吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 1163-1173.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210792
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于部分最大可满足性问题的动态系统中最小故障检测隔离集求解方法
欧阳丹彤1,2( ),孙睿2,3,田新亮1,2,张立明1,2(
),孙睿2,3,田新亮1,2,张立明1,2( ),刘萍萍1,2
),刘萍萍1,2
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
3.吉林大学 软件学院,长春 130012
Approach for generating minimal fault detectability and isolability set in dynamic system based on partial maximum satisfiability problem
Dan-tong OUYANG1,2( ),Rui SUN2,3,Xin-liang TIAN1,2,Li-ming ZHANG1,2(
),Rui SUN2,3,Xin-liang TIAN1,2,Li-ming ZHANG1,2( ),Ping-ping LIU1,2
),Ping-ping LIU1,2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
3.College of Software,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
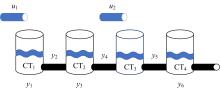
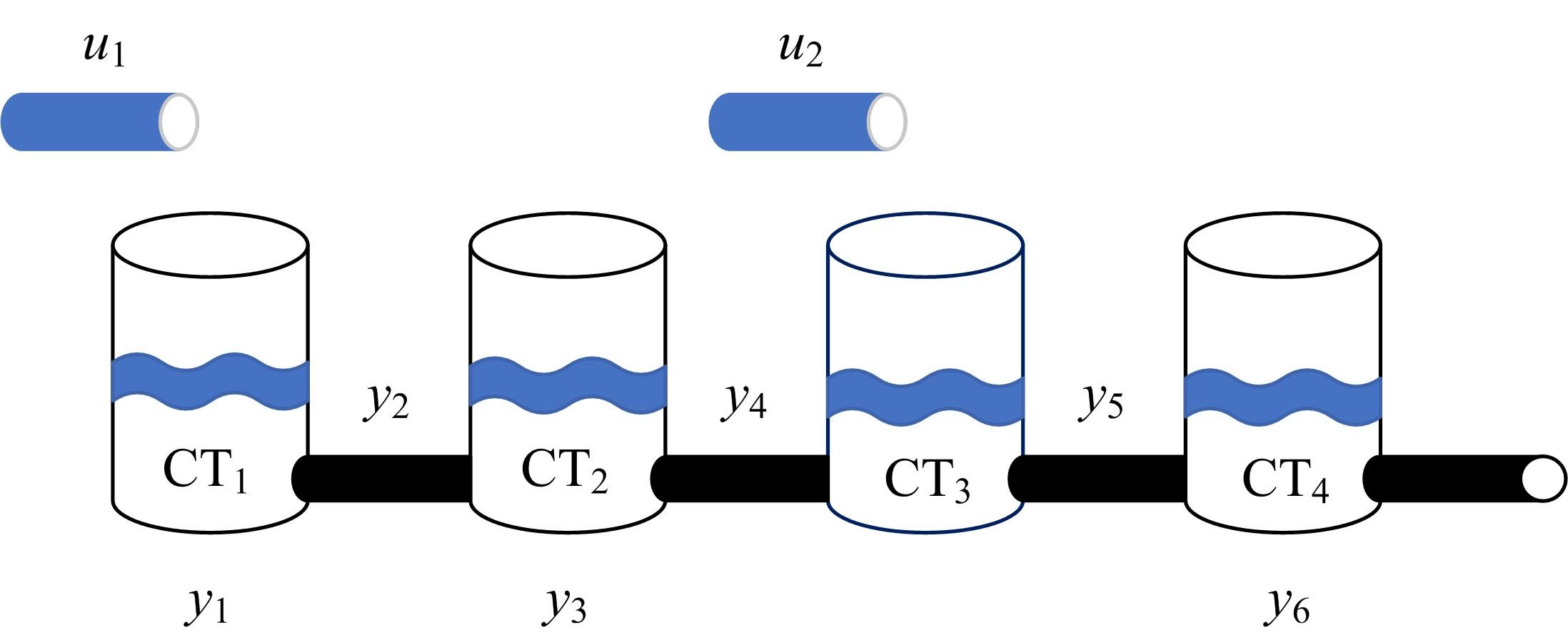
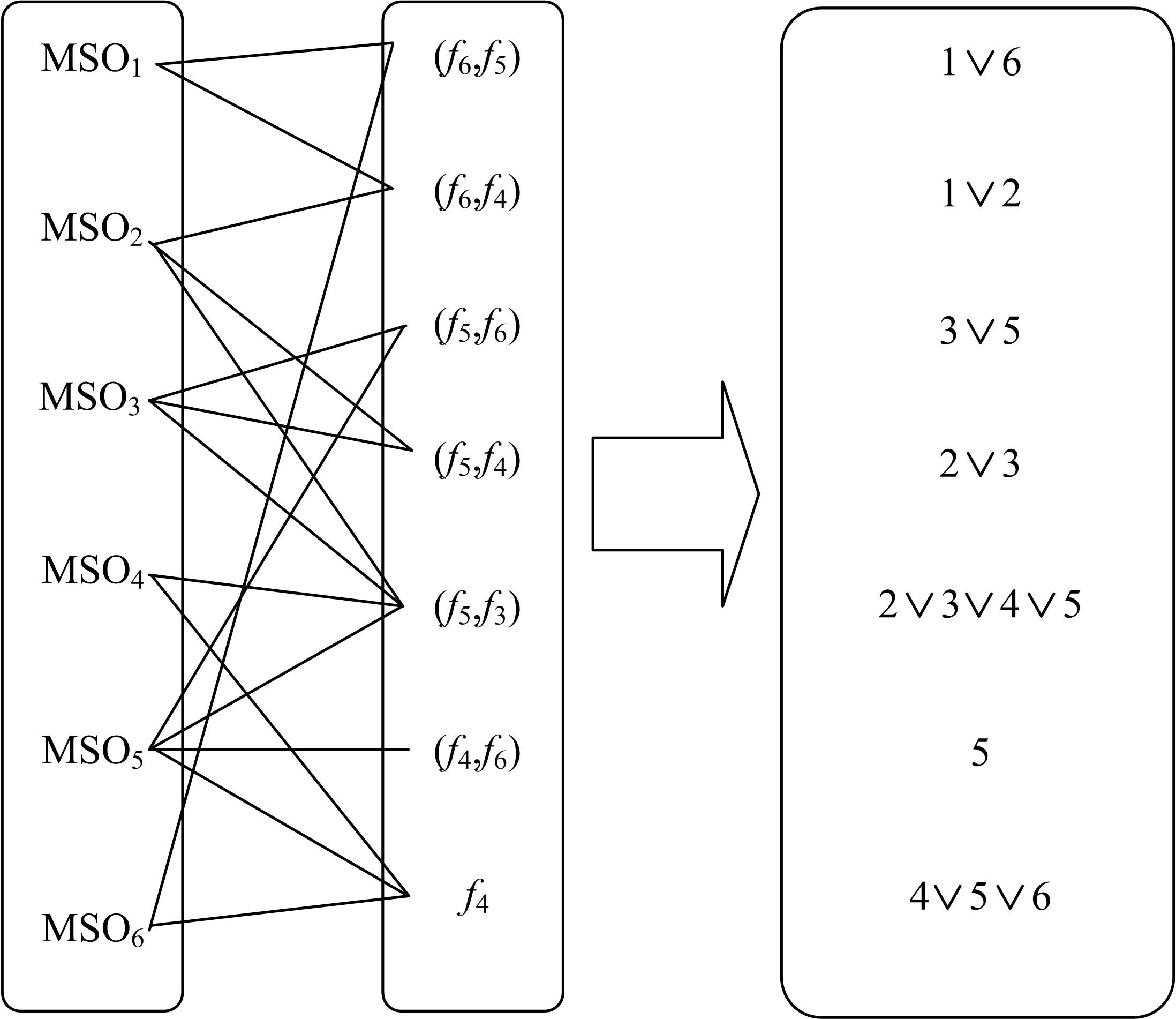
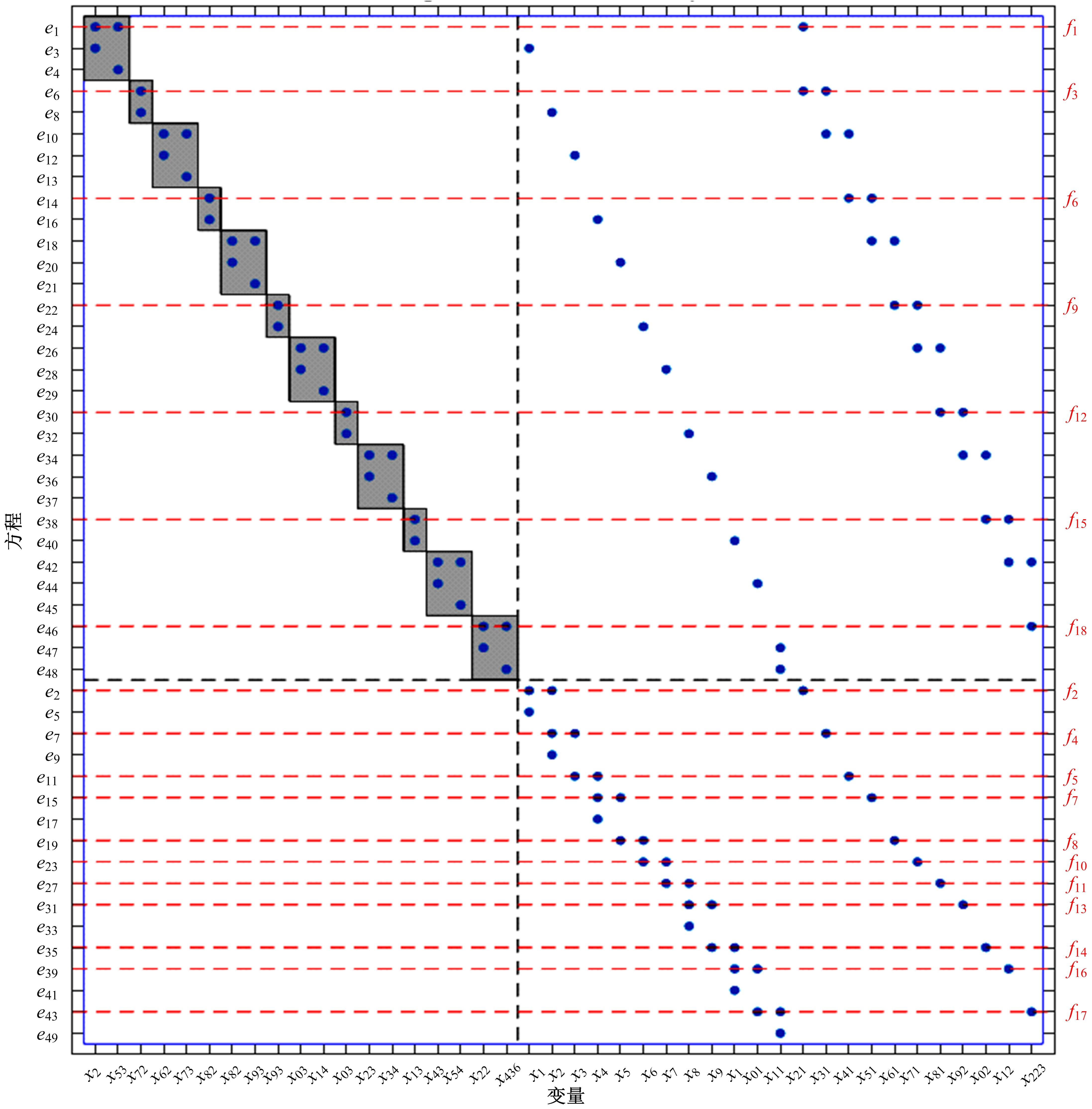
选择一组能够检测并隔离所有故障的故障检测隔离集(FDIS)是动态系统基于模型故障检测与隔离(FDI)的重要步骤,该步骤通常要求FDIS的基数最小,即求解最小故障检测隔离集(MFDIS),MFDIS的求解时间随着问题规模增大呈指数级增长。BILP(Binary integer linear programming)完备方法是现行动态系统中通用和最高效的MFDIS求解方法,但该方法的求解效率有待提高。本文首次提出了基于部分最大可满足性问题(PMS)的MFDIS求解方法。提出极小超定方程集(MSO)的概念,将部分MSO集合用MSO等价集表示,以缩减问题规模。将MFDIS求解问题转化为PMS问题,进而提高求解效率。实验结果表明,本文方法将问题规模平均约简至原来的8.22%;与BILP方法相比,本文方法的求解效率提高了4.18~9.5倍。
中图分类号:
- TP306
| 1 | Hwang I, Kim S, Kim Y, et al. A survey of fault detection, isolation, and reconfiguration methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2010, 18(3): 636-653. |
| 2 | De Kleer J, Williams B C. Diagnosing multiple faults[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 1987, 32(1): 97-130. |
| 3 | 欧阳丹彤, 刘伯文, 刘梦, 等. 结合电路结构基于分块的诊断方法[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(7): 38-44. |
