吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 1971-1981.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220355
• • 上一篇
质子交换膜燃料电池运行工况参数敏感性分析
杨子荣1,2( ),李岩1,3,冀雪峰1,2,刘芳3,郝冬1,2(
),李岩1,3,冀雪峰1,2,刘芳3,郝冬1,2( )
)
- 1.中汽研新能源汽车检验中心(天津)有限公司,天津 300399
2.中国汽车技术研究中心有限公司,天津 300399
3.河北工业大学 机械工程学院,天津 300401
Sensitivity analysis of operating parameters for proton exchange membrane fuel cells
Zi-rong YANG1,2( ),Yan LI1,3,Xue-feng JI1,2,Fang LIU3,Dong HAO1,2(
),Yan LI1,3,Xue-feng JI1,2,Fang LIU3,Dong HAO1,2( )
)
- 1.CATARC New Energy Vehicle Test Center (Tianjin) Co. ,Ltd. ,Tianjin 300399,China
2.China Automotive Technology and Research Center Co. ,Ltd. ,Tianjin 300399
3.School of Mechanical Engineering,Hebei University of Technology,Tianjin 300401,China
摘要:
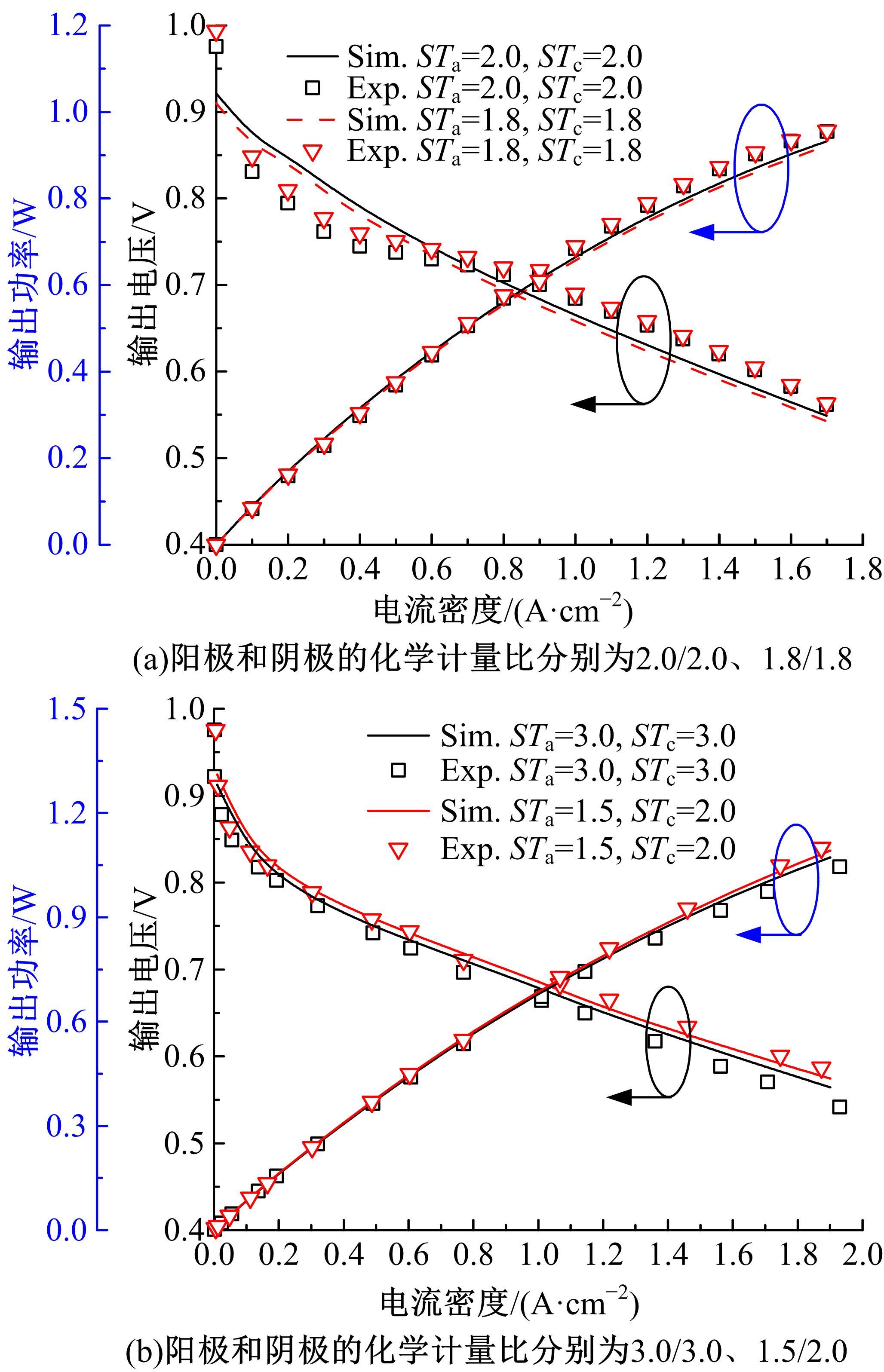
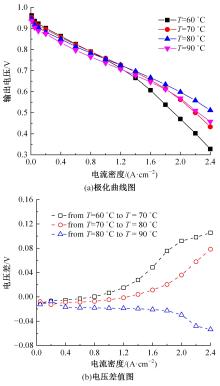
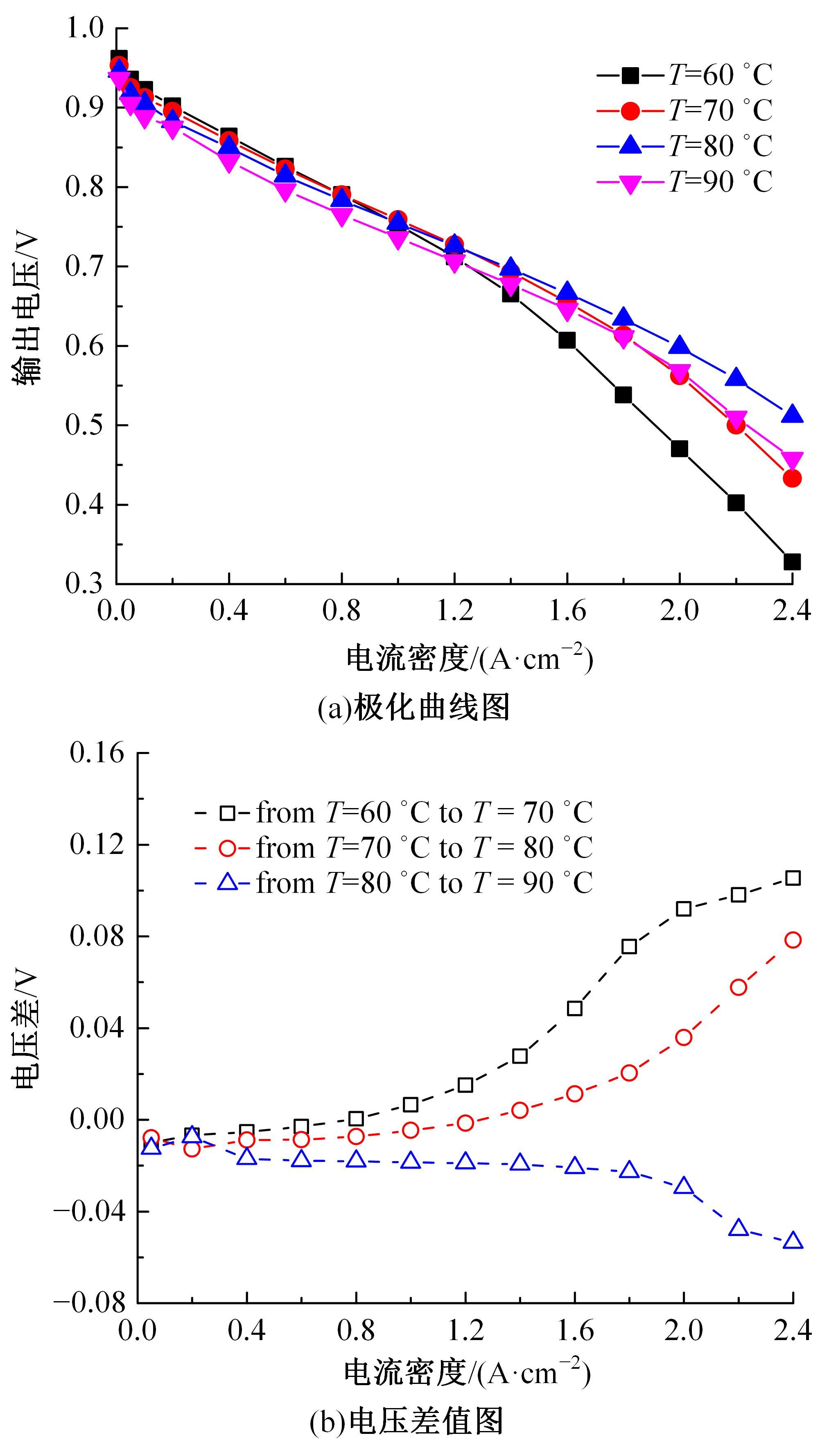
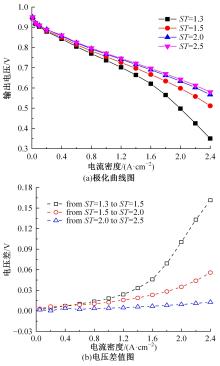
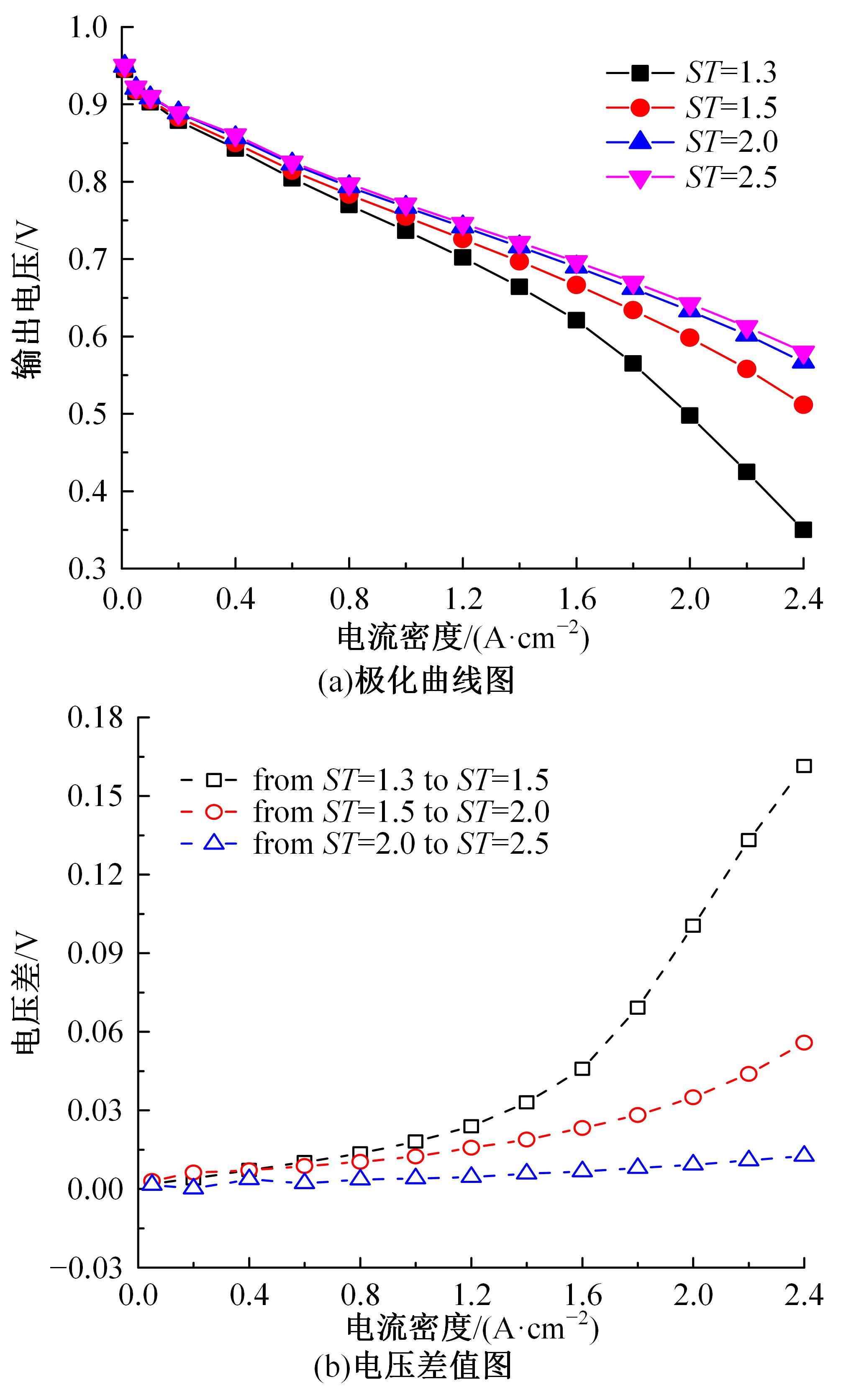
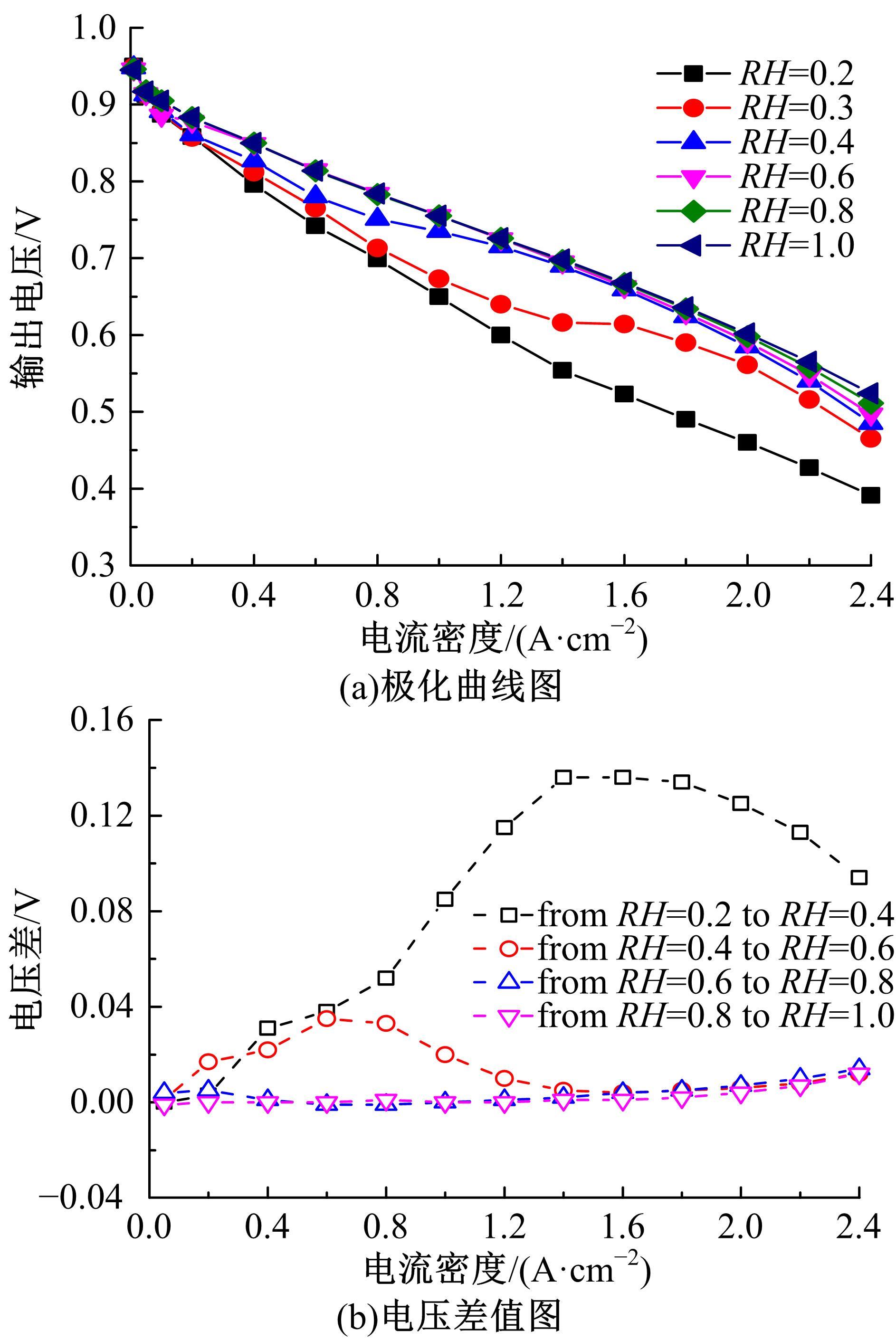
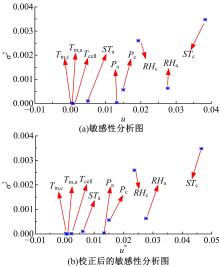
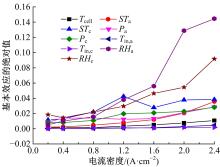
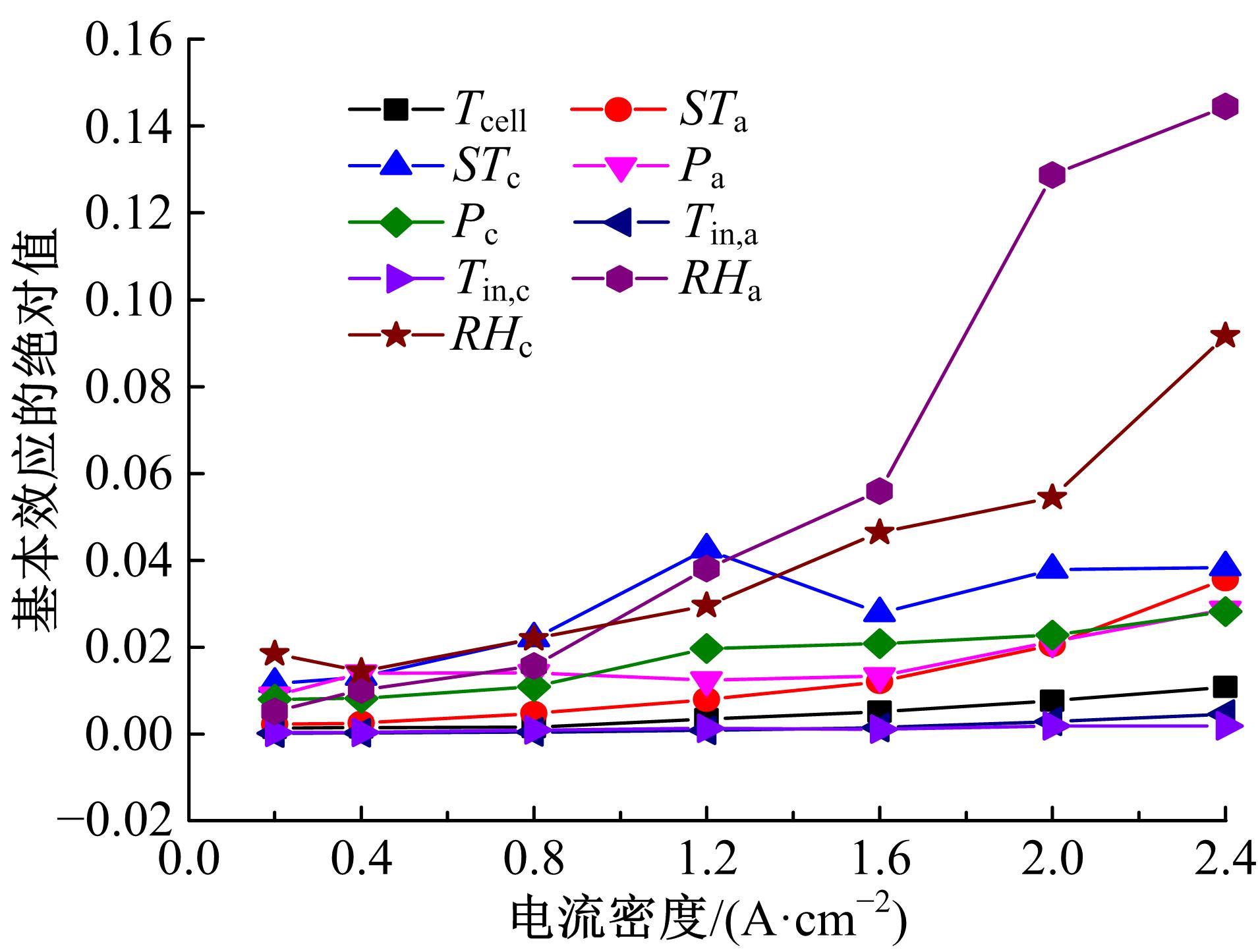
