吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 278-288.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180948
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于法向量距离分类的散乱点云数据去噪
- 1. 南昌大学 机电工程学院,南昌 330031
2. 赤峰学院 建筑与机械工程学院,内蒙古 赤峰 024000
3. 贵州师范大学,机电工程学院,贵阳 550025
Denoising of scattered point cloud data based on normal vector distance classification
Xiao-hui WANG1,2( ),Lu-shen WU1(
),Lu-shen WU1( ),Hua-wei CHEN3
),Hua-wei CHEN3
- 1. School of Mechatronic Engineering, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, China
2. School of Architectural and Mechanical Engineering, Chifeng University, Chifeng 024000, China
3. School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang 550025, China
摘要:
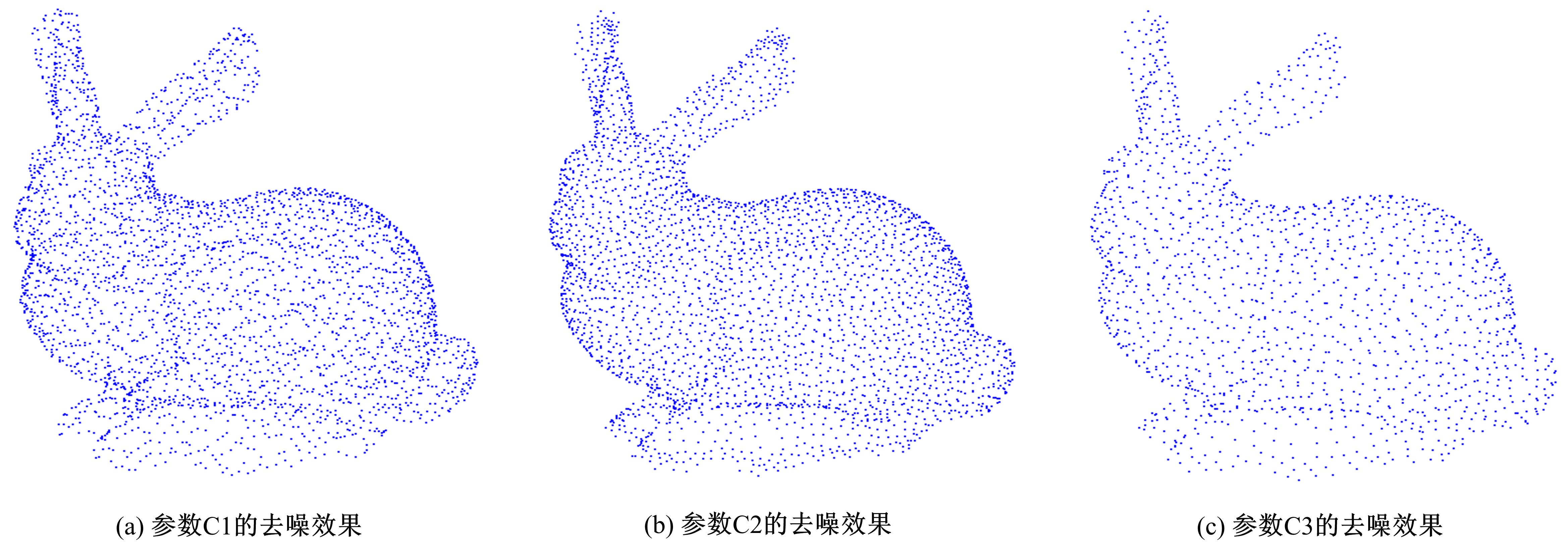
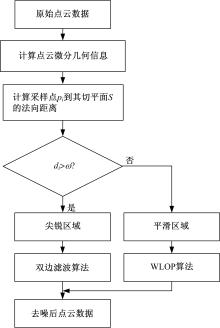
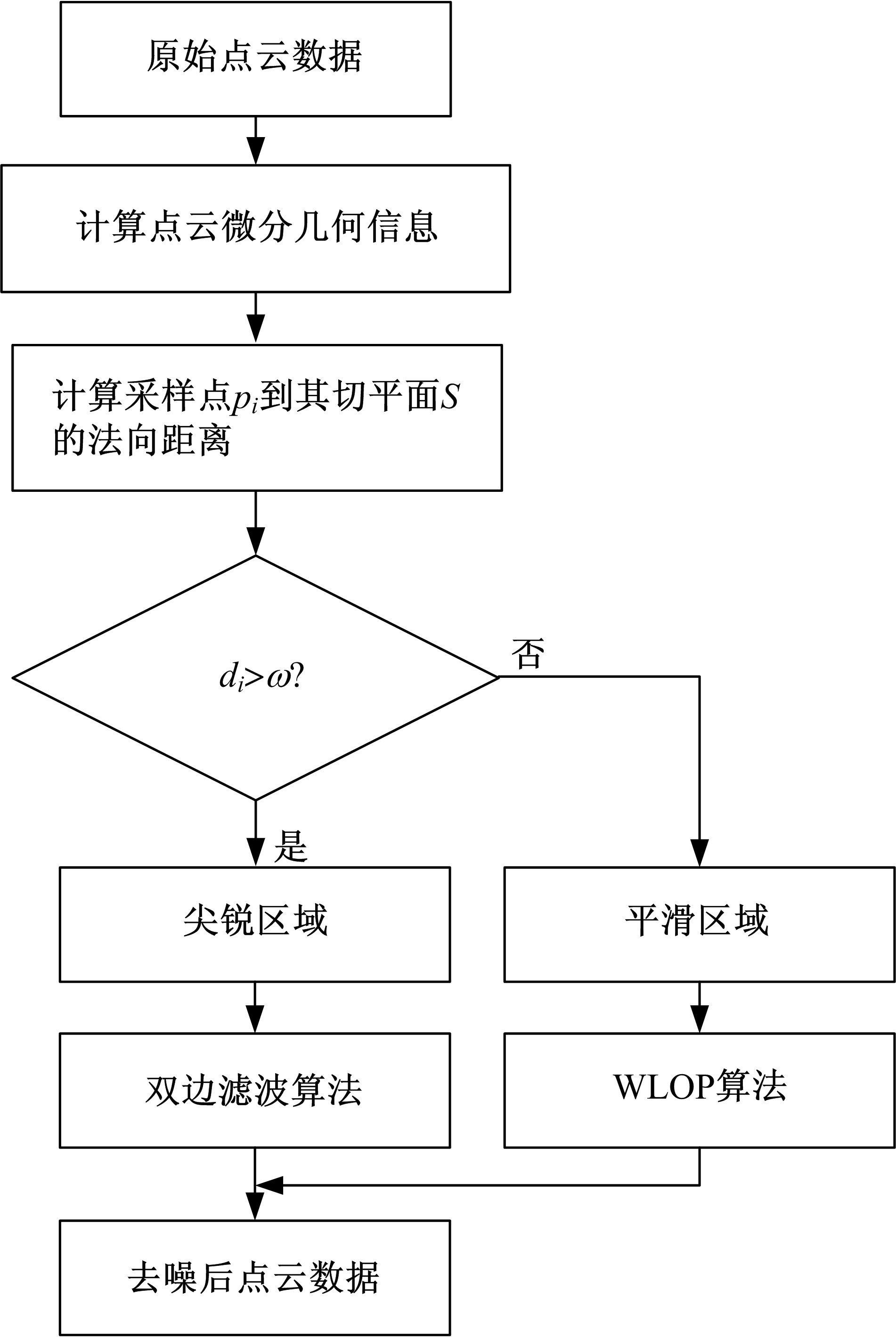
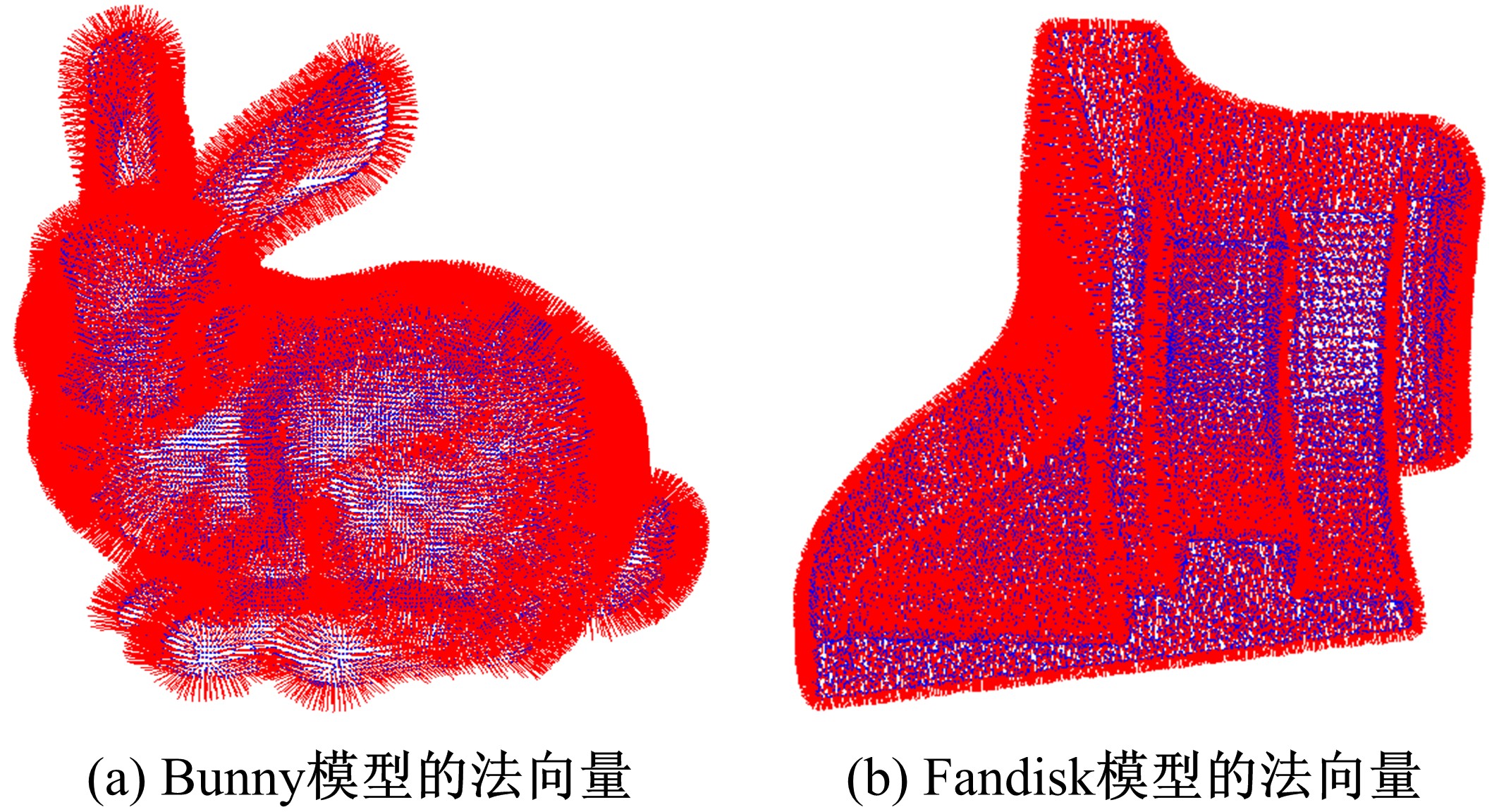
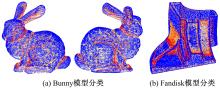
