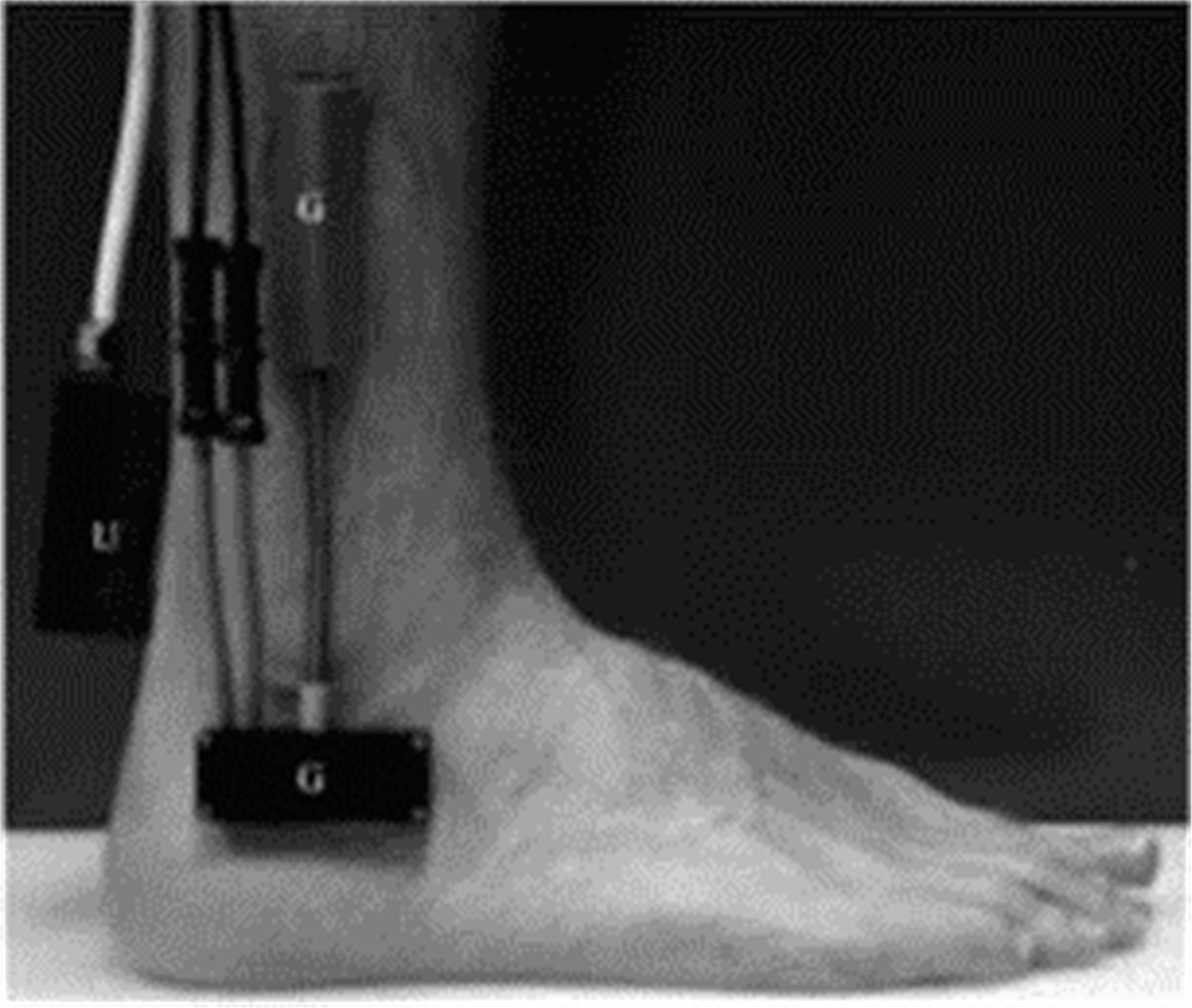
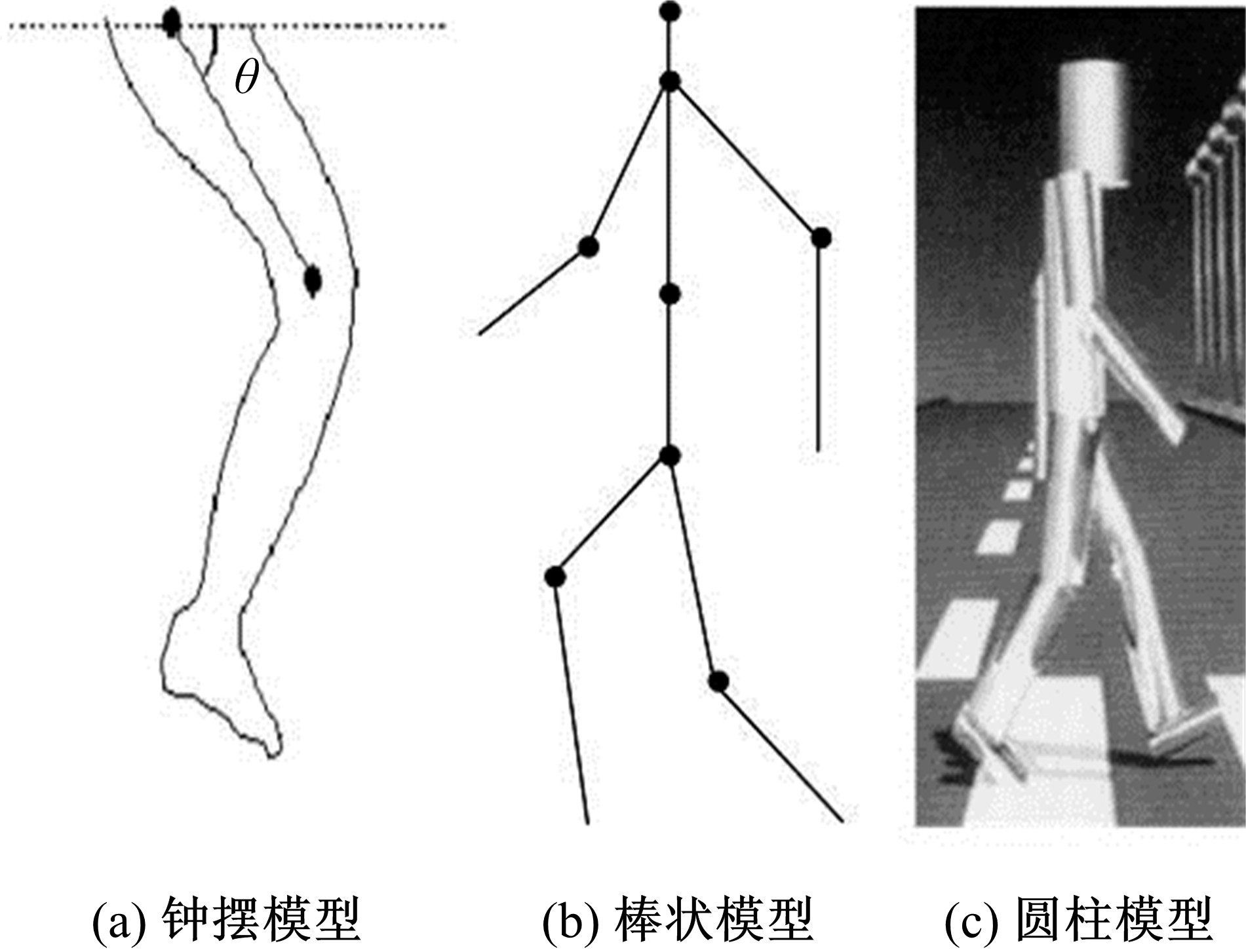
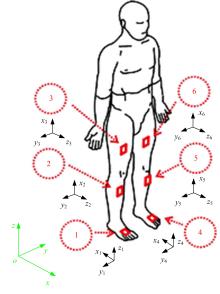
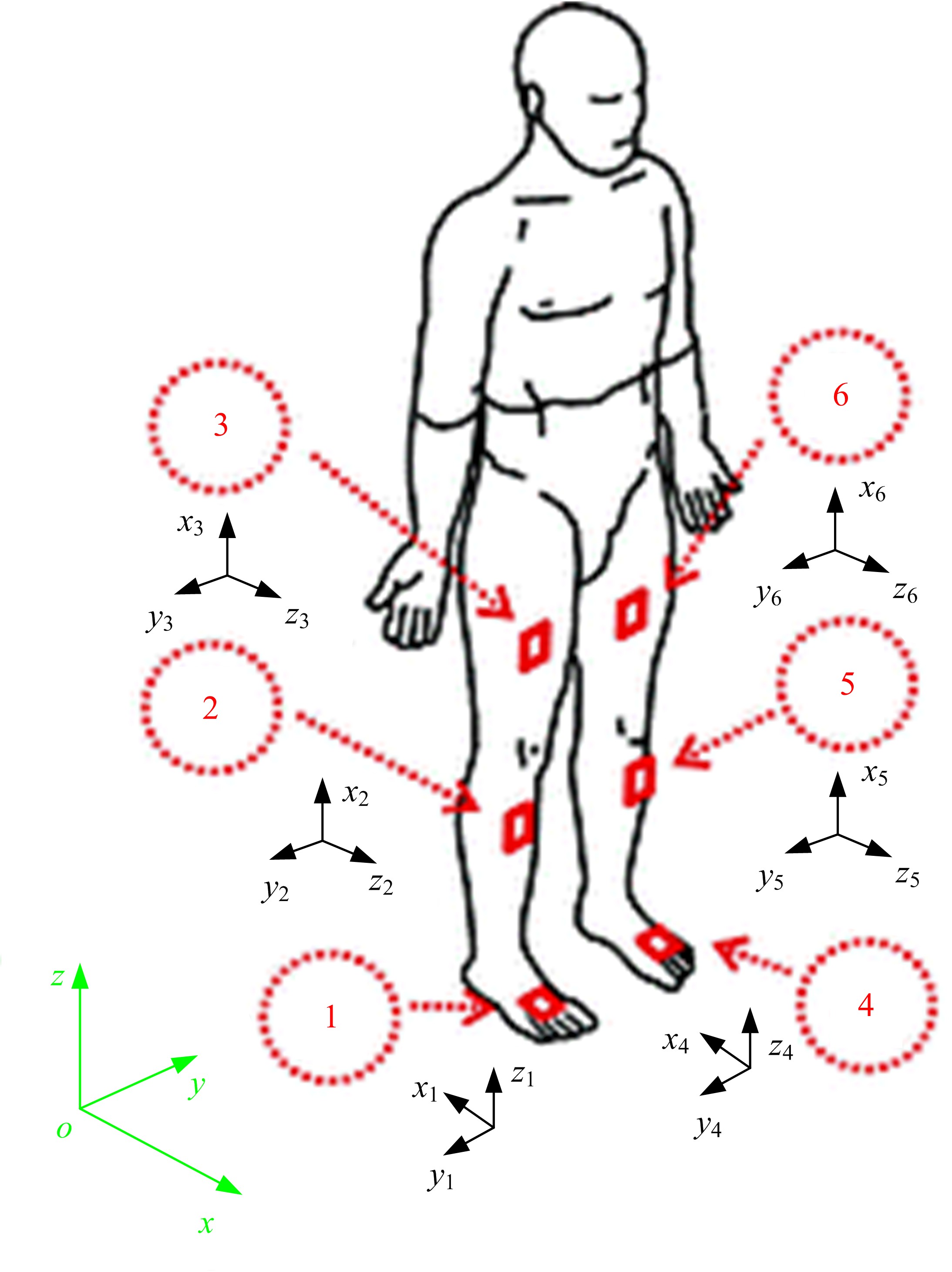
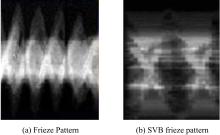
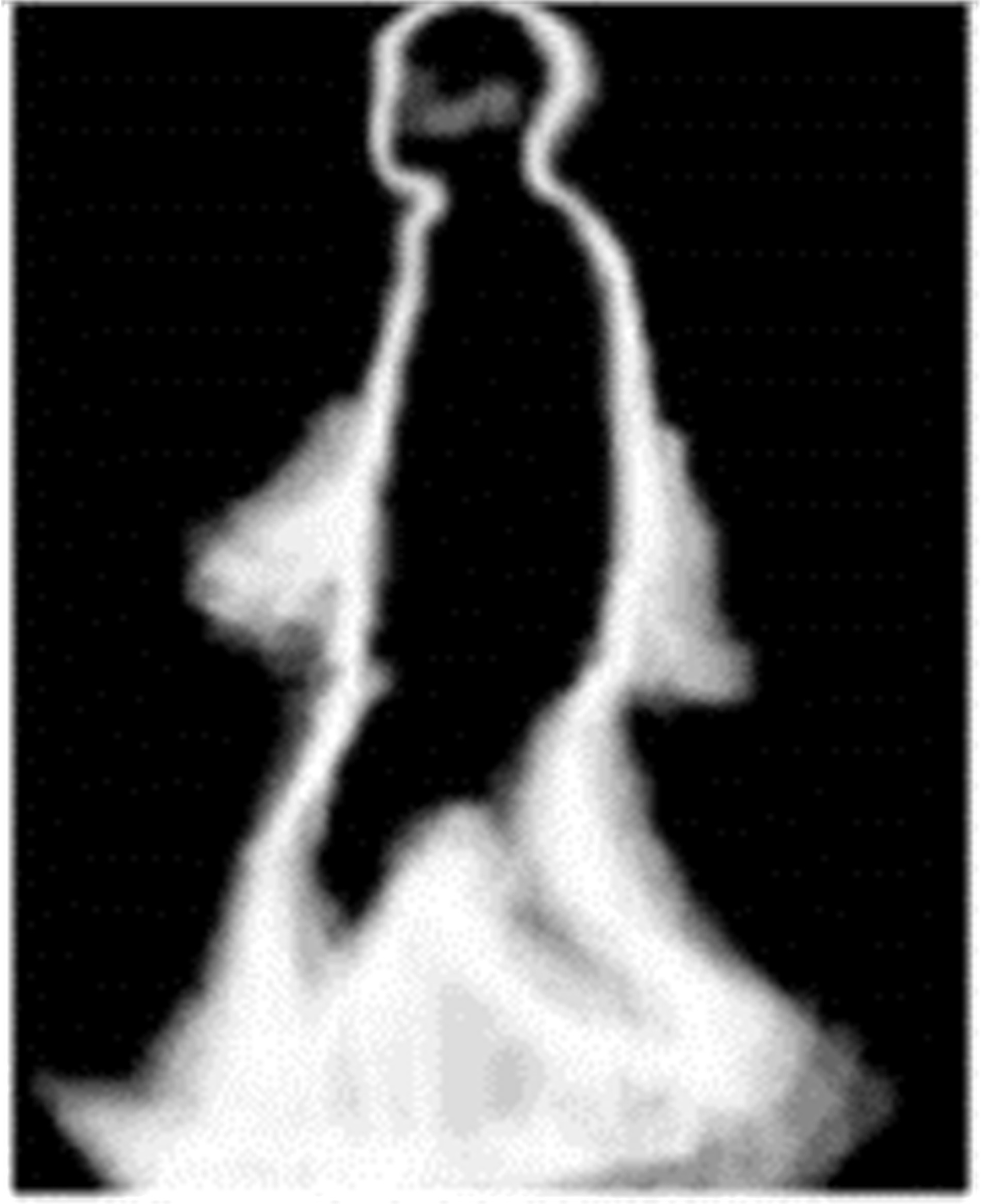
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 1-18.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190264
• 综述 •
人体步态识别方法与技术
- 1. 山东大学 控制科学与工程学院,济南 250061
2. 济南大学 自动化与电气工程学院,济南 250022
Methods and technologies of human gait recognition
Yi-bin LI1( ),Jia-min GUO1,Qin ZHANG1,2(
),Jia-min GUO1,Qin ZHANG1,2( )
)
- 1. School of Control Science and Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan 250061, China
2. School of Electrical Engineering, University of Jinan, Jinan 250022, China
摘要:
针对人体步态识别,从步态数据采集仪器、常见步态数据集、步态参数提取和步态识别方法4个方面分别展开综述。首先,介绍常用的步态数据采集仪器的优缺点、可靠性和应用场景;其次,从建立机构、样本容量、采样率、环境、仪器和变量6个方面对常用的步态数据集进行对比分析;然后,将现有步态参数提取方法分为基于模型的方法和基于非模型的方法进行详细阐述,进而在步态识别算法方面分别从支持向量机、自编码器和卷积神经网络三方面进行介绍,并对上述方法从身份识别和异常步态辨识两个应用方向分别展开对比;最后,结合实际应用指出当前研究存在的不足和未来的发展方向。
中图分类号:
- TP18
| 1 | Cao Y, Li B Z, Li Q N, et al. Kinect‐based gait analyses of patients with Parkinson's disease, patients with stroke with hemiplegia, and healthy adults[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2017, 23(5): 447-449. |
| 2 | Eltoukhy M, Kuenze C, Oh J, et al. Microsoft Kinect can distinguish differences in over-ground gait between older persons with and without Parkinson's disease[J]. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2017, 44: 1-7. |
| 3 | Wang T, Wang Z, Zhang D, et al. Recognizing Parkinsonian gait pattern by exploiting fine-grained movement function features[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 2016, 8(1): 1-22. |
| 4 | Mileti I, Germanotta M, Di Sipio E, et al. Measuring Gait Quality in Parkinson’s Disease through Real-Time Gait Phase Recognition[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(3): 919. |
| 5 | Cui C, Bian G B, Hou Z G, et al. Simultaneous recognition and assessment of post-stroke hemiparetic gait by fusing kinematic, kinetic, and electrophysiological data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2018, 26(4): 856-864. |
| 6 | Benson L C, Clermont C A, Bošnjak E, et al. The use of wearable devices for walking and running gait analysis outside of the lab: a systematic review[J]. Gait & Posture, 2018, 63: 124-138. |
| 7 | Simon S R. Quantification of human motion: gait analysis—benefits and limitations to its application to clinical problems[J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 2004, 37(12): 1869-1880. |
| 8 | Figueiredo J, Santos C P, Moreno J C. Automatic recognition of gait patterns in human motor disorders using machine learning: a review[J]. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2018,53:1-12. |
| 9 | Huang P S, Harris C J, Nixon M S. Recognising humans by gait via parametric canonical space[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Engineering, 1999, 13(4): 359-366. |