| Ouyang Dan-tong, Liu Bo-wen, Liu meng, et al. A block-based diagnostic method combinbing with the circuit structure[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(7): 38-44. | |
| 4 | Svard C, Nyberg M, Frisk E, et al. Realizability constrained selection of residual generators for fault diagnosis with an automotive engine application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, 2013, 43(6): 1354-1369. |
| 5 | Falkenberg T, Gregersen R, Blanke M. Navigation system fault diagnosis for underwater vehicle[J].IFAC-Papers on Line, 2014, 47(3): 9654-9660. |
| 6 | Svard C, Nyberg M. Automated design of an FDI-system for the wind turbine benchmark [J]. IFAC-Papers on Line, 2011, 44(1): 8307-8315. |
| 7 | Jung D. A generalized fault isolability matrix for improved fault diagnosability analysis[C]//The 3rd Conference on Control and Fault-Tolerant Systems (SysTol), Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 519-524. |
| 8 | Sankavaram C, Kodali A, Pattipati K R, et al. Incremental classifiers for data-driven fault diagnosis applied to automotive systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2015, 3: 407-419. |
| 9 | Jung D, Sundström C. A combined data-driven and model-based residual selection algorithm for fault detection and isolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems, 2019, 27(2): 616-630. |
| 10 | Frisk E, Krysander M. Residual selection for consistency based diagnosis using machine learning models[J]. IFAC-Papers on Line, 2018, 51(24): 139-146. |
| 11 | Jung D, Frisk E. Residual selection for fault detection and isolation using convex optimization[J]. Automatica, 2018, 97: 143-149. |
| 12 | 田乃予, 欧阳丹彤, 刘梦, 等. 基于子集一致性检测的诊断解极小性判定方法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2019, 56(7): 1396-1407. |
