吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 577-590.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.Jdxbgxb.20230411
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
污染天气居民通勤模式选择影响因素的链式效用
- 1.长安大学 运输工程学院,西安 710064
2.中交第一公路勘察设计研究院有限公司,西安 710075
Chain-effect utility of factors influencing residents' commuting mode choice in polluted weather
Yu-ran LI1( ),Fei WANG2,Cai-hua ZHU1,Fei HAN1,Yan LI1(
),Fei WANG2,Cai-hua ZHU1,Fei HAN1,Yan LI1( )
)
- 1.College of Transportation Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.CCCC First Highway Consultants Co. ,Ltd. ,Xi'an 710075,China
摘要:
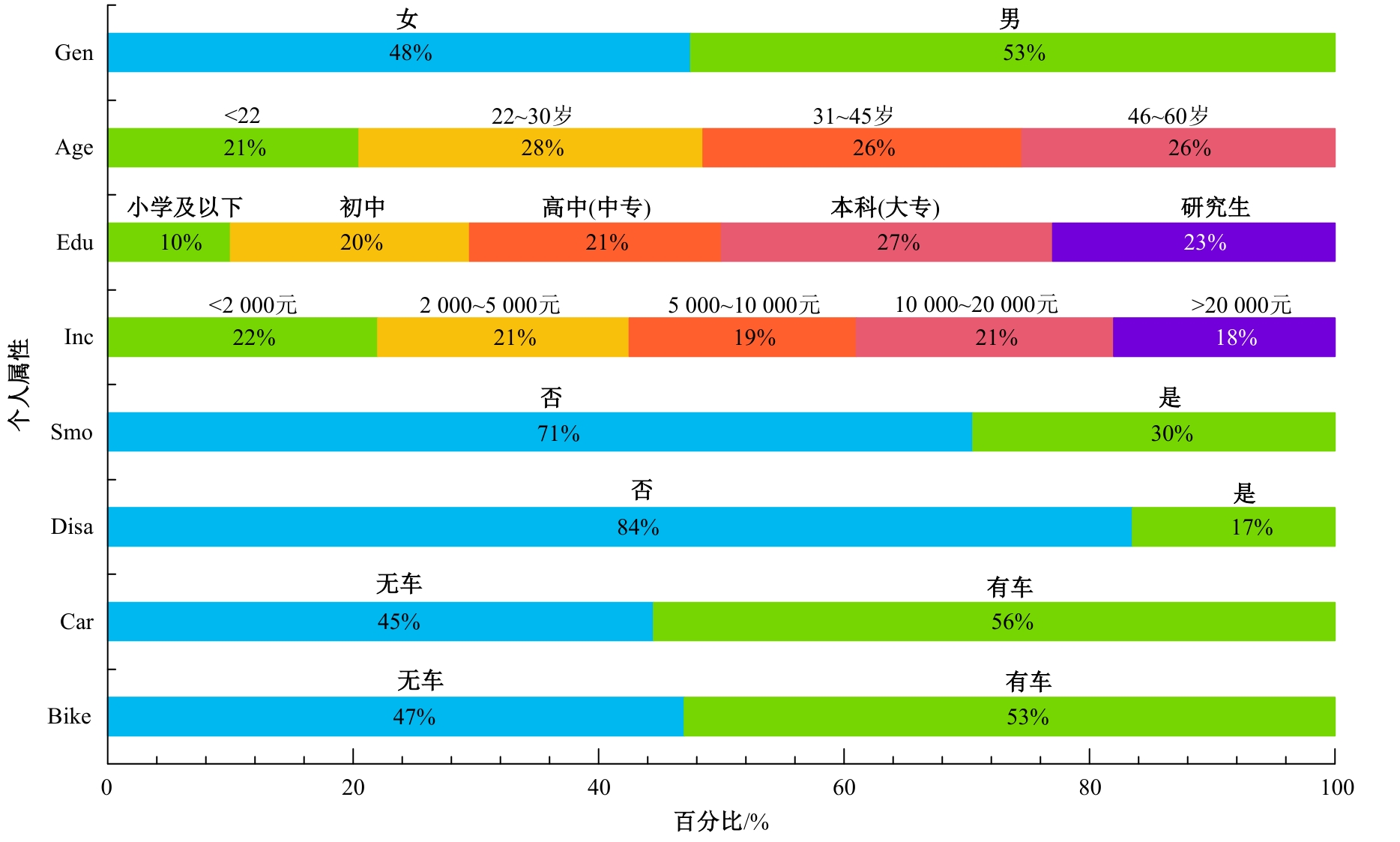
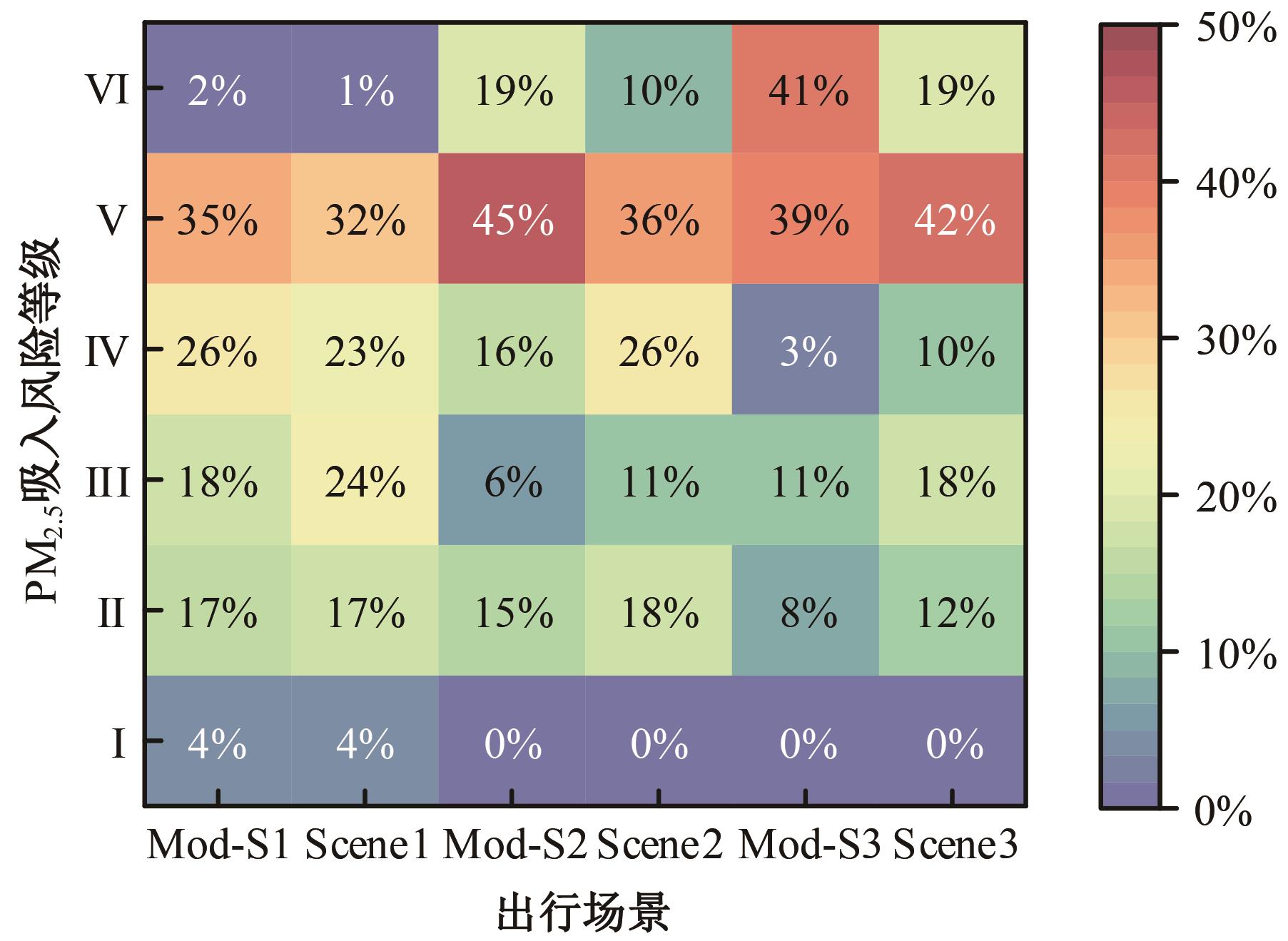
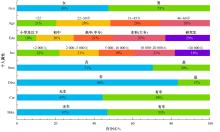
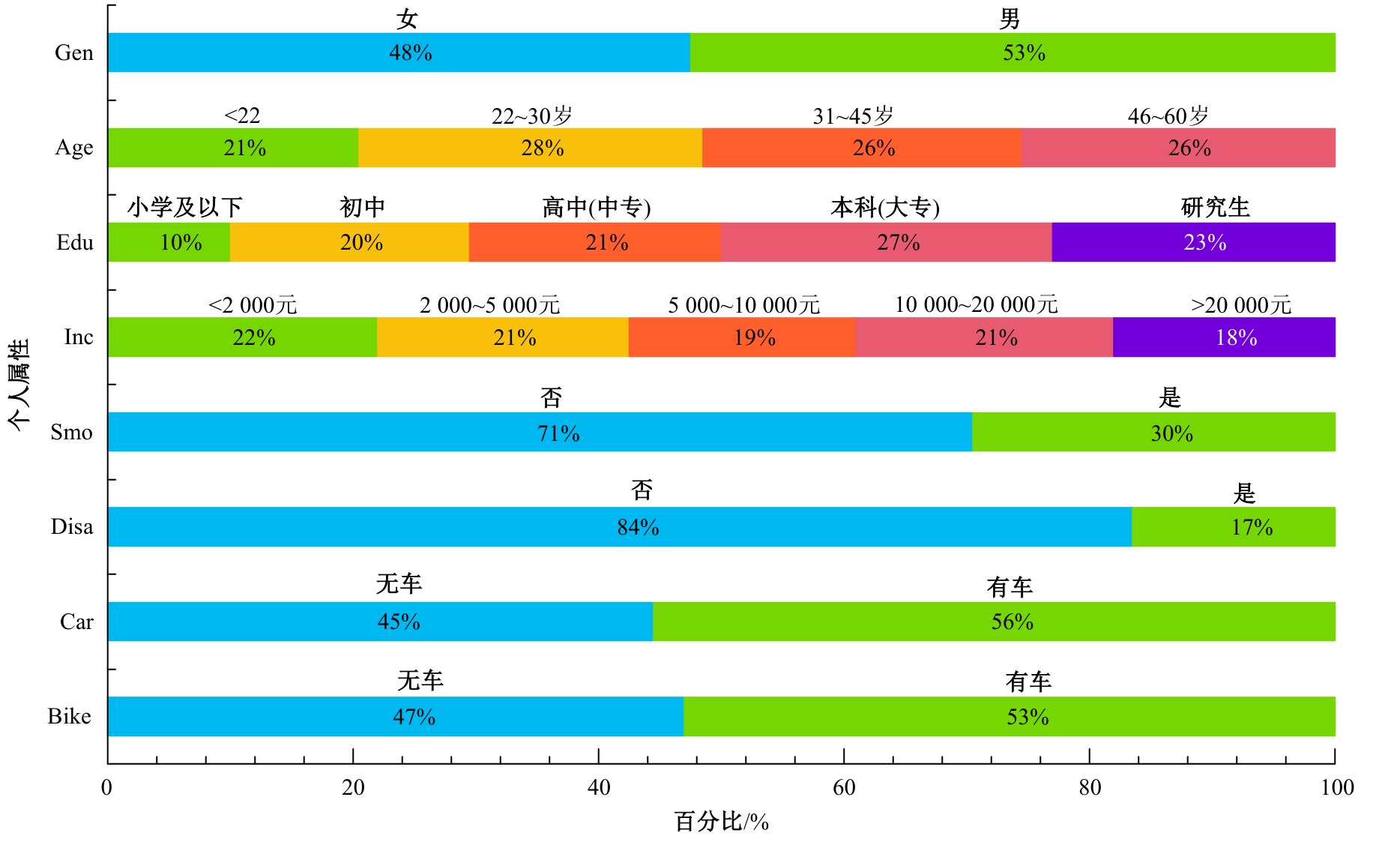
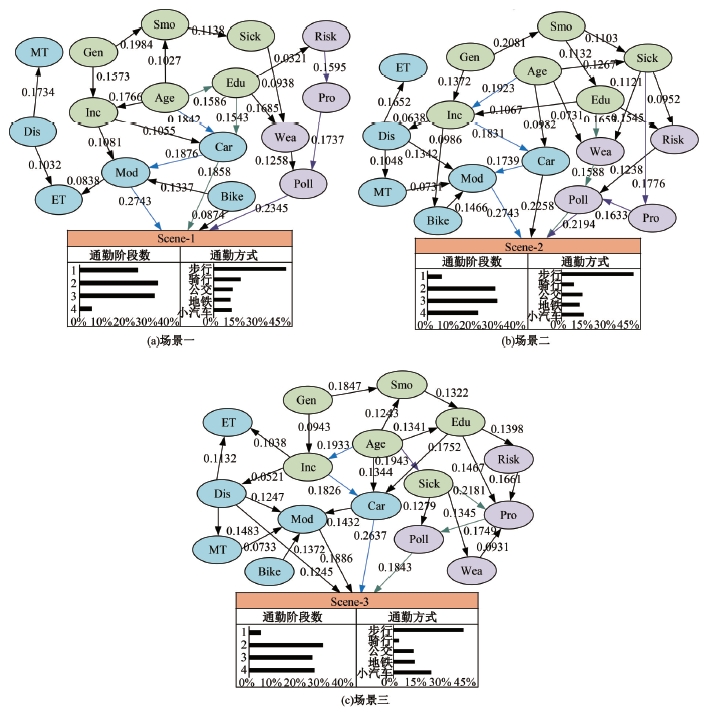
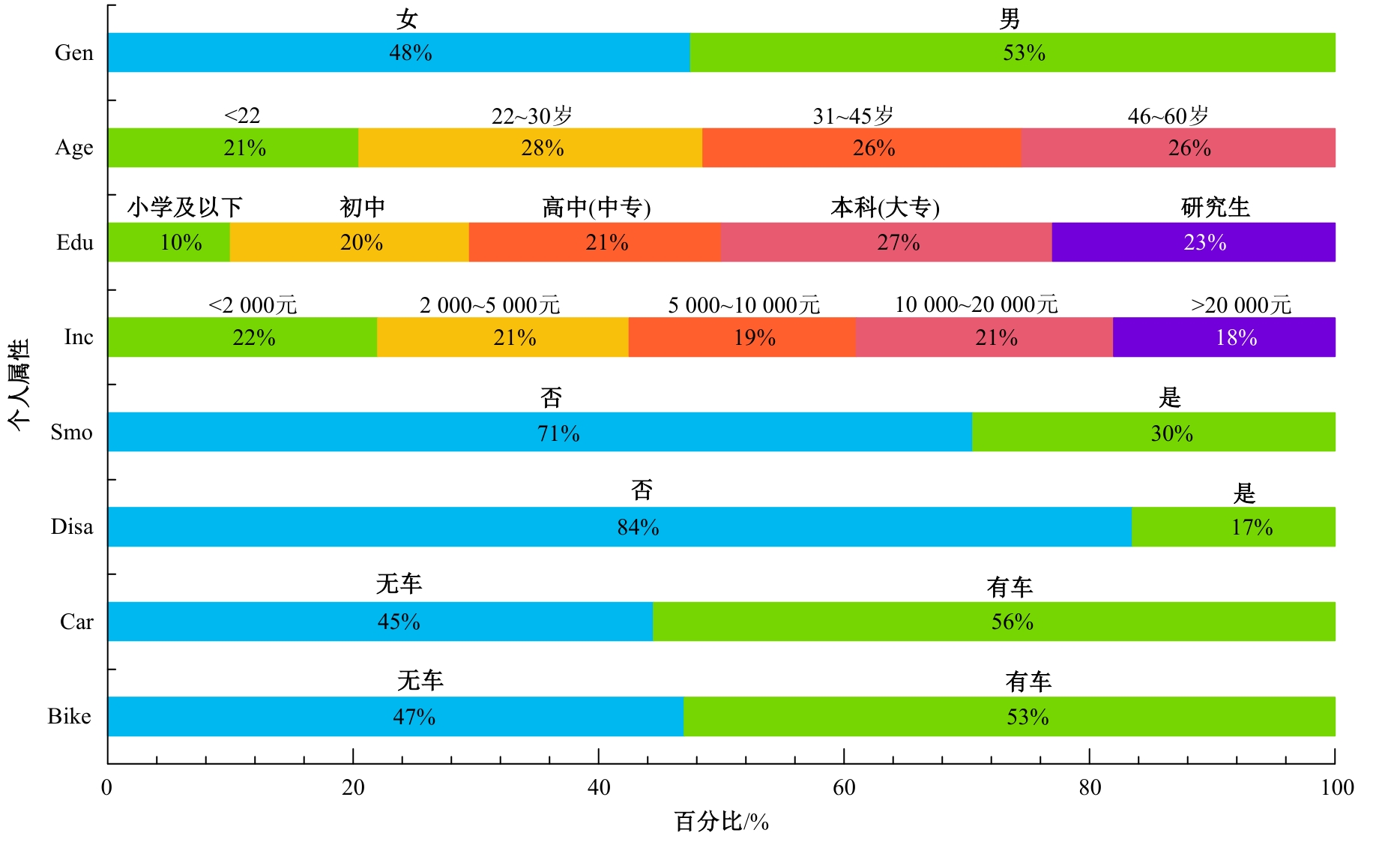
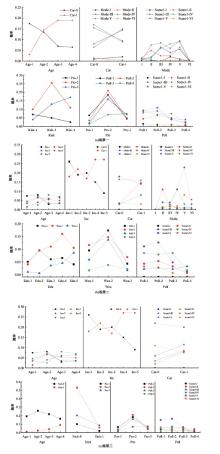
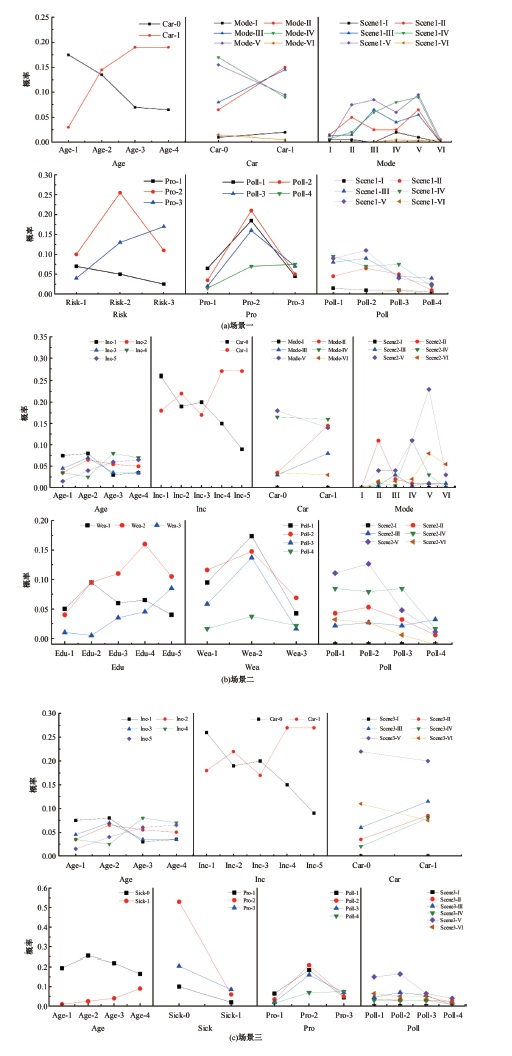
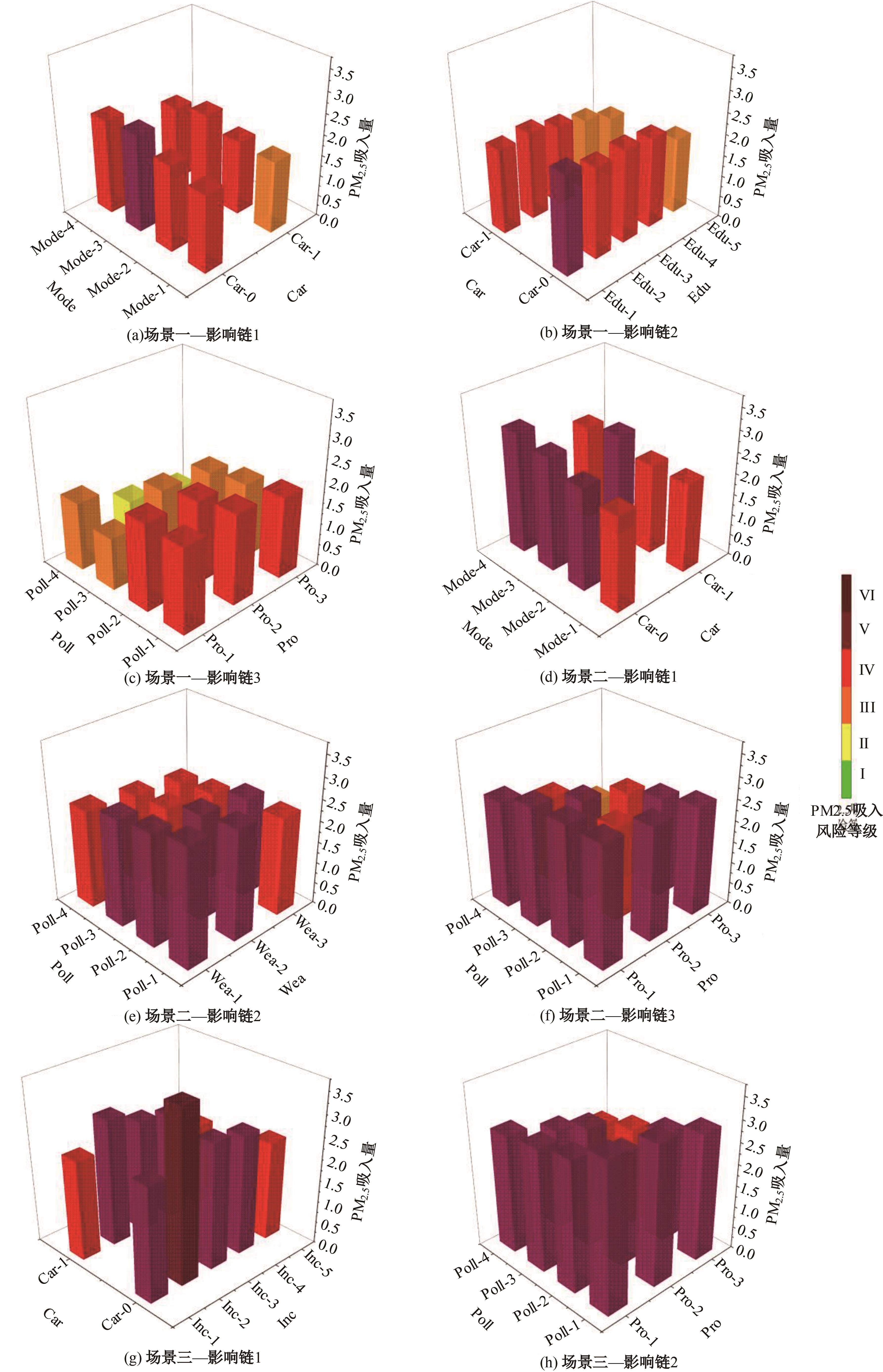