| 10 | Collins R T, Gross R, Shi J. Silhouette-based human identification from body shape and gait[C]∥Proceedings of Fifth IEEE International Conference on. Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Washington, DC, USA, 2002: 366-371. |
| 11 | Han J, Bhanu B. Individual recognition using gait energy image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2006(2): 316-322. |
| 12 | Lam T H W, Lee R S T. A new representation for human gait recognition: motion silhouettes image (MSI)[C]∥International Conference on Biometrics. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 612-618. |
| 13 | Prakash C, Kumar R, Mittal N. Recent developments in human gait research: parameters, approaches, applications, machine learning techniques, datasets and challenges[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2018, 49(1): 1-40. |
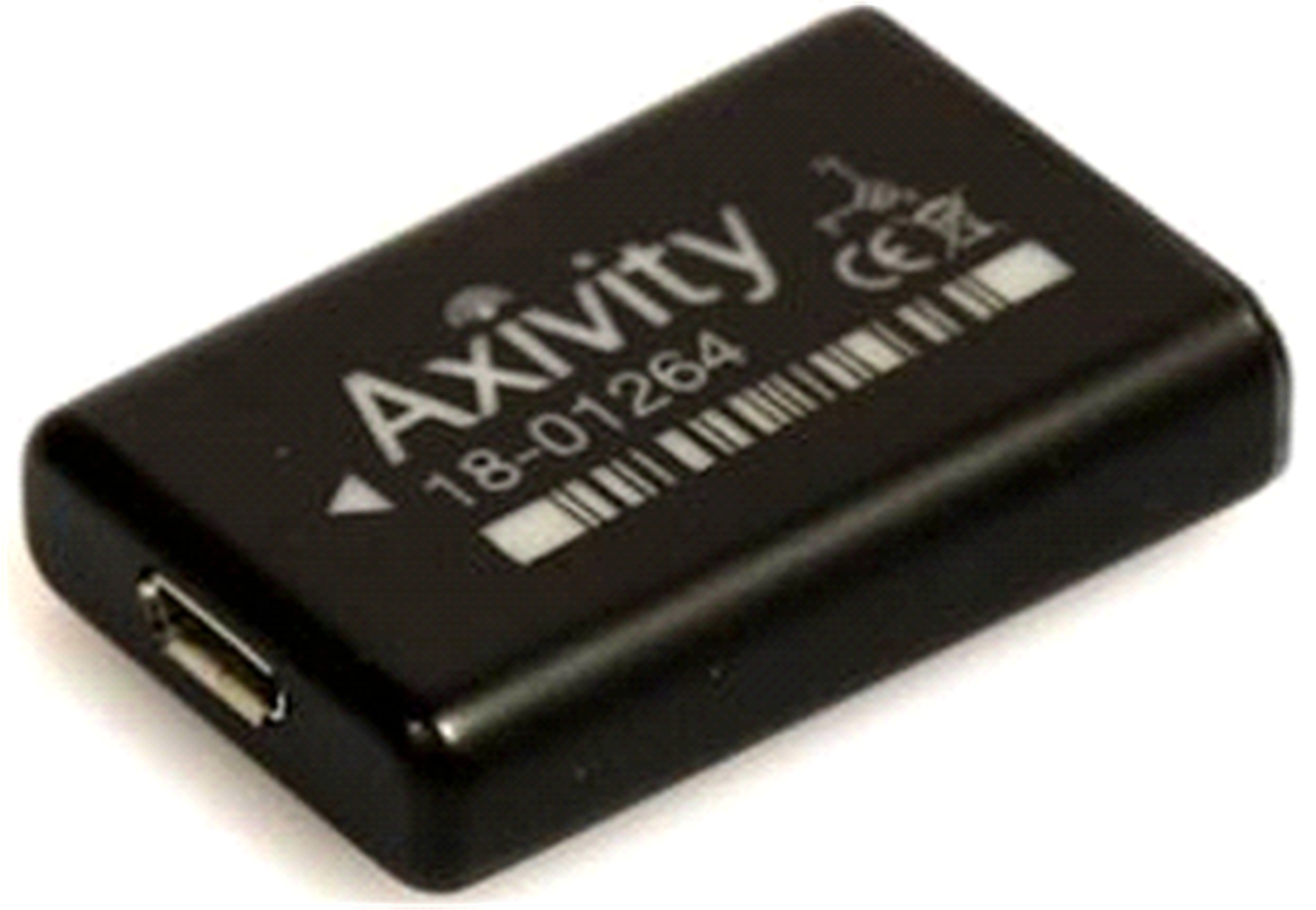
| 14 | Yang C C, Yeh-Liang H. A review of accelerometry-based wearable motion detectors for physical activity monitoring[J]. Sensors, 2010, 10(8): 7772-7788. |
| 15 | 埃里克·F·布赖恩. 用加速度计感测转向轴倾斜角和外倾角[P]. 中国:1768246 A,2006-08-17. |
| 16 | Büsching F, Kulau U, Gietzelt M, et al. Comparison and validation of capacitive accelerometers for health care applications[J]. Computer Methods & Programs in Biomedicine, 2012, 106(2): 79-88. |
| 17 | Bouten C V C, Koekkoek K T M, Verduin M, et al. A triaxial aceler-ometer and portable data processing unit for the assessment of daily physical activity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Bio-Medical Engineering, 1997, 44(3):136-147. |
| 18 | Godfrey A, Del D S, Barry G, et al. Within trial validation and reliability of a single tri-axial accelerometer for gait assessment[C]∥The 36th Annual International Conference of IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society,Chicago,IL,USA,2014:5892-5895. |
| 19 | Din S D, Godfrey A, Rochester L. Validation of an accelerometer to quantify a comprehensive battery of gait characteristics in healthy older adults and Parkinson's disease: toward clinical and at home use[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2016, 20(3):838-847. |
| 20 | Saunders J B, Inman V T, Eberhart H D. The major determinants in normal and pathological gait[J]. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 1953, 35(3): 543-558. |
| 21 | Williams G, Doughty K, Cameron K, et al. A smart fall and activity monitor for telecare applications[C]∥Proceedings of the of International Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Montreal, Que, Canada, 1998:1151-1154. |
| 22 | Weijer R, Hoozemans M, Van J D, et al. Self-perceived gait stability modulates the effect of daily life gait quality on prospective falls in older adults[J]. Gait & Posture, 2018,62:475-479. |
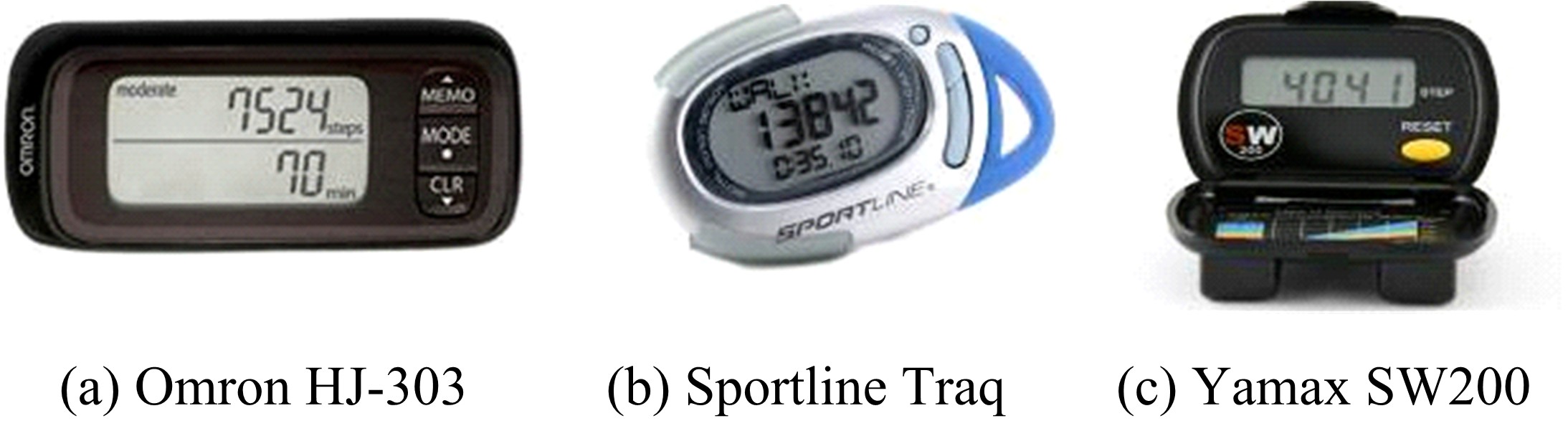
