吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1420-1426.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200515
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于深度强化学习的随机局部搜索启发式方法
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 软件学院,长春 130012
Stochastic local search heuristic method based on deep reinforcement learning
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.College of Software,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
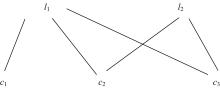
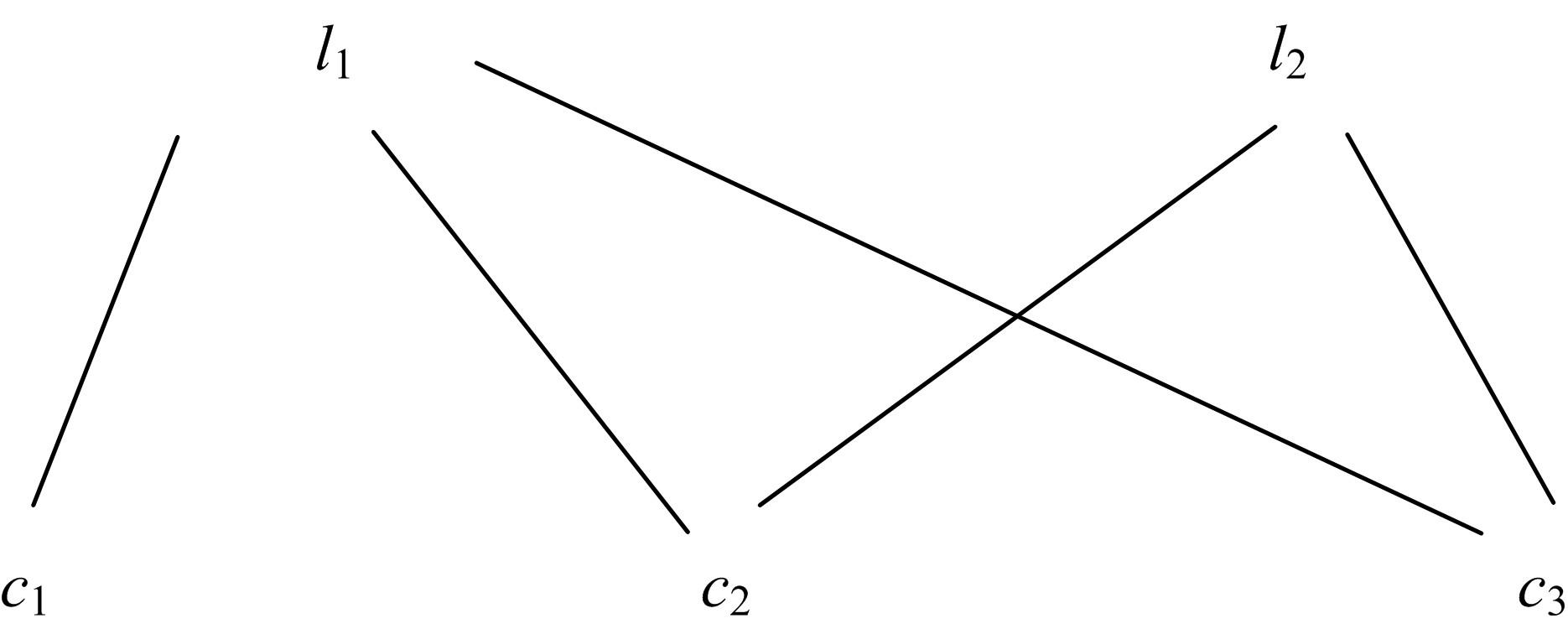
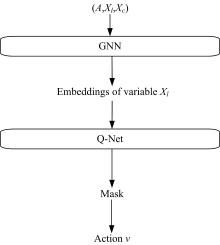
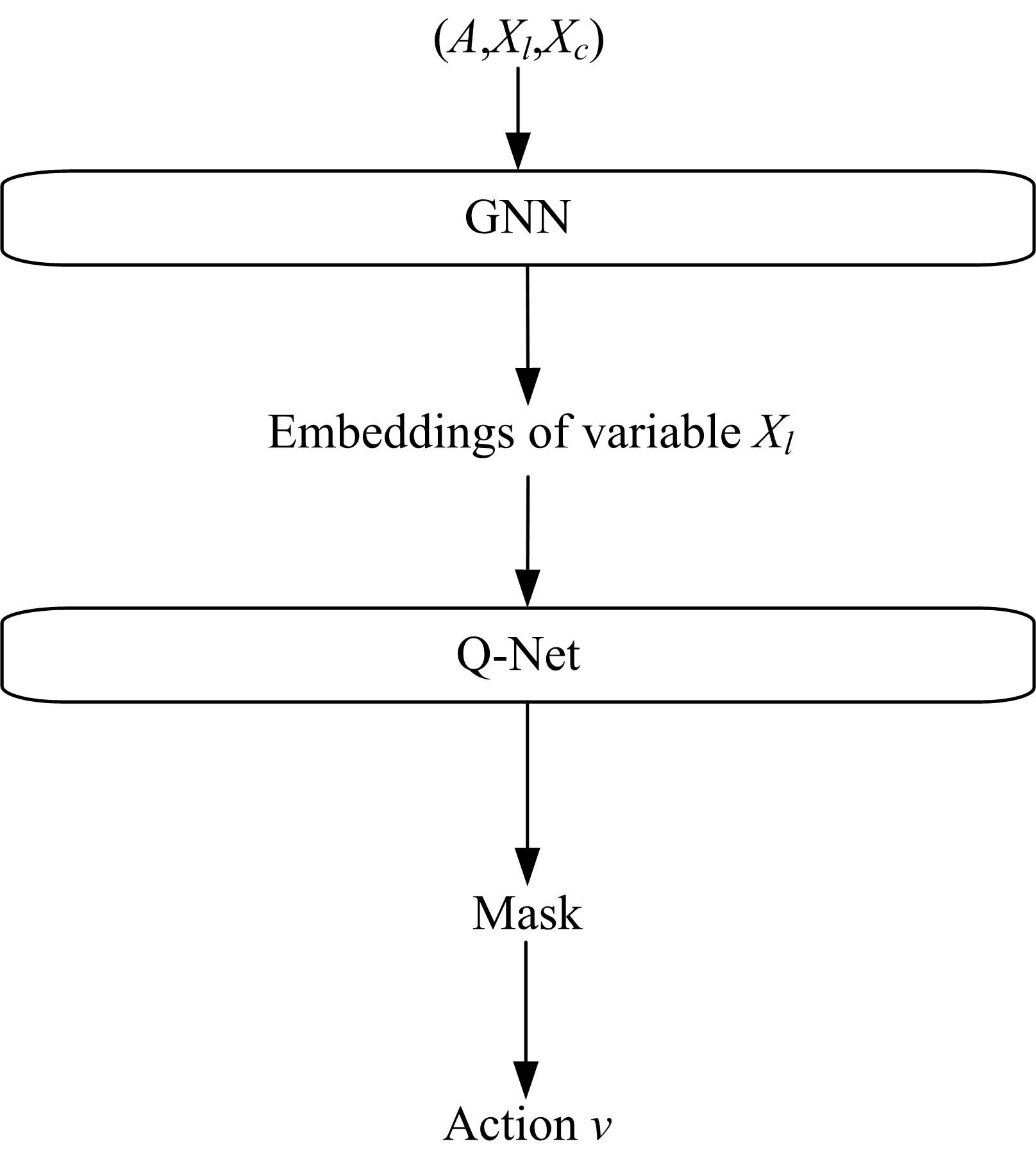
为了更充分地利用可满足问题(SAT)的数据分布中的信息,从而提升算法性能,提出了一种基于深度强化学习的随机局部搜索启发式方法。把随机局部搜索算法中变量的选择看作强化学习任务,训练强化学习Agent学习策略作为随机局部搜索算法选择翻转变量的启发式,以期望通过端到端的方式获得效率更好的翻转变量的选择方法。实验结果表明,本文方法是有效的,并且与经典随机局部搜索算法ProbSAT相比,本文方法在性能上也有一定的优势,可以在更少的决策步骤内求出问题的解。
中图分类号:
- TP181
| 1 | Cook S A. The complexity of theorem-proving procedures[C]∥Proceedings of the 3rd Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, New Orleans, USA, 1971: 151-158. |
| 2 | Audemard G, Simon L. Predicting learnt clauses quality in modern SAT solvers[C]∥International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hainan Island, China, 2009: 399-404. |
| 3 | Moskewicz M W, Madigan C F, Zhao Y, et al. Chaff: Engineering an efficient SAT solver [C]∥Proceedings of the 38th Annual Design Automation Conference, Las Vegas, USA, 2001: 530-535. |
| 4 | Eén N, Sörensson N. An extensible SAT-solver[C]∥International Conference on Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing, Santa Margherita Ligure, Italy,2003: 502-518. |
| 5 | Cai S, Su K. Local search for Boolean Satisfiability with configuration checking and subscore[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2013, 204: 75-98. |
| 6 | Shang Y, Wah B W. A discrete Lagrangian-based global-search method for solving satisfiability problems[J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 1998, 12(1): 61-99. |
| 7 | Balint A, Schöning U. Choosing probability distributions for stochastic local search and the role of make versus break[C]∥International Conference on Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing, Trento, Italy, 2012: 16-29. |