为探究不同污染程度天气下居民知晓污染物吸入状况和风险时的完整通勤模式决策行为,构建了改进的基于节点次序最大相关-最小冗余的贪婪贝叶斯网络模型以分析不同影响因素的链式效用。告知居民其当前通勤模式的风险等级及不同出行方式的污染物吸入量,设计问卷以获取居民的污染天气出行意向。通过引入互信息论构建基于节点次序最大相关-最小冗余贪婪贝叶斯网络结构学习算法,在学习贝叶斯网络结构的基础上进行参数学习和网络推理,挖掘基于变量间因果关系的链式影响效用。对西安市居民的调查数据分析结果表明:轻度污染下影响程度最大的变量链为年龄-有无私家车-日常通勤模式-污染天气通勤模式,39%的居民重新选择的通勤模式风险等级低于日常通勤模式。重度污染下的影响因素链式效用表现为年龄-月收入-有无私家车-污染天气通勤模式,相邻变量间的相关关系分别呈正相关、正相关、正相关和负相关。研究揭示了不同污染条件下影响居民通勤方式的链式效用,有利于制定更具建设性的诱导策略以帮助居民健康出行。
中图分类号:
- U268.6
| 1 | 魏彤, 李政蕾, 陈昱, 等. 长三角居民PM2.5暴露水平下降健康经济效益评估[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(6): 3211-3219. |
| Wei Tong, Li Zheng-lei, Chen Yu, et al. Assessment of the health and economic benefits of declining PM2.5 levels in the yangtze river delta[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(6): 3211-3219. | |
| 2 | Behrentz E, Sabin L D, Winter A M, et al. Relative importance of school bus-related microenvironments to children's pollutant exposure[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2005, 55(10): 1418-1430. |
| 3 | Zhu C H, Fu Z K, Liu L J, et al. Health risk assessment of PM2.5 on walking trips[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11: 19249. |
| 4 | 熊秀琴, 李怡雪, 赵昂, 等. 北京市地铁车厢内PM2.5污染情况及通勤人员的相关认知[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2018, 35(7): 583-588. |
