吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1506-1517.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200247
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
负载型四足步行平台对角步态重量自适应行走控制
- 1.北京特种工程设计研究院,北京 100028
2.陆军装甲兵学院 车辆工程系,北京 100072
3.北京特种车辆研究所,北京 100072
Weight adaptive control for trotting gait of load-carrying quadruped walking vehicle
Yong-ying TAN1( ),Shan-zhen YI1,Da-bing XUE2,Xiao-ming WANG1,Lei YUAN3
),Shan-zhen YI1,Da-bing XUE2,Xiao-ming WANG1,Lei YUAN3
- 1.Beijing Special Engineering and Design Institute,Beijing 100028,China
2.Department of Automobile Engineering,Academy of Army Armored Forces,Beijing 100072,China
3.Beijing Special Vehicle Research Institute,Beijing 100072,China
摘要:
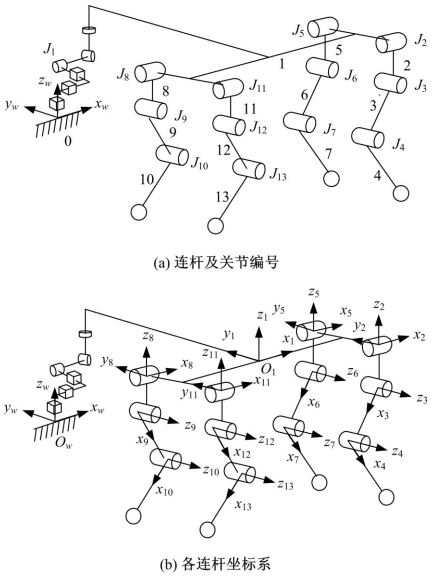
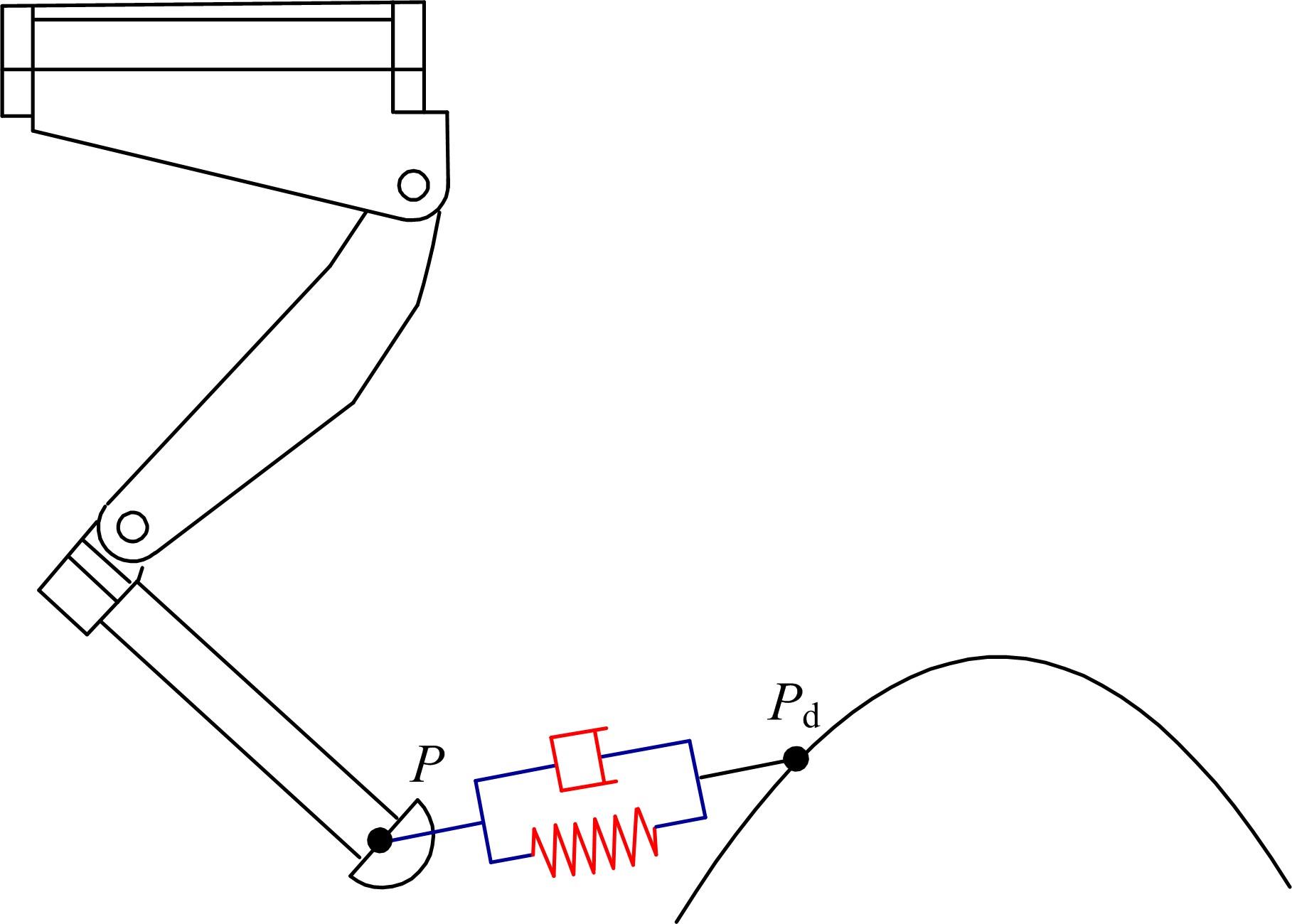
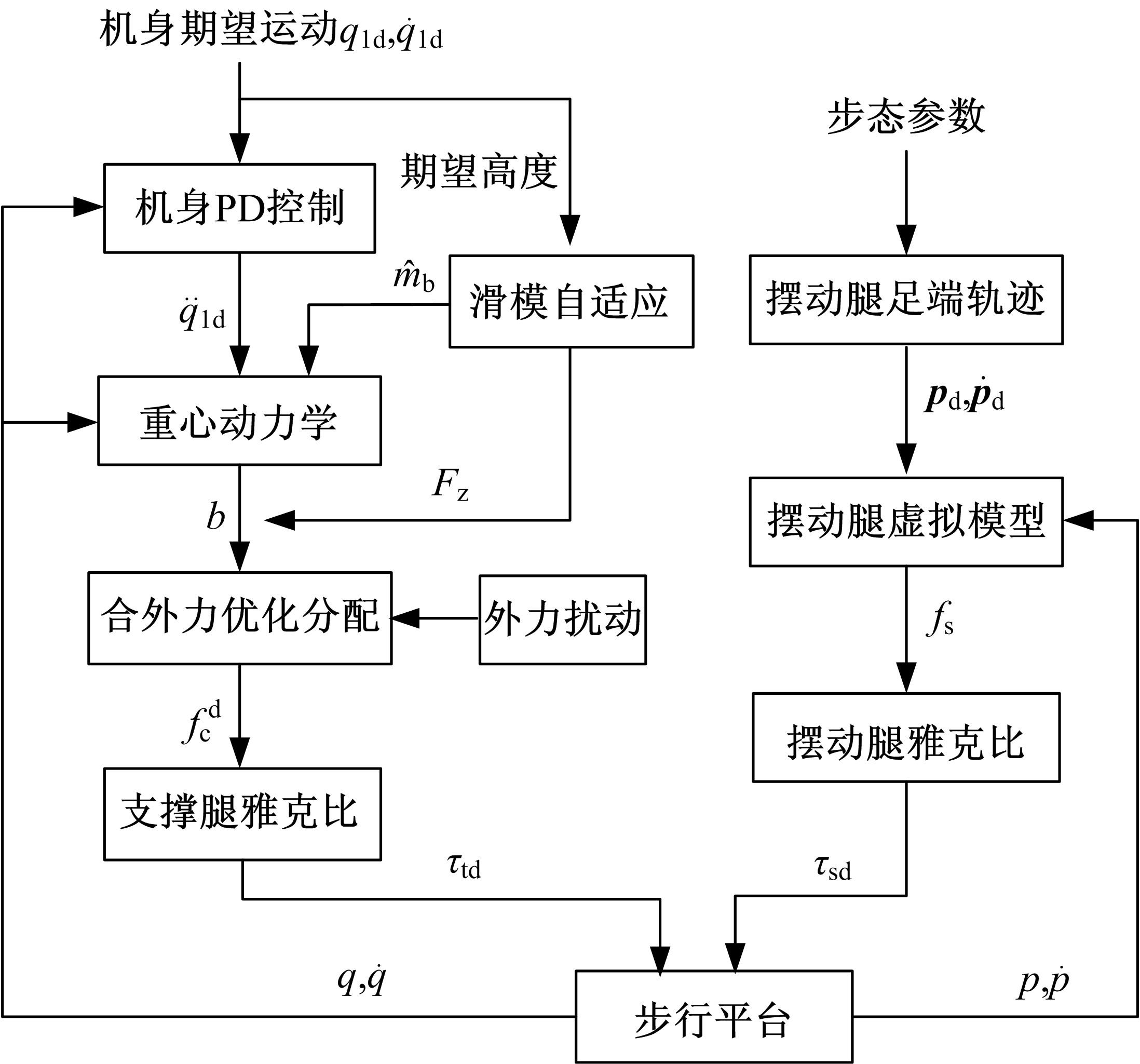
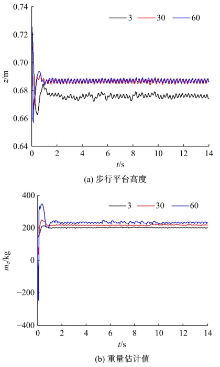
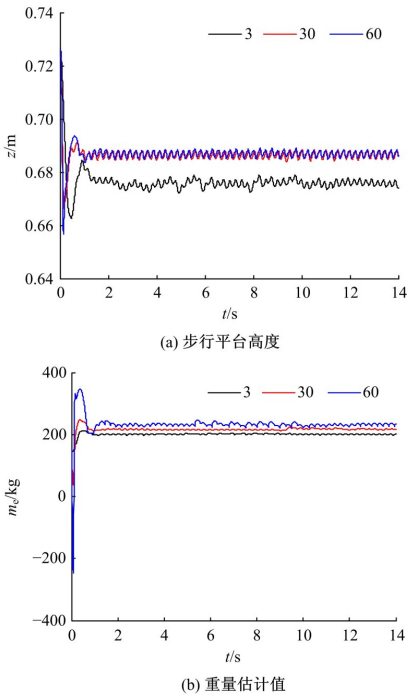
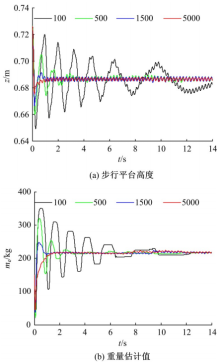
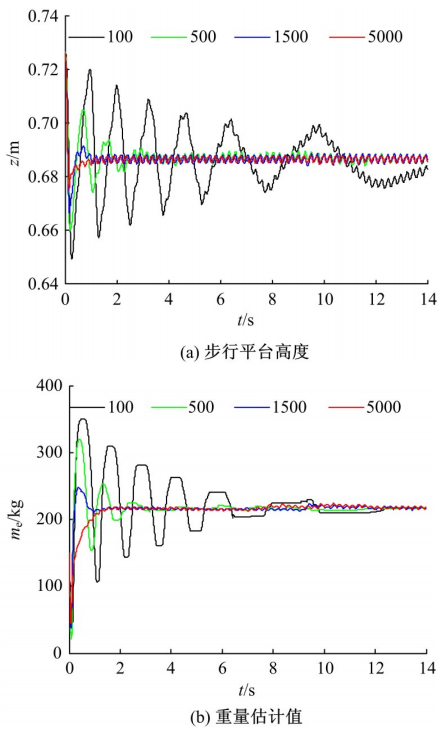