| 23 | Steeves J A, Tyo B, Connolly C, et al. Validity and Reliability of the Omron HJ-303 GoSmart tri-axis accelerometer-based pedometer: 2023[J]. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 2010, 42(7):1014-1020. |
| 24 | Sotoperezdecelis E, Kim H, Rojocastillo M P, et al. A pilot study of an accelerometer-equipped smartphone to monitor older adults with cancer receiving chemotherapy in Mexico[J]. Journal of Geriatric Oncology, 2017, 9(2):145-151. |
| 25 | 侯向锋, 刘蓉, 周兆丰. 加速度传感器MMA7260在步态特征提取中的应用[J]. 传感技术学报, 2007, 20(3):507-511. |
| Hou Xiang-feng, Liu Rong, Zhou Zhao-feng. Application of accelerometer MMA7260 in the gait feature extraction[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2007, 20(3):507-511. | |
| 26 | 刘蓉, 黄璐, 李少伟,等. 基于步态加速度的步态分析研究[J]. 传感技术学报, 2009, 22(6):893-896. |
| Liu Rong, Huang Lu, Li Shao-wei, et al. Gait analysis based on gait acceleration[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2009, 22(6):893-896. | |
| 27 | Zhang Y, Pan G, Jia K, et al. Accelerometer-based gait recognition by sparse representation of signature points with clusters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 45(9):1864-1875. |
| 28 | Medda A, Vaughan A, Liu B, et al. Activity recognition using statistical gait parameters from a single accelerometer[C]∥Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA,2014:189-193. |
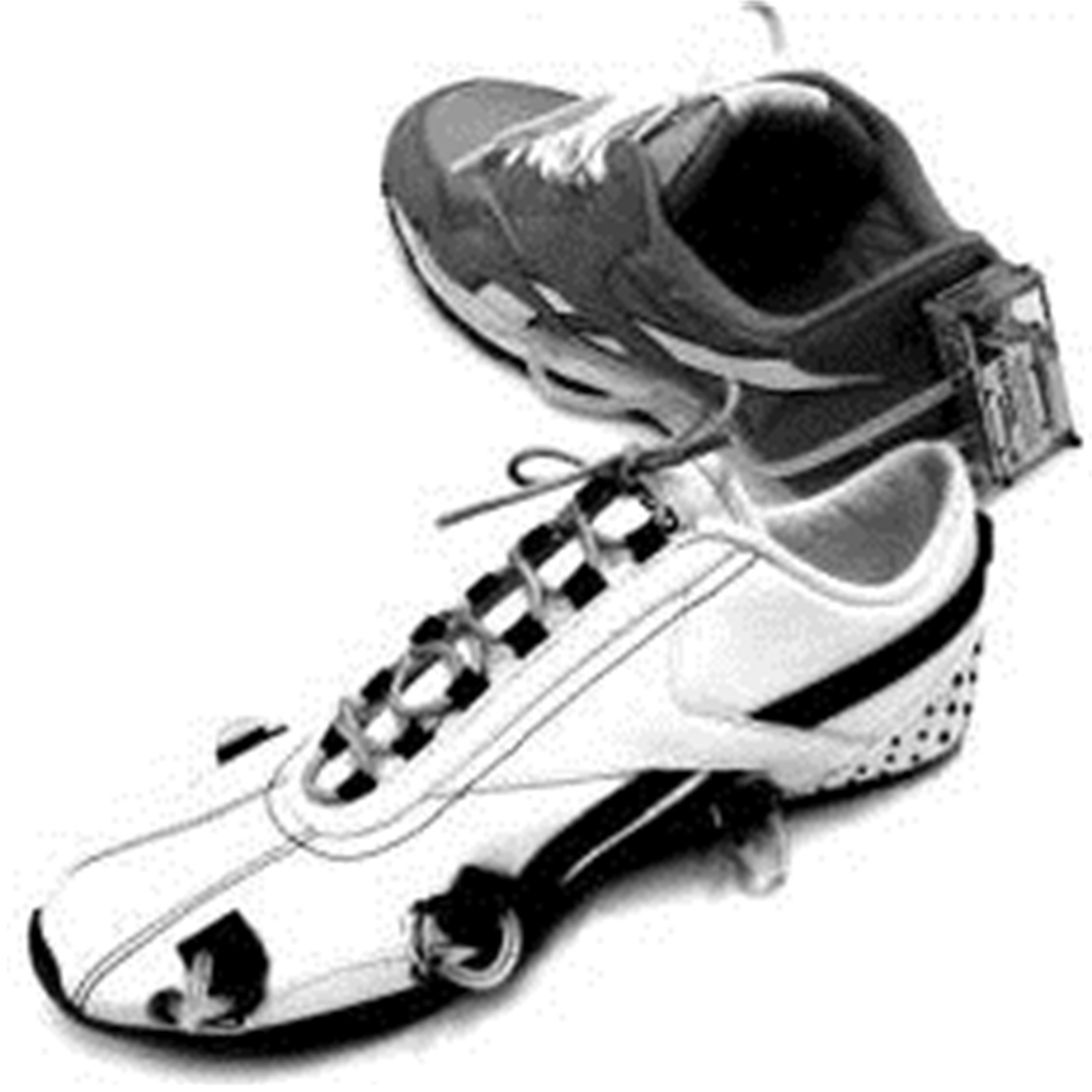
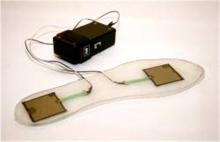
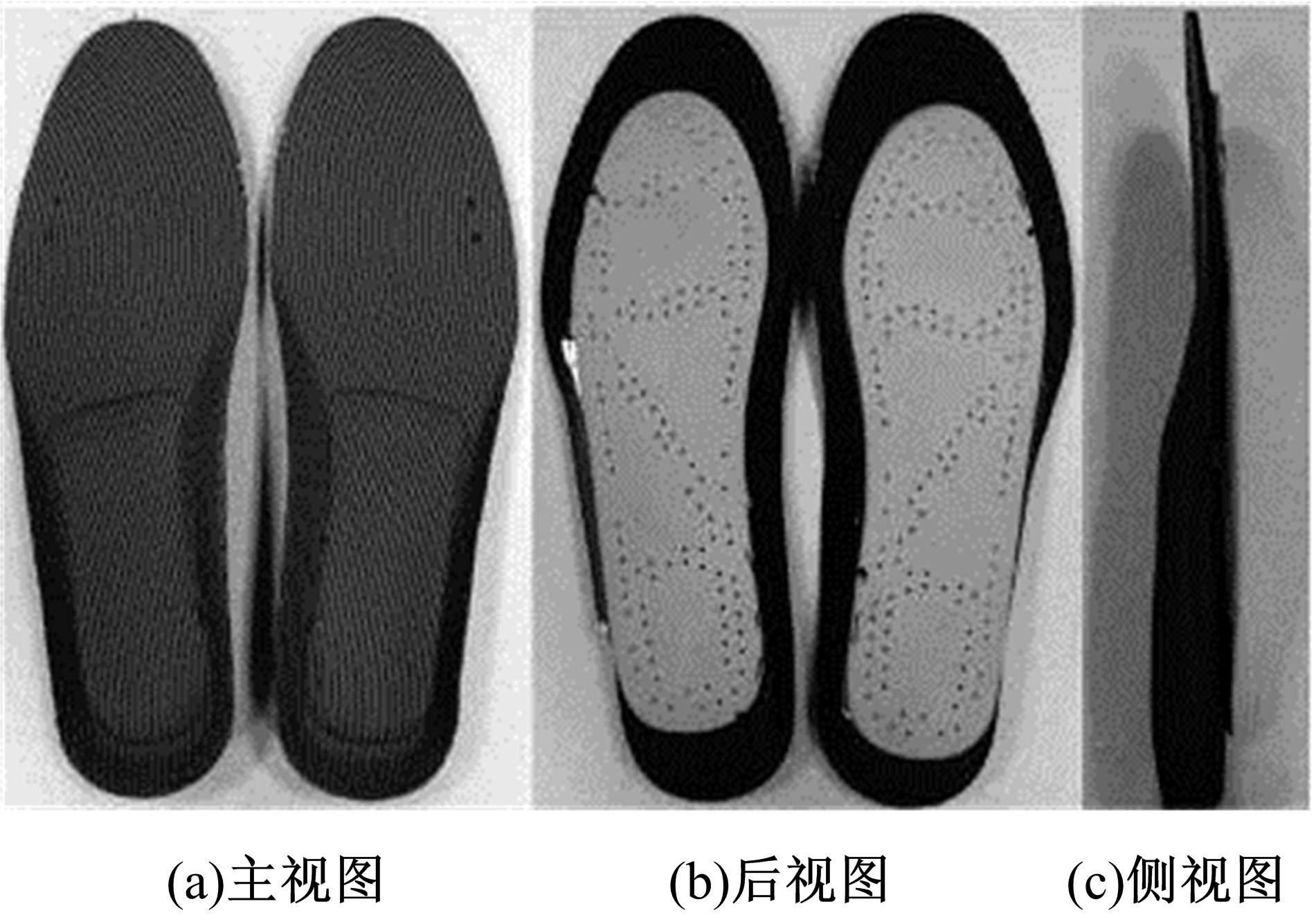
| 29 | Manupibul U, Charoensuk W, Kaimuk P. Design and development of SMART insole system for plantar pressure measurement in imbalance human body and heavy activities[C]∥International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Biotechnology, Shanghai,China, 2015:1-5. |
| 30 | Kong K, Tomizuka M. A gait monitoring system based on air pressure sensors embedded in a shoe[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2009, 14(3):358-370. |
| 31 | Redd C B, Bamberg S J M. A wireless sensory feedback device for real-time gait feedback and training[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2012, 17(3):425-433. |
| 32 | Lin F, Wang A, Zhuang Y, et al. Smart insole: a wearable sensor device for unobtrusive gait monitoring in daily life[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2016, 12(6): 2281-2291. |
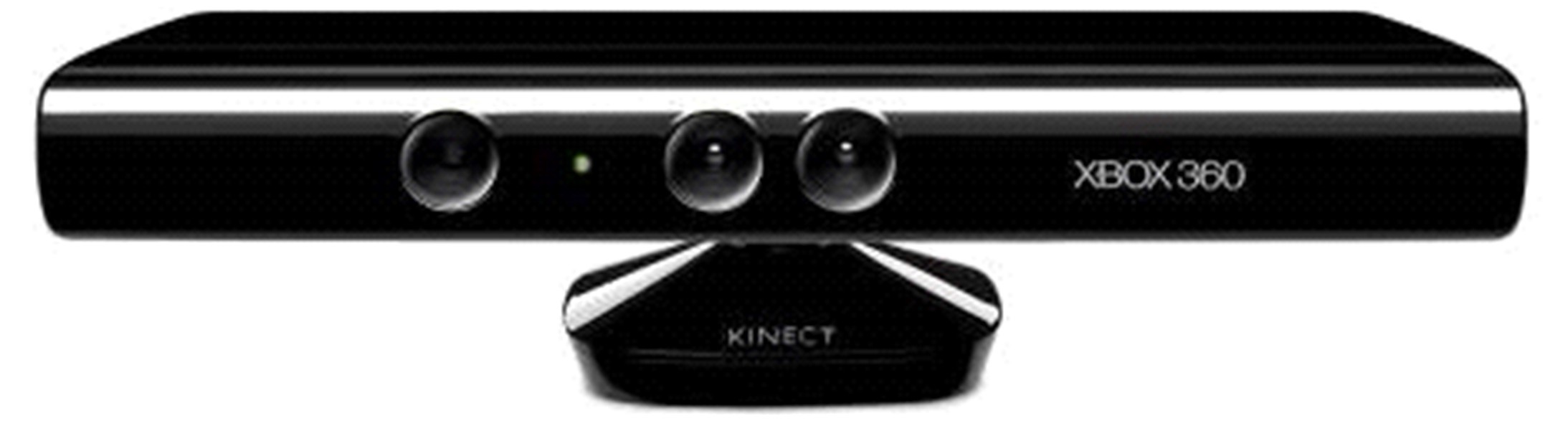
| 33 | Creaby M W, May K, Bennell K L. Insole effects on impact loading during walking[J]. Ergonomics, 2011, 54(7): 665-671. |
| 34 | Chen D, Cai Y, Huang M C. Customizable pressure sensor array: design and evaluation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(15):6337-6344. |
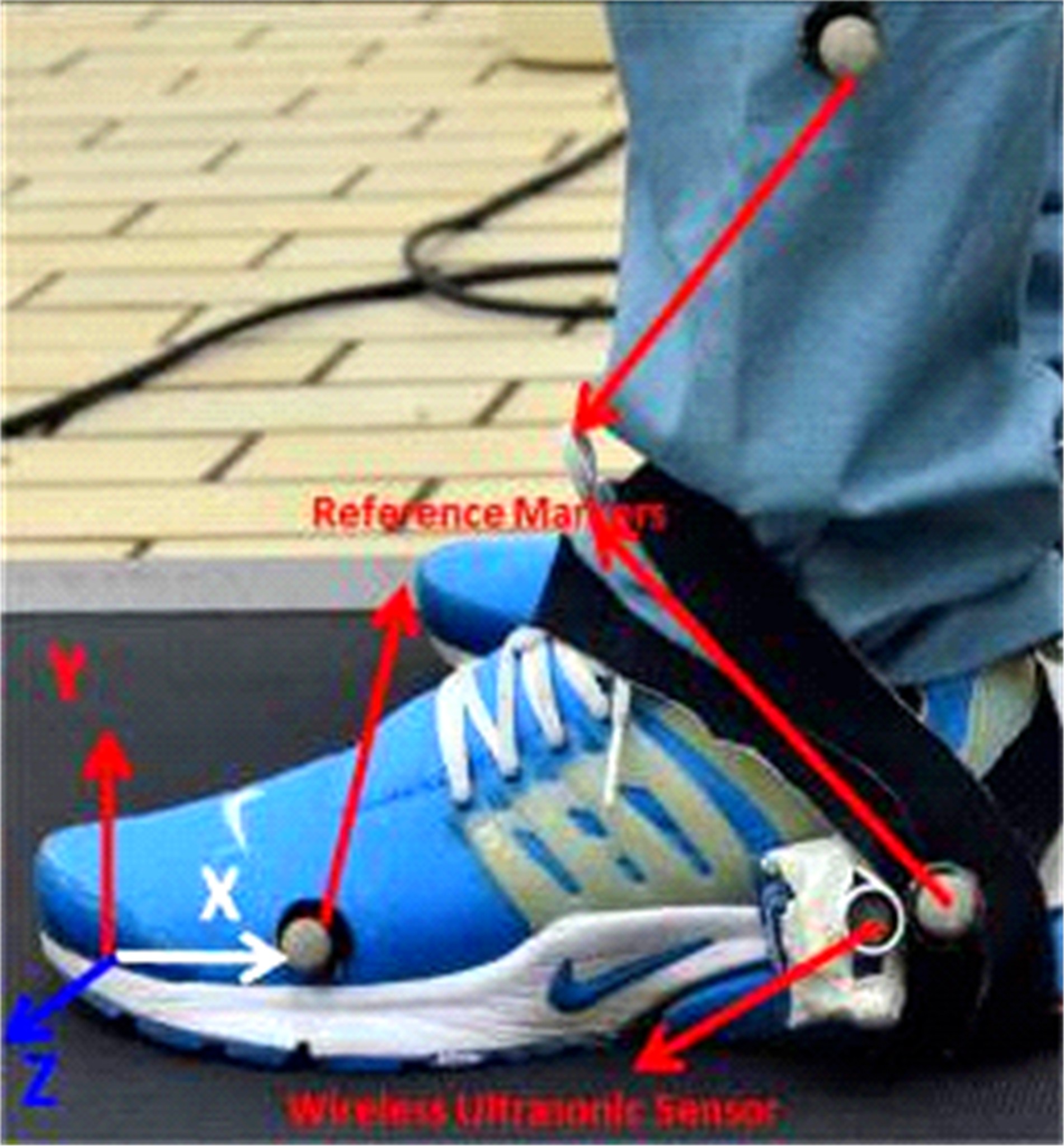
| 35 | Qi Y, Soh C B, Gunawan E, et al. Ambulatory measurement of three-dimensional foot displacement during treadmill walking using wearable wireless ultrasonic sensor network[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical & Health Informatics, 2015, 19(2): 446-452. |
