吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 704-711.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200767
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于改进的ResNeSt驾驶员头部状态分类算法
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
3.吉林航盛电子有限公司,吉林省 吉林市 132013
Classification of drivers' head status based on improved ResNeSt
Qian-yi XU1,2( ),Gui-he QIN1,2,Ming-hui SUN1,2(
),Gui-he QIN1,2,Ming-hui SUN1,2( ),Cheng-xun MENG3
),Cheng-xun MENG3
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computing and Knowledge Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
3.Jilin Hangsheng Electronics Co. ,Jilin 132013,China
摘要:
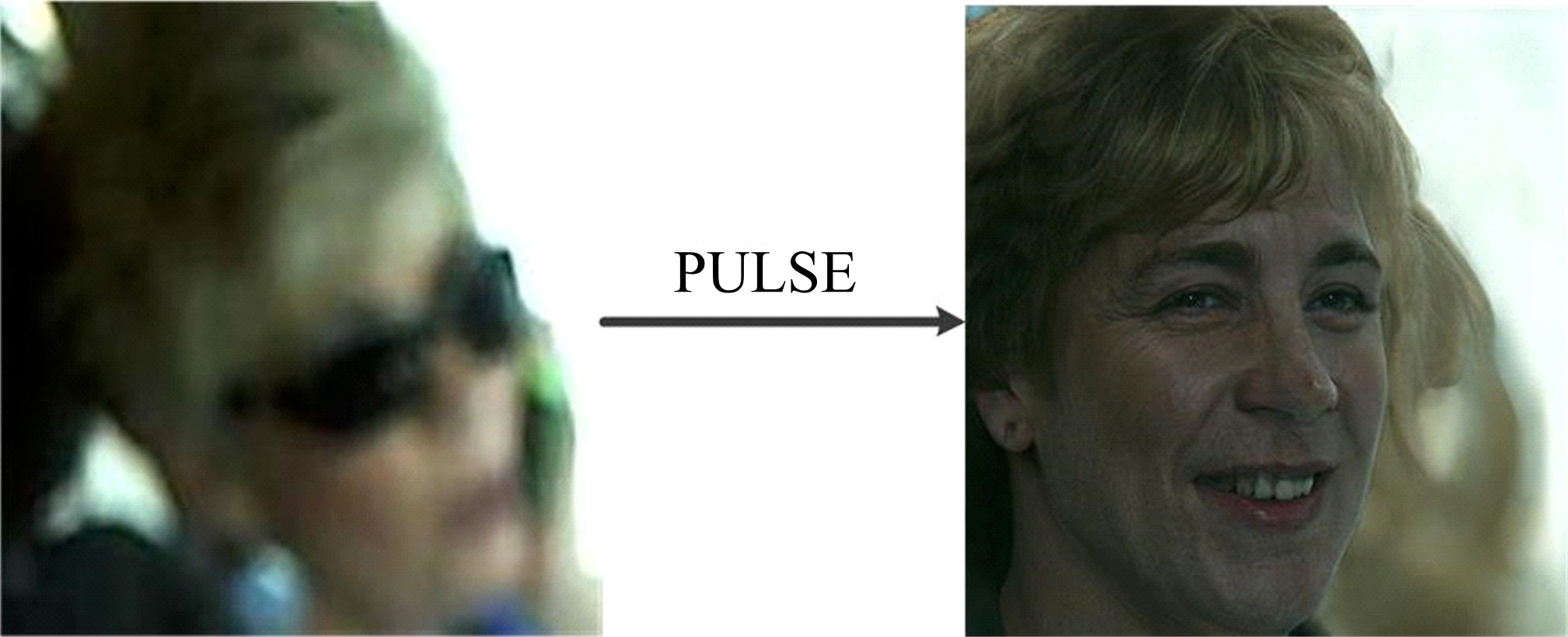
为快速准确地在驾驶行程中获取驾驶员头部状态以识别驾驶员状态,提出了基于改进的ResNeSt分类算法,使用Yolov4作为检测驾驶员头部的算法获取头部图像;同时,针对数据集类不平衡的问题,通过使用PULSE方法将对焦失败的图像还原,将数据补充完整;最终,实验结果达到80.51%的分类准确率,表明本文算法具有一定有效性和准确性。
中图分类号:
- TP391.9
| 1 | Li L, Song J Y, Wang F Y, et al. IVS 05: new developments and research trends for intelligent vehicles[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2005, 20(4): 10-14. |
| 2 | Li L, Wang F Y. Advanced Motion Control and Sensing for Intelligent Vehicles[M]. Springer Science & Business Media, 2007. |
| 3 | Jain A, Singh A, Koppula H S, et al. Recurrent neural networks for driver activity anticipation via sensory-fusion architecture[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Stockholm, Sweden, 2016: 3118-3125. |