建立了一维瞬态多相流燃料电池机理模型和全局敏感性分析模型,研究了运行温度、气体压强、化学计量比以及相对湿度对输出性能的影响规律和影响程度。结果表明:高功率负荷条件下,运行温度的变化会造成更明显的性能波动;提高进气压强和化学计量比能够增强输出性能;相对湿度过低产生的“膜干”现象在低电流密度区域更加明显;经过敏感性量化分析,本文将9类工况参数划分为高敏感、较敏感和不敏感参数;随着电流密度的增大,阴极进气化学计量比、阴阳极进气湿度的敏感性较大且整体呈上升趋势。
中图分类号:
- TM911.42
| 1 | 高帷韬, 雷一杰, 张勋, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池研究进展[J].化工进展, 2022, 41(3): 1539-1555. |
| Gao Wei-tao, Lei Yi-jie, Zhang Xun, et al. An overview of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(3): 1539-1555. | |
| 2 | 侯中军, 江洪春, 王仁芳, 等. 轿车用燃料电池发动机示范应用稳定性[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(): 131-136. |
| Hou Zhong-jun, Jiang Hong-chun, Wang Ren-fang, et al. Performance stability of fuel cell engine applied in the fuel cell car demonstration[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(Sup.2): 131-136. | |
| 3 |
孙闫,夏长高,尹必峰,等. 燃料电池电动汽车的能量管理[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版. DOI:10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210773 .
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210773 |
|
Sun Yan, Xia Chang-gao, Yin Bi-feng, et al. Energy management strategyof fuel cell electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition).DOI:10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210773 .
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210773 |
|
