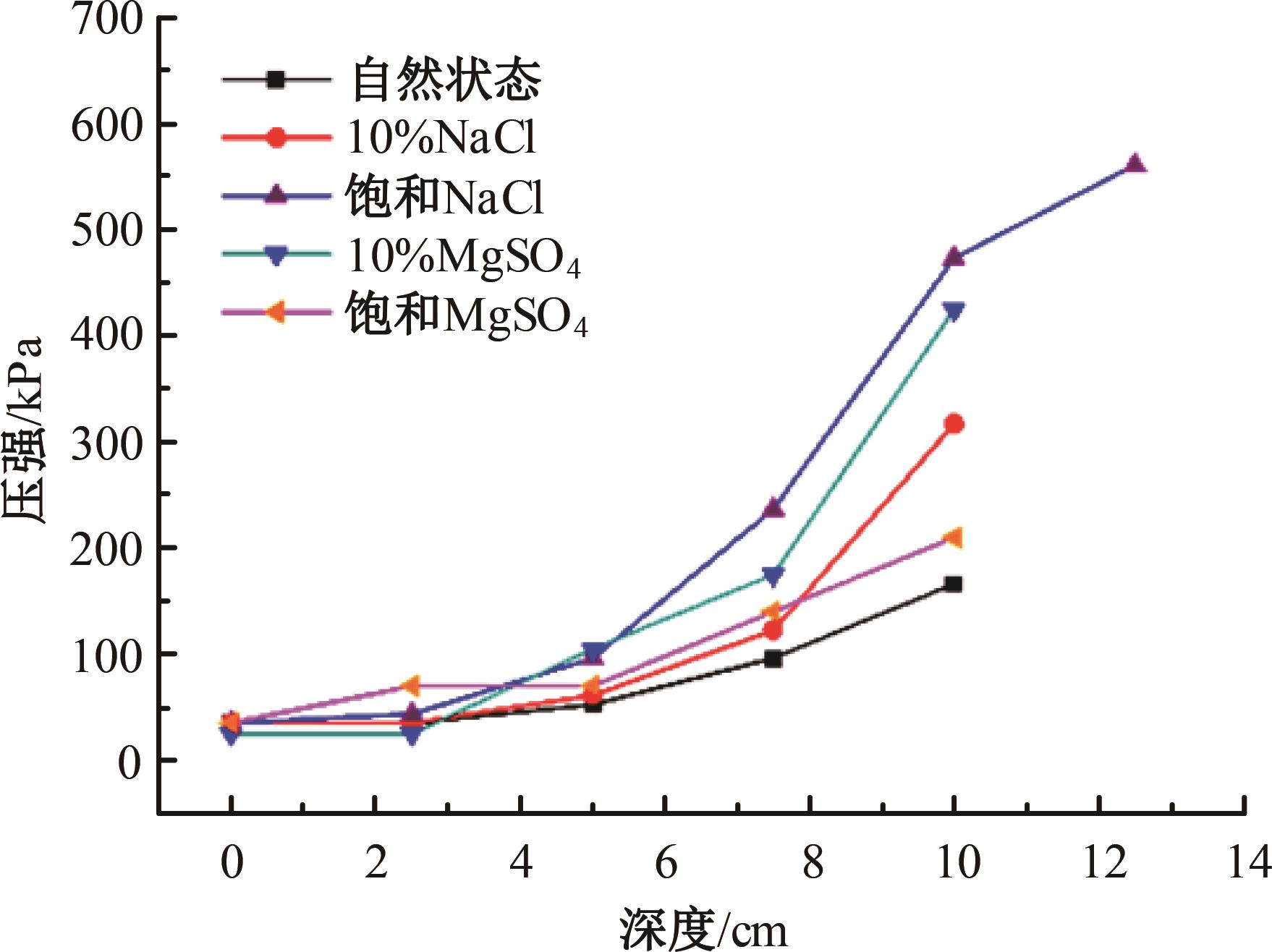
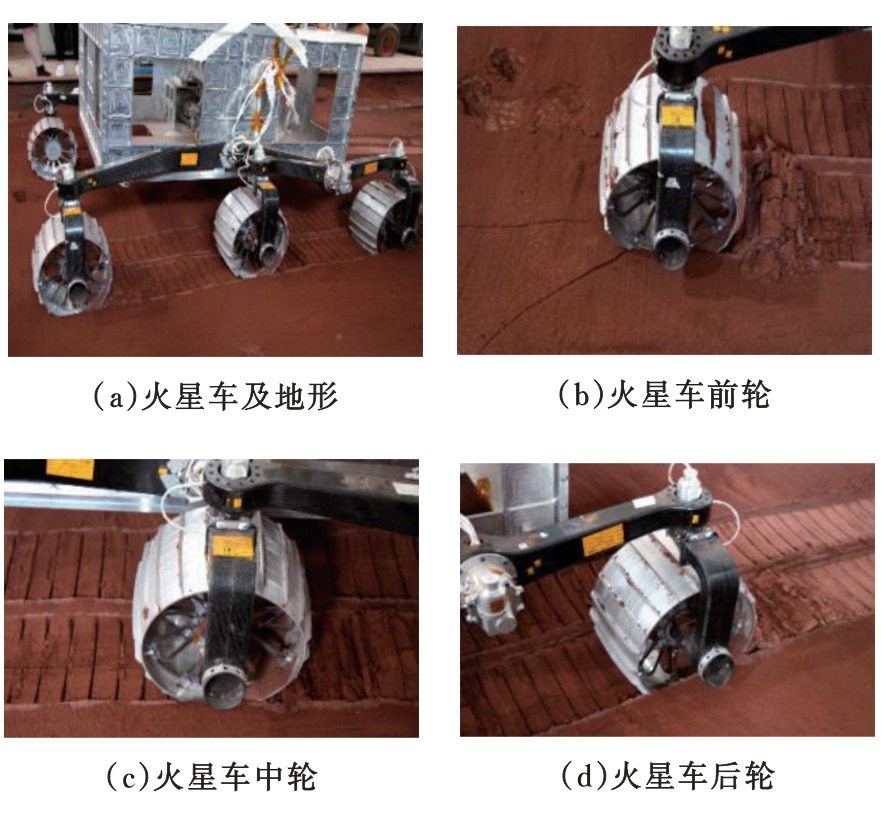
火星表面除松散火壤外,还有一类特别的火壤类型——硬壳类火星地面,该火壤表层为脆性,底层为松软沙粒,对巡视器移动具有迷惑性。研究以Mars-1和Mars-3模拟火壤为对象,通过喷洒蒸馏水、MgSO4和NaCl溶液,自然风干形成硬质土壳结构。对所得土壳进行承压、贯入阻力和火星车通过性试验研究,结果表明:细颗粒Mars-1采用饱和NaCl溶液时结壳效果最好,面积最大且整体性强;粗颗粒的Mars-3采用10%MgSO4溶液时结壳效果最好,面积较小,土壳厚度较厚但易碎。Mars-1结壳速度较Mars-3快。承压特性分析中,Mars-1土壳破坏点峰值载荷随NaCl浓度的提高而降低,随MgSO4浓度的提高而升高。两种土样均采用10%NaCl溶液结壳时,贯入阻力最大。对于Mars-1,贯入阻力随NaCl浓度的增加而增加,随着MgSO4浓度的增加而降低。所制备薄壳地形,满足火星车通过性试验需求。以上研究可为星球车行走机构优化设计和通过性能评估提供参考和依据。
中图分类号:
- V476.4
| 1 | 吴伟仁, 刘旺旺, 唐玉华, 等. 深空探测几项关键技术及发展趋势[J]. 国际太空, 2013, 420(12): 45-51. |
| Wu Wei-ren, Liu Wang-wang, Tang Yu-hua, et al. Development trends of deep space exploration and several key technologies[J]. Space Exploration, 2013, 420(12): 45-51. | |
| 2 | 李超, 董治宝, 吕萍, 等. 火星沙丘地貌的形态学窥究[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(1): 80-90. |
| Li Chao, Dong Zhi-bao, Ping Lyu, et al. A morphological insight into the Martian dune geomorphology[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(1): 80-90. | |
| 3 | Wong J Y. Terr Mechanics and Off-road Vehicles[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1989. |
| 4 | Greeley R, Squyres S W, Arvidson R E, et al. Wind-related processes detected by the spirit rover at gusev crater, mars[J]. Science, 2004, 305: 810-813. |
| 5 | Hannan M, Rickman D, Chavers G, et al. Flight testing of guidance, navigation and control systems on the mighty eagle robotic lander test bed[C]∥ AIAA SciTech 2015, Kissimmee, USA, 2015: 20150002955. |
| 6 | Yuan B, Wang C, Zou M, et al. Experimental study on the durability of China's Mars rover's mobility system[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2021, 34(5): 0001292. |
| 7 | Team R. Characterization of the martian surface deposits by the Mars pathfinder rover, sojourner[J]. Science, 1997, 278: 1765-1768. |