| Xiong Xiu-qin, Li Yi-xue, Zhao Ang, et al. PM2.5 concentrations in subway cars in Beijing and related awareness of subway passengers[J]. Journal of Environmental & Occupational Medicine, 2018, 35(7): 583-588. | |
| 5 | Fan S, Minjie J, Tao Z, et al. Satisfaction differences in bus traveling among low-income individuals before and after COVID-19 [J]. Transportation Research, Part A: Policy and Practice, 2022, 160: 311-332. |
| 6 | 马壮林, 崔姗姗, 胡大伟. 限行政策下城市居民低碳出行意向[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(11): 2607-2617. |
| Ma Zhuang-lin, Cui Shan-shan, Hu Da-wei. Urban residents' low⁃carbon travel intention after implementation of driving restriction policy[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2607-2617. | |
| 7 | Mashrur R. Commute mode switch and its relationship to life events, built-environment, and attitude change[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2023, 120: No.103777. |
| 8 | Paulssen M, Temme D, Vij A, et al. Values, attitudes and travel behavior: a hierarchical latent variable mixed Logit model of travel mode choice[J]. Transportation, 2014, 41(4): 873-888. |
| 9 | 马莹莹, 陆思园, 张晓明, 等. 考虑个体风险偏好差异的高速公路出行选择模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1673-1683. |
| Ma Ying-ying, Lu Si-yuan, Zhang Xiao-ming, et al. Model of highway travel selection considering individual risk preference difference[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1673-1683. | |
| 10 | Pnevmatikou A M, Karlaftis M G, Kepaptsoglou K. Metro service disruptions: how do people choose to travel?[J]. Transportation, 2015, 42(6): 933-949. |
| 11 | Agustin J V, Ricardo G, Paul B, et al. Characterising public transport shifting to active and private modes in South American capitals during the COVID-19 pandemic[J]. Transportation Research, Part A: Policy and Practice, 2022, 164: 186-205. |
| 12 | 柳伍生, 潘自翔, 魏隽君, 等. 地铁站点运营中断下周边乘客的出行行为研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2020, 17(11): 2953-2961. |
| Liu Wu-sheng, Pan Zi-xiang, Wei Juan-jun, et al. Research on the travel behavior of subway passengers under the influence of operation interruption[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(11): 2953-2961. | |