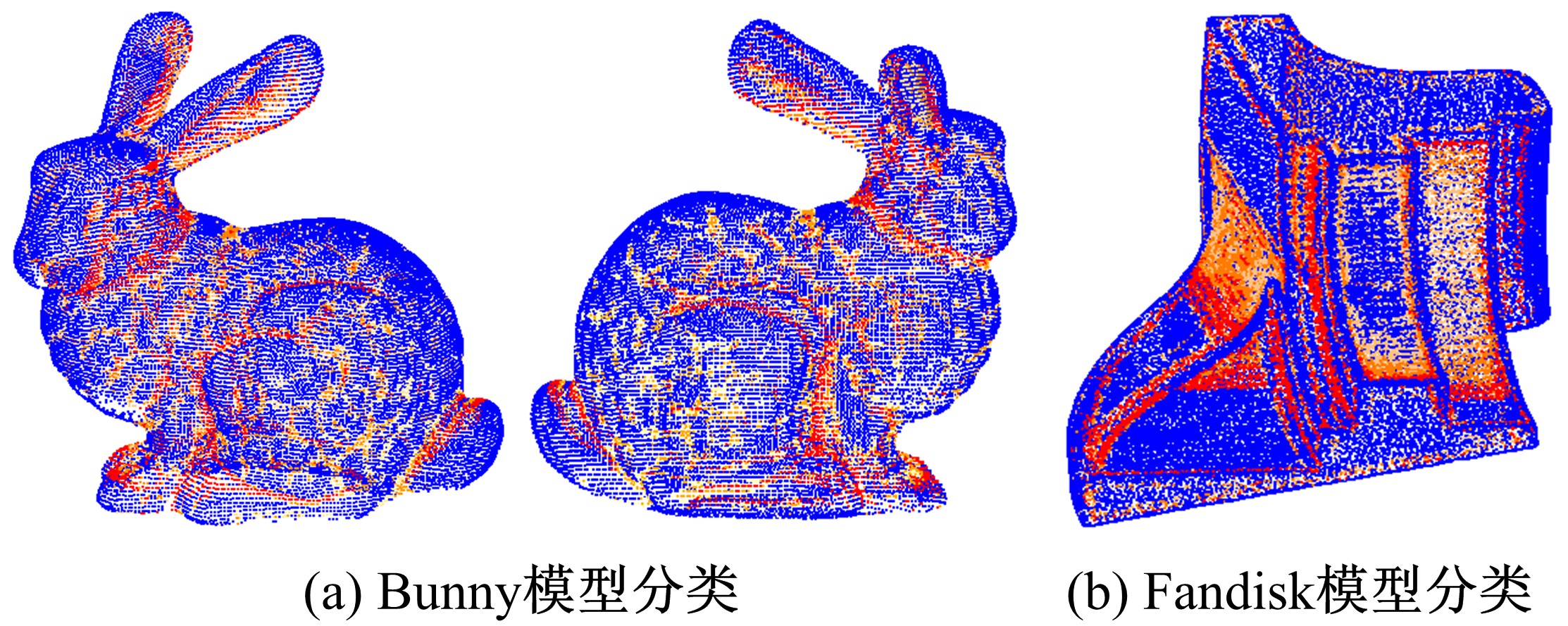
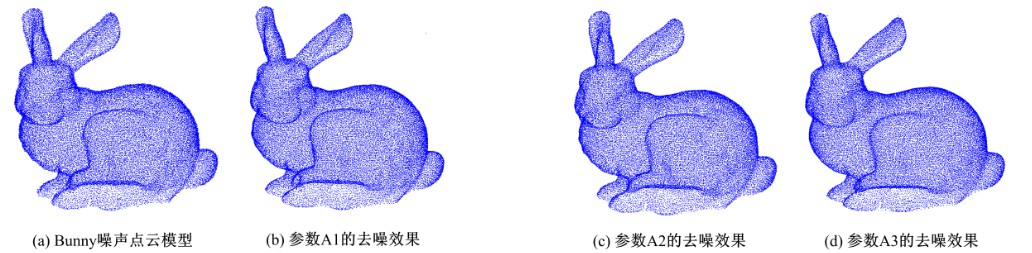
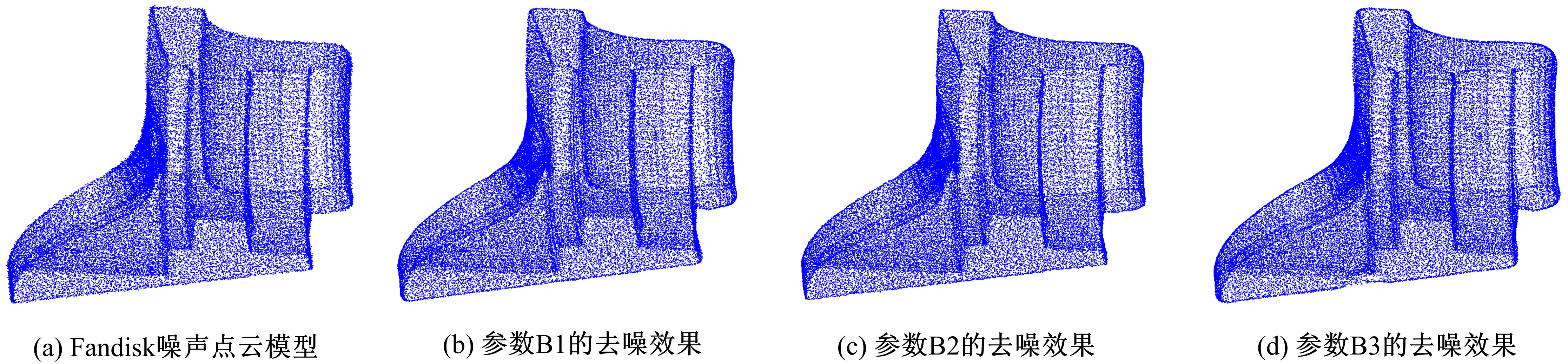
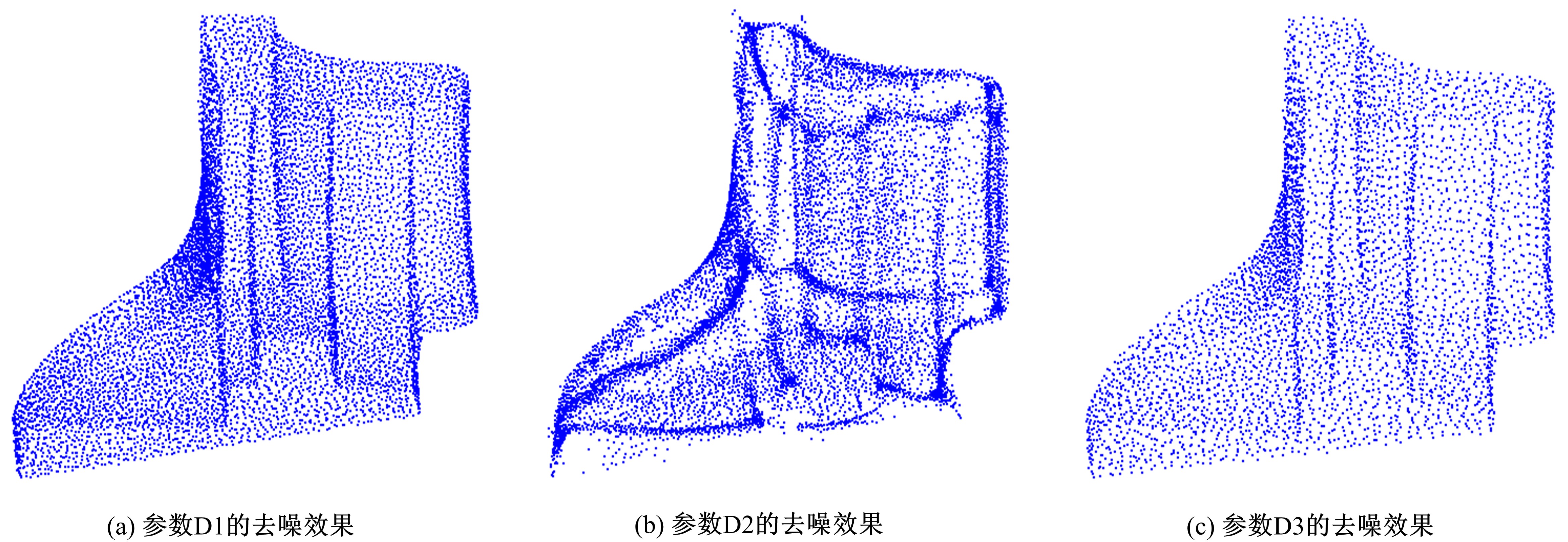
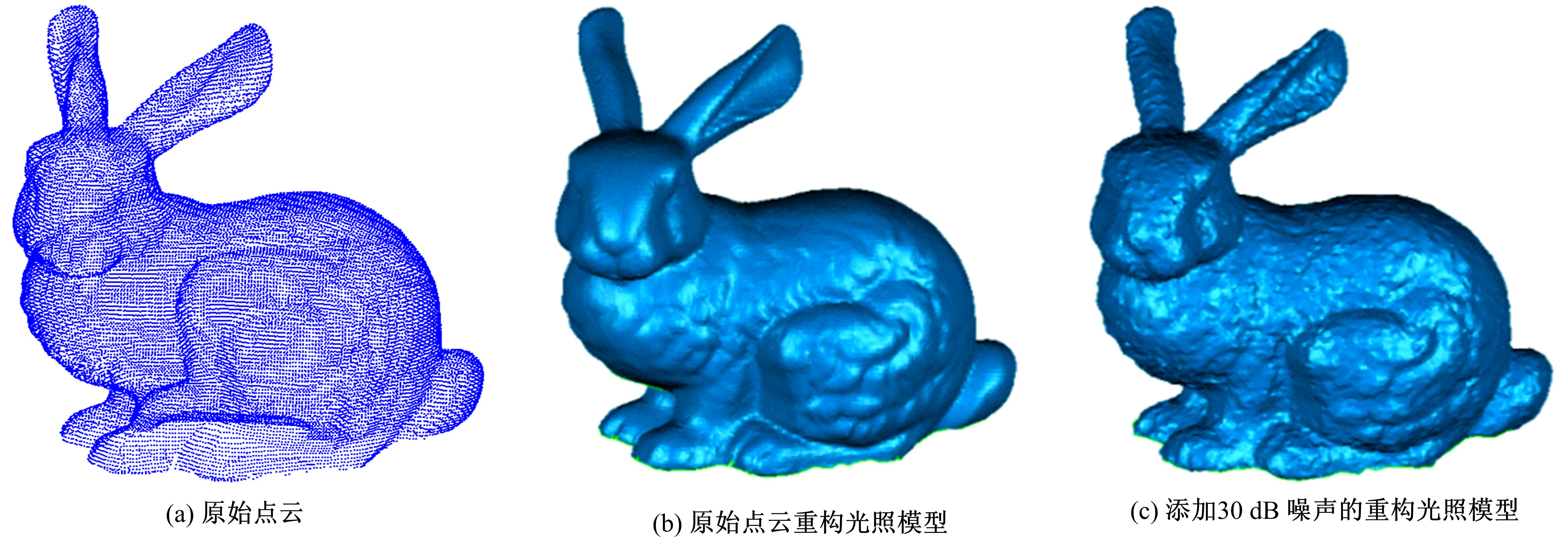
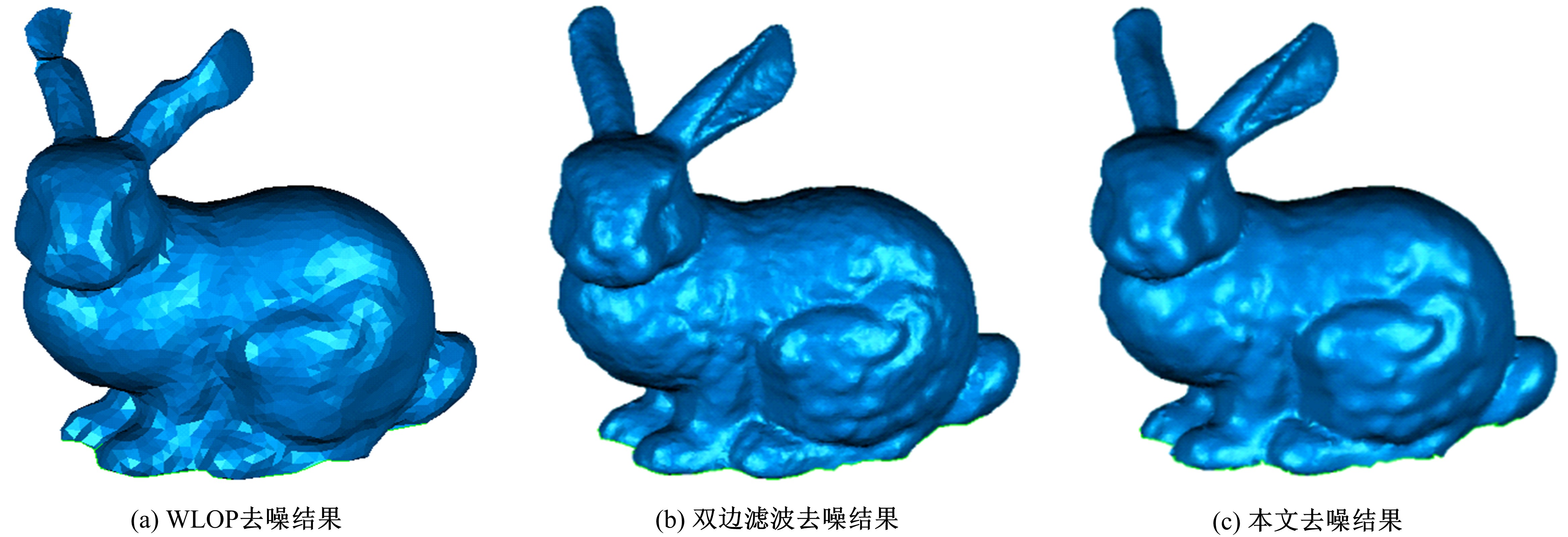
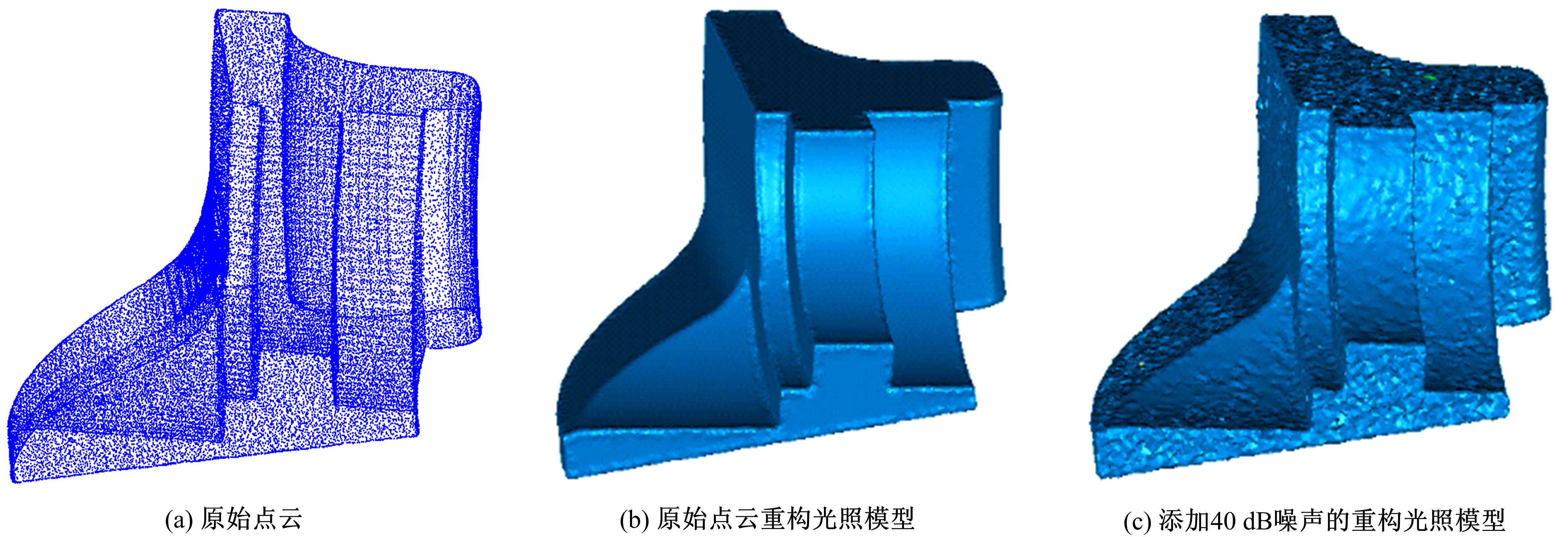
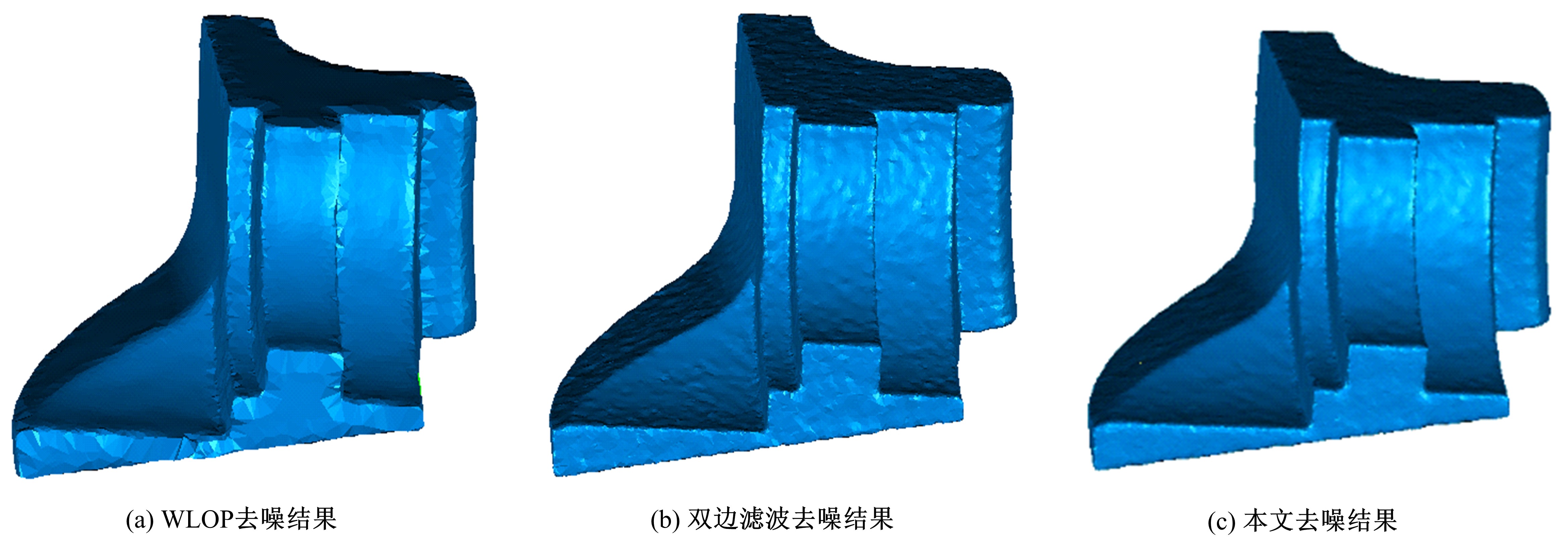
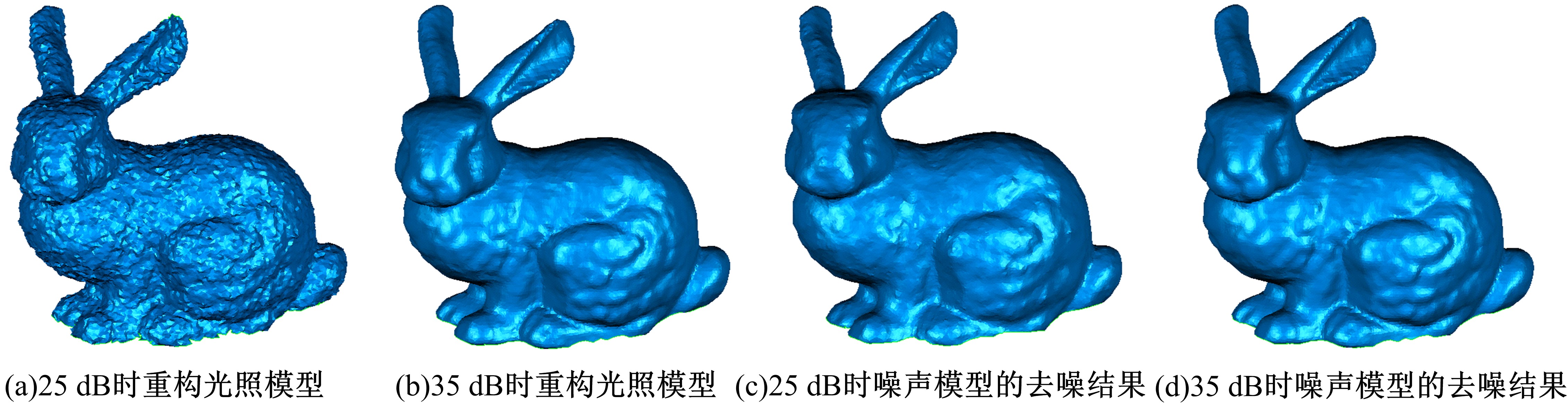
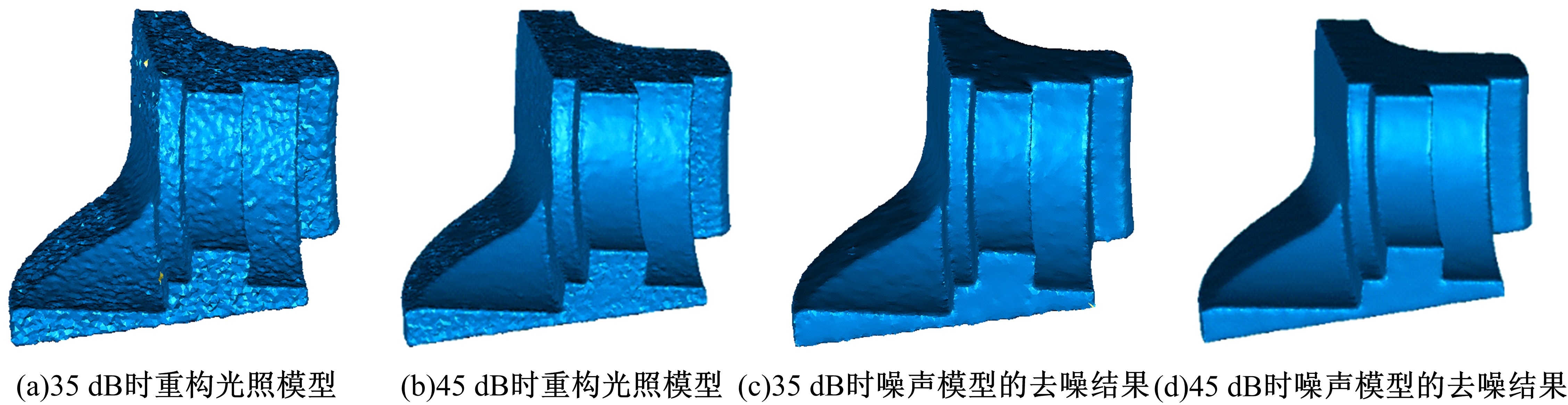
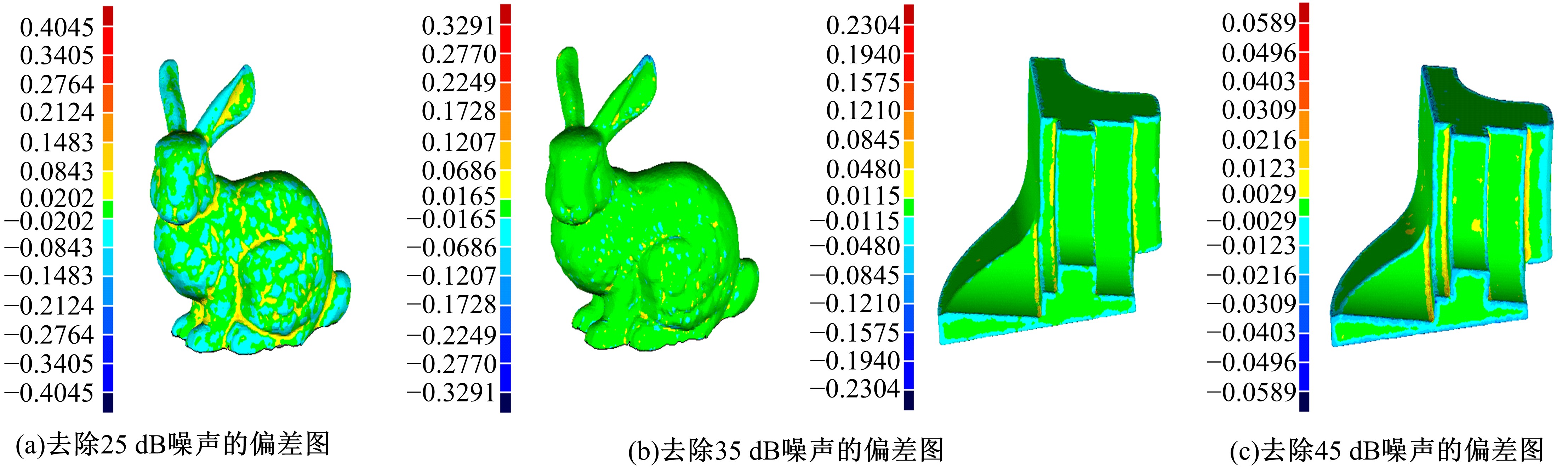
在三维点云数据的去噪中,很难实现既保持尖锐区域的特征,又使平滑区域高度光顺。为此,提出了一种基于法向量距离分类的去噪方法。首先计算点云数据的微分几何信息。采用鲁棒的方法对点云数据进行法矢量估算,并将其法矢量方向调整到一致。再根据采样点的局部二次曲面拟合来估算点云数据的曲率;然后通过计算从采样点到其切平面的法向距离,将点云数据划分为平滑区域和尖锐区域,并采用加权局部最优投影算法和双边滤波算法分别对平滑区域和尖锐区域进行滤波去噪。选用Bunny和Fandisk点云模型,分别采用单一的加权局部最优投影算法、双边滤波算法及两者相结合算法对点云模型进行去噪测试。测试结果表明:所提方法可有效去除噪声模型中的孤点,提高点云分布的均匀性;增强点云模型平滑区域的光顺度,保持了尖锐区域中的几何特征并避免了过度光顺和细节特征失真。对比测试数据可知,降噪点云模型的误差和偏差较小,Bunny模型的平均误差为0.001 1 mm,Fandisk模型的平均误差为0.000 7 mm。