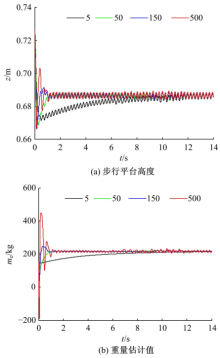
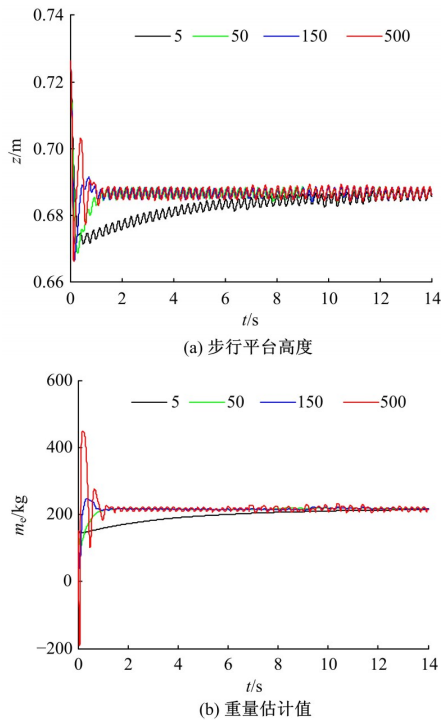
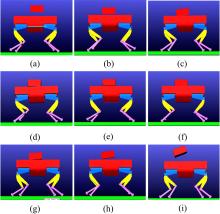
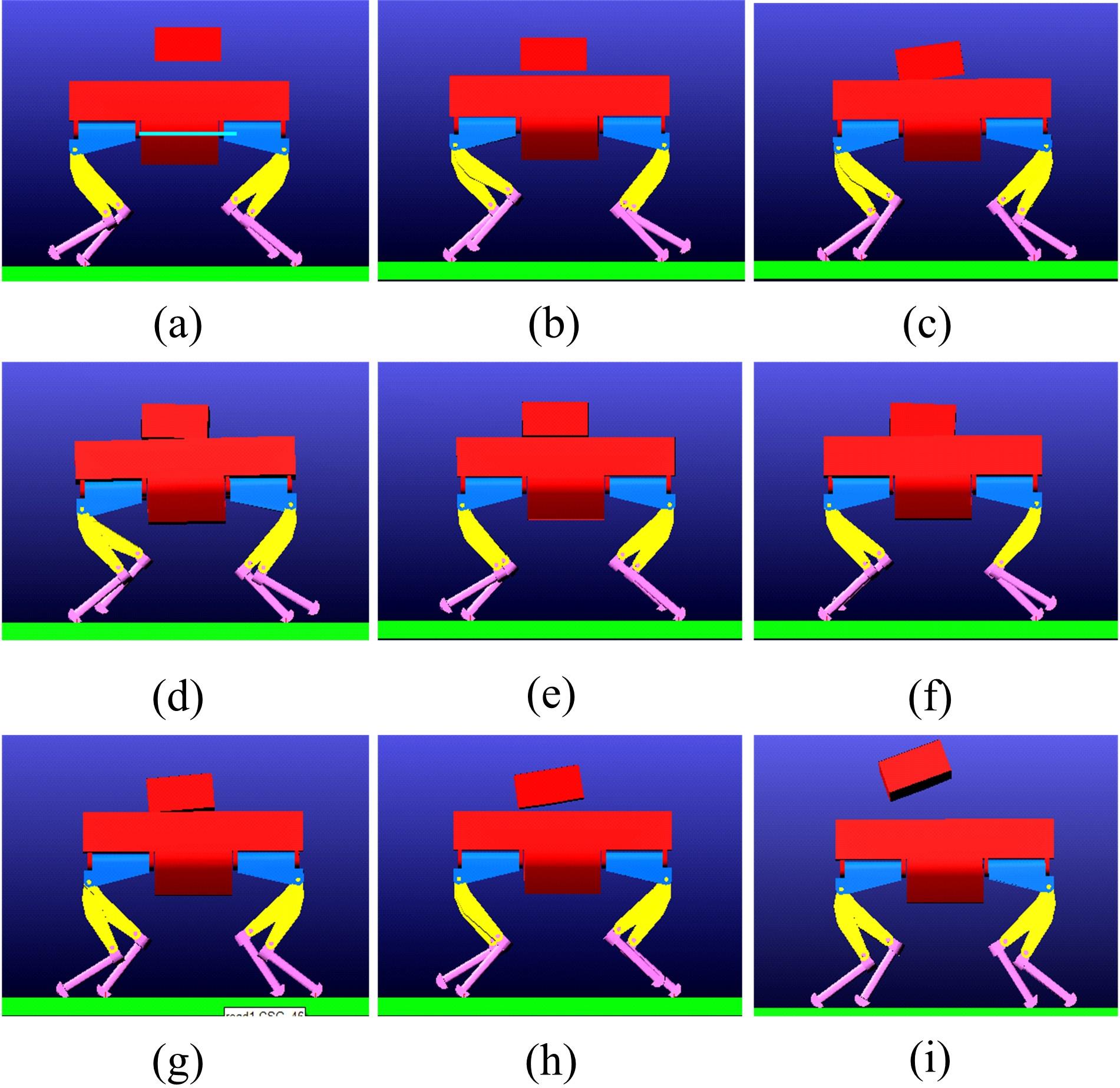
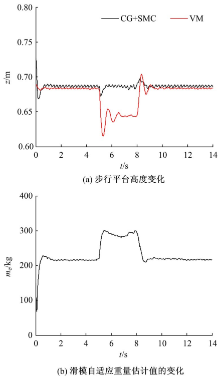
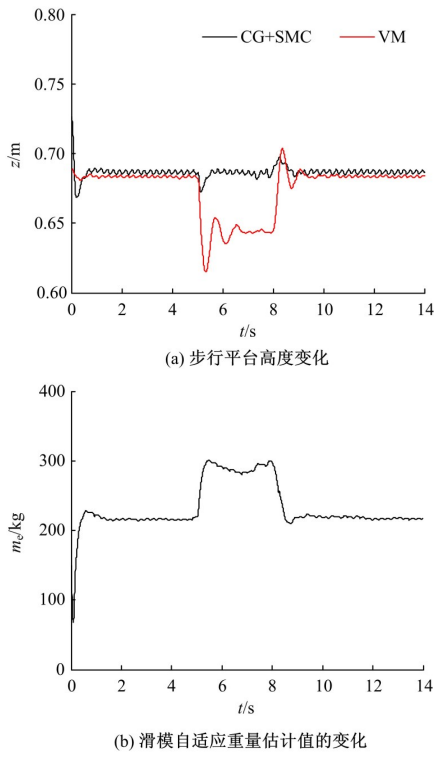
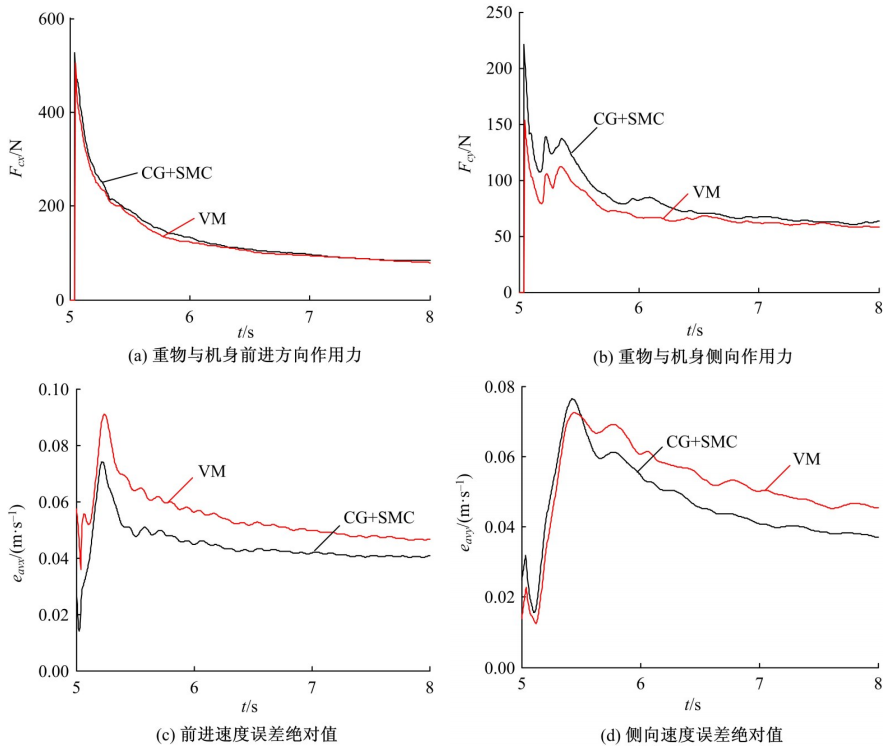
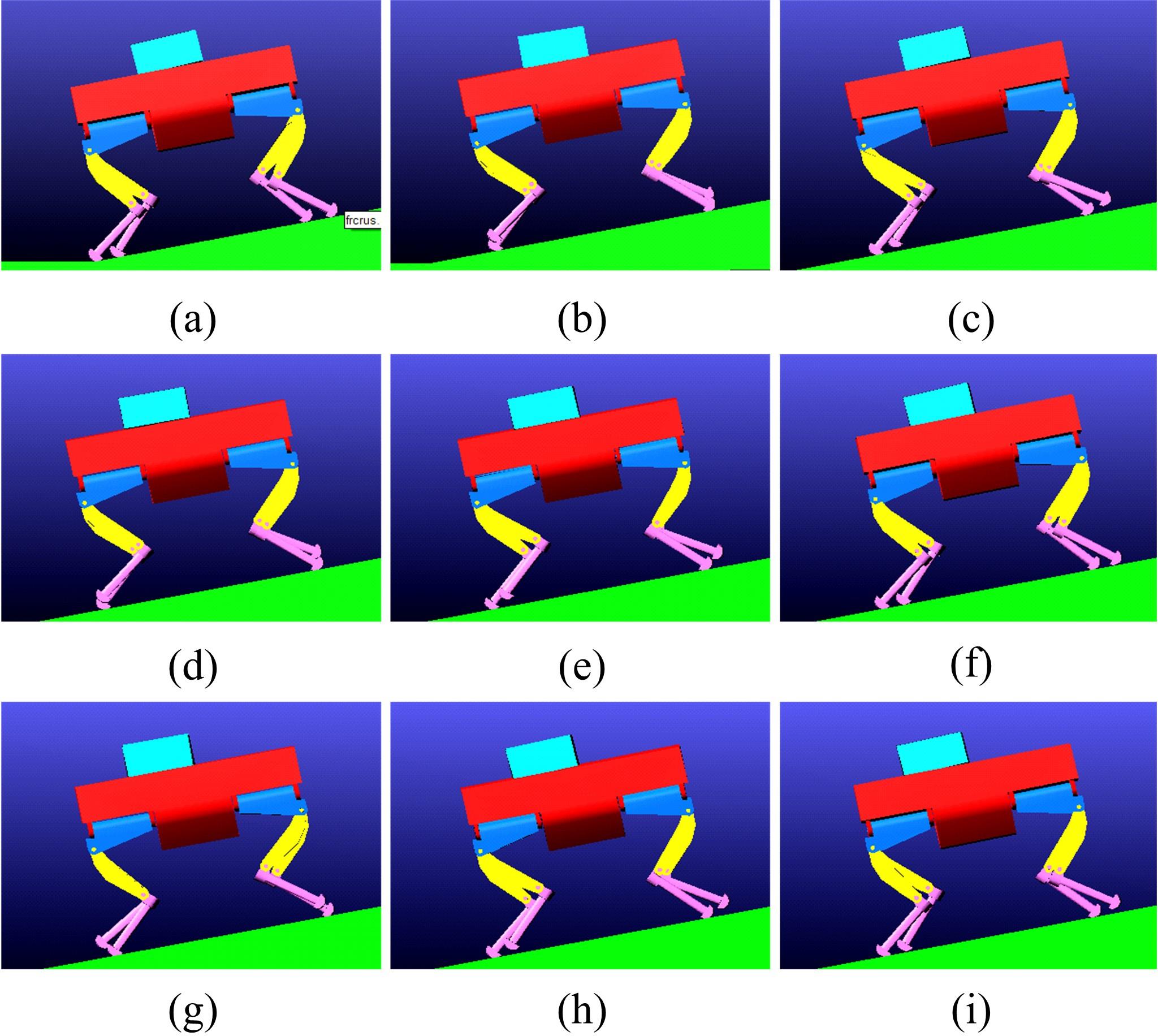
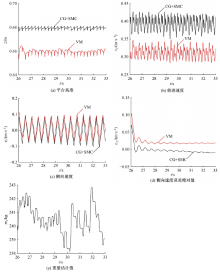
针对负载型四足步行平台重量变化时控制问题,提出了基于重心动力学与滑模自适应的控制方法。将步行平台的控制分为机身的控制及摆动腿的控制两部分,应用重心动力学与任务空间PD控制方法进行机身的运动控制,应用虚拟模型控制方法进行摆动腿的运动控制。而后,在平台高度方向应用滑模自适应控制算法,实现步行平台对重量变化的适应及重量识别,结合重心动力学提高平台前进速度及侧向速度跟踪的准确性。运用Adams和Simulink对步行平台重量变化时平地及斜坡对角步态行走进行仿真,并与虚拟模型控制方法进行对比。结果表明,重心动力学及滑模自适应控制算法实现了步行平台对重量的自适应性,且减小了前进速度和侧向速度跟踪误差,证明了所提控制方法的有效性。
中图分类号:
- TP242.6
| 1 | Hu Nan, Li Shao-yuan, Gao Feng. Multi-objective hierarchical optimal control for quadruped rescue robot[J]. International Journal of Control Automation & Systems, 2018(1): 1-12. |
| 2 | 韩宝玲, 赵锐, 罗庆生, 等. 基于粒子群算法的四足机器人静步态优化方法[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2017, 37(5): 461-465. |
