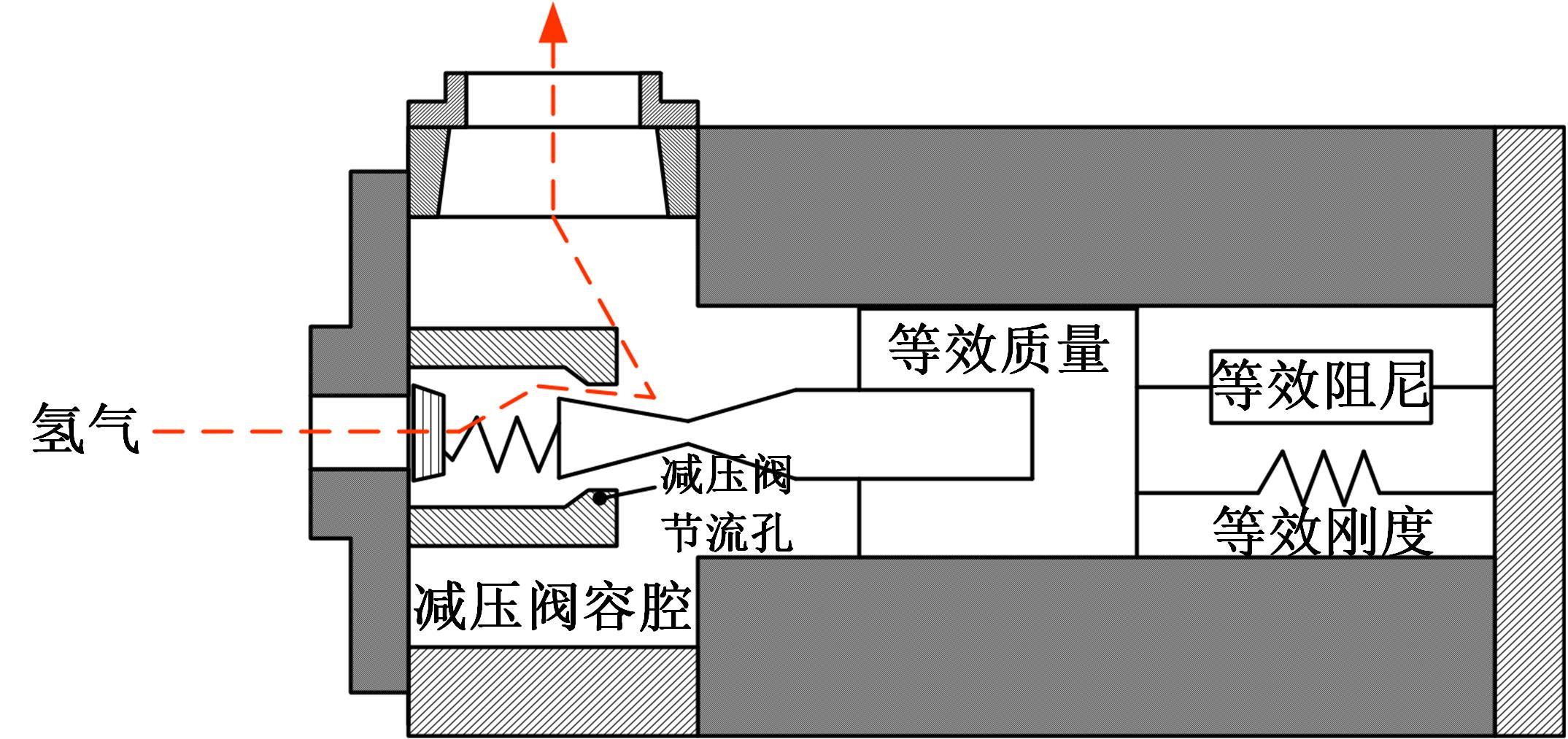
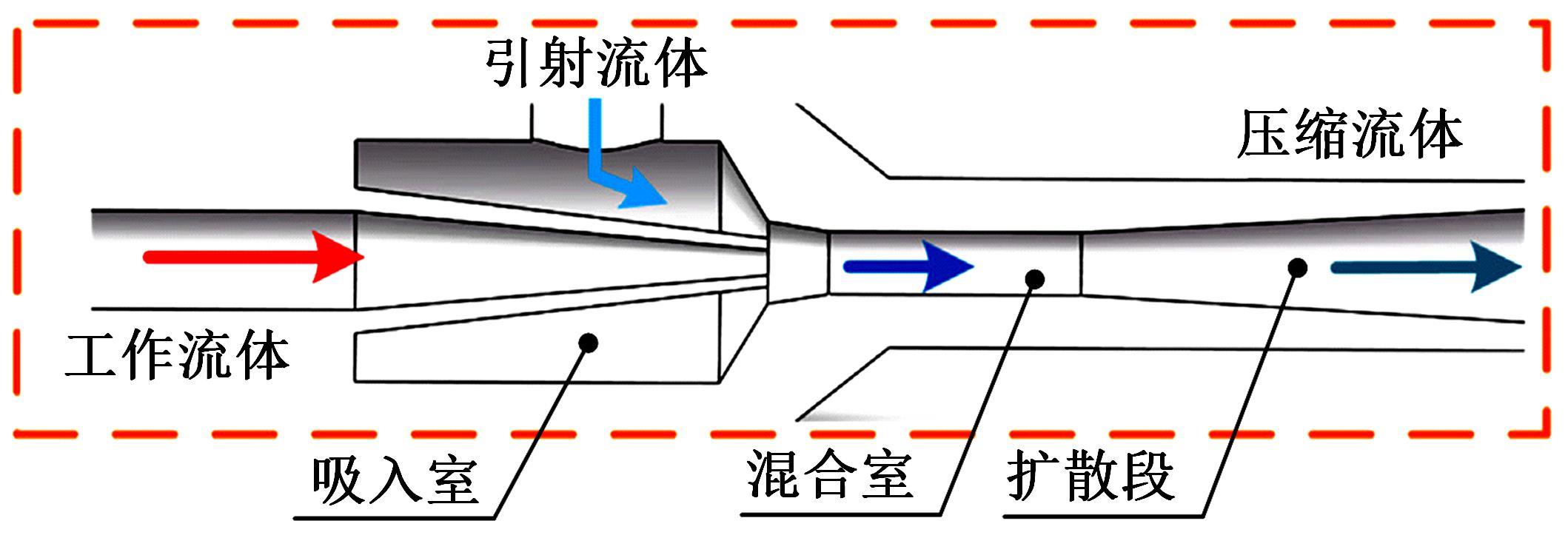
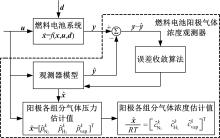
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 1957-1970.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220261
• •
基于模型的质子交换膜燃料电池系统阳极气体浓度估计技术综述
池训逞1( ),侯中军2,魏伟3,4,夏增刚2,庄琳琳2,郭荣1(
),侯中军2,魏伟3,4,夏增刚2,庄琳琳2,郭荣1( )
)
- 1.同济大学 汽车学院,上海 201804
2.上海捷氢科技股份有限公司 系统开发部,上海 201800
3.中科军联(张家港)新能源科技有限公司 技术中心,江苏 张家港 215600
4.上海醇加能源科技有限公司 技术中心,上海 201600
Review of model⁃based anode gas concentration estimation techniques of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system
Xun-cheng CHI1( ),Zhong-jun HOU2,Wei WEI3,4,Zeng-gang XIA2,Lin-lin ZHUANG2,Rong GUO1(
),Zhong-jun HOU2,Wei WEI3,4,Zeng-gang XIA2,Lin-lin ZHUANG2,Rong GUO1( )
)
- 1.School of Automotive Studies,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.Department of System Development,Shanghai Hydrogen Propulsion Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Shanghai 201800,China
3.CAS&M (Zhangjiagang) New Energy Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Zhangjiagang 215600,China
4.Shanghai Alcplus Energy Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Shanghai 201600,China
摘要:
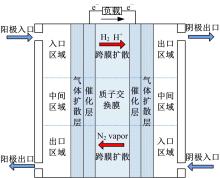
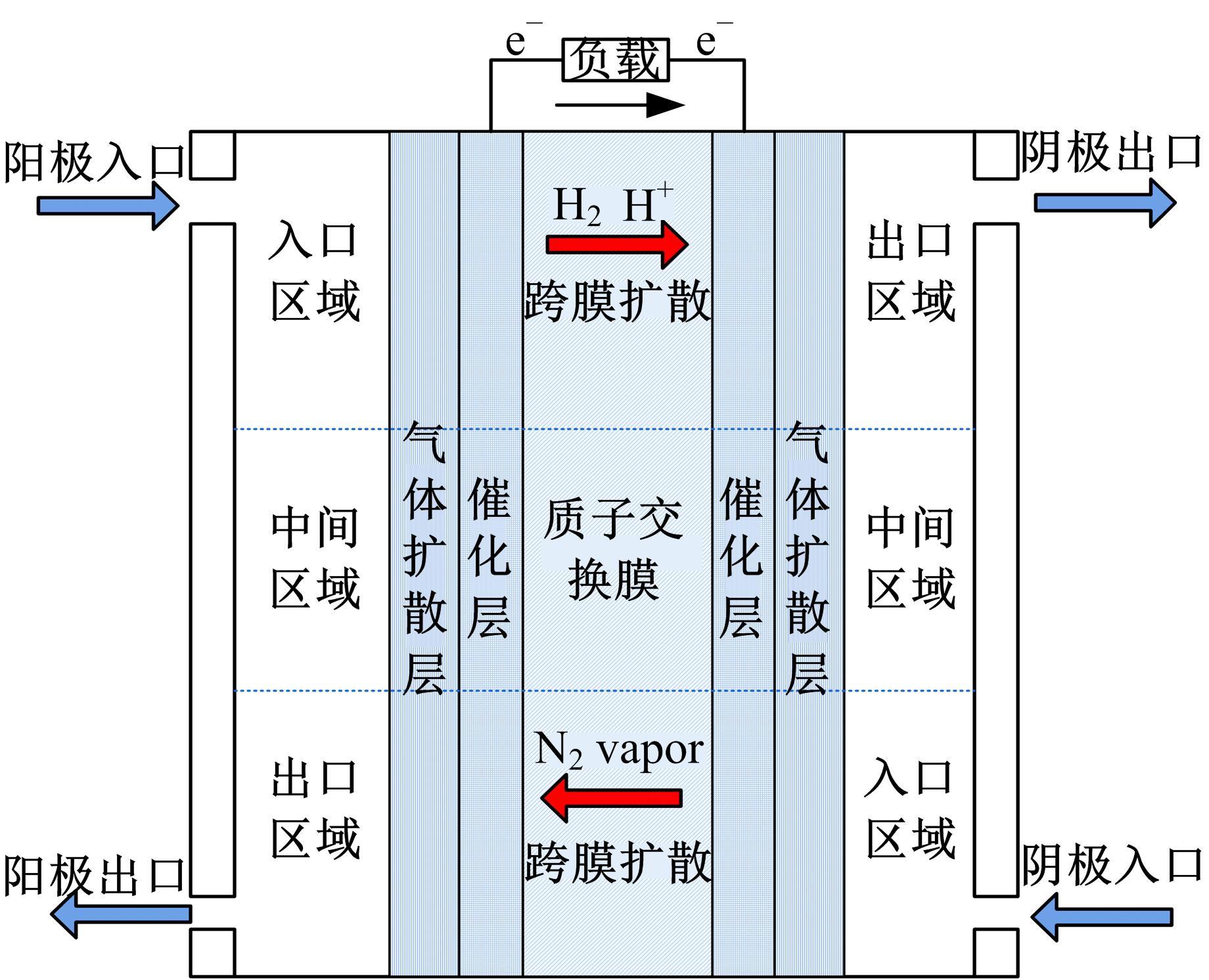
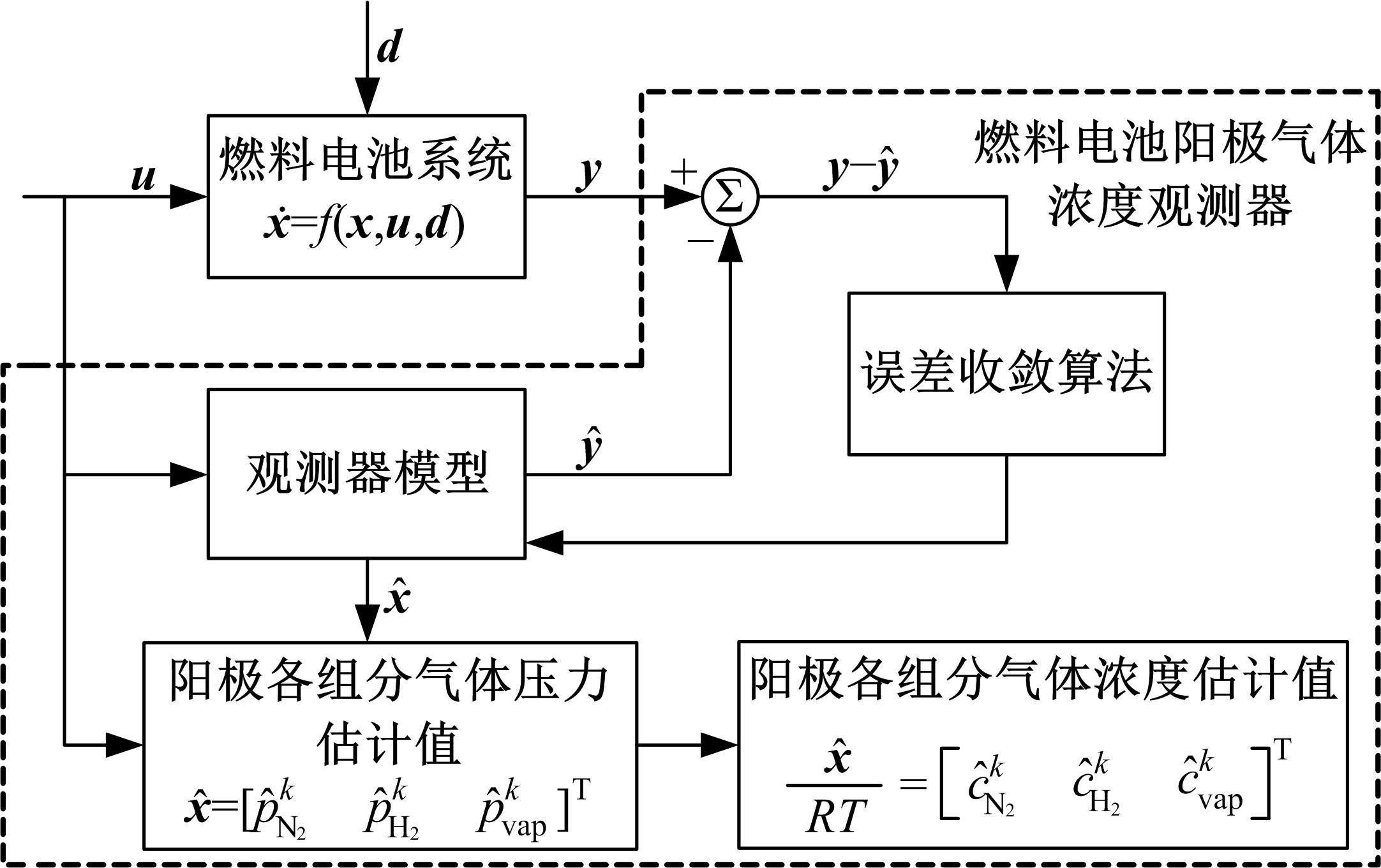
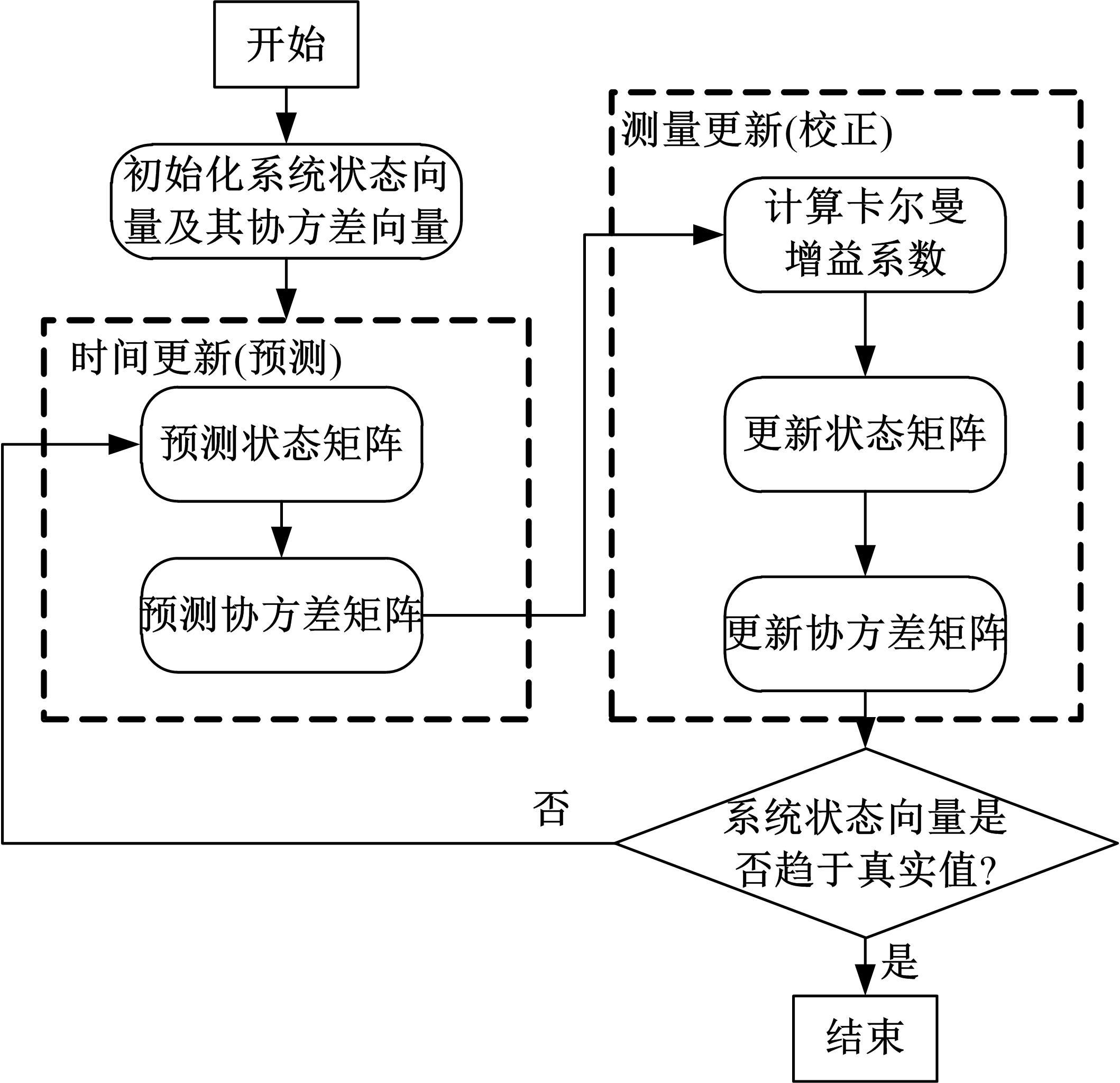
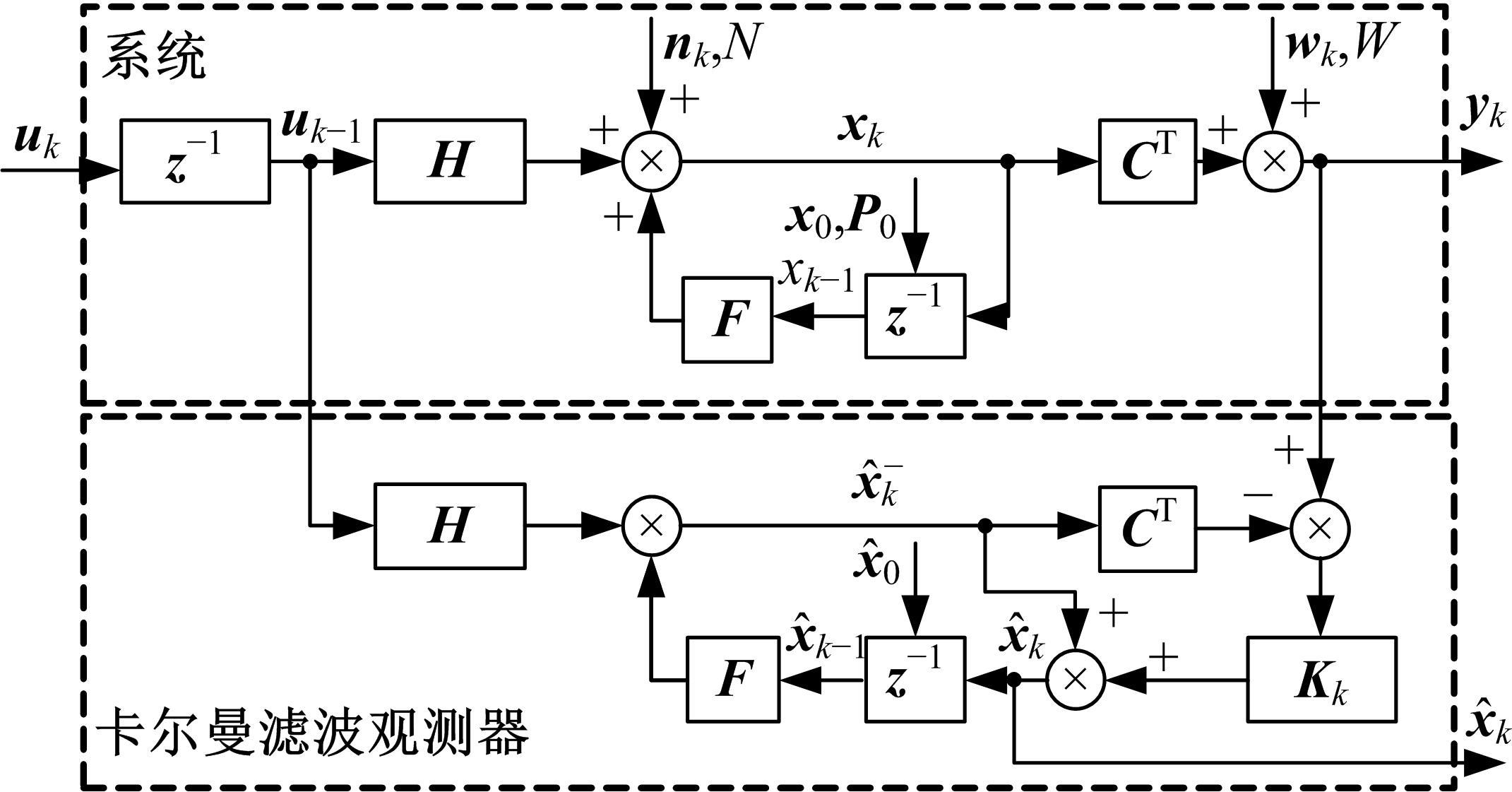
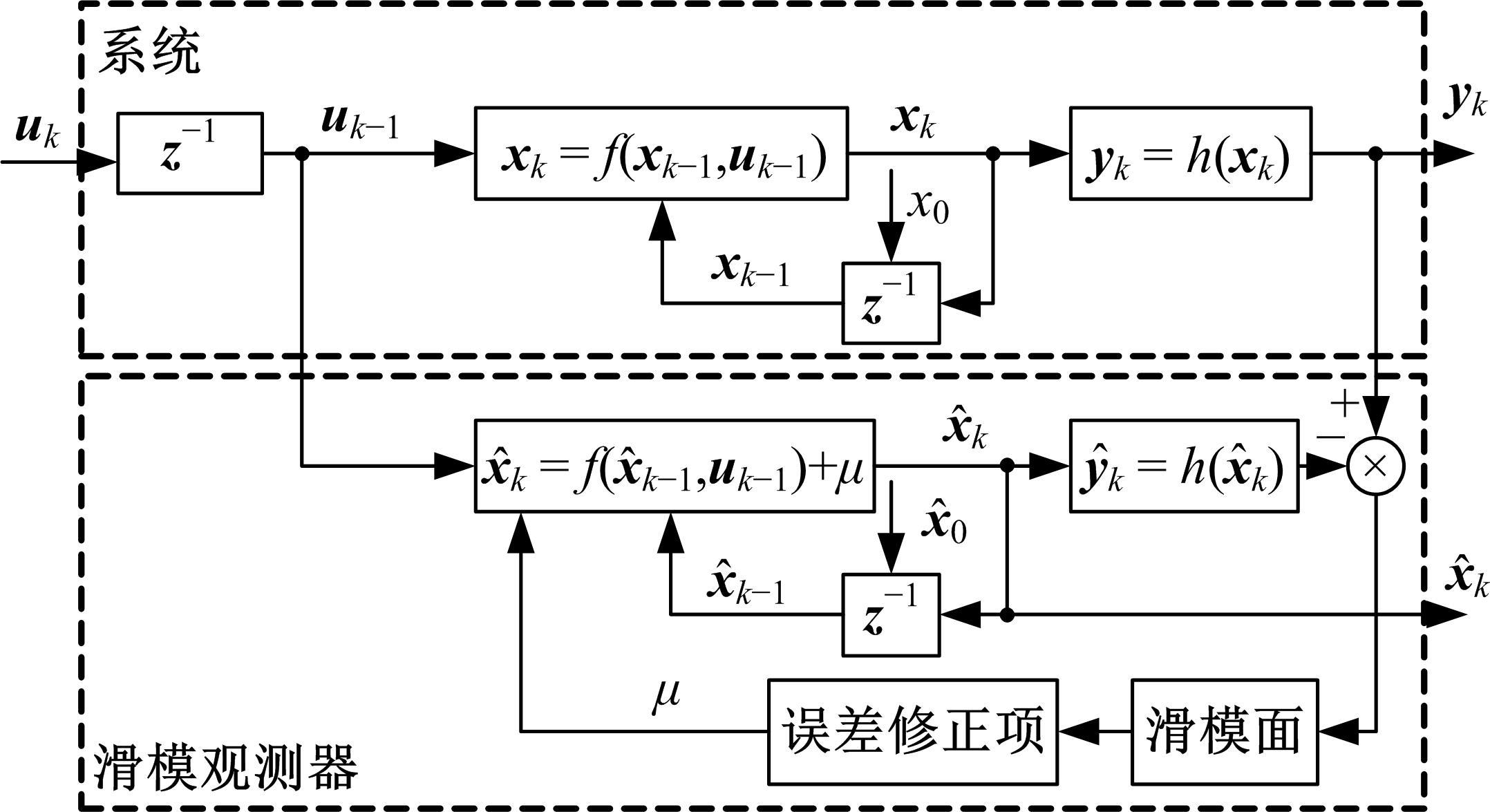
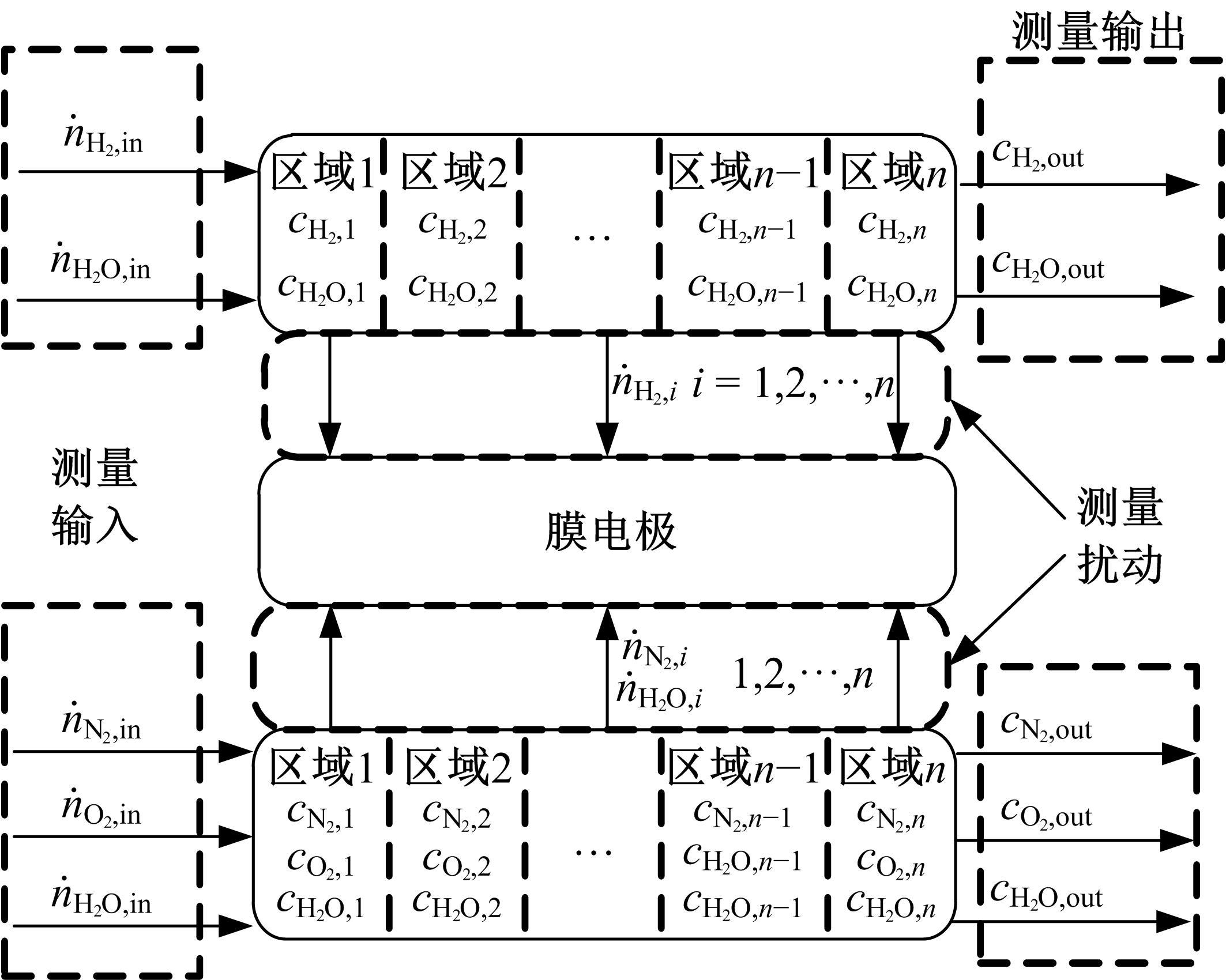
为了对质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC)系统进行管理以延长其寿命,需要设计基于模型的状态观测器对内部状态进行实时监测,并通过反馈控制将其控制在预期水平。由于PEMFC阳极氢气浓度直接决定了系统的输出性能,并且不断循环的氢气以及氮气因跨膜扩散在阳极不断累积,导致阳极气体浓度估计困难。因此,本文着重介绍了PEMFC阳极气体浓度估计的前沿技术,并对现有研究存在的问题和未来发展趋势进行了阐述,以期为PEMFC气、水、热管理的研究做出贡献。
中图分类号:
- TM911
| 1 | 周雅夫, 邵芳雪, 黄立建, 等. 燃料电池车用新型低纹波DC/DC变换器设计[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(4): 1201-1208. |