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Taubin G . A signal processing approach to fair surface design[C]∥Proceedings of the 22nd annual conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New York, USA, 1995: 351-358. |
| 2 | Desbrun M , Meyer M , Schröder P . et al . Implicit fairing of irregular meshes using diffusion and curvature flow[C]∥Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Los Angeles, United States, 1999: 317-324. |
| 3 | Fleishman S , Drori I , Cohen-Or D . Bilateral mesh denoising[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2003, 22(3): 950-953. |
| 4 | Jones T R , Durand F , Desbrun M . Non-iterative, feature-preserving mesh smoothing[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2003, 22(3): 943-949. |
| 5 | 杜小燕,姜晓峰,郝传刚,等 . 点云模型的双边滤波去噪算法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2010, 27(7): 245-246. |
| Du Xiao-yan , Jiang Xiao-feng , Hao Chuan-gang , et al . Bilateral filtering denoising algorithm for point cloud model[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2010, 27(7): 245-246. | |
| 6 | 曹爽,岳建平,马文 . 基于特征选择的双边滤波点云去噪算法[J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2013(增刊2): 351-354. |
| Cao Shuang , Yue Jian-ping , Ma Wen . Bilateral filtering denoise algorithm for point cloud based on feature selection[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2013(Sup.2): 351-354. | |
| 7 | 袁华,庞建铿,莫建文 . 基于噪声分类的双边滤波点云去噪算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2015, 35(8): 2305-2310. |
| Yuan Hua , Pang Jian-keng , Mo Jian-wen . Denoising algorithm for bilateral filtered point cloud based on noise classification[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2015, 35(8): 2305-2310. | |
| 8 | 李鹏飞,吴海娥,景军锋,等 . 点云模型的噪声分类去噪算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2016, 52(20): 188-192. |