| Tian Nai-yu, Ouyang Dan-tong, Liu Meng, et al. A method of minimality-checking of fiagnosis based on subset consistency detection[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(7): 1396-1407. | |
| 13 | Nejjari A F, Sarrate E R, Rosich O A.Optimal sensor placement for fuel cell system diagnosis using BILP formulation[C]∥The 18th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Marrakech, Morocco, 2010: 1296-1301. |
| 14 | Khorasgani H, Biswas G. Structural fault detection and isolation in hybrid systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2018, 15(4): 1585-1599. |
| 15 | Pérez-Zuiga G, Rivas-Perez R, Sotomayor J, et al. Fault detection and isolation system based on structural analysis of an industrial seawater reverse osmosis desalination plant[J]. Processes, 2020, 8(9): 1100. |
| 16 | Khorasgani H, Biswas G, Jung D. Minimal structurally overdetermined sets selection for distributed fault detection[C]∥Proceedings of the 26th International Workshop on Principles of Diagnosis, Paris, France, 2015: 75-82. |
| 17 | Krysander M, Åslund J, Nyberg M. An efficient algorithm for finding minimal over-constrained sub-systems for model-based diagnosis[J]. IEEE Trans on Systems,Man and Cybernetics–Part A: Systems and Humans, 2008, 38(1): 197-206. |
| 18 | Svard C, Nyberg M. Residual generators for fault diagnosis using computation sequences with mixed causality applied to automotive systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics–Part A: Systems and Humans, 2010, 40(6): 1310-1328. |
| 19 | Blanke M, Kinnaert M, Lunze J, et al. Diagnosis and fault-tolerant control[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2006. |
| 20 | Krysander M, Åslund J, Frisk E. A structural algorithm for finding testable sub-models and multiple fault isolability analysis[C]∥The 21st International Workshop on Principles of Diagnosis (DX-10), Portland, USA, 2010: |
