吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 1140-1145.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200056
• 农业工程·仿生工程 • 上一篇
仿蜂窝防护结构的承载特性
于征磊1,2( ),信仁龙2,陈立新2,朱奕凝3,张志辉2,曹青2,金敬福2(
),信仁龙2,陈立新2,朱奕凝3,张志辉2,曹青2,金敬福2( ),赵杰亮4
),赵杰亮4
- 1.吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
2.吉林大学 工程仿生教育部重点实验室,长春 130022
3.延边大学 农学院,吉林 延吉 133002
4.北京理工大学 机械与车辆学院,北京 100081
Load bearing characteristics of honeycomb protection structure
Zheng-lei YU1,2( ),Ren-long XIN2,Li-xin CHEN2,Yi-ning ZHU3,Zhi-hui ZHANG2,Qing CAO2,Jing-fu JIN2(
),Ren-long XIN2,Li-xin CHEN2,Yi-ning ZHU3,Zhi-hui ZHANG2,Qing CAO2,Jing-fu JIN2( ),Jie-liang ZHAO4
),Jie-liang ZHAO4
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
3.Agriculture College,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
4.Department of Mechanical Engineering,Beijing Institute of Technology,Beijing 100081,China
摘要:
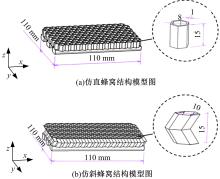
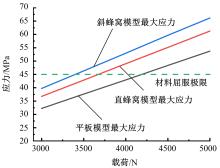
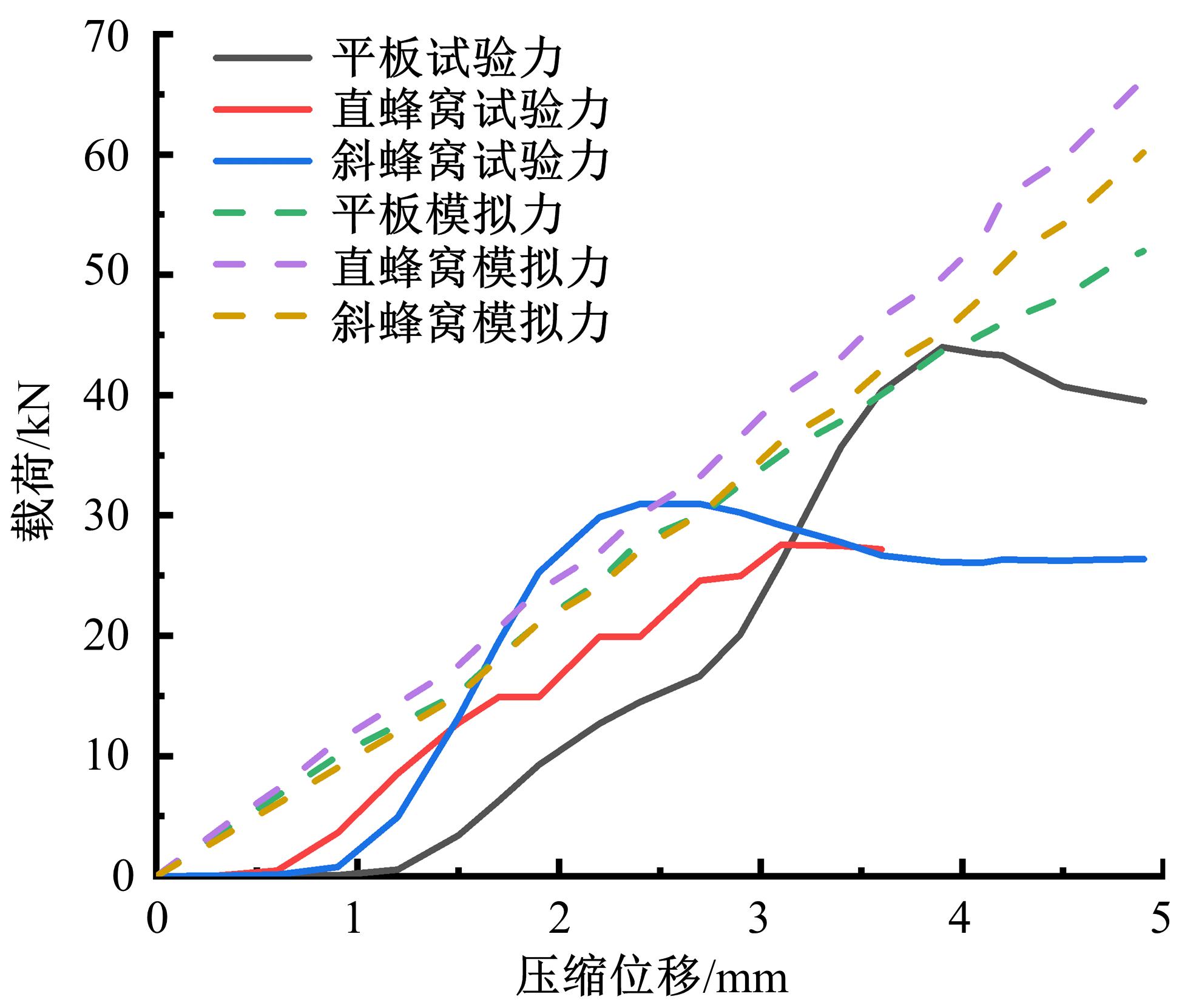
为满足对结构安全方面的要求,本文借鉴蜂窝结构强度比高、力学性能优异的特性,运用结构仿生学原理设计并建立了简化的仿直蜂窝、仿斜蜂窝和平板结构3种模型。在5种不同工况下利用有限元分析软件OptiStruct对3种模型进行了承载特性分析,运用3D打印技术制备3种模型,并对样件进行力学特性试验。根据模拟结果与试验数据对比分析得到以下结论:仿斜蜂窝结构各位置的应力数值相近,仿斜蜂窝具有良好力学传导特性;在相同质量情况下,仿斜蜂窝结构的承载能力较仿直蜂窝结构提高12%,较平板结构提高150%,其承载能力有着较大的优势,所以仿斜蜂窝结构较为合理。本文的研究实现了对仿蜂窝结构的承载性能分析,为防护结构轻量化设计提供了参考。
中图分类号:
- TB17
| 1 | 王显会, 师晨光, 周云波, 等. 车辆底部防护蜂窝夹层结构抗冲击性能分析[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2016, 36(11): 1122-1126. |
| Wang Xian-hui, Shi Chen-guang, Zhou Yun-bo, et al. Analysis on impact resistance of honeycomb sandwich structure for vehicle bottom protection[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016, 36(11): 1122-1126. | |
| 2 | 崔岸, 刘芳芳, 张晗, 等. 车身泡沫填充铝合金波纹夹芯板结构性能分析与优化[J]. 汽车工程, 2019, 41(10): 1221-1227. |
| Cui An, Liu Fang-fang, Zhang Han, et al. Structural performance analysis and optimization of aluminum body foam filled corrugated sandwich plate [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2019, 41(10): 1221-1227. | |
| 3 | Mamalis A G, Manolakos D, Ioannidis M, et al. On the experimental investigation of crash energy absorption inlaminate splaying collapse mode of FRP tubular components[J]. Composite Structure, 2015, 70(4): 413-429. |
