吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 515-524.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200822
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
新型弓腰式移动底盘的设计及通过性分析
聂建军1( ),闫修鹏1,2,马宗正2,解晓琳3,郭家杰3,吕亚磊1
),闫修鹏1,2,马宗正2,解晓琳3,郭家杰3,吕亚磊1
- 1.中原工学院 机电学院,郑州 451191
2.河南工程学院 机械工程学院,郑州 451191
3.河南科技大学 农业装备工程学院,河南 洛阳 471000
Design and trafficability analysis of new bow waist mobile chassis
Jian-jun NIE1( ),Xiu-peng YAN1,2,Zong-zheng MA2,Xiao-lin XIE3,Jia-jie GUO3,Ya-lei LYU1
),Xiu-peng YAN1,2,Zong-zheng MA2,Xiao-lin XIE3,Jia-jie GUO3,Ya-lei LYU1
- 1.School of Mechatronics Engineering,Zhongyuan University of Technology,Zhengzhou 451191,China
2.School of Mechanical Engineering,Henan University of Engineering,Zhengzhou 451191,China
3.College of Agricultural Equipment Engineering,Henan University of Science and Technology,Luoyang 471000,China
摘要:
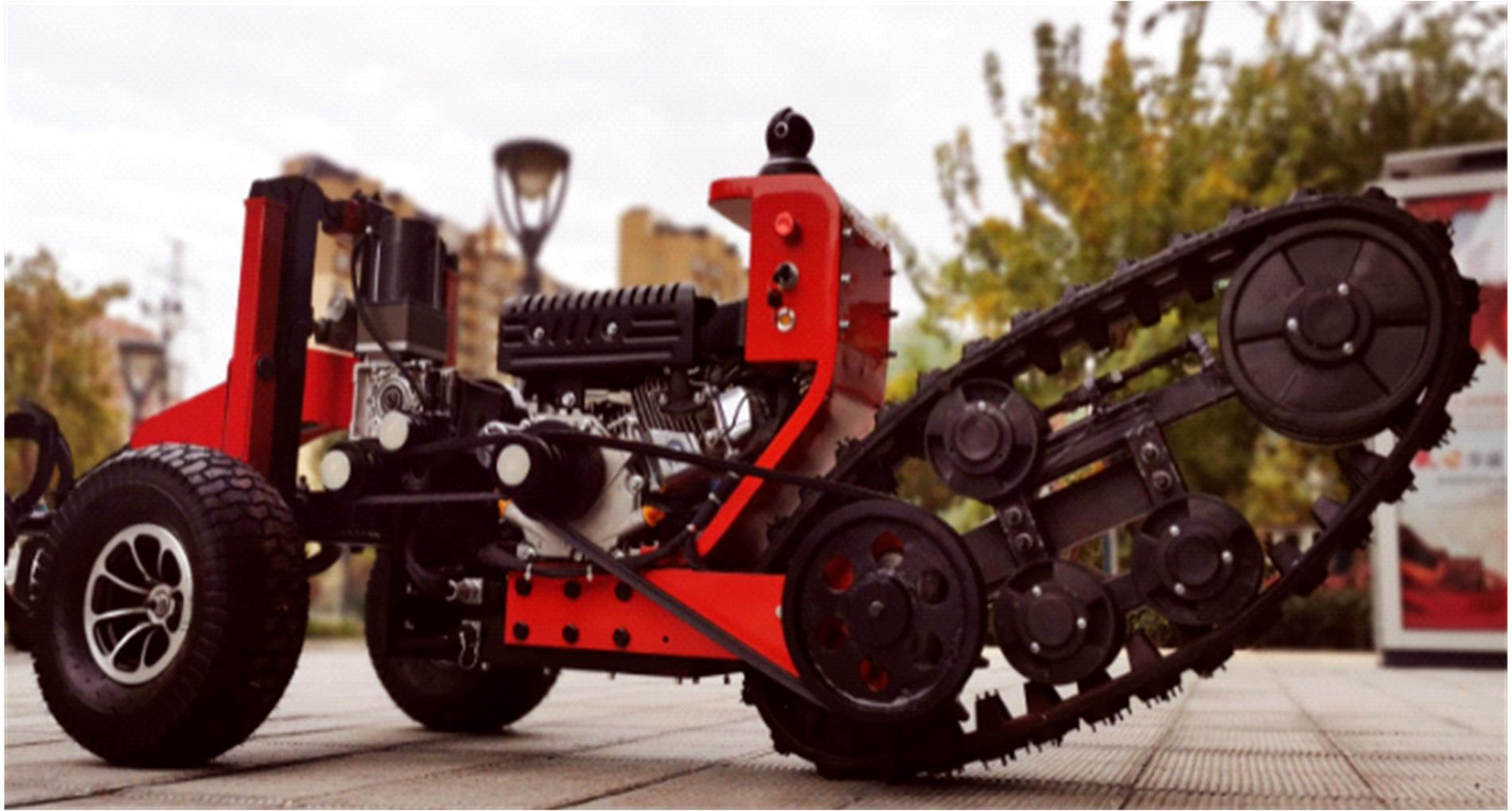
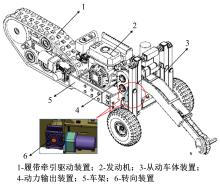
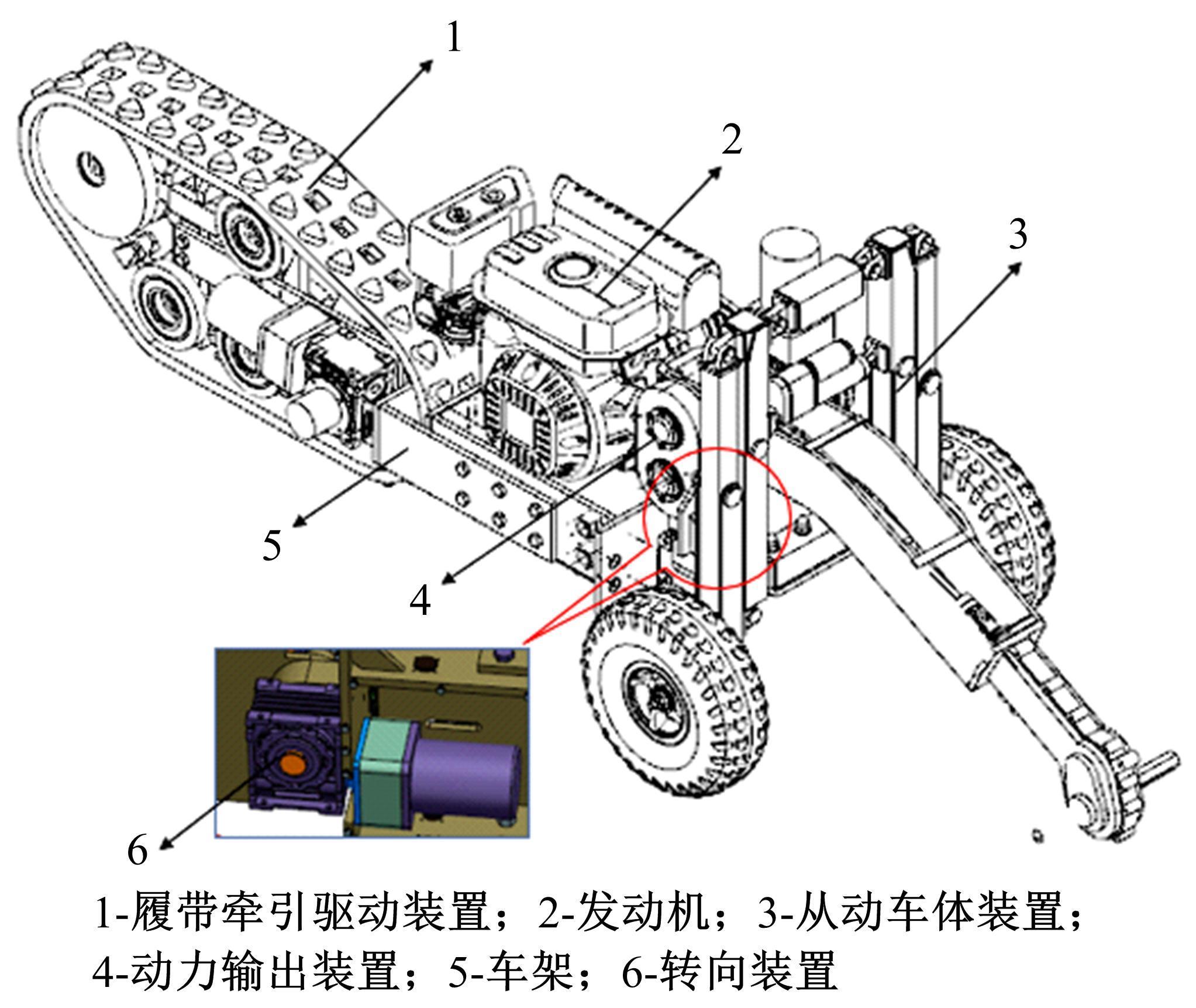
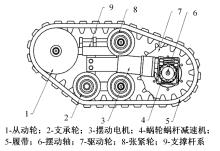
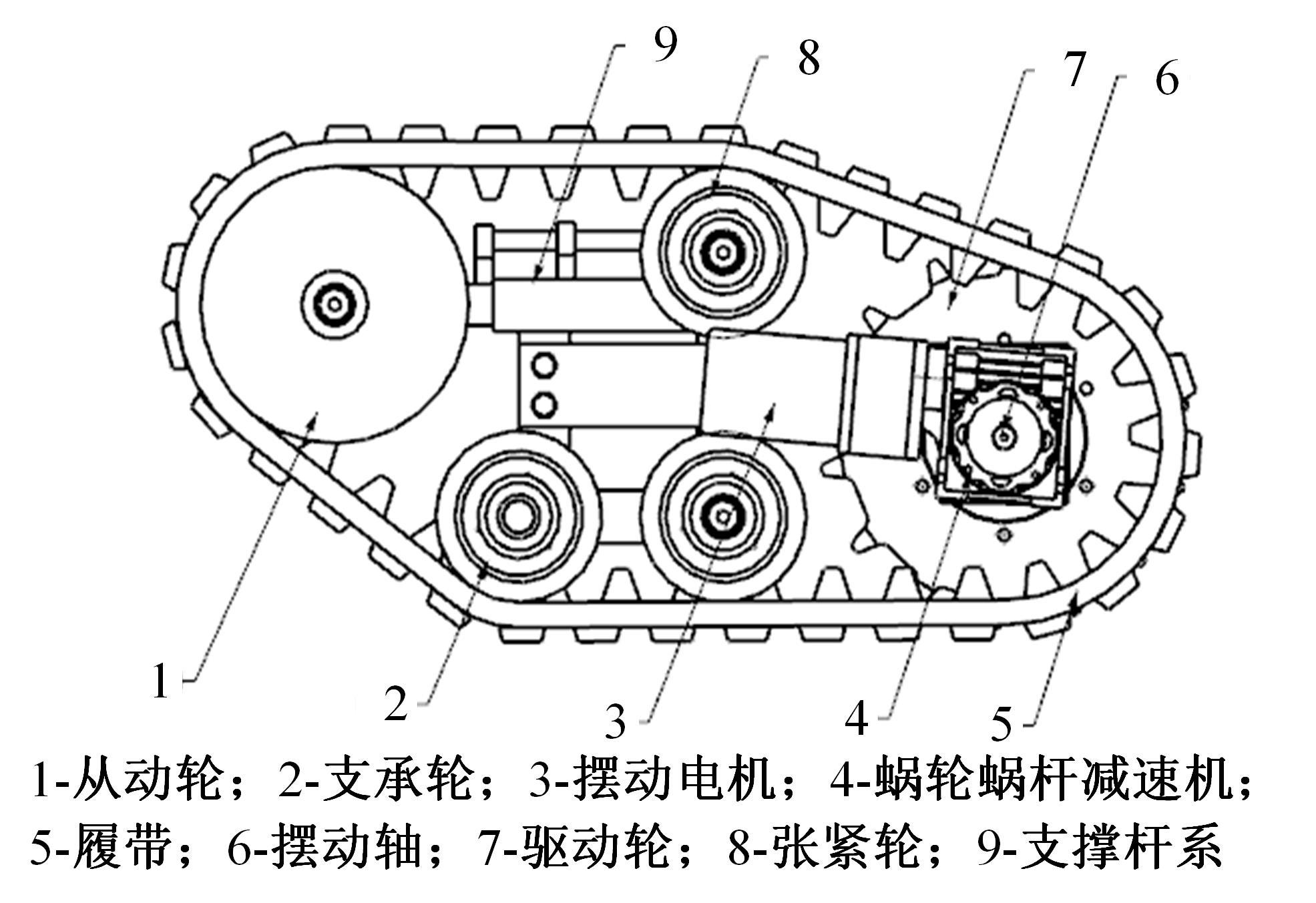
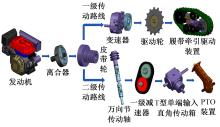