| Han Bao-ling, Zhao Rui, Luo Qing-sheng, et al. Static gait optimization method for quadruped robot based on particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2017, 37(5): 461-465. | |
| 3 | 丁良宏. BigDog四足机器人关键技术分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2015, 51(7): 1-23. |
| Ding Liang-hong. Key technology analysis of BigDog quadruped robot[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(7): 1-23. | |
| 4 | Raibert M, Blankespoor K, Nelson G, et al. Bigdog, the rough-terrain quadruped robot[C]∥Proceedings of the 17th IFAC World Congress, Laxenburg, Austria, 2008: 10822-10825. |
| 5 | Michael K. Meet Boston dynamics' LS3-the latest robotic war machine[Z/OL].[2015-07-29]. . |
| 6 | Raibert M H. Legged Robots That Balance[M]. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 1986: 29-55. |
| 7 | Ring rose R. Automatically tuning control systems for Simulated legged robots[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI'94, Seattle, WA, 1994: 1297-1302. |
| 8 | Pratt J E. Virtual model control of a biped walking robot[D]. Boston, USA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1995. |
| 9 | 张国腾, 荣学文, 李贻斌, 等.基于虚拟模型的四足机器人对角小跑步态控制方法[J]. 机器人, 2016, 38(1): 65-74. |
| Zhang Guo-teng, Rong Xue-wen, Li Yi-bin, et al. Control of quadrupedal trotting based on virtual model[J]. Robot, 2016, 38(1): 65-74. | |
| 10 | 柴汇, 荣学文, 唐兴鹏, 等. 基于能量规划的崎岖地面四足机器人平面跳跃控制[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017, 47(2): 557-566. |
| Chai Hui, Rong Xue-wen, Tang Xing-peng, et al. Gait based hopping control of quadruped robot on uneven terrain with energy planning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(2): 557-566. | |
| 11 | 陈腾, 李贻斌, 荣学文. 四足机器人动步态下实时足底力优化方法的设计与验证[J]. 机器人, 2019, 41(1): 1-10. |
| Chen Teng, Li Yi-bin, Rong Xue-wen. Design and verification of real time plantar force optimization for quadruped robots in dynamic gait[J]. Robot, 2019, 41(1): 1-10. | |
| 12 | Chew C M, Pratt G A. Adaptation to load variations of a planar biped: Height control using robust adaptive control[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2001, 35(1):1-22. |