| 4 | Agustina G, Correa L, Orosco E, et al. Automatic detection of drowsiness in EEG records based on multimodal analysis[J]. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2013, 36(2): 244-249. |
| 5 | Patrick K C A, Imtiaz S A, Bowyer S, et al. An algorithm for automatic detection of drowsiness for use in werable EEG systems[C]∥Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Orlando, FL, 2016: 3523-3526. |
| 6 | Zhao S, Xu G, Tao T. Detecting of driver's drowsiness using multiwavelet packet energy spectrum[C]∥Proceedings of the 2nd International Congress on Image and Signal, Tianjin, China, 2009: 1-5. |
| 7 | He Q, Li W, Fan X. Estimation of driver's fatigue based on steering wheel angle[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference of Engineering Psychology and Cognitive Ergonomics, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011: 145-155. |
| 8 | Zhang X B, Cheng B, Feng J J. Real-time detection method of driver fatigue state based on steering wheel operation[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University Science and Technology, 2010, 7(1): 1072-1076. |
| 9 | Tawari A, Trivedi M M. Robust and continuous estimation of driver gaze zone by dynamic analysis of multiple face videos[C]∥IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium Proceedings, Dearborn, MI, 2014: 344-349. |
| 10 | Choi I H, Kim Y G. Head pose and gaze direction tracking for detecting a drowsy driver[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014: 807-814. |
| 11 | Zhao L, Wang Z, Wang X, et al. Human fatigue expression and bimodal deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2016, 25(5): 53024-53034. |
| 12 | Halim Z, Kalsoom R, Baig A R. Profiling drivers based on driver dependent vehicle driving features[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2016, 44: 645-664. |
| 13 | Jabon M, Bailenson J, Pontikakis E, et al. Facial expression analysis for predicting unsafe driving behavior[J]. IEEE Pervasive Computing, 2011, 10(4): 84-95. |
| 14 | Papageorgiou C P, Oren M, Poggio T. A general framework for object detection[C]∥6th International Conference on Computer Vision, Bombay, India, 1998: 555-562. |
| 15 | Lowe D G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features[C]∥Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 1999: 1150-1157. |
| 16 | Dalal N, Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]∥Proceedings of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, California, 2005: 886-893. |
| 17 | Donahue J, Jia Y, Vinyals O, et al. DeCAF: a deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition[J]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, arXiv: 1310.1531. |
| 18 | Lienhart R, Maydt J. An extended set of haar-like features for rapid object detection[C]∥Proceedings of International Conference on Image Processing, Rochester, NY, USA, 2002: 900-903. |