| Zhou Ya-fu, Shao Fang-xue, Huang Li-jian, et al. Design of a new low ripple DC/DC converter for fuel cell vehicles[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 50(4): 1201-1208. | |
| 2 | 张少哲, 戴海峰, 袁浩, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池电化学阻抗谱敏感性研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(14): 40-51. |
| Zhang Shao-zhe, Dai Hai-feng, Yuan Hao, et al. Sensibility study on electrochemical impedance of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(14): 40-51. | |
| 3 | 吴中乐. 基于观测器的燃料电池氢气供给控制[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学控制科学与工程学院, 2018. |
| Wu Zhong-le. Observer based fuel delivery control for PEMFC fuel cells[D]. Hangzhou: College of Control Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, 2018. | |
| 4 | Jiao J R, Chen F X. Humidity estimation of vehicle proton exchange membrane fuel cell undervariable operating temperature based on adaptive sliding mode observation[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 313:No.118779. |
| 5 | 周伟, 朱鑫宁, 连云崧, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池的三维流场技术研究进展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(8): 2-12. |
| Zhou Wei, Zhu Xin-ning, Lian Yun-song, et al. Research progress on three-dimensional flow field technology of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(8): 2-12. | |
| 6 | 周苏, 胡哲, 谢非. 车用质子交换膜燃料电池空气供应系统自适应解耦控制方法研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2020, 42(2): 172-177. |
| Zhou Su, Hu Zhe, Xie Fei. Study on adaptive decoupling control algorithm for air supply system of vehicle proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2020, 42(2): 172-177. | |
| 7 | 严彦, 周利彪, 白文涛, 等. 燃料电池用空气压缩机的研究现状[J]. 机电工程, 2021, 38(12): 1513-1519. |
| Yan Yan, Zhou Li-biao, Bai Wen-tao, et al. Research status of air compressors in fuel cells[J]. Journal of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, 2021, 38(12): 1513-1519. | |
| 8 | 霍海波, 杨海东, 周帅福, 等. PEMFC系统故障诊断的研究[J]. 电池, 2020, 50(3): 289-292. |