| 36 | Qi Y, Soh C B, Gunawan E, et al. Assessment of foot trajectory for human gait phase detection using wireless ultrasonic sensor network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems & Rehabilitation Engineering, 2016, 24(1):88-97. |
| 37 | Wearing S C, Reed L, Hooper S L, et al. Running shoes increase achilles tendon load in walking: an acoustic propagation study[J]. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 2014, 46(8):1604-1609. |
| 38 | Wulf M, Wearing S C, Hooper S L, et al. achilles tendon loading patterns during barefoot walking and slow running on a treadmill: An ultrasonic propagation study[J]. Scand J Med Sci Sports, 2016, 25(6):868-875. |
| 39 | Little J, Boyd J. Recognizing people by their gait: the shape of motion[J]. Videre: Journal of Computer Vision Research, 1998, 1(2): 1-32. |
| 40 | Tanawongsuwan R, Bobick A. Gait recognition from time-normalized joint-angle trajectories in the walking plane[C]∥IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Kauai, HI, USA,2001:726-731. |
| 41 | Park Steve, Amos Y, Daniel S, et al. Human identification at a distance at gatech[DB/OL][2018-8-25]. https:∥www.cc.gatech.edu/cpl/projects/hid/ |
| 42 | Gross R, Shi J. The cmu motion of body (mobo) database[R]. Pittsburgh: Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, 2001. |
| 43 | Sarkar S, Phillips P J, Liu Z, et al. The humanid gait challenge problem: data sets, performance, and analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(2): 162-177. |
| 44 | Wang L, Tan T, Ning H, et al. Silhouette analysis-based gait recognition for human identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(12): 1505-1518. |
| 45 | Yu S, Tan D, Tan T. A framework for evaluating the effect of view angle, clothing and carrying condition on gait recognition[C]∥The 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Hong Kong, China, 2006: 441-444. |
| 46 | Tan D, Huang K, Yu S, et al. Uniprojective features for gait recognition[C]∥International Conference on Biometrics. Berlin: Springer, 2007: 673-682. |
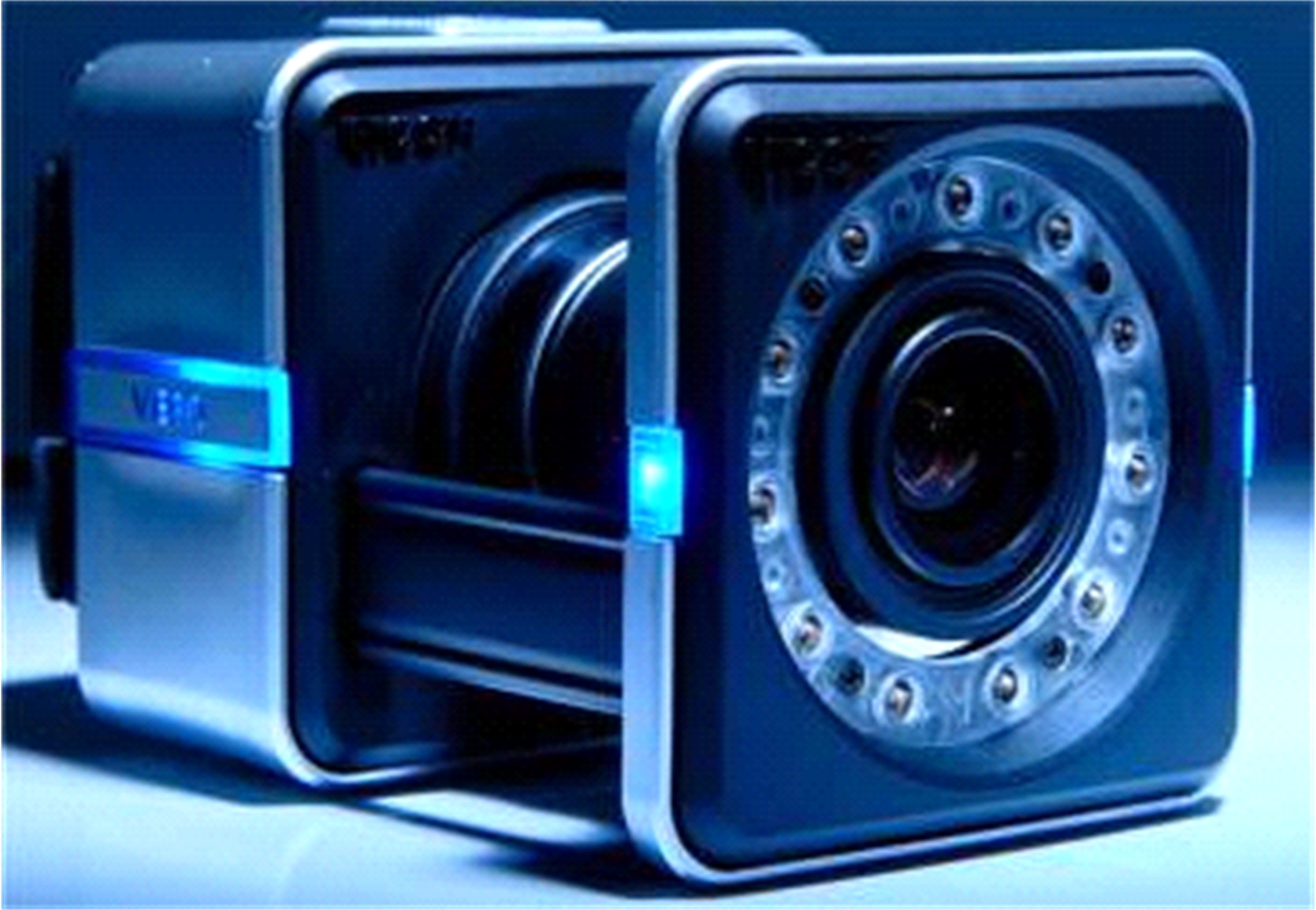
| 47 | Vicon Vantage Reference[M/OL]. [2019-02-28]. https:∥. |
| 48 | Go Further With Vicon MX T-Series[M/OL].[2019-02-28].https:∥www.vicon.com/downloads/documentation/go-further-with-vicon-mx-t-series,2018. |
| 49 | Pfister A, West A M, Bronner S, et al. Comparative abilities of Microsoft Kinect and Vicon 3D motion capture for gait analysis[J]. Journal of medical Engineering & Technology, 2014, 38(5): 274-280. |
| 50 | Eltoukhy M, Oh J, Kuenze C, et al. Improved kinect-based spatiotemporal and kinematic treadmill gait assessment[J]. Gait & Posture, 2017, 51: 77-83. |
| 51 | Eltoukhy M, Kuenze C, Oh J, et al. Microsoft Kinect can distinguish differences in over-ground gait between older persons with and without Parkinson's disease[J]. Medical Engineering &Physics, 2017, 44: 1-7. |