| 4 | Chen H C, Liu B, Zhang T, et al. Influencing sensitivities of critical operating parameters on PEMFC output performance and gas distribution quality under different electrical load conditions[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 255: No. 113849. |
| 5 | Miansari M, Sedighi K, Amidpour M, et al. Experimental and thermodynamic approach on proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 190(2): 356-361. |
| 6 | Barakat E G, Abdel-Rahman A K, Ahmed M A, et al. An experimental study of operational parameters on the performance of PEMFCs[C]∥Asme International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition. British Columbia, Canada, 2010, 927-933. |
| 7 | Zhang Q, Lin R, Cui X, et al. Experimental study of variable operating parameters effects on overall PEMFC performance and spatial performance distribution[J]. Energy, 2016, 115(1): 550-560. |
| 8 | Liu Y F, Fan L, Pei P C, et al. Asymptotic analysis for the inlet relative humidity effects on the performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 231: 573-584. |
| 9 | Baschuk J, Li X G. Modelling of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells with variable degrees of water flooding[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2000, 86(1/2): 181-196. |
| 10 | Mann R F, Amphlett J C, Hooper M, et al. Development and application of a generalised steady-state electrochemical model for a PEM fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2000, 86(1/2): 173-180. |
| 11 | Bernardi D M. Water-balance calculations for solid-polymerelectrolyte fuel cells[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1990, 137(11): 3344-3350. |
| 12 | Yang Z R, Du Q, Jia Z W, et al. A comprehensive proton exchange membrane fuel cell system model integrating various auxiliary subsystems[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 256: No. 113959. |
| 13 | Bao C, Bessler W G. Two-dimensional modeling of a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell with long flow channel. Part I. Model development[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275: 922-934. |
| 14 | Jiao K, Li X G. Effect of surface dynamic wettability in proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(17): 9095-9103. |
| 15 | Liao X, Liu K, Le J, et al. Extended affine arithmetic-based global sensitivity analysis for power flow with uncertainties[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2020, 115: No. 105440. |