| 19 | Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, Ohio, 2014: 580-587. |
| 20 | Blaschko M B, Lampert C H. Learning to localize objects with structured output regression[C]∥Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, Heidelber, 2008: 2-15. |
| 21 | Sermanet P, Eigen D, Zhang X, et al. Overfeat: integrated recognition, localization and detection using convolutional networks[J]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, arXiv: 1312.6229. |
| 22 | Uijlings J R, van de Sande K E, Gevers T, et al. Selective search for object recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 104(2): 154-171. |
| 23 | Zitnick C L, Dollar P. Edge boxes: locating object proposals from edges[C]∥Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 391-405. |
| 24 | Bochkovskiy A, Wang C Y, Liao H Y M. YOLOv4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, arXiv:2004.10934. |
| 25 | 李志军, 杨楚皙, 刘丹, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的信息流增强图像压缩方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1788-1795. |
| Li Zhi-jun, Yang Chu-xi, Liu Dan, et al. Deep convolutional networks based image compression with enhancement of information flow[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1788-1795. | |
| 26 | 刘国华, 周文斌. 基于卷积神经网络的脉搏波时频域特征混叠分类[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1818-1825. |
| Liu Guo-hua, Zhou Wen-bin. Pulse wave signal classification algorithm based on time⁃frequency domain feature aliasing using convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1818-1825. | |
| 27 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),Las Vegas, USA, 2016:770-778. |
| 28 | Xie S, Girshick R, Dollár P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hawaii, USA, 2017: 1492-1500. |
| 29 | Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132-7141. |
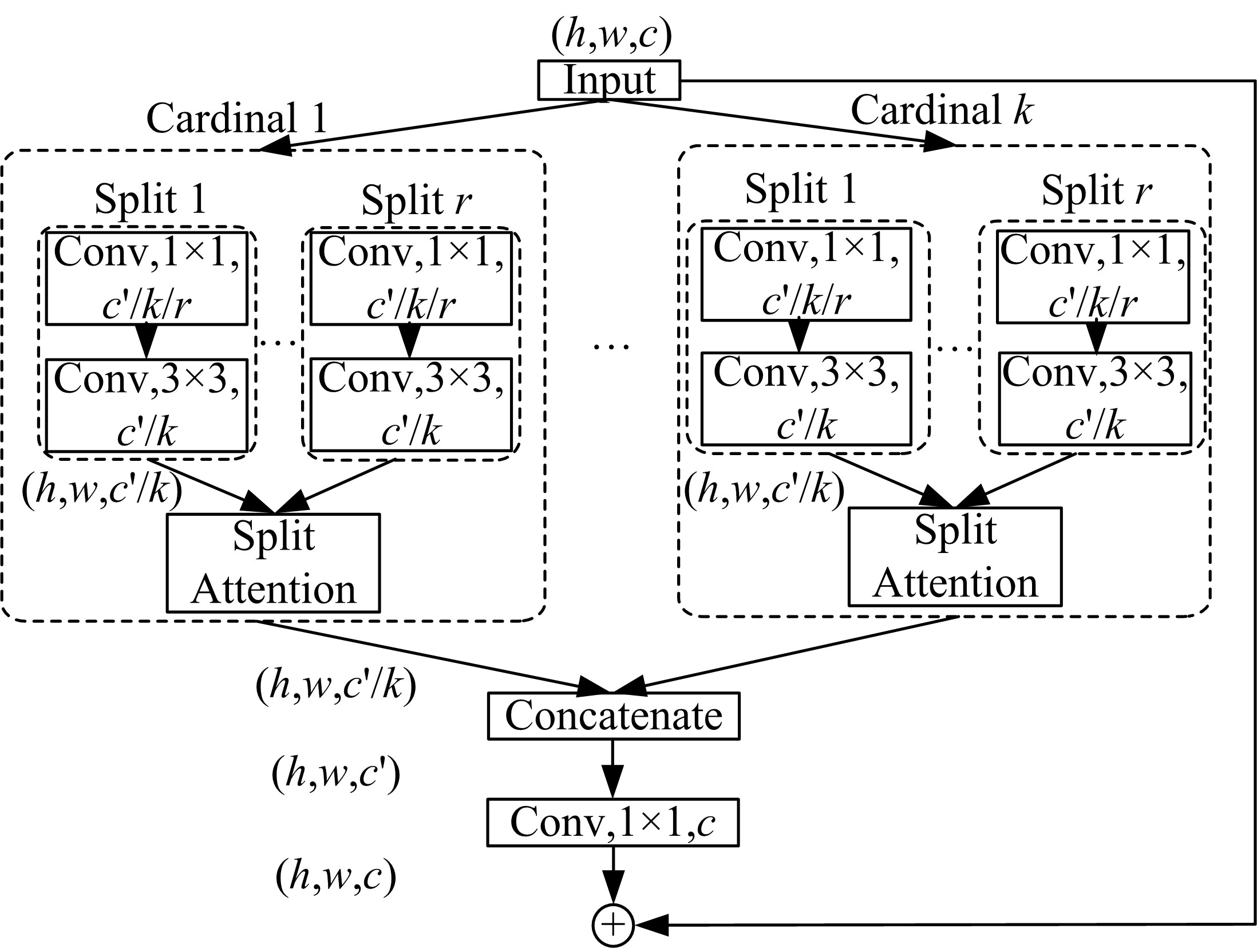
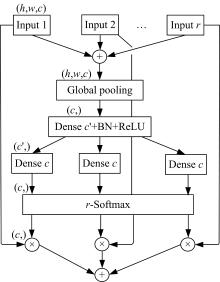
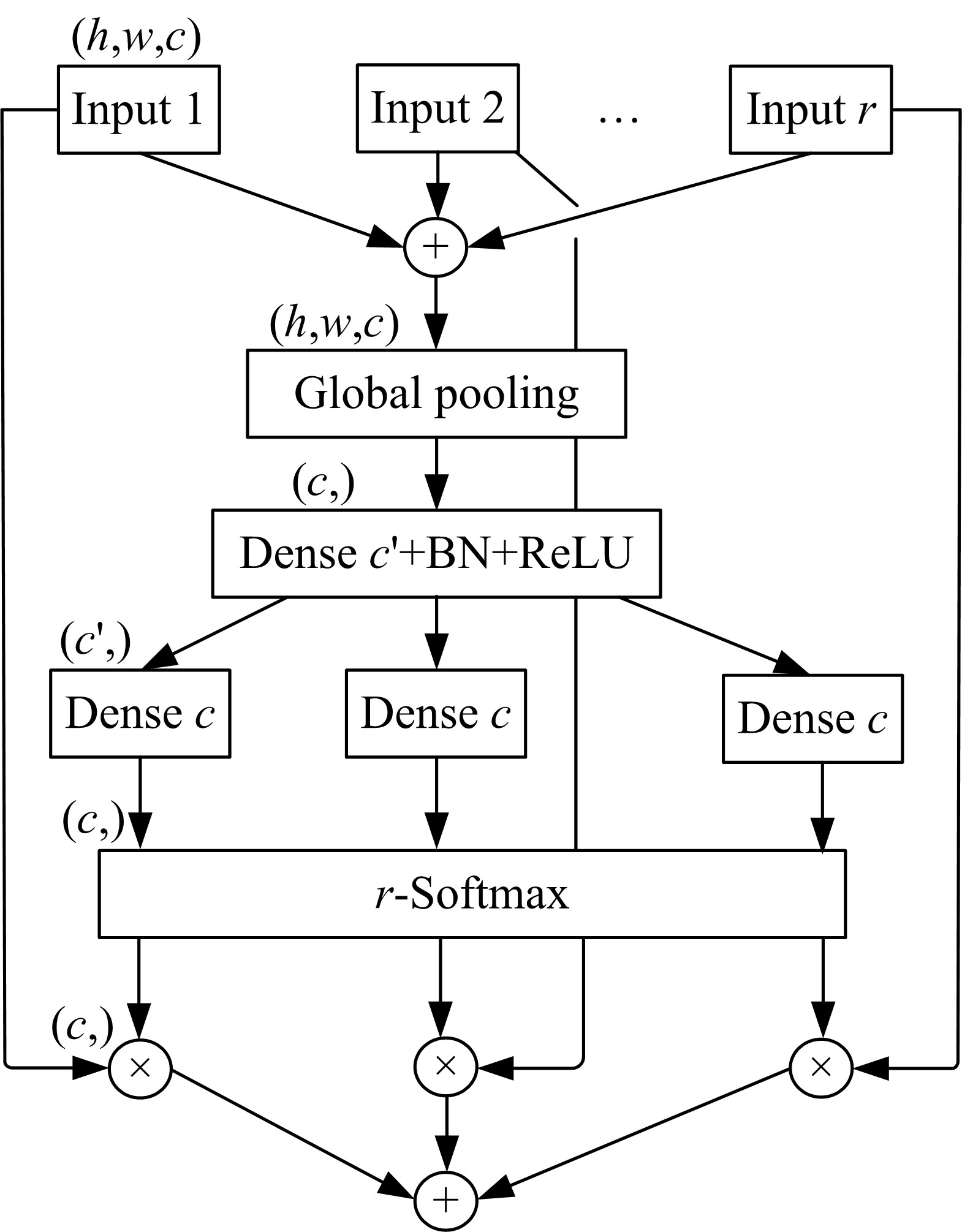
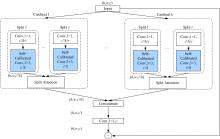
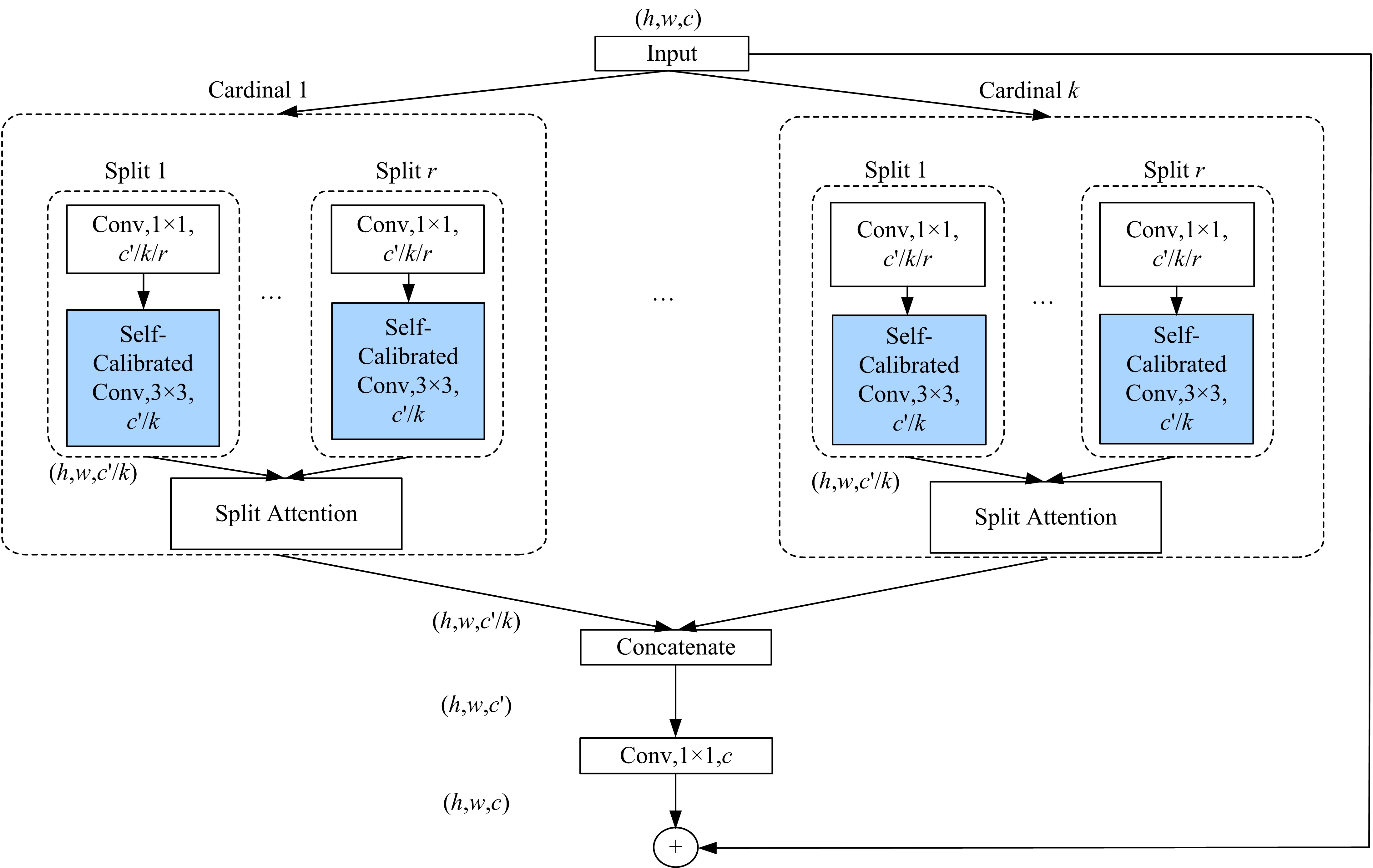
| 30 | Zhang H, Wu C R, Zhang Z Y, et al. ResNeSt: split-attention networks[J]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, arXiv:2004.08955. |
| 31 | Competition Kaggle. State Farm Distracted Driver Detection[DB/OL]. [2019-10-12]. |
| 32 | Redmon J, Farhadi A. Yolov3: an incremental improvement[J]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, arXiv:1804.02767. |
| 33 | Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hawaii, USA, 2017: 4700-4708. |
| 34 | Li X, Wang W, Hu X, et al. Selective kernel networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Angeles, USA, 2019: 510-519. |
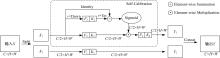
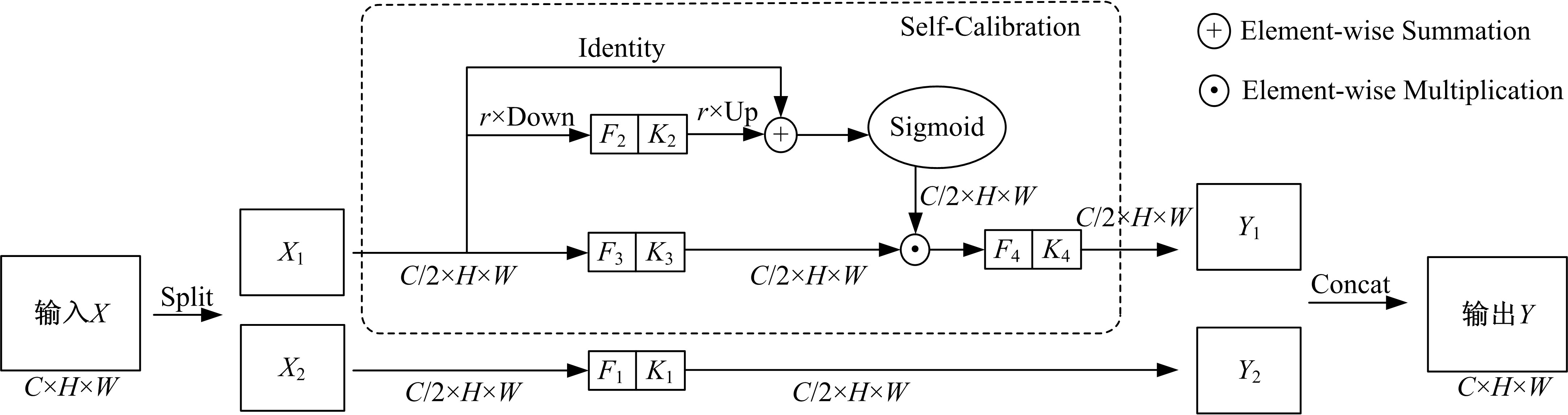