| 13 | Li Zhi-jun, Ge Shu-zhi. Adaptive robust controls of biped robots[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2013, 7(2): 161-175. |
| 14 | Orin D E, Goswami A, Lee S H. Centroidal dynamics of a humanoid robot[J]. Autonomous Robot, 2013, 35(2): 161-176. |
| 15 | Focchi M, Prete A, Havoutis I, et al. High-slope terrain locomotion for torque-controlled quadruped robots[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2017, 41(1): 259-272. |
| 16 | Winkler A W, Bellicoso C D, Hutter M, et al. Gait and trajectory optimization for legged systems through phase-based end-effector parameterization[J]. IEEE Robotics & Automation Letters, 2018, 3(3): 1560-1567. |
| 17 | Featherstone R, Orin D E. Chapter 2: Dynamics, in Springer Handbook of Robotics[M]. New York: Springer, 2008: 35-62. |
| 18 | Roberson R E, Schwertassek R. Dynamics of Multibody Systems[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1988. |
| 19 | Wensing P M, Orin D E. Improved computation of the humanoid centroidal dynamics and application for whole-body control[J]. International Journal of Humanoid Robotics, 2016, 13(1): 1-23. |
| 20 | Lee S H, Goswami A. A momentum-based balance controller for humanoid robots on non-level and non-stationary ground[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2012, 33(4): 399-414. |
| 21 | Winkler A W, Bellicoso C D, Hutter M,et al. Gait and trajectory optimization for legged systems through phase-based end-effector parameterization[J]. IEEE Robotics & Automation Letters, 2018, 3(3):1560-1567. |
| 22 | Gehring C, Coros S, Hutter M, et al. Practice makes perfect: an optimization-based approach to controlling agile motions for a quadruped robot[J]. IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 2016, 23(1): 34-43. |
| 23 | Chen Teng, Sun Xiao-bo, Xu Ze, et al. A trot and flying trot control method for quadruped robot based on optimal foot force distribution[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2019, 16(4): 621-632. |