| Huo Hai-bo, Yang Hai-dong, Zhou Shuai-fu, et al. Research status quo of fault diagnosis for a PEMFC system[J]. Battery Bimonthly, 2020, 50(3): 289-292. | |
| 9 | 方川. 基于降维模型的燃料电池发动机控制方法研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学车辆与运载学院, 2017. |
| Fang Chuan. Fuel cell engine control based on reduced dimension model[D]. Beijing: School of Vehicle and Mobility, Tsinghua University, 2017. | |
| 10 | 韩济泉, 孔祥程, 冯健美, 等. 大功率燃料电池汽车氢循环系统性能分析[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(1): 1-7, 35. |
| Han Ji-quan, Kong Xiang-cheng, Feng Jian-mei, et al. Performance analysis of hydrogen recirculation system of high power fuel cell vehicles[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(1): 1-7, 35. | |
| 11 | 刘子伟. 燃料电池供氢系统建模与控制策略研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学机械与电子控制工程学院, 2021. |
| Liu Zi-wei. Research on modeling and control strategy of fuel cell hydrogen supply system[D]. Beijing: School of Mechanical, Electronic and Control Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2021. | |
| 12 | Huang Z, Jian Q, Zhao J. Experimental study on improving the dynamic characteristics of open-cathode PEMFC stack with dead-end anode by condensation and circulation of hydrogen[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(38): 19858-19868. |
| 13 | Hu Z, Yu Y, Wang G J, et al. Anode purge strategy optimization of the polymer electrode membrane fuel cell system under the dead-end anode operation[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 320: 68-77. |
| 14 | Wang B, Deng H, Jiao K. Purge strategy optimization of proton exchange membrane fuel cell with anode recirculation[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 225: 1-13. |
| 15 | Shen K Y, Park S, Kim Y-B. Hydrogen utilization enhancement of proton exchange membrane fuel cell with anode recirculation system through a purge strategy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(33): 16773-16786. |
