吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 293-302.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190970
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于多任务学习的传统服饰图像双层标注
- 1.北京邮电大学 计算机学院,北京 100876
2.北京邮电大学 数字媒体与设计艺术学院,北京 100876
3.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
Double-layer annotation of traditional costume images based on multi-task learning
Hai-ying ZHAO1( ),Wei ZHOU2,Xiao-gang HOU1,Xiao-li ZHANG3
),Wei ZHOU2,Xiao-gang HOU1,Xiao-li ZHANG3
- 1.School of Computer Science,Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876,China
2.School of Digital Media and Design Art,Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876,China
3.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
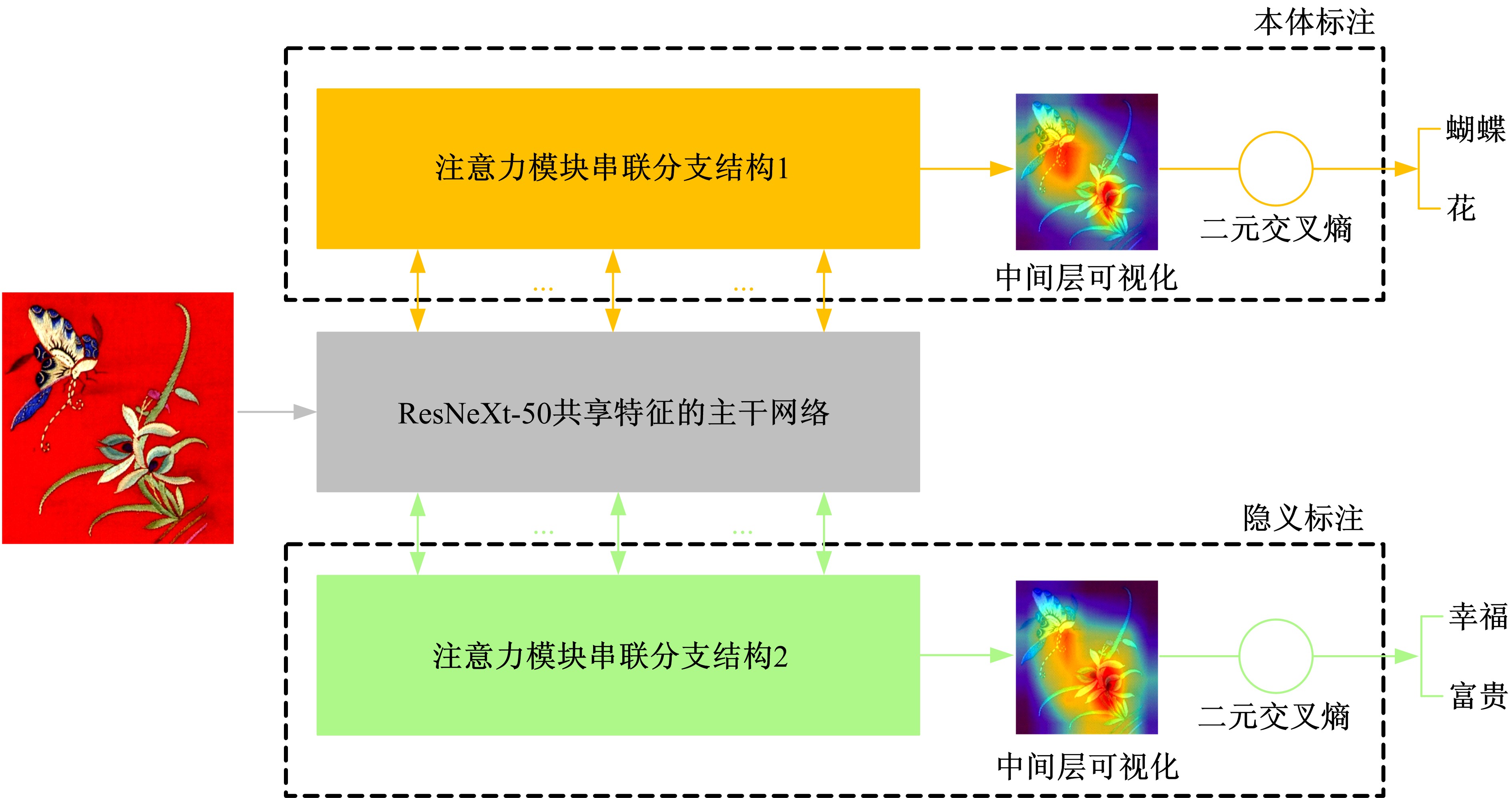
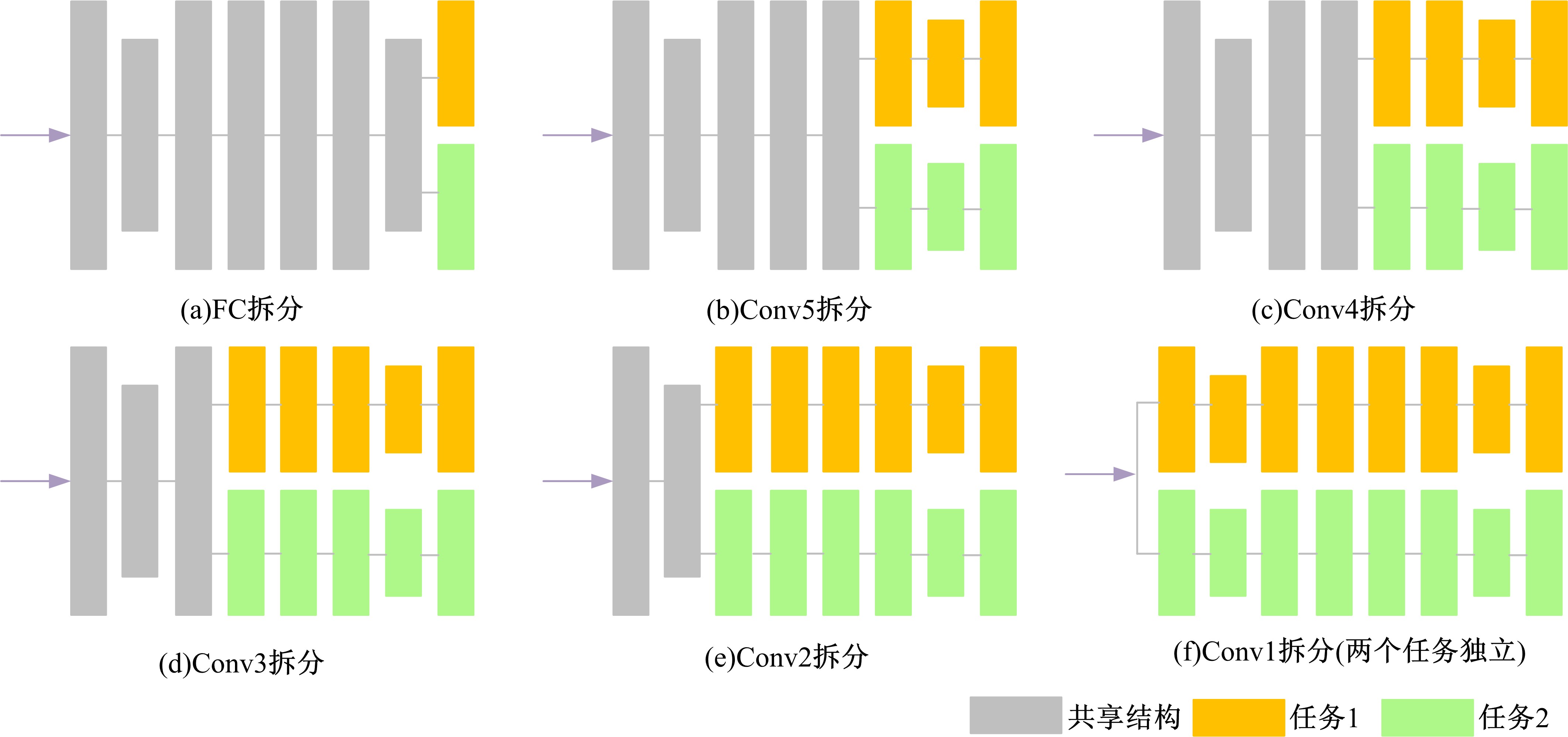
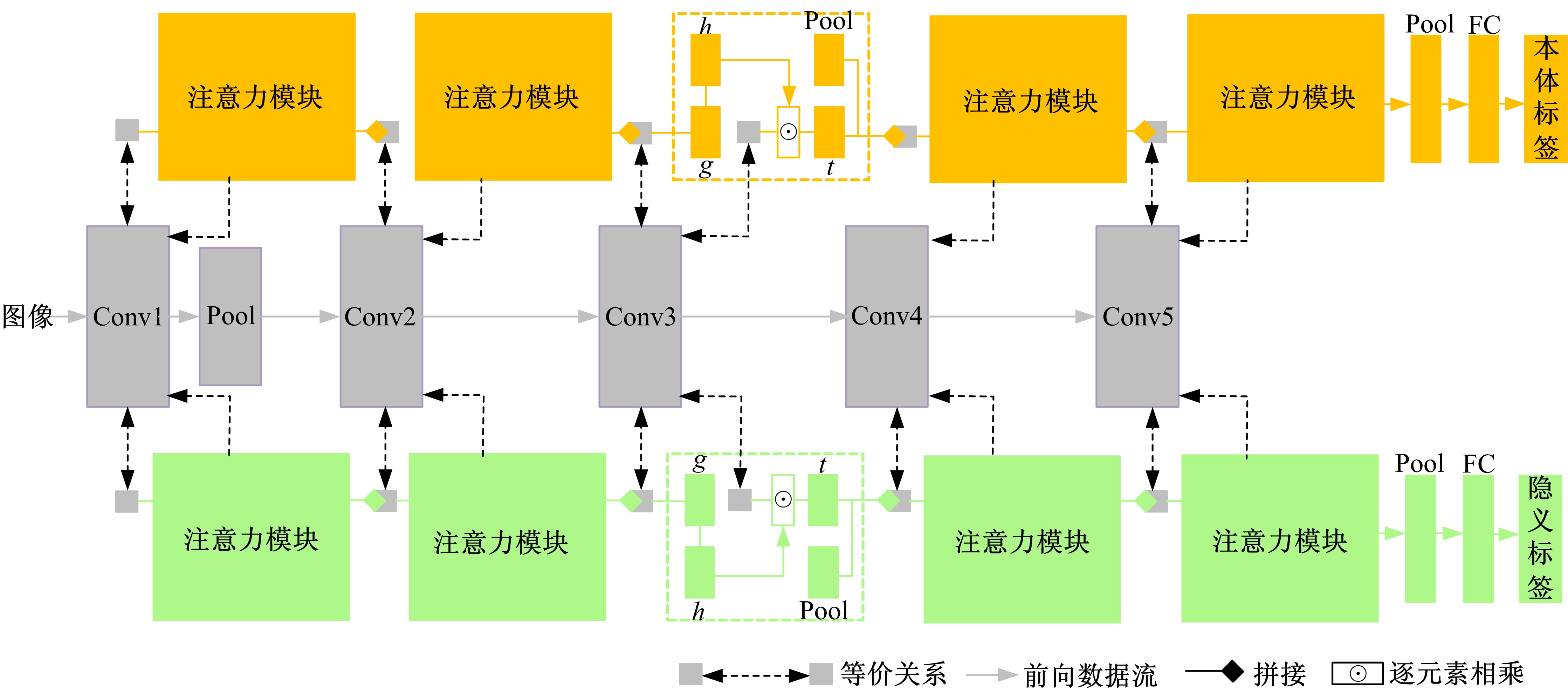
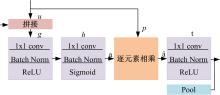
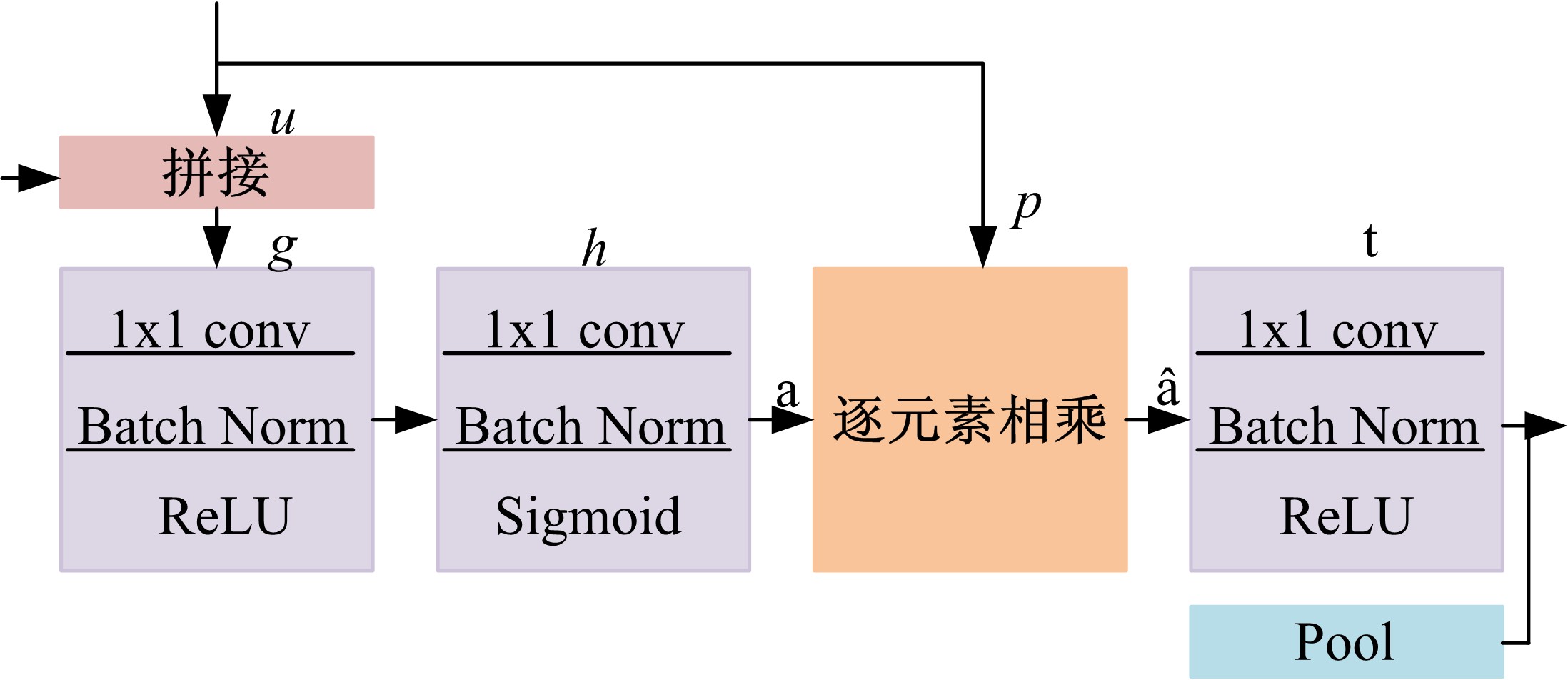
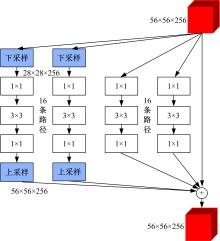
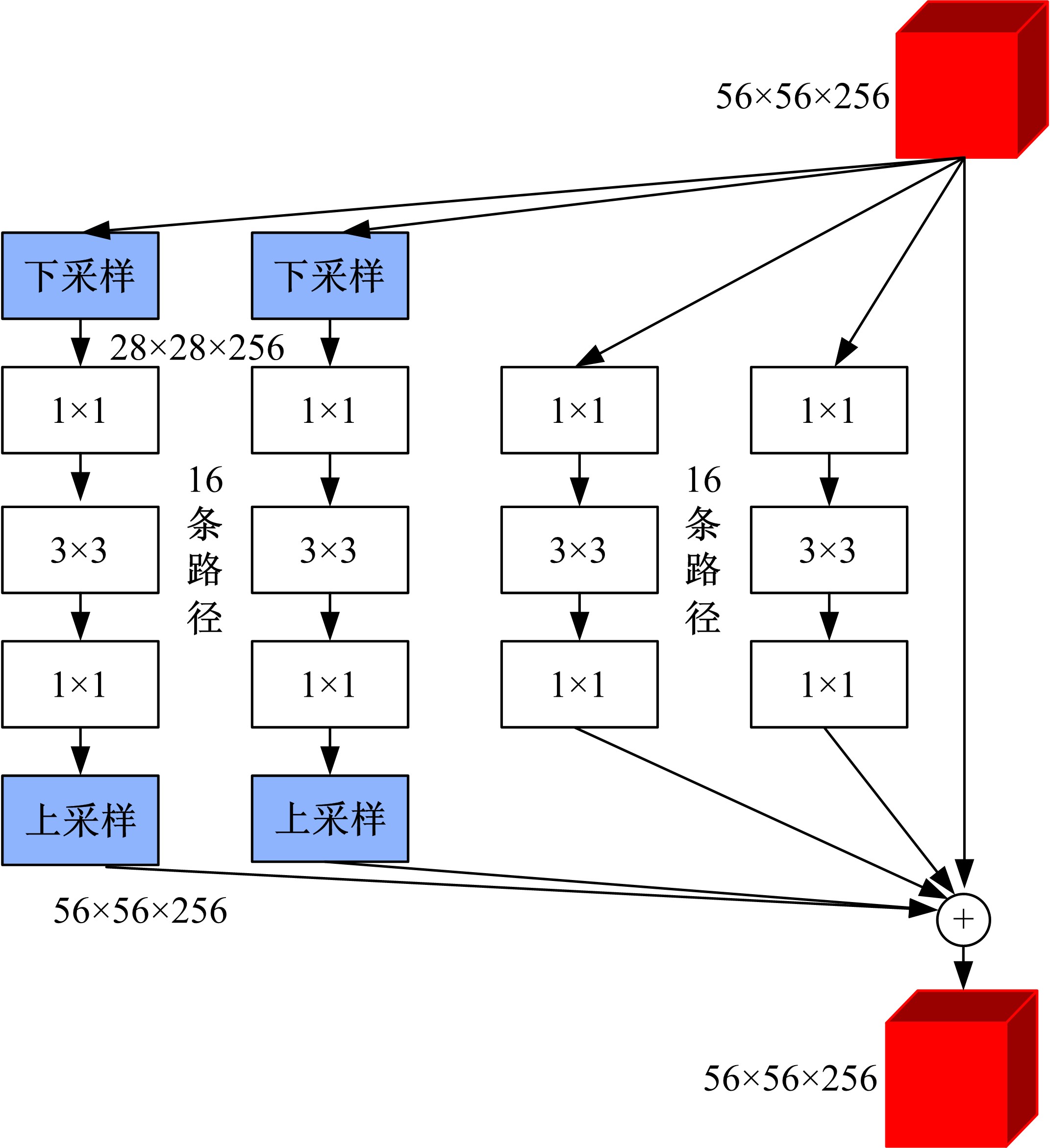
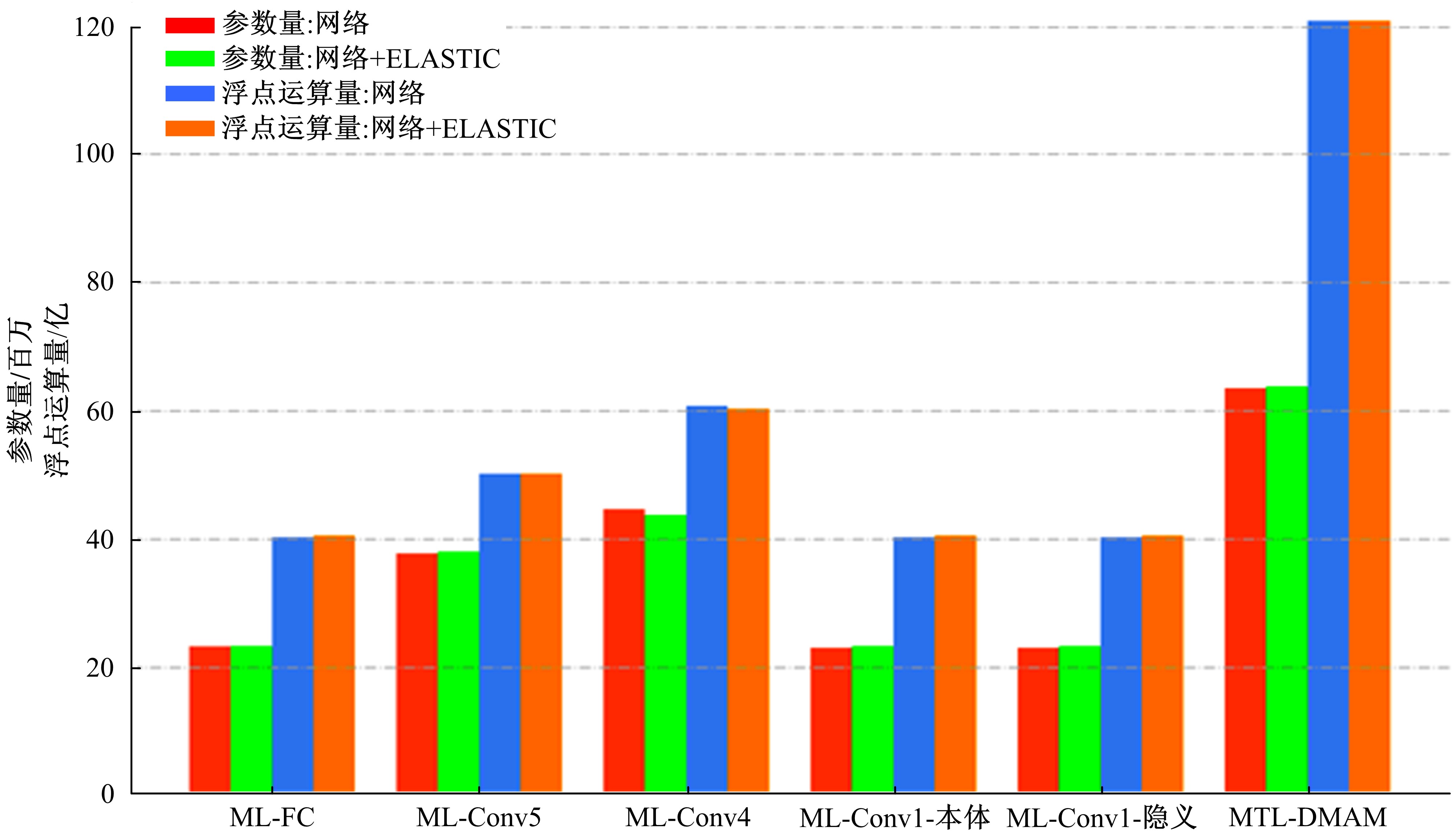
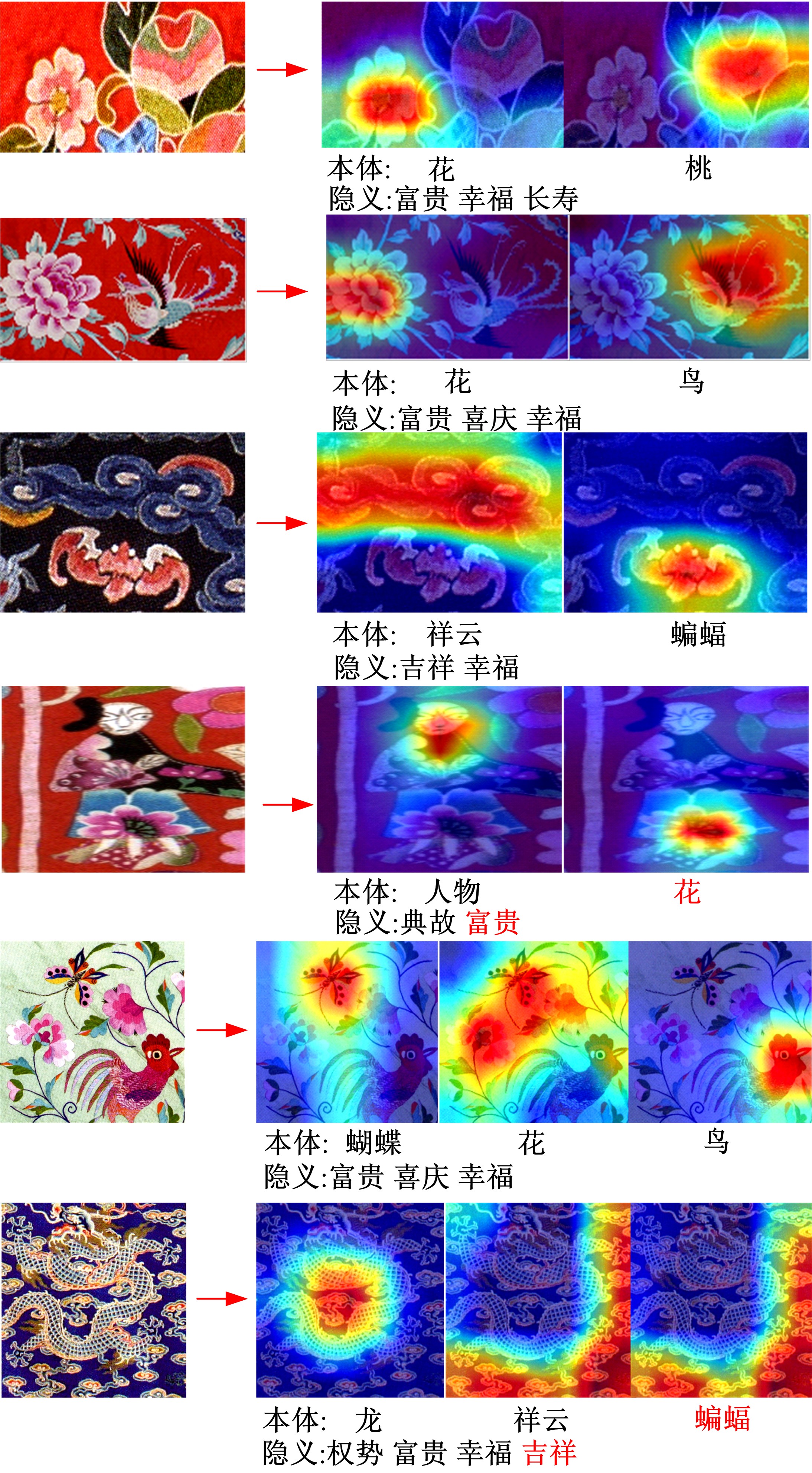