| 24 | Zhang Guo-teng, Rong Xue-wen, Chai Hui, et al. Torso motion control and toe trajectory generation of a trotting quadruped robot based on virtual model control[J]. Advanced Robotics, 2015,30(4): 284-297. |
| 25 | Slotine J J E, Coetsee J A. Adaptive sliding controller synthesis for non-linear systems[J]. International Journal of Control, 2007, 38(2): 1631-1651. |
| [1] | 李战东,陶建国,罗阳,孙浩,丁亮,邓宗全. 核电水池推力附着机器人系统设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1820-1826. |
| [2] | 柴汇, 荣学文, 唐兴鹏, 李贻斌, 张勤, 李岳炀. 基于能量规划的崎岖地面四足机器人平面跳跃控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 557-566. |
| [3] | 杨智勇, 吴功平, 王伟, 郭磊, 杨守东, 曹琪, 张义杰, 胡鹏. 高压巡检机器人下坡节能控速方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 567-576. |
| [4] | 曹福成, 邢笑雪, 李元春, 赵希禄. 下肢康复机器人轨迹自适应滑模阻抗控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1602-1608. |
| [5] | 张帅帅, 荣学文, 李贻斌, 李彬. 崎岖地形环境下四足机器人的静步态规划方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1287-1296. |
| [6] | 霍希建, 刘伊威, 姜力, 夏晶, 刘宏. 具有关节限位的7R仿人机械臂逆运动学优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 213-220. |