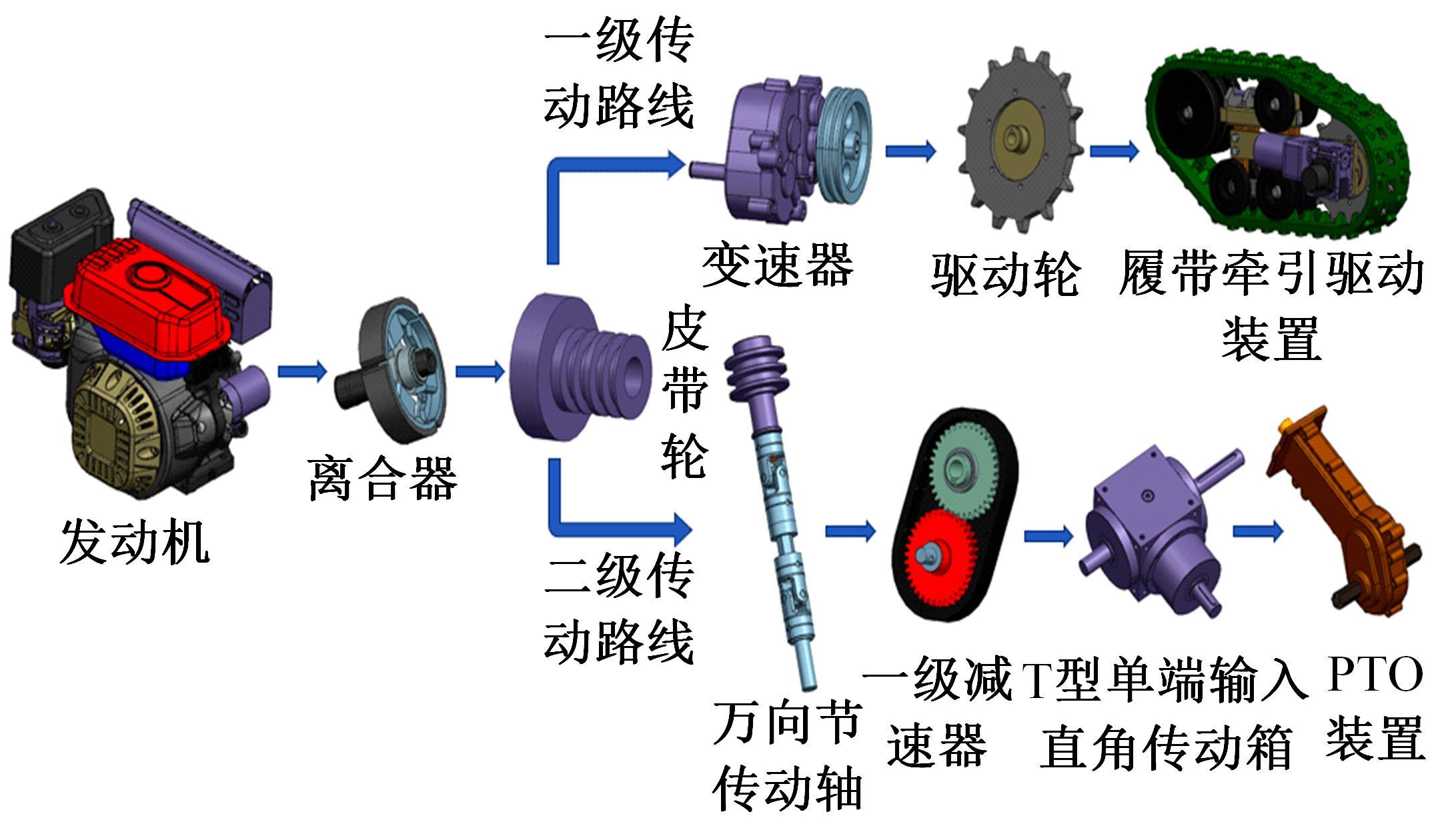
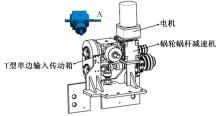
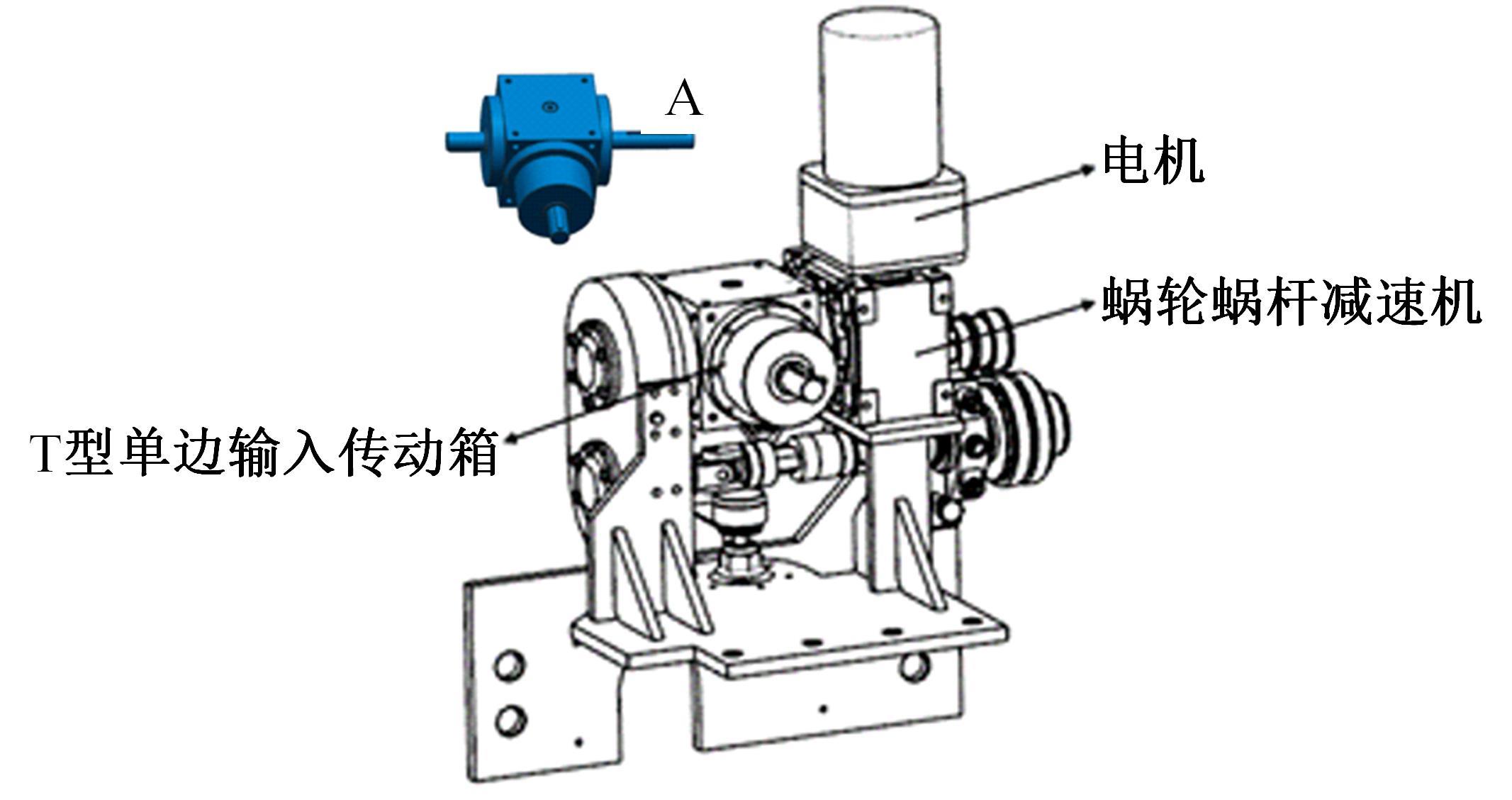
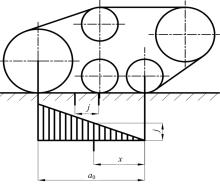
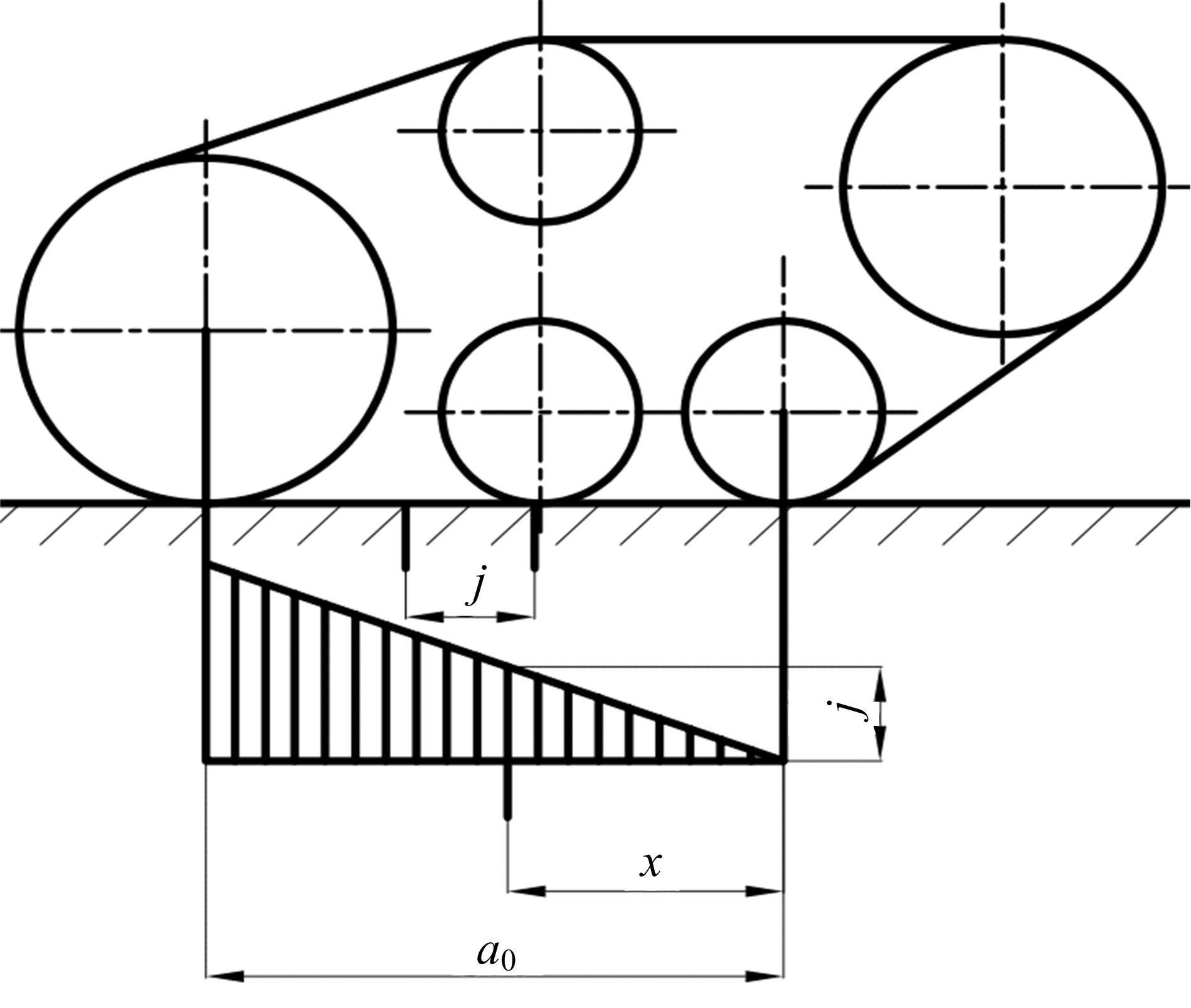
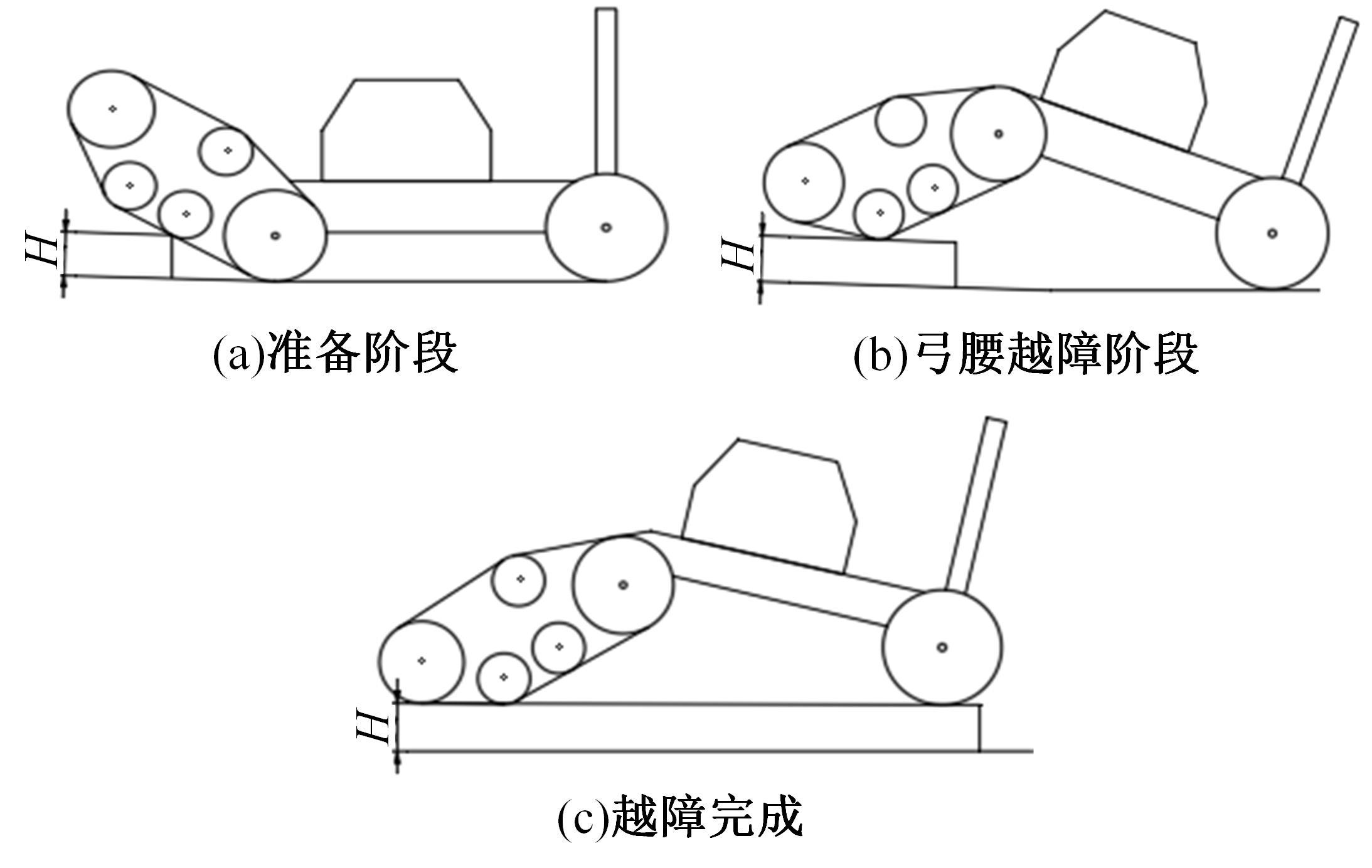
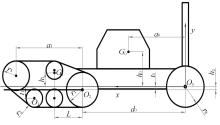
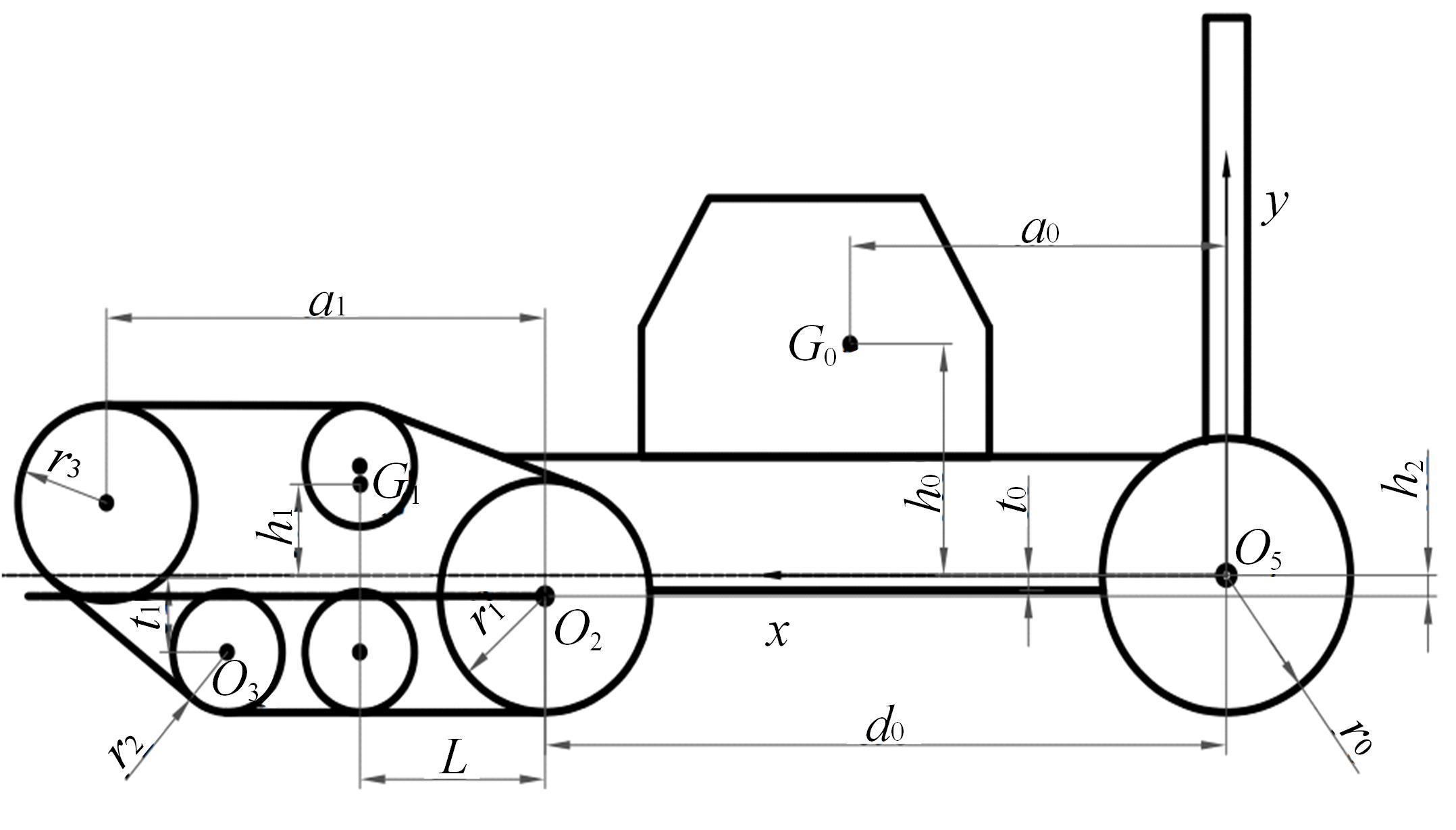
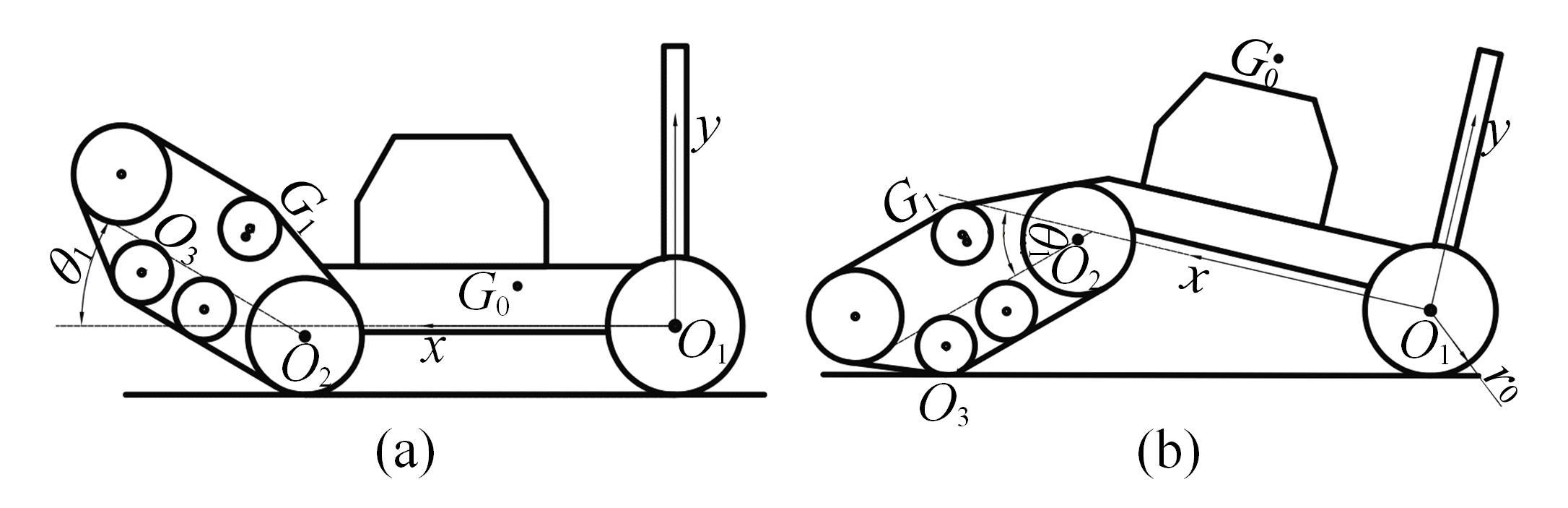
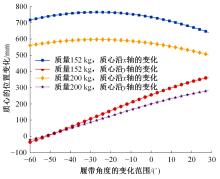
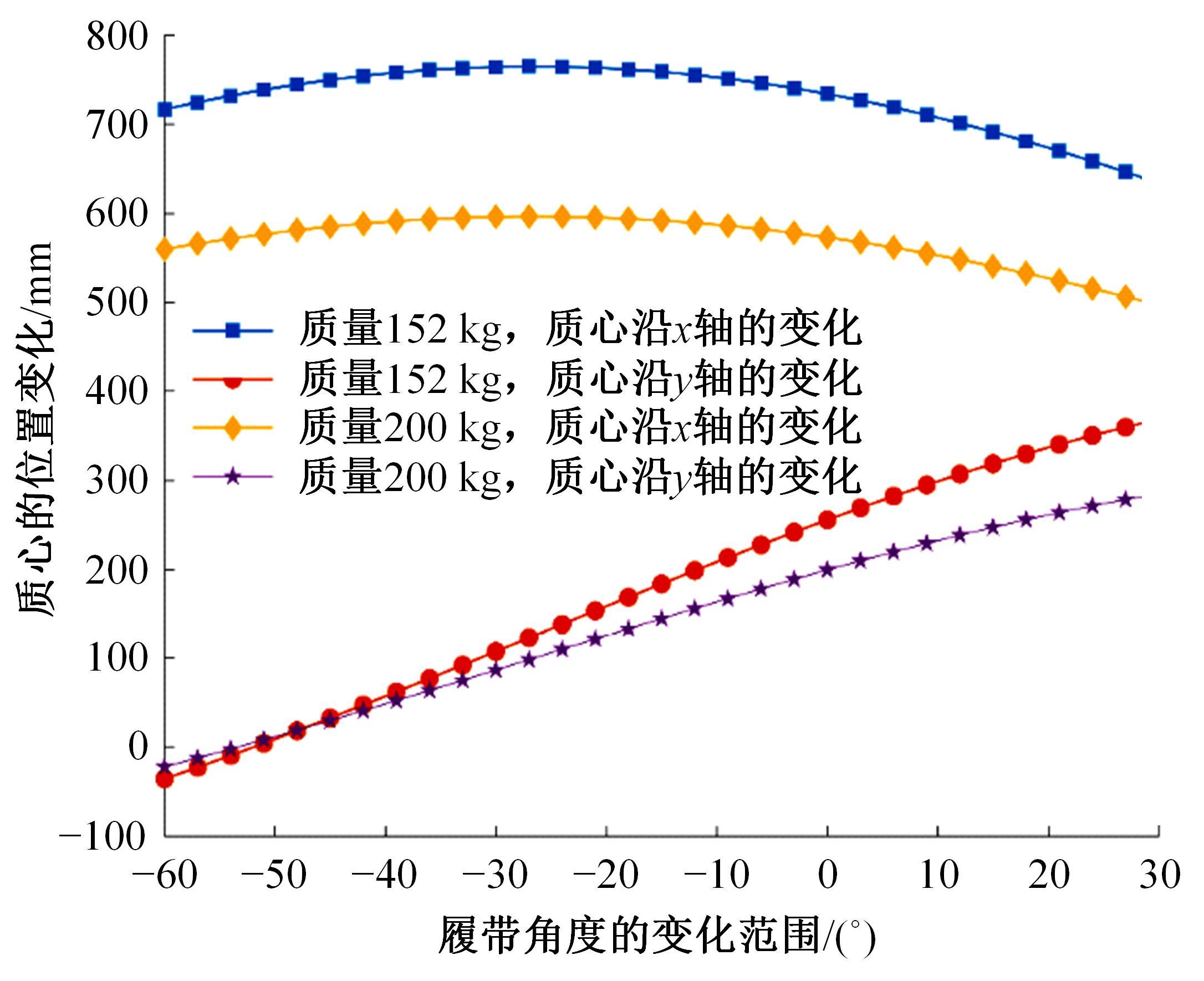
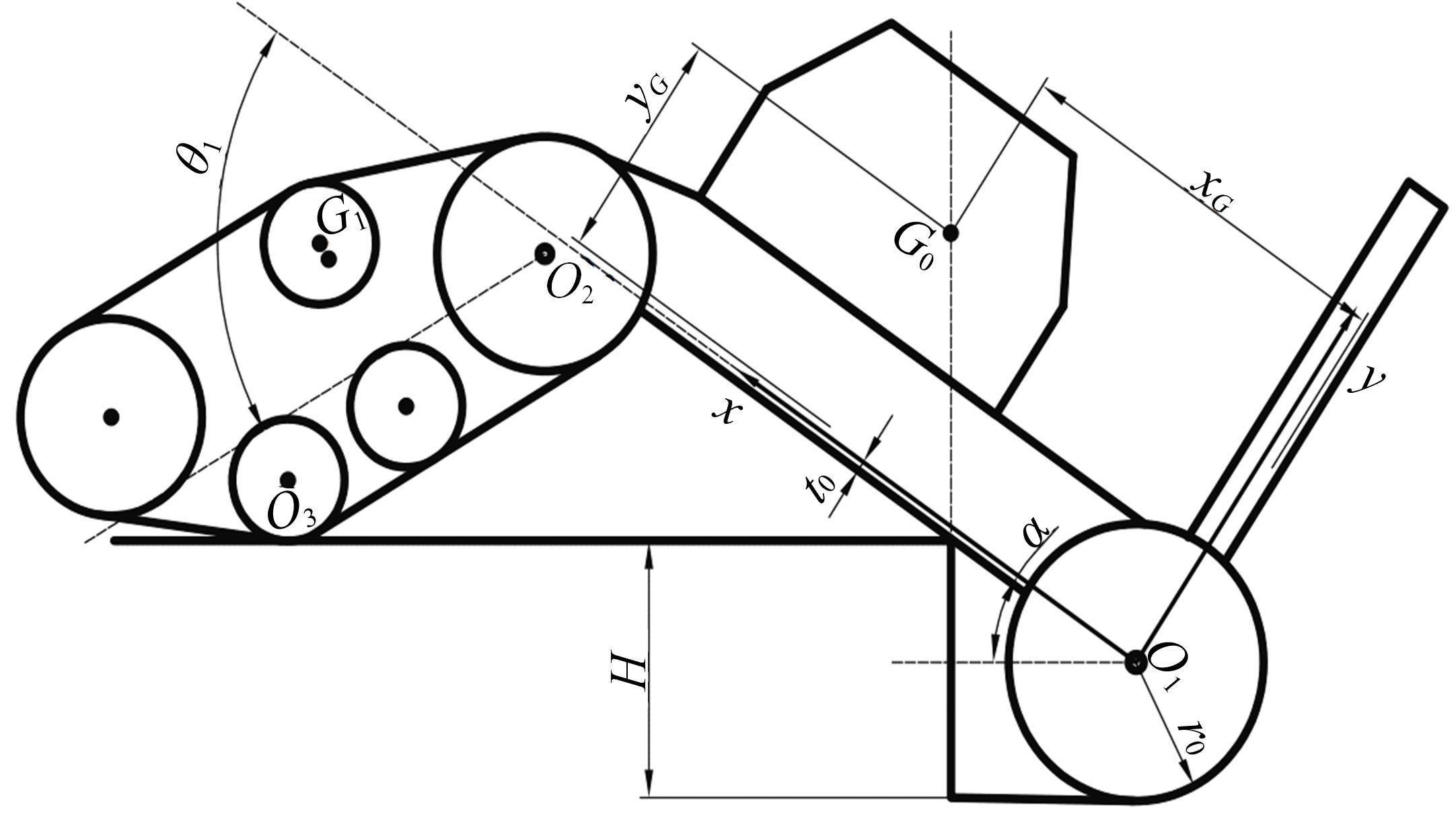
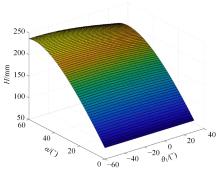
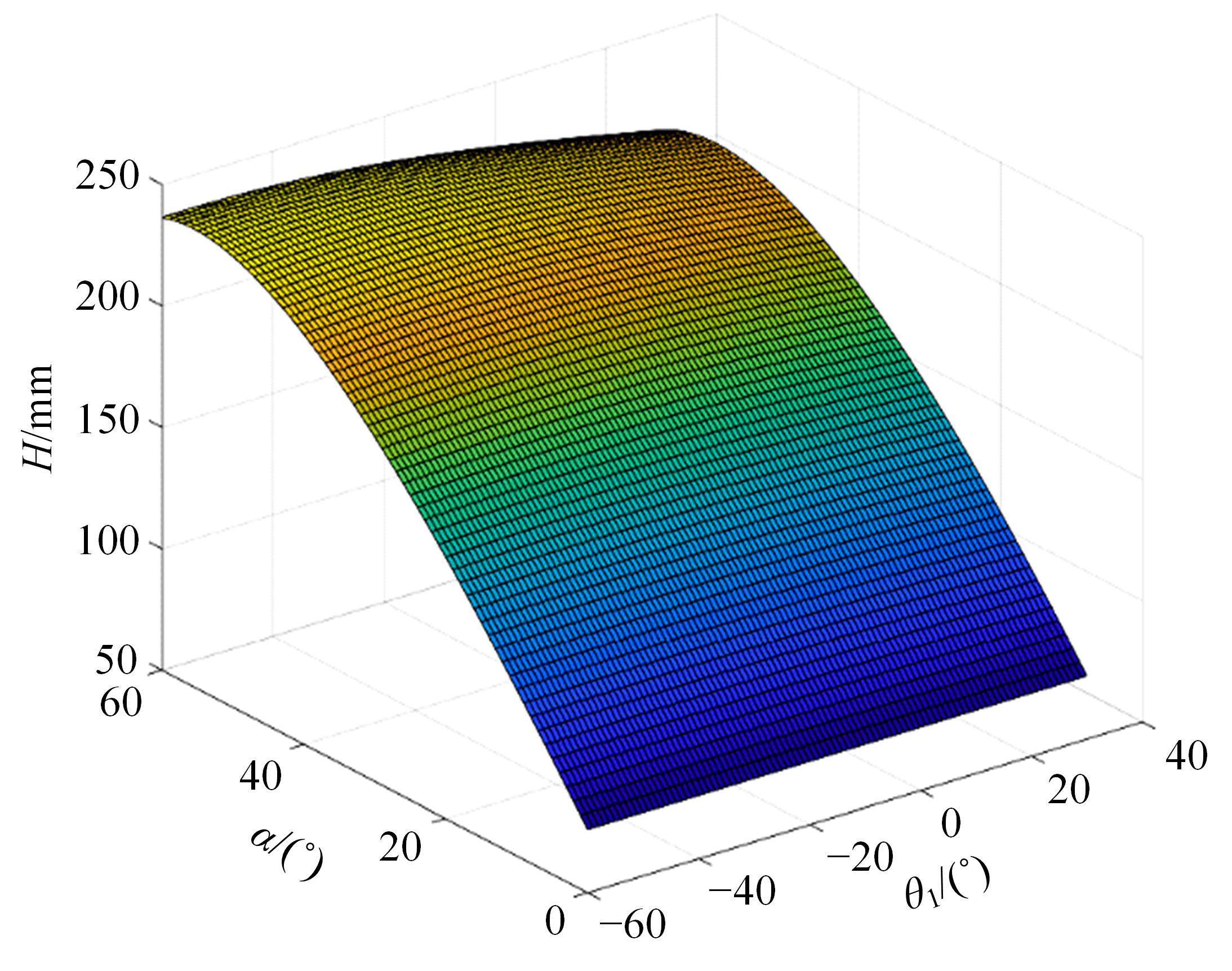
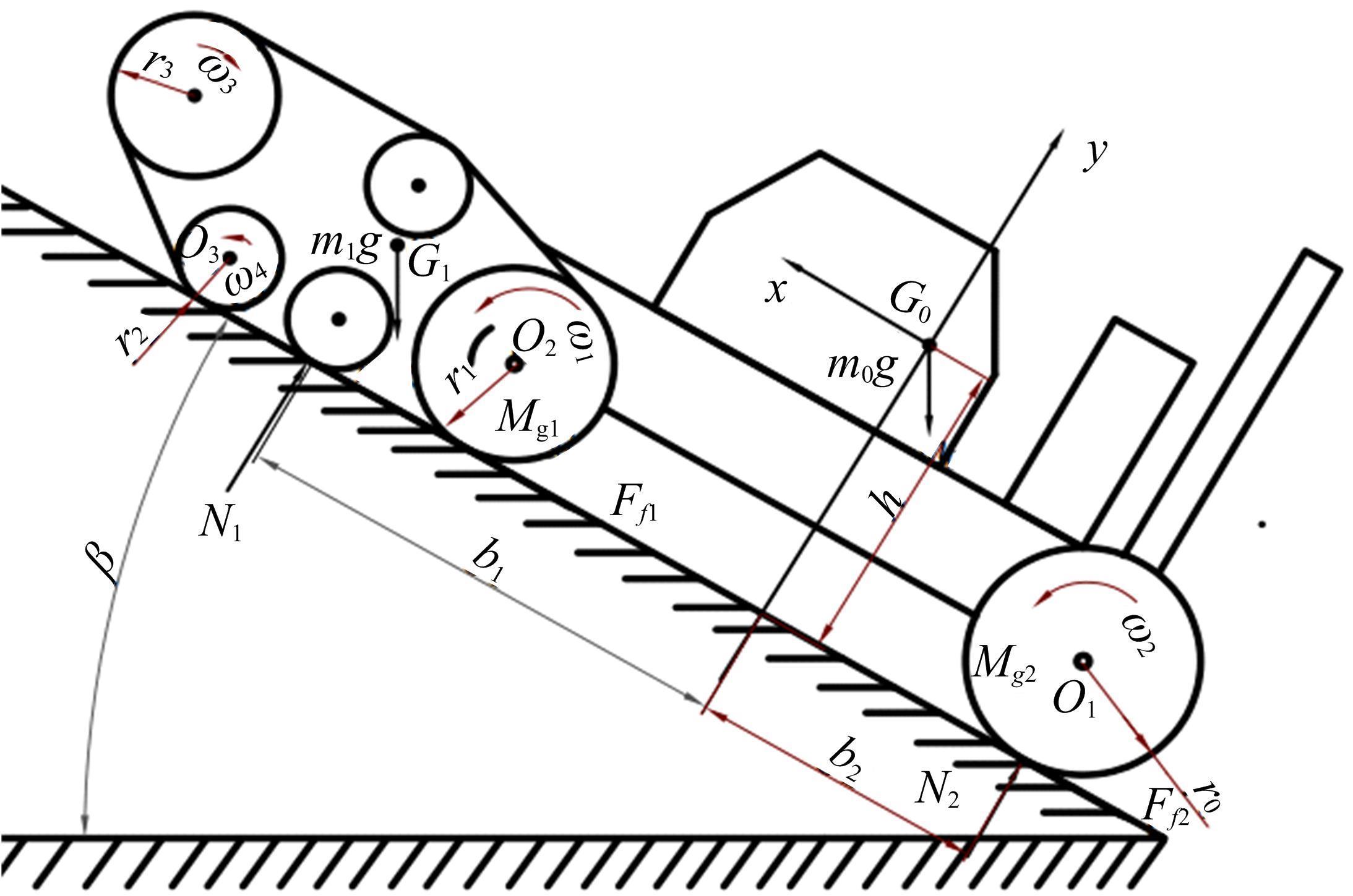
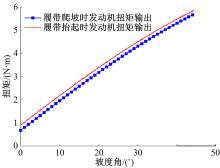
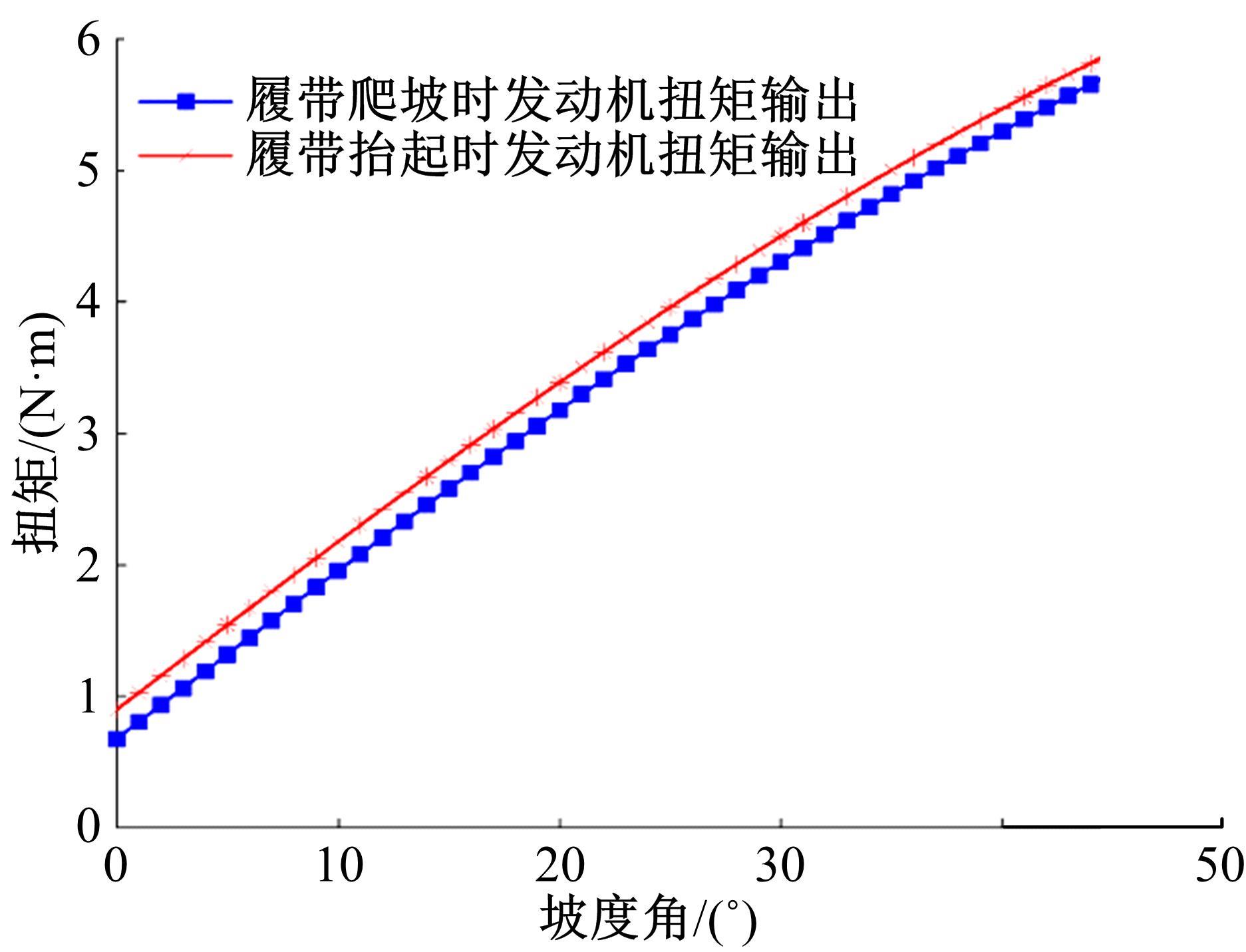
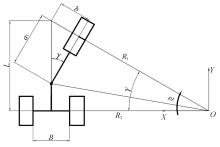
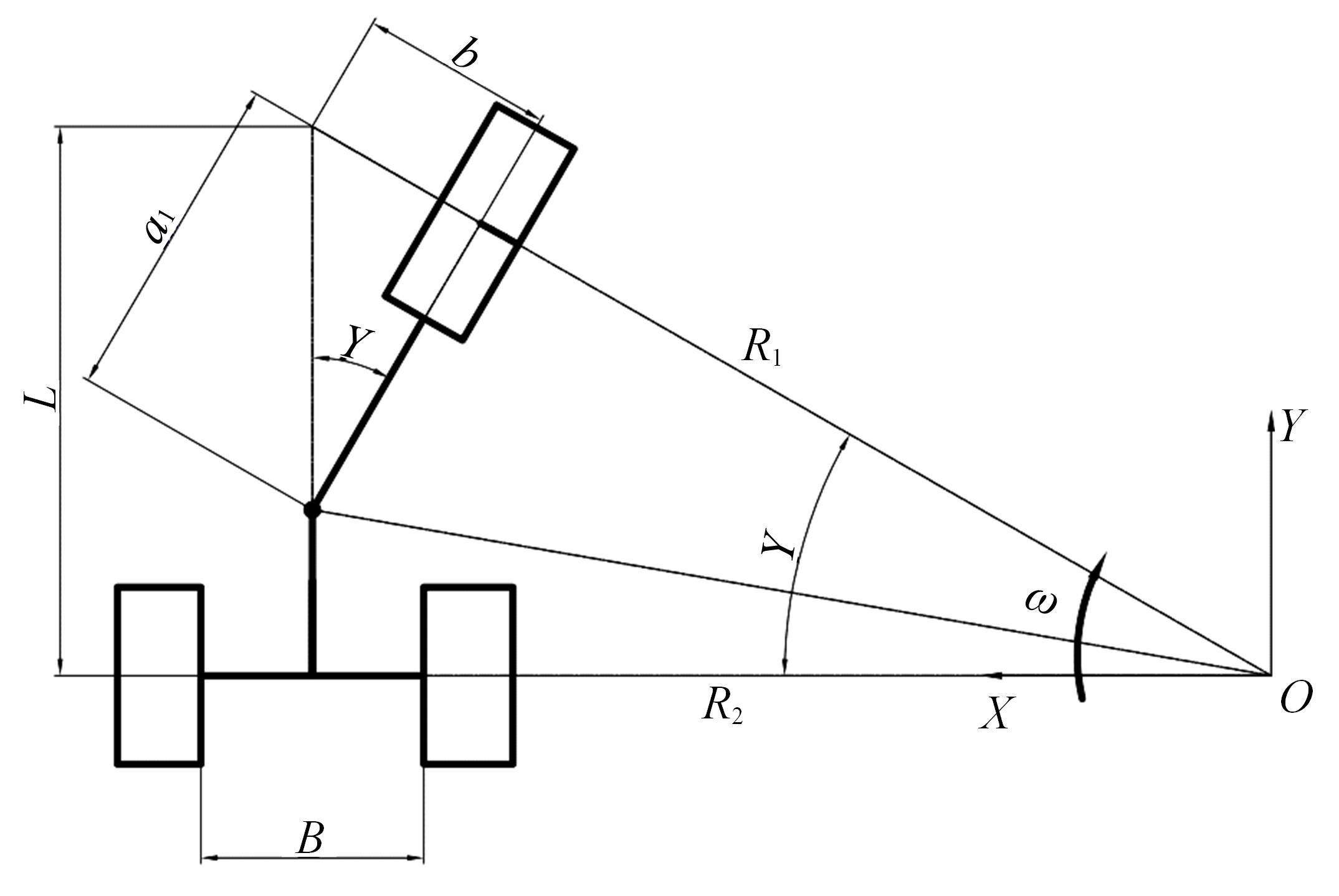
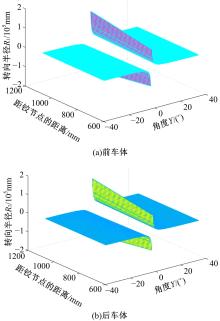
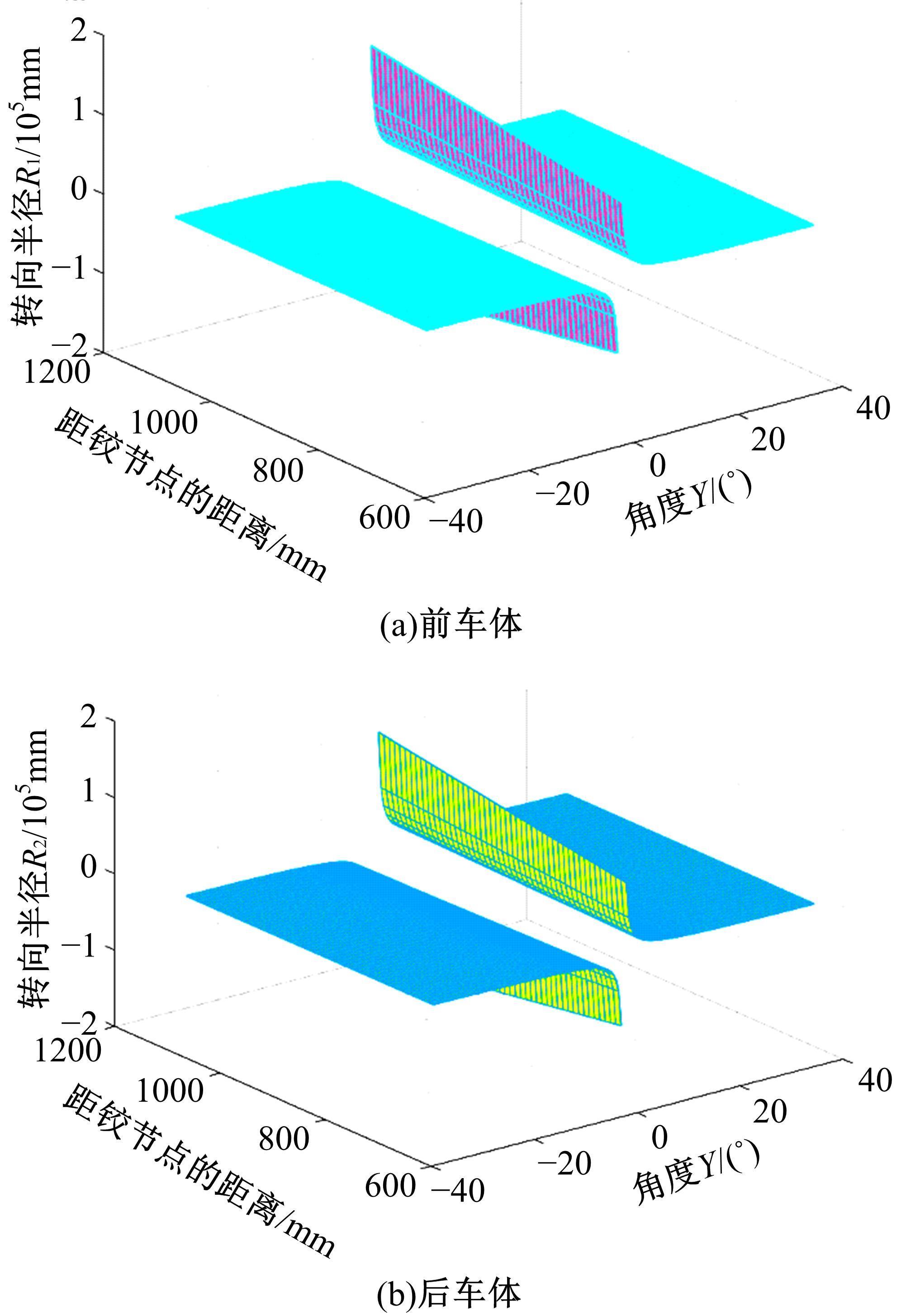
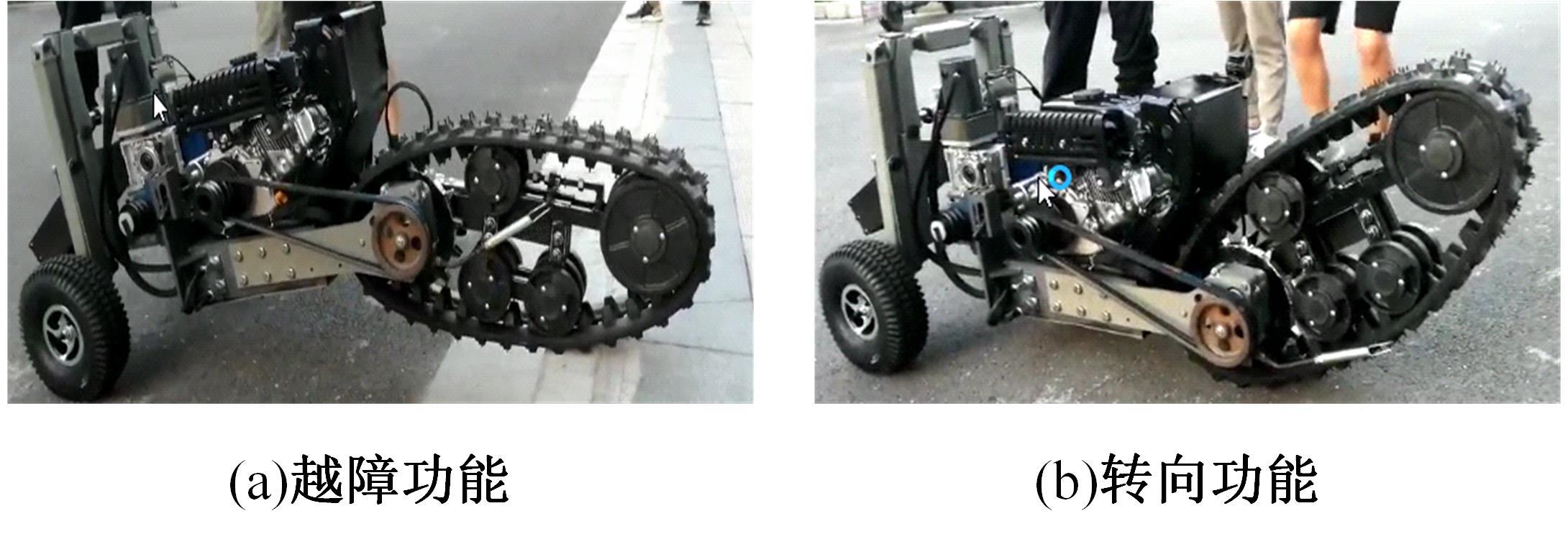
针对狭窄的丘陵山地耕作环境,设计了一种新型弓腰式移动底盘。该底盘的履带驱动装置能够被动自适应地形变化,亦能主动调整履带与地面的接触角度,提高履带的附着性能。首先,阐述了该移动底盘的机构设计和传动原理。其次,探究了履带在松软路面上行驶时土壤阻力和附着力大小的影响因素,分析了姿态变化与越障高度的关系,得到了该底盘在弓腰姿态时能够达到的最大越障垂直高度为241.53 mm。再次,通过纵向爬坡稳定性分析和折腰转向过程的几何分析,计算出最大爬坡度为41.23°、最小转向半径为1.297 m。最后,通过越障和机动性能试验验证了理论分析的可靠性。结果表明,所设计的底盘改变姿态后越障性能提高,具有较好的纵坡稳定性和灵活的机动性,能够满足复杂耕作环境中的作业需求,在农业、林业等领域具有广阔的应用前景。