| 16 | Cheng Z Y, Luo L Z, Huang B, et al. Effect of humidification on distribution and uniformity of reactants and water content in PEMFC[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(52): 26560-26574. |
| 17 | Fan L H, Zhang G B, Jiao K. Characteristics of PEMFC operating at high current density with low external humidification[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 150: 763-774. |
| 18 | Hu D H, Wang Y T, Li J W, et al. Investigation of optimal operating temperature for the PEMFC and its tracking control for energy saving in vehicle applications[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 249: No. 114842. |
| 19 | Liu Y, Tu Z, Chan S H. Performance enhancement in a H2/O2 PEMFC with dual-ejector recirculation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(25): 12698-12710. |
| 20 | Xue H, Wang L, Zhang H, et al. Design and investigation of multi-nozzle ejector for PEMFC hydrogen recirculation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(28): 14500-14516. |
| 21 | Zhao D D, Xia L, Dang H B, et al. Design and control of air supply system for PEMFC UAV based on dynamic decoupling strategy[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 253: No. 115159. |
| 22 | Baik K D, Kim M S. Characterization of nitrogen gas crossover through the membrane in proton-exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(1): 732-739. |
| 23 | Xu L F, Hu J, Cheng S L, et al. Nonlinear observation of internal states of fuel cell cathode utilizing a high-order sliding-mode algorithm[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 356: 56-71. |
| 24 | Jiao K, Alaefour I E, Li X G, et al. Simultaneous measurement of current and temperature distributions in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(8): 2967-2982. |
| 25 | Hu J M, Xu L F, Li J Q, et al. Model-based estimation of liquid saturation in cathode gas diffusion layer and current density difference under proton exchange membrane fuel cell flooding[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(41): 14187-14201. |