| Li Peng-fei , Wu Hai-e , Jing Jun-feng , et al . Noise classification denoising algorithm for point cloud model[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2016, 52(20): 188-192. | |
| 9 | Lipman Y , Cohen-Or D , Levin D ,et al . Parameterization-free projection for geometry reconstruction[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2007, 26(3): 1276405. |
| 10 | Huang H , Li D , Zhang H , et al . Consolidation of unorganized point clouds for surface reconstruction[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2009, 28(5): 1-7. |
| 11 | 杨焕宇 .面向虚拟现实的三维点云数据处理关键技术研究[D]. 上海:东华大学信息科学与技术学院, 2016. |
| Yang Huan-yu . Research on key technologies of 3D point clouds data processing for virtual reality[D]. Shanghai: School of Information Science and Technology, Donghua University, 2016. | |
| 12 | Liu S , Chan K C , Wang C C . Iterative consolidation of unorganized point clouds[J]. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 2012, 32(3): 70-83. |
| 13 | 李宝 . 三维点云的鲁棒处理技术研究[D]. 长沙:国防科学技术大学研究生院, 2011. |
| Li Bao . Robust processing of 3D point clouds[D]. Changsha: Graduate School, National University of Defense Technology, 2011. | |
| 14 | 孙钰科 . 三维激光点云数据的处理及应用研究[D]. 上海:上海师范大学旅游学院, 2018. |
| Sun Yu-ke . Research on processing and application of 3D laser point cloud data[D]. Shanghai: School of Tourism,Shanghai Normal University, 2018. | |
| 15 | Hoppe H , DeRose T , Duchamp T , et al . Surface reconstruction from unorganized points[J]. ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics, 1992, 26(2): 71-78. |
| 16 | Wang Y , Feng H Y , Engin S . An adaptive normal estimation method for scanned point clouds with sharp features[J]. CAD computer-Aided Design, 2013, 45(11): 1333-1348. |
| 17 | 贺美芳 . 基于散乱点云数据的曲面重建关键技术研究[D]. 南京:南京航空航天大学CAD/CAM工程研究中心, 2006. |