中图分类号:
- TP242.3
| 1 | 崔思远, 金雪婷, 曹光乔. 我国丘陵山区农机化水平影响因素及区划研究-基于全国丘陵山区238个县(市)的调研数据中国农业资源与区划[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2018, 39 (11): 129-134. |
| Cui Si-yuan, Jin Xue-ting, Cao Guang-qiao. Study on the factors affecting the level of agricultural mechanization and regional division in hilly and mountainous areas of China—based on 238 counties (cites) investigations in hilly and mountainous areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2018, 39(11): 129-134. | |
| 2 | Wang Y J, Yang F Z, Pan G T, et al. Design and testing of a small remote-control hillside tractor[J]. Transactions of the ASABE, 2014, 57(2): 363-370. |
| 3 | 刘妤, 张拓, 谢铌, 等. 小型农用履带底盘多体动力学建模及验证[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(7): 39-46. |
| Liu Yu, Zhang Tuo, Xie Ni, et al. Multi-body dynamic modeling and verification of small agricultural crawler chassis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(7): 39-46. | |
| 4 | 李江, 王玉亮, 李瑞川, 等. 丘陵山地四轮驱动拖拉机驱动力主动分配系统研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2019, 41(8):227-235. |
| Li Jiang, Wang Yu-liang, Li Rui-chuan, et al. Research on driving force allocation system of four wheel drive tractor in hilly area[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2019, 41(8):227-235. | |
| 5 | 潘冠廷, 杨福增, 孙景彬, 等. 小型山地履带拖拉机爬坡越障性能分析与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(9): 374-383. |
| Pan Guan-ting, Yang Fu-zeng, Sun Jing-bin, et al. Analysis and test of the obstacle negotiation performance of a small hillside crawler tractor during climbing process[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(9): 374-383. | |
| 6 | 彭贺, 马文星, 王忠山, 等. 丘陵山地拖拉机车身调平控制仿真分析与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(1): 157-165. |
| Peng He, Ma Wen-xing, Wang Zhong-shan, et al. Control system of self-leveling in hilly tractor body through simulation and experiment[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 157-165. | |
| 7 | 丛茜, 徐金, 马博帅, 等. 基于虚拟仿真的拖拉机后悬挂检测装置设计与实验[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(2): 754-760. |