针对当前图像多标签标注方法只能标注图像内容信息(本体),而不能同时标注图像寓意信息(隐义)的问题,提出了一种基于多任务学习的双层多标签标注模型(MTL-DMAM)。首先将图像的本体标注和隐义标注视为两个关联任务,以ResNeXt-50作为共享特征的主干网络,然后利用注意力机制分别为每个任务构建一个分支结构,实现了图像双层标注,同时为消除图像内各物体大小差异对标注结果的影响,在模型中加入ELASTIC结构,进一步提高了模型性能。在对比实验中,本文模型在单任务MS-COCO数据集和多任务传统服饰数据集上优于其他同类模型。最后,利用Grad-cam方法可视化模型MTL-DMAM在标注时重点关注的图像区域,实验结果表明本文模型能有效学习标签对应的图像显著特征。
中图分类号:
- TP181
| 1 | 赵鑫全. 互联网时代文化消费如何升级[J]. 人民论坛, 2019(23): 132-133. |
| Zhao Xin-quan. How to upgrade cultural consumption in internet era[J]. People's Tribune, 2019(23): 132-133. | |
| 2 | 张会, 陈晨. "互联网+"背景下的汉语国际教育与文化传播[J]. 语言文字应用, 2019(2): 30-38. |
| Zhang Hui, Chen Chen. The international Chinese language education and cultural communication under "internet plus"[J]. Applied Linguistics, 2019(2): 30-38. | |
| 3 | Mehta S, Rastegari M, Shapiro L, et al. Espnetv2: a light-weight, power efficient, and general purpose convolutional neural network[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 9190-9200. |
| 4 | Wang H, Kembhavi A, Farhadi A, et al. ELASTIC: improving CNNs with dynamic scaling policies[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 2258-2267. |