| 26 | Verma A, Pitchumani R. Influence of membrane properties on the transient behavior of polymer electrolyte fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 268: 733-743. |
| 27 | Siege C. Review of computational heat and mass transfer modeling in polymer-electrolyte-membrane (PEM) fuel cells[J]. Energy, 2008, 33(9): 1331-1352. |
| 28 | Ziogou C, Voutetakis S, Papadopoulou S, et al. Modeling, simulation and experimental validation of a PEM fuel cell system[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2011, 35(9): 1886-1900. |
| 29 | 洪凌. 车用燃料电池发电系统氢气回路控制[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学控制科学与工程学院, 2017. |
| Hong Ling. Fuel delivery control for vehicular fuel cell power systems[D]. Hangzhou: College of Control Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, 2017. | |
| 30 | Hong L, Chen J, Liu Z Y, et al. A nonlinear control strategy for fuel delivery in PEM fuel cells considering nitrogen permeation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(2): 1565-1576. |
| 31 | Liu Z, Chen J, Liu H, et al. Anode purge management for hydrogen utilization and stack durability improvement of PEM fuel cell systems[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 275: No. 115110. |
| 32 | Lira S, Puig V, Quevedo J, et al. LPV observer design for PEM fuel cell system: application to fault detection[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(9): 4298-4305. |
| 33 | Lira S, Puig V, Quevedo J, et al. LPV model-based fault diagnosis using relative fault sensitivity signature approach in a PEM fuel cell[C]∥18th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Marrakech, Morocco, 2010: 1284-1289. |
| 34 | Lira S, Puig V, Quevedo J. Robust LPV model-based sensor fault diagnosis and estimation for a PEM fuel cell system[C]∥2010 Conference on Control and Fault-Tolerant Systems, Nice, France, 2010: 819-824. |