| 16 | Min C H, He Y L, Liu X L, et al. Parameter sensitivity examination and discussion of PEM fuel cell simulation model validation: part II: results of sensitivity analysis and validation of the model[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 160(1): 374-385. |
| 17 | Laoun B, Naceur M W, Khellaf A, et al. Global sensitivity analysis of proton exchange membrane fuel cell model[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(22): 9521-9528. |
| 18 | Jiang Y, Yang Z R, Jiao K,et al. Sensitivity analysis of uncertain parameters based on an improved proton exchange membrane fuel cell analytical model[J]. Energy Conversion & Management, 2018, 164: 639-654. |
| 19 | 焦魁 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池水热管理[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2020. |
| 20 | Yang Z R, Du Q, Huo S, et al. Effect of membrane electrode assembly design on the cold start process of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(40): 25372-25387. |
| 21 | Huo S, Jiao K, Park J W. On the water transport behavior and phase transition mechanisms in cold start operation of PEM fuel cell[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 233-234: 776-788. |
| 22 | Wu K C, Xie X, Wang B W, et al. Two-dimensional simulation of cold start processes for proton exchange membrane fuel cell with different hydrogen flow arrangements[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(35): 17795-17812. |
| 23 | Yao L, Peng J, Zhang J B, et al. Numerical investigation of cold-start behavior of polymer electrolyte fuel cells in the presence of super-cooled water[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(32): 15505-15520. |
| 24 | Gwak G H, Ko J H, Ju H. Numerical investigation of cold-start behavior of polymer-electrolyte fuel-cells from subzero to normal operating temperatures- effects of cell boundary and operating conditions[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(36): 21927-21937. |
| 25 | Yang Z R, Du Q, Huo S, et al. Effect of membrane electrode assembly design on the cold start process of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(40): 25372-25387. |
| 26 | Wang B, Wu K, Yang Z, et al. A quasi-2D transient model of proton exchange membrane fuel cell with anode recirculation[J]. Energy Conversion & Management, 2018, 171: 1463-1475. |
| 27 | Abdollahzadeh M, Ribeirinha P, Boaventura M, et al. Three-dimensional modeling of PEMFC with contaminated anode fuel[J]. Energy, 2018, 152: 939-959. |