| 5 | Mehta S, Hajishirzi H, Rastegari M. DiCENet: dimension-wise convolutions for efficient networks[J]. arXiv, 2019:1906.03516. |
| 6 | Zhang J, Ding S, Zhang N. An overview on probability undirected graphs and their applications in image processing[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 321: 156-168. |
| 7 | 陈绵书, 于录录, 苏越, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的多标签图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020,50(3):1077-1084. |
| Chen Mian-shu, Yu Lu-lu, Su Yue, et al. Multi-label images classification based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2020,50(3): 1077-1084. | |
| 8 | Ding S, Du P, Zhao X, et al. BEMD image fusion based on PCNN and compressed sensing[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(20): 10045-10054. |
| 9 | 王柯俨, 胡妍, 王怀, 等. 结合天空分割和超像素级暗通道的图像去雾算法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(4): 1377-1384. |
| Wang Ke-yan,Hu Yan,Wang Huai, et al. Image dehazing algorithm by sky segmentation and superpixel⁃level dark channel[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1377-1384. | |
| 10 | 谌华, 郭伟, 闫敬文, 等. 基于深度学习的SAR图像道路识别新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020,50(5):1778-1787. |
| Chen Hua,Guo Wei,Yan Jing-wen, et al. A new deep learning method for roads recognition from SAR images[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2020,50(5):1778-1787. | |
| 11 | Gong Y, Jia Y, Leung T, et al. Deep convolutional ranking for multilabel image annotation[J]. arXiv, 2013:1312.4894. |
| 12 | Wang J, Yang Y, Mao J, et al. CNN-RNN: a unified framework for multi-label image classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 2285-2294. |
| 13 | Li Y, Song Y, Luo J. Improving pairwise ranking for multi-label image classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 3617-3625. |
| 14 | Cevikalp H, Benligiray B, Gerek O N, et al. Semi-Supervised robust deep neural networks for multi-label classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 9-17. |
| 15 | Zhang J, Wu Q, Shen C, et al. Multilabel image classification with regional latent semantic dependencies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(10): 2801-2813. |