| 4 | 吴娜,庄健,张克松,等. 毛蚶贝壳曲面承压力学特性及断裂机理 [J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(3): 897-902. |
| Wu Na, Zhuang Jian, Zhang Ke-song, et al. Compression mechanical properties and fracture mechanism of Scapharca Subcrenata shell[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019,49(3):897-902. | |
| 5 | 于征磊,郭雪,董新桔,等. 基于NiTi合金的仿生防护结构自恢复特性 [J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(3): 1138-1143. |
| Yu Zheng-lei, Guo Xue, Dong Xin-ju, et al. Restore characteristics of NiTi alloy bionics protective self⁃repairing structure[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(3): 1138-1143. | |
| 6 | Hong S, Pan J, Tyan T, et al. Quasi-static crush behavior of aluminum honeycomb specimens under compression dominant combined loads[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2005, 22(1): 73-109. |
| 7 | Wang Zhong-gang. Recent advances in novel metallic honeycomb structure[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 166: 731-741. |
| 8 | 高旭. 塑料蜂窝夹层结构抗弯性能研究与优化[D]. 大连:大连理工大学汽车工程学院, 2018. |
| Gao Xu. Study and optimization of flexural resistance of plastic honeycomb sandwich structure[D]. Dalian: School of Automotive Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 9 | Wang Zhong-gang, Yao Shu-guang, Lu Zhai-jun, et al. Matching effect of honeycomb-filled thin-walled square tube-experiment and simulation[J]. Composite Structure, 2016, 157: 494-505. |
| 10 | Zhu Guo-hua, Li Shun-feng, Sun Guang-yong, et al. On design of graded honeycomb filler andtubal wall thickness for multiple load cases[J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2016, 109: 377-389. |
| 11 | Thomas E L, Youngkeun H. Numerical modeling of impact-damaged sandwich composites subjected to compression-after-impact loading[J]. Composite Structure, 2003, 61(1): 115-128. |
| 12 | Cricrì G, Perrella M, Calì C. Honeycomb failure processes under in-plane loading[J]. Composites Part B, 2013, 45(1): 1079-1090. |
| 13 | Hu Ling-ling, You Fan-fan, Yu Tong-xi. Effect of cell-wall angle on the in-plane crushing behaviour of hexagonal honeycombs[J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 46: 511-523. |