| 35 | Hua Z G, Zheng Z X, Pahon E, et al. A review on lifetime prediction of proton exchange membrane fuel cells system[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 529: No. 231256. |
| 36 | Böhler L, Ritzberger D, Hametner C, et al. Constrained extended Kalman filter design and application for on-line state estimation of high-order polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell systems[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(35): 18604-18614. |
| 37 | Chen K, Laghrouche S, Djerdir A. Performance analysis of PEM fuel cell in mobile application under real traffic and environmental conditions[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 227: No. 113602. |
| 38 | Xu L F, Hu Z Y, Fang C, et al. Anode state observation of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell based on unscented Kalman filter and relative humidity sensor before flooding[J]. Renewable Energy, 2021, 168: 1294-1307. |
| 39 | Piffard M, Gerard M, Bideaux E, et al. Control by state observer of PEMFC anodic purges in dead-end operating mode[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2015, 48(15): 237-243. |
| 40 | Vepa R. Adaptive state estimation of a PEM fuel cell[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2012, 27(2): 457-467. |
| 41 | Arcak M, Görgün H, Pedersen L M, et al. A nonlinear observer design for fuel cell hydrogen estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2004, 12(1): 101-110. |
| 42 | Morales J, Astorga C, Reyes J, et al. Application of a nonlinear observer for estimation of variables in a PEM fuel cell system[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2017, 39: 1323-1332. |
| 43 | Matraji I, Ahmed F S, Laghrouche S, et al. Comparison of robust and adaptive second order sliding mode control in PEMFC air-feed systems[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(30): 9491-9504. |