| Cong Qian, Xu Jin, Ma Bo-shuai, et al. Design and test of tractor hydraulic suspension system testing device based on virtual simulation[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 754-760. | |
| 8 | Gao Q M, Gao F, Tian L, et al. Design and development of a variable ground clearance, variable wheel track self-leveling hillside vehicle power chassis (V2-HVPC)[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2014, 56: 77-90. |
| 9 | 吴永栓, 孙晨阳, 周学剑, 等. 小型履带自走式电动多功能作业平台的设计及试验[J]. 湖南农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 45(6): 664-668. |
| Wu Yong-shuan, Sun Chen-yang, Zhou Xue-jian, et al. Design and test of the small size crawler-type self-propelled electric multifunctional operation platform[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2019,45(6): 664-668. | |
| 10 | 谢铌. 小型山地履带底盘坡地行驶性能分析与试验研究[D]. 重庆:重庆理工大学机械工程学院, 2020. |
| Xie Ni. Analysis and experimental study on the running performance of the small crawler chassis for mountain on slope[D]. Chongqing: Institute of Mechanical Engineering, Chongqing University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 11 | 赵建柱, 王枫辰, 于斌, 等. 农用仿形履带式动力底盘设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报: 2014, 45(9): 20-24. |
| Zhao Jian-zhu, Wang Feng-chen, Yu Bin, et al. Research on all terrain profiling crawler power chassis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(9): 20-24. | |
| 12 | 刘平义, 王振杰, 李海涛, 等. 行星履带式农用动力底盘设计与越障性能研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2014, 45():17-23. |
| Liu Ping-yi, Wang Zhen-jie, Li Hai-tao, et al. Design and overcoming obstacles ability research of tracked driving chassis with planetary structure[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(Sup.1):17-23. | |
| 13 | 王川伟, 马琨, 杨林, 等. 四摆臂-六履带机器人单侧台阶障碍越障仿真与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(10): 46-53. |
| Wang Chuan-wei, Ma Kun, Yang Lin, et al. Simulation and experiment on obstacle surmounting performance of four swing arms and six tracked robot under unilateral step environment[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(10): 46-53. | |
| 14 | 张明路, 李敏, 田颖, 等. 单履带被动自适应机器人设计与运动学分析[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 46(3): 69-74. |
| Zhang Ming-lu, Li Min, Tian Ying, et al. Design and kinematics analysis of single crawler wheel-track compound passive adaptive mobile robot[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(3): 69-74. | |