| [7] | 刘逸群, 邓宗全, 赵亮, 丁亮, 佟志忠, 高海波. 液压驱动六足机器人步行腿性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1512-1518. |
| [8] | 管成,王飞,张登雨. 基于NURBS的挖掘机器人时间最优轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 540-546. |
| [9] | 王海燕,李贻斌,宁龙霄. 液压驱动双足机器人运动系统的设计及实现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 750-756. |
| [10] | 高黎黎, 卢韶芳, 郭富强, 张超. 高密度组合结构光编码方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊1): 344-347. |
| [11] | 唐术锋,朱延河,赵 杰,张玉华. 新型自重构机器人钩爪式连接机构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(04): 1086-1090. |
| [12] | 张荣辉1,王海玮2,贾宏光3,陈涛3,张跃3. 捷联式惯性导航系统初始对准扰动补偿控制算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 811-0815. |
| [13] | 葛连正, 赵立军, 李瑞峰, 于殿勇. 移动机器人非线性前置追踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 806-0810. |
| [14] | 张阳, 王宣银. 基于人眼特性的视频稳定方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(02): 529-0533. |
| [15] | 兰天, 刘伊威, 陈养彬, 金明河, 樊绍巍, 刘宏. 模块化嵌入式五指机器人灵巧手手指控制系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(02): 517-0522. |
|
||