| 44 | Kim E-S, Kim C-J, Eom K-S. Nonlinear observer design for PEM fuel cell systems[C]∥2007 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Seoul, Korea, 2007: 1835-1839. |
| 45 | Piffard M, Gerard M, Fonseca R D. Sliding mode observer for proton exchange membrane fuel cell: automotive application[J]. Journal of Power Sources, Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 388: 71-77. |
| 46 | Liu J X, Lin W Y, Alsaadi F, et al. Nonlinear observer design for PEM fuel cell power systems via second order sliding mode technique[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 168: 145-151. |
| 47 | Sankar K, Jana A K. Nonlinear multivariable sliding mode control of a reversible PEM fuel cell integrated system[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 171: 541-565. |
| 48 | Chen H C, Zhao X, Qu B W, et al. An evaluation method of gas distribution quality in dynamic process of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Applied Energy, 232, 2018: 26-35. |
| 49 | Mangold M, Bück A, Hanke-Rauschenbach R. Passivity based control of a distributed PEM fuel cell model[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2010, 20(3): 292-313. |
| 50 | Luna J, Husar A, Serra M. Nonlinear distributed parameter observer design for fuel cell systems[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(34): 11322-11332. |
| 51 | Luna J, Usai E, Husar A, et al. Nonlinear observation in fuel cell systems: a comparison between disturbance estimation and high-order sliding-mode techniques[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(43): 19737-19748. |
| 52 | Luna J, Ocampo-Martinez C, Serra M. Nonlinear predictive control for the concentrations profile regulation under unknown reaction disturbances in a fuel cell anode gas channel[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 282: 129-139. |
| 53 | Luna J, Jemei S, Yousfi-Steiner N, et al. Nonlinear predictive control for durability enhancement and efficiency improvement in a fuel cell power system[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 328: 250-261. |