| 52 | Tanaka R, Takimoto H, Yamasaki T, et al. Validity of time series kinematical data as measured by a markerless motion capture system on a flatland for gait assessment[J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 2018, 71: 281-285. |
| 53 | Tanawongsuwan R, Bobick A. Gait recognition from time-normalized joint-angle trajectories in the walking plane[C]∥Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Kauai, HI, USA, 2001. |
| 54 | Seely R D, Samangooei S, Middleton L, et al. The university of southampton multi-biometric tunnel and introducing a novel 3d gait dataset[C]∥IEEE Second International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems,Arlington, VA, USA,2008. |
| 55 | Shutler J D, Grant M G, Nixon M S, et al. On a Large Sequence-Based Human Gait Database[M].Berlin: Springer, 2004:66-71. |
| 56 | Department of Intelligent Media, The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research, University Osaka. OU-ISIR biometric database [DB/OL]. [2019-2-28]. http:∥www.am.sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp/BiometricDB/GaitLP.html,2018. |
| 57 | Yu S, Wang Q, Huang Y. A large RGB-D gait dataset and the baseline algorithm[C]∥The 8th Chinese Conference on Biometric Recognition,Jinan,China,2013: 417-424. |
| 58 | Andersson V O, de Araújo R M. Person identification using anthropometric and gait data from kinect sensor[C]∥AAAI, Austin, Texas, USA, 2015: 425-431. |
| 59 | PhysioBank databases[DB/OL]. [2019-2-28]. https:∥physionet.org/physiobank/database/#gait. |
| 60 | Cunado D, Nixon M S, Carter J N. Using gait as a biometric, via phase-weighted magnitude spectra[C]∥LNCS, 1997, 1206: 93-102. |
| 61 | Okusa K, Kamakura T. Human gait modeling and statistical registration for the frontal view gait data with application to the normal/abnormal gait analysis[C]//IAENG Transactions on Engineering Technologies. Dordrecht:Springer, 2014: 525-539. |
| 62 | Guo Y, Xu G, Tsuji S. Understanding human motion patterns[C]∥Proceedings of the 12th IAPR International. Conference on Pattern Recognition, Jerusalem, Israel, 1994: 325-329. |
| 63 | Rohr K. Towards model-based recognition of human movements in image sequences[J]. CVGIP-Image Understanding, 1994, 59(1): 94-115. |
| 64 | Howe N R, Leventon M E, Freeman W T. Bayesian reconstruction of 3d human motion from single-camera video[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000: 820-826. |
| 65 | Human Interface Guidelines[M/OL].[2019-3-3]. http: Springer,. |
| 66 | Gordon Rachel. Artificial intelligence senses people through walls[DB/OL]. [2019-2-28]. https:∥. |
| 67 | Sutherland D. The development of mature gait[J]. Gait & Posture, 1997, 6(2): 163-170. |
| 68 | Nguyen T N, Huynh H H, Meunier J. Skeleton-based abnormal gait detection[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(11): 1792. |