| 15 | 齐文超, 李彦明, 陶建峰, 等. 丘陵山地拖拉机姿态主动调整系统设计与实验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(7): 381-388. |
| Qi Wen-chao, Li Yan-ming, Tao Jian-feng, et al. Design and experiment of active attitude adjustment system for hilly area tractors[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(7): 381-388. | |
| 16 | 彭贺, 马文星, 赵恩鹏, 等. 丘陵山地轮式拖拉机车身调平系统设计与物理模型试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(14): 36-44. |
| Peng He, Ma Wen-xing, Zhao En-peng, et al. Design and physical model experiment of body leveling system for roller tractor in hilly and mountainous region[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(14): 36-44. | |
| 17 | 金诚谦, 杨腾祥, 刘岗微, 等. 履带式联合收获机全向调平底盘设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(11): 393-402. |
| Jin Cheng-qian, Yang Teng-xiang, Liu Gang-wei, et al. Design and test of posture controlled chassis for caterpillar combine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(11): 393-402. | |
| 18 | 魏楷峰. 基于DEM-MBD双向耦合的履带车辆松软地面转向阻力研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学生物与农业工程学院, 2020. |
| Wei Kai-feng. Research on steering resistance of tracked vehicle on soft ground based on DEM-MBD simulation[D]. Changchun: College of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Jilin University, 2020. | |
| 19 | 余志生.汽车理论 [M].6版. 北京:机械工业出版社, 2019. |
| 20 | 李雨潭, 朱华, 高志军, 等. 履带机器人通用地面力学模型分析与底盘设计[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2015, 36(8): 1126-1130. |
| Li Yu-tan, Zhu Hua, Gao Zhi-jun, et al. A universal terramechanics model and the chassis design of a tracked robot[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2015, 36(8): 1126-1130. | |
| 21 | Gao F, Zeng W, Jiang H, et al. Design and terrainability analysis of a novel mobile robot with variable-diameter wheels[C]∥Proceedings of International Conference on Energy, Power and Mechanical Engineering, Guangzhou, China, 2019: 135-143. |
| [1] | 赵伟, 孙汉旭, 贾庆轩, 张延恒, 于涛. 具有两种运动模式的球形机器人动力学建模与设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1386-1394. |
| [2] | 贺辉, 宋大凤, 杨南南, 雷雨春, 曾小华, 聂利卫, 王继新. 轮毂马达液驱系统控制与仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 27-31. |
|
||