| 35 | Liu J J, Hou Q, Cheng M M, et al. Improving convolutional networks with self-calibrated convolutions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10096-10105. |
| [1] | 宋元,周丹媛,石文昌. 增强OpenStack Swift云存储系统安全功能的方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 314-322. |
| [2] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| [3] | 陈绵书, 苏越, 桑爱军, 李培鹏. 基于空间矢量模型的图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 943-951. |
| [4] | 范敏, 韩琪, 王芬, 宿晓岚, 徐浩, 吴松麟. 基于多层次特征表示的场景图像分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1909-1917. |
| [5] | 胡冠宇, 乔佩利. 基于云群的高维差分进化算法及其在网络安全态势预测上的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 568-577. |
| [6] | 陈涛, 邓辉舫, 刘靖. 基于密度聚类和多示例学习的图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 1126-1134. |
| [7] | 齐滨, 赵春晖, 王玉磊. 基于支持向量机与相关向量机的高光谱图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 143-147. |
| [8] | 陈载清, 石俊生, 白凤翔. 基于模糊粗糙集的图像自动分类研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 209-212. |
| [9] | 佟金, 王亚辉, 樊雪梅, 张书军, 陈东辉. 生鲜农产品冷链物流状态监控信息系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(06): 1707-1711. |
| [10] | 王瀛, 郭雷, 梁楠. 基于核熵成分分析的高光谱遥感图像分类算法[J]. , 2012, (06): 1597-1601. |
| [11] | 刘萍萍1,2,赵宏伟1,2,耿庆田1,戴金波1. 基于局部特征和视皮层识别机制的图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(05): 1401-1406. |
| [12] | 曹春红,张斌,李小琳 . 基于模糊支持向量机的医学图像分类技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(03): 630-0633. |
|
||