| He Mei-fang . Research on key techniques of surface reconstruction based on scattered point cloud data[D]. Nanjing: CAD/CAM Engineering Research Center, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2006. |
| [1] | 张笑东,夏筱筠,吕海峰,公绪超,廉梦佳. 大数据网络并行计算环境中生理数据流动态负载均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 247-254. |
| [2] | 邓钧忆,刘衍珩,冯时,赵荣村,王健. 基于GSPN的Ad⁃hoc网络性能和安全平衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 255-261. |
| [3] | 李雄飞,王婧,张小利,范铁虎. 基于SVM和窗口梯度的多焦距图像融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 227-236. |
| [4] | 王洪雁,邱贺磊,郑佳,裴炳南. 光照变化下基于低秩稀疏表示的视觉跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 268-277. |
| [5] | 周炳海,吴琼. 考虑工具和空间约束的机器人装配线平衡优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2069-2075. |
| [6] | 车翔玖,刘华罗,邵庆彬. 基于Fast RCNN改进的布匹瑕疵识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2038-2044. |
| [7] | 赵宏伟,王鹏,范丽丽,胡黄水,刘萍萍. 相似性保持实例检索方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2045-2050. |
| [8] | 沈军,周晓,吉祖勤. 服务动态扩展网络及其结点系统模型的实现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2058-2068. |
| [9] | 周柚,杨森,李大琳,吴春国,王岩,王康平. 基于现场可编程门电路的人脸检测识别加速平台[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2051-2057. |
| [10] | 李宾,周旭,梅芳,潘帅宁. 基于K-means和矩阵分解的位置推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1653-1660. |
| [11] | 李雄飞,宋璐,张小利. 基于协同经验小波变换的遥感图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1307-1319. |
| [12] | 刘元宁,刘帅,朱晓冬,霍光,丁通,张阔,姜雪,郭书君,张齐贤. 基于决策粒子群优化与稳定纹理的虹膜二次识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1329-1338. |
| [13] | 李宾,申国君,孙庚,郑婷婷. 改进的鸡群优化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1339-1344. |
| [14] | 翟凤文,党建武,王阳萍,金静,罗维薇. 基于扩展轮廓的快速仿射不变特征提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1345-1356. |
| [15] | 孙延君,申铉京,陈海鹏,赵永哲. 基于局部平面线性点的翻拍图像鉴别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1320-1328. |
|
||