| 16 | Wang Z, Chen T, Li G, et al. Multi-label image recognition by recurrently discovering attentional regions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 464-472. |
| 17 | Zhu F, Li H, Ouyang W, et al. Learning spatial regularization with image-level supervisions for multi-label image classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 5513-5522. |
| 18 | Luo Y, Jiang M, Zhao Q. Visual attention in multi-label image classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 1-8. |
| 19 | Guo H, Zheng K, Fan X, et al. Visual attention consistency under image transforms for multi-label image classification[C]∥ IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 729-739. |
| 20 | 张钰, 刘建伟, 左信. 多任务学习[J]. 计算机学报, 2020,43(7):1340-1378. |
| Zhang Yu, Liu Jian-wei, Zuo Xin. Survey of multi-task learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020,43(7):1340-1378. | |
| 21 | Kao Y, He R, Huang K. Deep aesthetic quality assessment with semantic information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(3): 1482-1495. |
| 22 | Misra I, Shrivastava A, Gupta A, et al. Cross-stitch networks for multi-task learning[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 3994-4003. |
| 23 | Vandenhende S, de Brabandere B, van Gool L. Branched multi-task networks: deciding what layers to share[J]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: arXiv: 1904.02920. |
| 24 | Liu S, Johns E, Davison A J. End-to-end multi-task learning with attention[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA,2019: 1871-1880. |
| 25 | 王松, 党建武, 王阳萍, 等. 基于3D运动历史图像和多任务学习的动作识别[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020,50(4):1495-1502. |
| Wang Song,Dang Jian-wu,Wang Yang-ping,et al. Action recognition based on 3D motion history image and multi-task learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020,50(4): 1495-1502. | |
| 26 | 赵海英, 陈洪, 贾耕云, 等. 基于字典学习的民族文化图案语义标注[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2019, 49(2): 172-187. |
| Zhao Hai-ying, Chen Hong, Jia Geng-yun, et al. Semantic annotation of national cultural patterns based on dictionary learning[J]. Science in China (Information Sciences), 2019, 49(2): 172-187. | |
