吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 268-277.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180801
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
光照变化下基于低秩稀疏表示的视觉跟踪方法
- 1. 大连大学 信息工程学院,辽宁 大连 116622
2. 泉州信息工程学院 电子与通信工程学院,福建 泉州362000
Visual tracking method based on low⁃rank sparse representation under illumination change
Hong-yan WANG1( ),He-lei QIU1,Jia ZHENG1,Bing-nan PEI2
),He-lei QIU1,Jia ZHENG1,Bing-nan PEI2
- 1. College of Information Engineering, Dalian University, Dalian 116622, China
2. College of Electronic and Communication Engineering, Quanzhou University of Information Engineering, Quanzhou 362000, China
摘要:
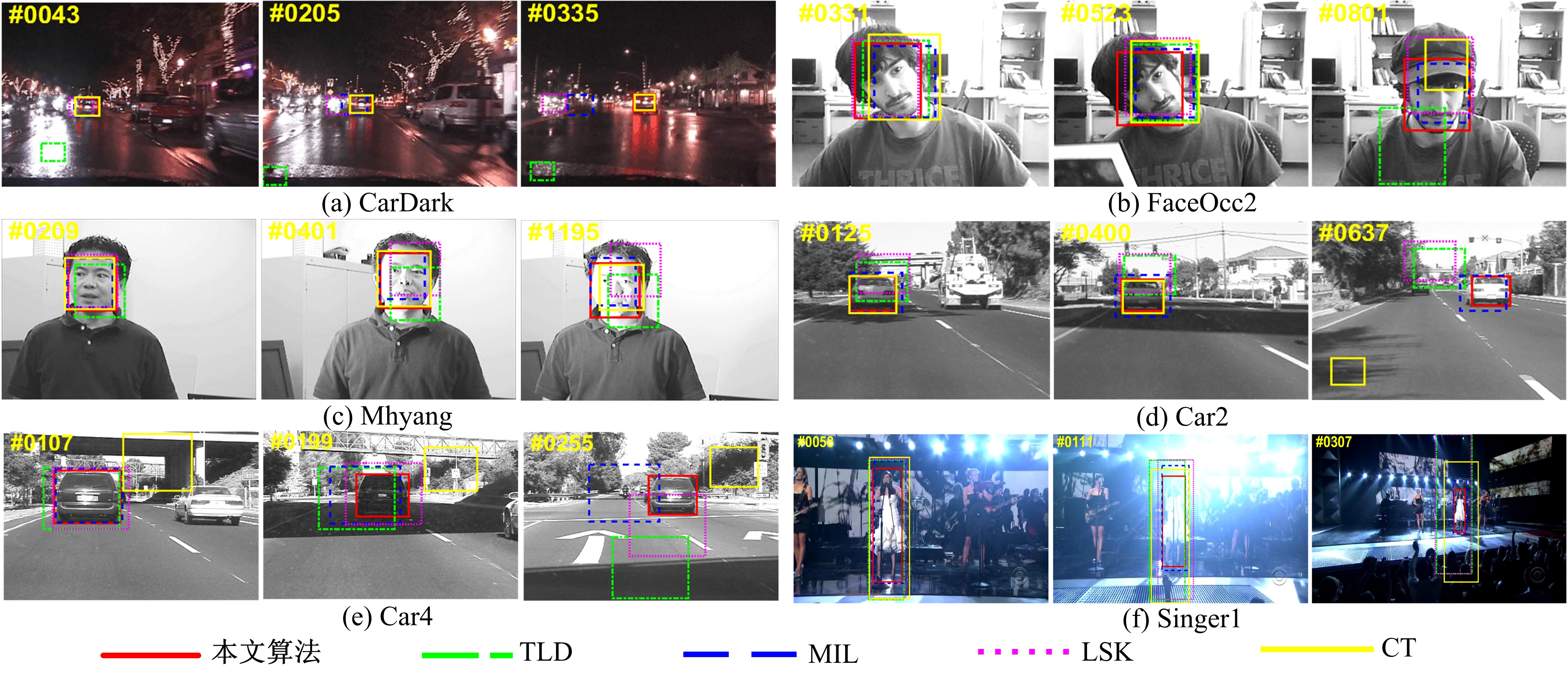
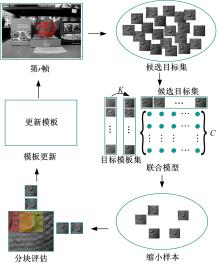
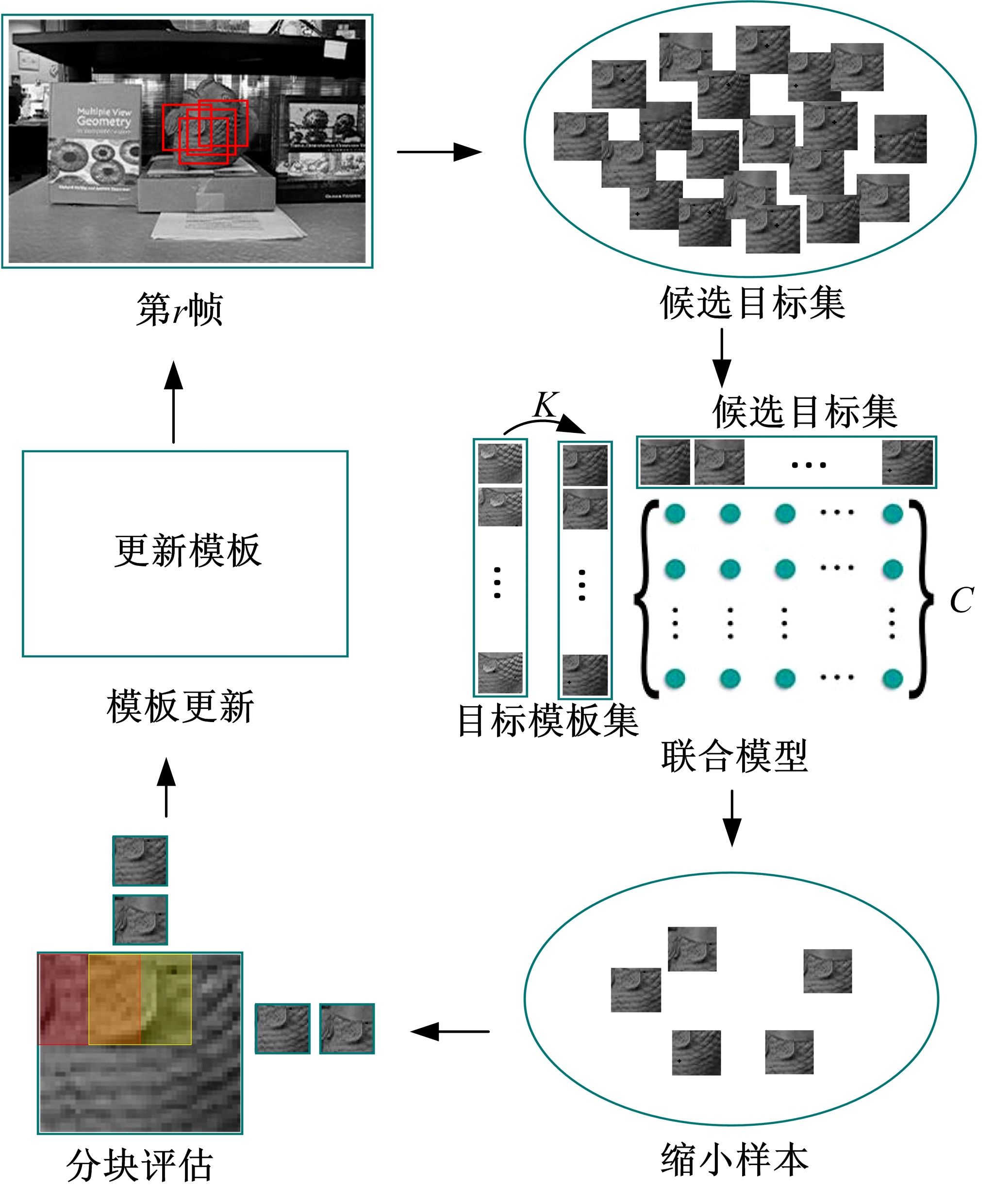
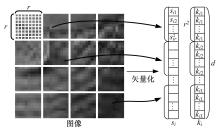
针对光照变化引起目标跟踪性能显著下降的问题,提出一种光照补偿和低秩稀疏表示联合优化的视觉跟踪方法。该方法首先基于模板与候选目标的平均亮度差异对模板光照补偿;而后利用候选目标逆向稀疏表示模板,并考虑候选目标间相似性以对稀疏编码矩阵实施低秩约束,且包含稀疏误差项以提高算法对局部遮挡的稳健性,从而获得光照补偿和低秩稀疏表示联合优化模型;最后,基于该模型所得稀疏编码矩阵快速剔除无关候选目标,并采用局部结构化评估方法实现目标精确跟踪。仿真结果表明,与现有主流算法相比,剧烈光照变化情况下,本文方法可显著改善目标跟踪精度及鲁棒性。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Fradi H, Luvison B, Pham Q C. Crowd behavior analysis using local mid-level visual descriptors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2017, 27(3): 589-602. |
| 2 | Yu G, Li C, Shang Z Y. Video monitoring method, video monitoring system and computer program product[P]. US:9792505, 2017-10-17. |
| 3 | Ueng S K, Chen G Z. Vision based multi-user human computer interaction[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2016, 75(16): 10059-10076. |
| 4 | Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M H. Object tracking benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834-1848. |
| 5 | Pan Z, Liu S, Fu W. A review of visual moving target tracking[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 76(16): 16989-17018. |
| 6 | 李根, 李文辉. 基于思维进化算法的人脸特征点跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2015, 45(2): 606-612. |
| Li Gen, Li Wen-hui. Facial feature tracking based on mind evolutionary algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(2): 606-612. | |
| 7 | 才华, 陈广秋, 刘广文, 等. 遮挡环境下多示例学习分块目标跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017, 47(1): 281-287. |
| Cai Hua, Chen Guang-qiu, Liu Guang-wen, et al. Novelty fragments-based target tracking with multiple instance learning under occlusions[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(1): 281-287. | |