| 69 | Glowinski S, Blazejewski A, Krzyzynski T. Human gait feature detection using inertial sensors wavelets[M]∥ Glowinski S,Blazejewski A,Krzyzynski T,ed. Wearable Robotics: Challenges and Trends, Springer, Cham, 2017: 397-401. |
| 70 | Cahill-Rowley K, Rose J. Temporal-spatial gait parameters and neurodevelopment in very-low-birth-weight preterm toddlers at 18-22 months[J]. Gait & Posture, 2016, 45: 83-89. |
| 71 | Ochi F, Esquenazi A, Hirai B, et al. Temporal—spatial feature of gait after traumatic brain injury[J]. The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 1999, 14(2): 105-115. |
| 72 | Esquenazi A, Ofluoglu D, Hirai B, et al. The effect of an ankle-foot orthosis on temporal spatial parameters and asymmetry of gait in hemiparetic patients[J]. PM&R, 2009, 1(11): 1014-1018. |
| 73 | 张勤, 李岳炀, 李贻斌,等. 基于Kinect的学步期幼儿自然步态特征提取[J]. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(6): 1096-1106. |
| Zhang Qin, Li Yue-yang, Li Yi-bin, et al. Extraction of toddler's natural gait based on kinect[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(6):1096-1106. | |
| 74 | Kamruzzaman J, Begg R K. Support vector machines and other pattern recognition approaches to the diagnosis of cerebral palsy gait[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2006, 53(12): 2479-2490. |
| 75 | Chen S W, Lin S H, Liao L D, et al. Quantification and recognition of parkinsonian gait from monocular video imaging using kernel-based principal component analysis[J]. Biomedical Engineering Online, 2011, 10(1): 99. |
| 76 | Qi Y, Soh C B, Gunawan E, et al. Estimation of spatial-temporal gait parameters using a low-cost ultrasonic motion analysis system[J]. Sensors, 2014, 14(8): 15434-15457. |
| 77 | Dempster W T, Gaughran G R L. Properties of body segments based on size and weight[J]. American Journal of Anatomy, 1967, 120(1): 33-54. |
| 78 | Ober D B, Neugebauer S P, Sallee P A. Training and feature-reduction techniques for human identification using anthropometry[C]∥Fourth IEEE International Conference on Biometrics: Theory Applications and Systems (BTAS), Washington, DC, USA, 2010: 1-8. |
| 79 | Johnson A Y, Bobick A F. A multi-view method for gait recognition using static body parameters[C]∥International Conference on Audio-and Video-Based Biometric Person Authentication, Washington, DC, US, 2001: 301-311. |
| 80 | 贲晛烨, 徐森, 王科俊. 行人步态的特征表达及识别综述[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2012(1): 71-81. |
| Xian-ye Ben, Xu Sen, Wang Ke-jun. Review on pedestrian gait feature expression and recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2012(1): 71-81. | |
| 81 | Wang C, Zhang J, Pu J, et al. Chrono-gait image: a novel temporal template for gait recognition[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 2010: 257-270. |
| 82 | Ozen H, Boulgouris N V, Swash R. Gait recognition based on 3D holoscopic gait energy image[C]∥International Conference on 3D Immersion (IC3D), Brussels, Belgium,2017: 1-4. |