| 13 | 钟异莹, 陈坚, 邵毅明, 等. 考虑居住区位的公共交通出行行为分析模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(6): 219-225. |
| Zhong Yi-ying, Chen Jian, Shao Yi-ming, et al. Analysis model of travel behavior in public transportation considering residential location[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(6): 219-225. | |
| 14 | Borhan N M, Ibrahim H N A, Miskeen A A M. Extending the theory of planned behaviour to predict the intention to take the new high-speed rail for intercity travel in Libya: assessment of the influence of novelty seeking, trust and external influence[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2019, 130: 373-384. |
| 15 | Zhu C H, Xue Y B, Li Y R, et al. Assessment of particulate matter inhalation during the trip process with the considerations of exercise load[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 866(25): 161277. |
| 16 | Li Y, Wang F, Ke H, et al. A driver's physiology sensor-based driving risk prediction method for lane-changing process using hidden Markov model [J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(12): 2670. |
| 17 | 环境保护部. 中国人群暴露参数手册(成人卷)[M]. 北京:中国环境科学出版社, 2013. |
| 18 | 刘佳雨, 冷军强, 尚平, 等. 冰雪路面下高速公路事故及严重程度影响因素分析[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2022, 54(3): 57-64. |
| Liu Jia-yu, Leng Jun-qiang, Shang Ping, et al. Analysis of traffic crashes and injury severity influence factors for ice-snow covered freeway roads[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2022, 54(3): 57-64. | |
| 19 | 贾柳娜, 董绵绵, 贺楚超, 等. 一种优化节点序搜索算子的BN结构学习方法[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2023, 41(2): 419-427. |
| Jia Liu-na, Dong Mian-mian, He Chu-chao, et al. A bayesian network structure learning method for optimizing ordering search operator[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2023, 41(2): 419-427. | |
| 20 | Byun J E, Song J H. A general framework of Bayesian network for system reliability analysis using junction tree[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2021, 216: 107952. |
| 21 | 邸若海, 李叶, 万开方, 等. 基于改进QMAP的贝叶斯网络参数学习算法[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2021, 39(6): 1356-1367. |