| 8 | Wright J, Yang A Y, Ganesh A, et al. Robust face recognition via sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 31(2): 210-227. |
| 9 | Zhang J, Zhao D, Gao W. Group-based sparse representation for image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(8): 3336-3351. |
| 10 | Mei X, Ling H. Robust visual tracking using ℓ1 minimization[C]∥IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 2009: 1436-1443. |
| 11 | Xiao Z, Lu H, Wang D. Object tracking with L2-RLS[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Tsukuba, Japan, 2012: 1351-1354. |
| 12 | Zhang T, Liu S, Ahuja N, et al. Robust visual tracking via consistent low-rank sparse learning[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 111(2): 171-190. |
| 13 | He Z, Yi S, Cheung Y M, et al. Robust object tracking via key patch sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(2): 354-364. |
| 14 | Silveira G, Malis E. Real-time visual tracking under arbitrary illumination changes[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, USA, 2007: 1-6. |
| 15 | Nhat V Q, Lee G. Illumination invariant object tracking with adaptive sparse representation[J]. International Journal of Control Automation and Systems, 2014, 12(1): 195-201. |
| 16 | Jenkins M D, Barrie P, Buggy T, et al. Selective sampling importance resampling particle filter tracking with multibag subspace restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(1): 264-276. |
| 17 | Delail B A, Bhaskar H, Zemerly M J, et al. Robust likelihood model for illumination invariance in particle filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2018, 28(10): 2836-2848. |
| 18 | Sui Y, Zhang L. Robust tracking via locally structured representation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2016, 119(2): 110-144. |
| 19 | Zhang K, Zhang L, Yang M H. Real-time compressive tracking[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 864-877. |
| 20 | Peng Y, Ganesh A, Wright J, et al. RASL: robust alignment by sparse and low-rank decomposition for linearly correlated images[J]. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2010: 763-770. |
| 21 | Polson N, Sokolov V. Bayesian particle tracking of traffic flows[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(2): 345-356. |
| 22 | Ross D A, Lim J, Lin R S, et al. Incremental learning for robust visual tracking[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2008, 77(1-3): 125-141. |