| 83 | He Y, Zhang J, Shan H, et al. Multi-task GANs for view-specific feature learning in gait recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(1): 102-113. |
| 84 | Lee H, Hong S, Nizami I F, et al. A noise robust gait representation: motion energy image[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2009, 7(4): 638-643. |
| 85 | Nizami I F, Hong S, Lee H, et al. Automatic gait recognition based on probabilistic approach[J]. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 2010, 20(4): 400-408. |
| 86 | Liu Y, Collins R, Tsin Y. Gait sequence analysis using frieze patterns[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2002: 657-671. |
| 87 | Lee S, Liu Y, Collins R. Shape variation-based frieze pattern for robust gait recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2007: 1-8. |
| 88 | Bashir K, Xiang T, Gong S. Gait recognition using gait entropy image[C]∥The 3rd International Conference on Imaging for Crime Detection and Prevention, London ,UK, 2009. |
| 89 | Liu Z, Yang G. Use wavelet transform to gait recognition[C]∥International Congress on Image & Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2016. |
| 90 | Wang H, Fan Y, Fang B, et al. Generalized linear discriminant analysis based on Euclidean norm for gait recognition[J]. International Journal of Machine Learning & Cybernetics, 2018, 9(4):569-576. |
| 91 | Zhang H, Ye C. RGB-D Camera Based Walking Pattern Recognition by Support Vector Machines for a Smart Rollator[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Robotics & Applications, 2017, 1(1):32-41. |
| 92 | Wang X, Wang J, Yan K. Gait recognition based on Gabor wavelets and (2D) 2 PCA[J]. Multimedia Tools & Applications, 2017(3):1-17. |
| 93 | Yu S, Chen H, Wang Q, et al. Invariant feature extraction for gait recognition using only one uniform model[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 239(C):81-93. |
| 94 | Yeoh T W, Aguirre H E, Tanaka K. Stacked progressive auto-encoders for clothing-invariant gait recognition[C]∥International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, Ystad, Sweden, 2017: 151-161. |
| 95 | Wang Y, Chen Y, Bhuiyan M Z A, et al. Gait-based Human identification using acoustic sensor and deep neural network[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018, 86: 1228-1237. |
| 96 | Shiraga K, Makihara Y, Muramatsu D, et al. GEINet: view-invariant gait recognition using a convolutional neural network[C]∥International Conference on Biometrics, Halmstad, Sweden, 2016:1-8. |
| 97 | Chen Q, Wang Y, Liu Z, et al. Feature map pooling for cross-view gait recognition based on silhouette sequence images[C]//IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Denver, CO, USA, 2017:54-61. |
| 98 | Wu Z, Huang Y, Wang L, et al. A comprehensive study on cross-view gait based human identification with deep CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(2):209-226. |