| Di Ruo-hai, Li Ye, Wan Kai-fang, et al. Bayesian network parameter learning algorithm based on improved QMAP[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2021, 39(6): 1356-1367. | |
| 22 | Schwarz G. Estimating dimensions of a model[J]. Annals of Statistics, 1978, 6(2): 461-464. |
| 23 | Jyoti K M, Anil N, Dan H, et al. Analysis of various transport modes to evaluate personal exposure to PM2.5 pollution in Delhi[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2021, 12(2): 417-431. |
| [1] | 高天洋,胡大伟,姜瑞森,吴雪,刘慧甜. 基于模块化车辆的区域灵活接驳公交线路优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 537-545. |
| [2] | 徐慧智,蒋时森,王秀青,陈爽. 基于深度学习的车载图像车辆目标检测和测距[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 185-197. |
| [3] | 郑长江,陶童统,陈志超. 基于流量可调重分配的级联失效模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2441-2450. |
| [4] | 温晓岳,钱国敏,孔桦桦,缪月洁,王殿海. TrafficPro:一种针对城市信控路网的路段速度预测框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2214-2222. |
| [5] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,严丽平. 基于随机充电需求的充电桩优化双层模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2238-2244. |
| [6] | 曲大义,刘浩敏,杨子奕,戴守晨. 基于车路协同的交通瓶颈路段车流动态分配机制及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2187-2196. |
| [7] | 陈桂珍,程慧婷,朱才华,李昱燃,李岩. 考虑驾驶员生理信息的城市交叉口风险评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1277-1284. |
| [8] | 赵晓华,刘畅,亓航,欧居尚,姚莹,郭淼,杨海益. 高速公路交通事故影响因素及异质性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 987-995. |
| [9] | 杨秀建,贾晓寒,张生斌. 考虑汽车队列动态特性的混合交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 947-958. |
| [10] | 范博松,邵春福. 城市轨道交通突发事件风险等级判别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [11] | 郑长江,胡欢,杜牧青. 考虑枢纽失效的多式联运快递网络结构设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2304-2311. |
| [12] | 王殿海,胡佑薇,蔡正义,曾佳棋,姚文彬. 基于BPR函数的城市道路间断流动态路阻模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1951-1961. |
| [13] | 李艳波,柳柏松,姚博彬,陈俊硕,渠开发,武奇生,曹洁宁. 考虑路网随机特性的高速公路换电站选址[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1364-1371. |
| [14] | 胡莹,邵春福,王书灵,蒋熙,孙海瑞. 基于共享单车骑行轨迹的骑行质量识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1040-1046. |
| [15] | 王占中,蒋婷,张景海. 基于模糊双边界网络模型的道路运输效率评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 385-395. |
|
||