| 54 | Chen J, Wu Z L, Wu C S, et al. Observer based fuel delivery control for PEM fuel cells with a segmented anode model[J]. Asian Journal of Control, 2019, 21(4): 1781-1795. |
| [1] | 刘汉武,雷雨龙,阴晓峰,付尧,李兴忠. 增程式电动汽车增程器多点控制策略优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1741-1750. |
| [2] | 王骏骋,吕林峰,李剑敏,任洁雨. 分布驱动电动汽车电液复合制动最优滑模ABS控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1751-1758. |
| [3] | 王奎洋,何仁. 基于支持向量机的制动意图识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1770-1776. |
| [4] | 高青,王浩东,刘玉彬,金石,陈宇. 动力电池应急冷却喷射模式实验分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1733-1740. |
| [5] | 郝帅,程川泰,王军年,张君媛,俞有. 运动型SUV驾驶室布置人机优化设计与测试评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1477-1488. |
| [6] | 张家旭,郭崇,王晨,赵健,王欣志. 基于半实物仿真平台的自动泊车系统性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1552-1560. |
| [7] | 杨红波,史文库,陈志勇,郭年程,赵燕燕. 基于某二级减速齿轮系统的齿面修形优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1541-1551. |
| [8] | 聂光明,谢波,田彦涛. 基于Frenet框架的协同自适应巡航控制算法设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1687-1695. |
| [9] | 华琛,牛润新,余彪. 地面车辆机动性评估方法与应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1229-1244. |
| [10] | 李雄,兰凤崇,陈吉清,童芳. Hybird III假人模型与CHUBM人体生物力学模型的正碰损伤对比[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1264-1272. |
| [11] | 刘兴涛,刘晓剑,武骥,何耀,刘新天. 基于曲线压缩和极限梯度提升算法的锂离子电池健康状态估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1273-1280. |
| [12] | 张英朝,李昀航,郭子瑜,王国华,张喆,苏畅. 长头重型卡车气动减阻优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 745-753. |
| [13] | 史文库,张曙光,张友坤,陈志勇,江逸飞,林彬斌. 基于改进海鸥算法的磁流变减振器模型辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 764-772. |
| [14] | 李杰,陈涛,郭文翠,赵旗. 汽车非平稳随机振动空间域虚拟激励法及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 738-744. |
| [15] | 李伟,宋海生,陆浩宇,史文库,王强,王晓俊. 复合材料板簧迟滞特性线性辨识方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 829-836. |
|
||