| 8 | Sheehan W, Bell J. Discovering Mars: a history of observation and exploration of the red planet[J]. University of Arizona Press, 2021, 2: 102307. |
| 9 | 蒋明镜, 戴永生, 张熇, 等. TJ-1 模拟月壤承载特性的现场试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(6): 1529-1535. |
| Jiang Ming-jing, Dai Yong-sheng, Zhang He, et al. Field experimental research on bearing properties of TJ-1 lunar soil simulant[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(6): 1529-1535. | |
| 10 | Hudson T L, Aharonson O. Diffusion barriers at Mars surface conditions: salt crusts, particle size mixtures, and dust[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2008, 113(9): 003026. |
| 11 | 薛龙,党兆龙,陈百超,等. 面向火星着陆器 缓冲试验的模拟火壤力学特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(1): 176-186. |
| Xue Long, Dang Zhao-long, Chen Bai-chao, et al. Terra-mechanics of Mars soil for martian lander's landing tests[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 176-186. | |
| 12 | 李建桥,薛龙,邹猛,等.已有模拟火壤力学性质分析及新火星壤研制[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版,2016, 46(1): 172-178. |
| Li Jian-qiao, Xue Long, Zou Meng, et al. Terra-mechanics characters and development of martian simulant regolith[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(1): 172-178. | |
| 13 | Westall F, Coates A J, Korablev O, et al. Habitability on early Mars and the search for biosignatures with the exomars rover[J]. Astrobiology, 2017, 17(6/7): 471-510. |
| 14 | Sullivan R, Anderson R, Biesiadecki J, et al. Cohesions, friction angles, and other physical properties of martian regolith from Mars exploration rover wheel trenches and wheel scuffs[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2011, 116(2): 2010JE02006. |
| [1] | 于征磊,信仁龙,陈立新,朱奕凝,张志辉,曹青,金敬福,赵杰亮. 仿蜂窝防护结构的承载特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1140-1145. |
|