| 21 | Reiter R. A theory of diagnosis from first principles [J].Artificial Intelligence, 1987, 32(1): 57-96. |
| 22 | Frisk E, Krysander M, Jung D. A toolbox for analysis and design of model based diagnosis systems for large scale models[J]. IFAC-Papers on Lines, 2017, 50(1): 3287-3293. |
| 23 | Robinson J A, Davis M, Logemann G, et al. A machine program for theorem-proving[J]. Journal of Symbolic Logic, 1967, 32(1): 118-394. |
| 24 | Cai S W, Luo C, Zhang H. From decimation to local search and back: a new approach to MaxSAT[C]∥Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Melbourne,Australia, 2017: 571-577. |
| 25 | 刘思光, 欧阳丹彤, 王艺源,等. 结合SE-Tree结构特征的极小碰集求解算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(11): 2556-2566. |
| Liu Si-guang, Ouyang Dan-tong, Wang Yi-yuan, et al. Minimal collision set solving algorithm combined with SE-Tree structural features[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development,2016, 53(11): 2556-2566. | |
| 26 | Koshimura M, Zhang T, Fujita H, et al. Qmaxsat: a partial max-sat solver[J]. Journal on Satisfiability Boolean Modeling & Computation,2012,8(1/2): 95-100. |
| 27 | Dulmage A L, Mendelsohn N S. Coverings of bipartite graphs[J]. Canadian Journal of Mathematics, 1958, 10: 517-534. |
| [1] | 欧阳丹彤,孙睿,田新亮,高博涵. 基于集合阻塞的不确定系统中传感器选择方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 547-554. |
| [2] | 王晓宇,欧阳丹彤,赵剑. 基于诊断器的可诊断性增量测试方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 222-228. |
| [3] | 欧阳丹彤, 耿雪娜, 郭劲松, 王晓宇. 基于矩阵计算极小碰集的启发式算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(01): 106-110. |
| [4] | 欧阳丹彤,焦玉,赵相福. 基于ATMS的冲突识别及诊断测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(06): 1601-1606`. |
|
||