| 14 | Zhang Yong, Chen Teng-teng, Xu Xiang, et al. Out-of-plane mechanical behaviors of a side hierarchical honeycomb[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2020, 140: 1-15. |
| 15 | 蔡云冰, 刘志鹏. 张子龙,等. 聚乳酸材料在3D打印中的研究与应用进展[J]. 应用化工, 2019, 48(6): 1463-1468. |
| Cai Yun-bing, Liu Zhi-peng, Zhang Zi-long, et al. Research and application progress of polylactic acid materials in 3D printing[J]. Applied Chemical Engineering, 2019, 48(6): 1463-1468. |
| [1] | 苏畅,韩颖,张英朝,苗振华. 轮辐设计特征参数对整车气动特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 107-113. |
| [2] | 谷诤巍,陈琳,赵立辉,徐虹,李欣,于歌. 轨道车辆窗下补强板冲压成形模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 504-511. |
| [3] | 陈鑫,王宁,沈传亮,冯晓,杨昌海. 后视镜造型对前侧窗气动噪声的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 426-436. |
| [4] | 曲兴田,王学旭,孙慧超,张昆,闫龙威,王宏一. 熔融沉积成型技术3D打印机加热系统的模糊自适应PID控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 77-83. |
| [5] | 刘春宝,陈山石,盛闯,钱志辉,任露泉,任雷. 蜘蛛生物液压驱动原理及其功能仿生探索[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 375-381. |
| [6] | 施卫平,赵旭,胡兴军,余天明,柳博文,段彦. 天然气开采阻水装置AICD的设计和数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1986-1991. |
| [7] | 宫亚峰,王博,谭国金,张立敏,吴文丁,毕海鹏. 吉林省两种典型装配式箱涵受力特性对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1865-1870. |
| [8] | 依卓,付文智,李明哲. 双层剖分式超高压模具数值模拟及实验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1593-1599. |
| [9] | 李欣,孙延朋,王丹,陈军绪,谷诤巍,徐虹. 汽车前地板成形有限元数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1608-1614. |
| [10] | 陈东良,臧睿,段鹏,赵伟鹏,翁旭涛,孙杨,唐艺鹏. 基于新月鱼尾推进理论的多连杆鱼骨仿生设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1246-1257. |
| [11] | 李欣,王丹,陈军绪,孙延朋,谷诤巍,徐虹. 手刹固定板冲压成形数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1258-1265. |
| [12] | 张学广,贾明萌,刘纯国,何广忠. 基于增量控制的型材拉弯轨迹设计及有限元仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1272-1279. |
| [13] | 吴娜,庄健,张克松,王慧鑫,马云海. 毛蚶贝壳曲面承压力学特性及断裂机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 897-902. |
| [14] | 郭昊添,徐涛,梁逍,于征磊,刘欢,马龙. 仿鲨鳃扰流结构的过渡段换热表面优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1793-1798. |
| [15] | 熙鹏,丛茜,王庆波,郭华曦. 仿生条纹形磨辊磨损试验及耐磨机理分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1787-1792. |
|
||