| 23 | Jia X, Lu H, Yang M H. Visual tracking via coarse and fine structural local sparse appearance models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(10): 4555-4564. |
| 24 | Kalal Z, Matas J, Mikolajczyk K. P-N learning: Bootstrapping binary classifiers by structural constraints[C]∥IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 49-56. |
| 25 | Babenko B, Yang M H, Belongie S. Visual tracking with online multiple instance learning[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 983-990. |
| 26 | Liu B, Huang J, Yang L, et al. Robust tracking using local sparse appearance model and K-selection[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2011: 1313-1320. |
| [1] | 张笑东,夏筱筠,吕海峰,公绪超,廉梦佳. 大数据网络并行计算环境中生理数据流动态负载均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 247-254. |
| [2] | 邓钧忆,刘衍珩,冯时,赵荣村,王健. 基于GSPN的Ad⁃hoc网络性能和安全平衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 255-261. |
| [3] | 李雄飞,王婧,张小利,范铁虎. 基于SVM和窗口梯度的多焦距图像融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 227-236. |
| [4] | 周炳海,吴琼. 考虑工具和空间约束的机器人装配线平衡优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2069-2075. |
| [5] | 车翔玖,刘华罗,邵庆彬. 基于Fast RCNN改进的布匹瑕疵识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2038-2044. |
| [6] | 赵宏伟,王鹏,范丽丽,胡黄水,刘萍萍. 相似性保持实例检索方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2045-2050. |
| [7] | 沈军,周晓,吉祖勤. 服务动态扩展网络及其结点系统模型的实现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2058-2068. |
| [8] | 周柚,杨森,李大琳,吴春国,王岩,王康平. 基于现场可编程门电路的人脸检测识别加速平台[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2051-2057. |
| [9] | 李宾,周旭,梅芳,潘帅宁. 基于K-means和矩阵分解的位置推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1653-1660. |
| [10] | 李雄飞,宋璐,张小利. 基于协同经验小波变换的遥感图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1307-1319. |
| [11] | 刘元宁,刘帅,朱晓冬,霍光,丁通,张阔,姜雪,郭书君,张齐贤. 基于决策粒子群优化与稳定纹理的虹膜二次识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1329-1338. |
| [12] | 李宾,申国君,孙庚,郑婷婷. 改进的鸡群优化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1339-1344. |
| [13] | 翟凤文,党建武,王阳萍,金静,罗维薇. 基于扩展轮廓的快速仿射不变特征提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1345-1356. |
| [14] | 孙延君,申铉京,陈海鹏,赵永哲. 基于局部平面线性点的翻拍图像鉴别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1320-1328. |
| [15] | 王楠,李金宝,刘勇,张玉杰,钟颖莉. TPR⁃TF:基于张量分解的时间敏感兴趣点推荐模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 920-933. |
|
||