| 27 | Xie S, Girshick R, Dollár P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 1492-1500. |
| 28 | Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. Computer Science, 2014: 1-14. |
| 29 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 30 | Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]∥Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 2818-2826. |
| 31 | Wu X Z, Zhou Z H. A unified view of multi-label performance measures[C]∥Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 3780-3788. |
| 32 | Selvaraju R R, Cogswell M, Das A, et al. Grad-cam: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 618-626. |
| [1] | 赵宏伟,刘晓涵,张媛,范丽丽,龙曼丽,臧雪柏. 基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. |
| [2] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| [3] | 欧阳丹彤,马骢,雷景佩,冯莎莎. 知识图谱嵌入中的自适应筛选[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 685-691. |
| [4] | 李贻斌,郭佳旻,张勤. 人体步态识别方法与技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 1-18. |
| [5] | 徐谦,李颖,王刚. 基于深度学习的行人和车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1661-1667. |
| [6] | 高万夫,张平,胡亮. 基于已选特征动态变化的非线性特征选择方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1293-1300. |
| [7] | 欧阳丹彤,肖君,叶育鑫. 基于实体对弱约束的远监督关系抽取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 912-919. |
| [8] | 顾海军, 田雅倩, 崔莹. 基于行为语言的智能交互代理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1578-1585. |
| [9] | 董飒, 刘大有, 欧阳若川, 朱允刚, 李丽娜. 引入二阶马尔可夫假设的逻辑回归异质性网络分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1571-1577. |
| [10] | 王旭, 欧阳继红, 陈桂芬. 基于垂直维序列动态时间规整方法的图相似度度量[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1199-1205. |
| [11] | 张浩, 占萌苹, 郭刘香, 李誌, 刘元宁, 张春鹤, 常浩武, 王志强. 基于高通量数据的人体外源性植物miRNA跨界调控建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1206-1213. |
| [12] | 李雄飞, 冯婷婷, 骆实, 张小利. 基于递归神经网络的自动作曲算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 866-873. |
| [13] | 刘杰, 张平, 高万夫. 基于条件相关的特征选择方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 874-881. |
| [14] | 黄岚, 纪林影, 姚刚, 翟睿峰, 白天. 面向误诊提示的疾病-症状语义网构建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 859-865. |
| [15] | 王旭, 欧阳继红, 陈桂芬. 基于多重序列所有公共子序列的启发式算法度量多图的相似度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 526-532. |
|
||