| 28 | Morris M D. Factorial sampling plans for preliminary computational experiments[J]. Technometrics, 1991, 33(2): 161-174. |
| 29 | Xia Z F, Chen H C, Zhang T, et al. Effect of channel-rib width ratio and relative humidity on performance of a single serpentine PEMFC based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(26):13076-13086. |
| 30 | Najmi A, Anyanwu I S, Xie X, et al. Experimental investigation and optimization of proton exchange membrane fuel cell using different flow fields[J]. Energy, 2021, 217: No. 119313. |
| 31 | Yang T, Sheu B, Ghalambaz M, et al. Effects of operating parameters and load mode on dynamic cell performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(2): 2474-2487. |
| 32 | Jiao K, Li X G. Water transport in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. Progress in Energy & Combustion Science, 2011, 37(3): 221-291. |
| 33 | Yin L Z, Qi L, Chen W R, et al. Experimental analysis of optimal performance for a 5 kW PEMFC system[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(11): 5499-5506. |
| [1] | 池训逞,侯中军,魏伟,夏增刚,庄琳琳,郭荣. 基于模型的质子交换膜燃料电池系统阳极气体浓度估计技术综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [2] | 徐振军,王浩,赵开元,郝博轶,李清清,王常浩. 复合太阳能的燃气机热泵热力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1759-1763. |
|
||