| 99 | Chen C, Liang J, Zhao H, et al. Gait recognition using hidden Markova model[C]∥International Conference on Natural Computation, Xi’an,China, 2006: 399-407. |
| 100 | Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2014: 2672-2680. |
| 101 | Yu S, Chen H, Reyes E B G, et al. Gait GAN: invariant gait feature extraction using generative adversarial networks[C]∥CVPR Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 532-539. |
| 102 | Das D. Human gait classification using combined HMM & SVM hybrid classifier[C]∥International Conference on Electronic Design, Computer Networks & Automated Verification (EDCAV), Shillong, India, 2015: 169-174. |
| 103 | Takemura N, Makihara Y, Muramatsu D, et al. On input/output architectures for convolutional neural network-based cross-view gait recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology,2019,29(9): 2708-2719. |
| 104 | Banaie M, Pooyan M, Mikaili M. Introduction and application of an automatic gait recognition method to diagnose movement disorders that arose of similar causes[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(6): 7359-7363. |
| 105 | Pogorelc B, Bosnić Z, Gams M. Automatic recognition of gait-related health problems in the elderly using machine learning[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2012, 58(2): 333-354. |
| [1] | 徐谦,李颖,王刚. 基于深度学习的行人和车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1661-1667. |
| [2] | 高万夫,张平,胡亮. 基于已选特征动态变化的非线性特征选择方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1293-1300. |
| [3] | 欧阳丹彤,肖君,叶育鑫. 基于实体对弱约束的远监督关系抽取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 912-919. |
| [4] | 顾海军, 田雅倩, 崔莹. 基于行为语言的智能交互代理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1578-1585. |
| [5] | 董飒, 刘大有, 欧阳若川, 朱允刚, 李丽娜. 引入二阶马尔可夫假设的逻辑回归异质性网络分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1571-1577. |
| [6] | 王旭, 欧阳继红, 陈桂芬. 基于垂直维序列动态时间规整方法的图相似度度量[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1199-1205. |
| [7] | 张浩, 占萌苹, 郭刘香, 李誌, 刘元宁, 张春鹤, 常浩武, 王志强. 基于高通量数据的人体外源性植物miRNA跨界调控建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1206-1213. |
| [8] | 李雄飞, 冯婷婷, 骆实, 张小利. 基于递归神经网络的自动作曲算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 866-873. |
| [9] | 刘杰, 张平, 高万夫. 基于条件相关的特征选择方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 874-881. |
| [10] | 黄岚, 纪林影, 姚刚, 翟睿峰, 白天. 面向误诊提示的疾病-症状语义网构建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 859-865. |
| [11] | 王旭, 欧阳继红, 陈桂芬. 基于多重序列所有公共子序列的启发式算法度量多图的相似度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 526-532. |
| [12] | 刘雪娟, 袁家斌, 许娟, 段博佳. 量子k-means算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 539-544. |
| [13] | 杨欣, 夏斯军, 刘冬雪, 费树岷, 胡银记. 跟踪-学习-检测框架下改进加速梯度的目标跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 533-538. |
| [14] | 李嘉菲, 孙小玉. 基于谱分解的不确定数据聚类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1604-1611. |
| [15] | 曲慧雁, 赵伟, 秦爱红. 基于优化算子的快速碰撞检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1598-1603. |
|
||