| 8 | Wang F, Jiang M, Qian C, et al. Residual attention network for image classification[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA,2017: 3156-3164. |
| 9 | Chiu C C, Sainath T N, Wu Y, et al. State-of-the-art speech recognition with sequence-to-sequence models[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, Alberta, Canada, 2018: 4774-4778. |
| 10 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Los Angeles,USA, 2017: 5998-6008. |
| 11 | Xu L, Hutter F, Hoos H H, et al. SATzilla: portfolio-based algorithm selection for SAT[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2008, 32: 565-606. |
| 12 | Liang J H, Ganesh V, Poupart P, et al. Learning rate based branching heuristic for SAT solvers [C]∥International Conference on Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing, Bordeaux, France, 2016: 123-140. |
| 13 | Liang J H, VK H G, Poupart P, et al. An empirical study of branching heuristics through the lens of global learning rate[C]∥International Conference on Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing, Melbourne, Australia,2017: 119-135. |
| 14 | Selsam D, Lamm M, Bünz B, et al. Learning a SAT solver from single-bit supervision[C]∥The 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2019. |
| 15 | Sutton R S, Barto A G. Reinforcement Learning: an Introduction[M]. Boston:MIT Press, 2018: 68-69. |
| 16 | Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529-533. |
| 17 | Mezard M, Zecchina R. Random k-satisifability problem: from an analytic solution to an efficient algorithm[J]. Physical Review E, 2002, 66 (5) :056126. |
| [1] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [2] | 魏晓辉,孙冰怡,崔佳旭. 基于图神经网络的兴趣活动推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 278-284. |
| [3] | 袁满,胡超,仇婷婷. 基于Linked data的数据完整性评估新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1826-1831. |
| [4] | 刘磊,瓮杰,郭德贵. 面向编译器测试的部分求值静态输入确定方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 262-267. |
| [5] | 杨顺,蒋渊德,吴坚,刘海贞. 基于多类型传感数据的自动驾驶深度强化学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1026-1033. |
| [6] | 马健, 樊建平, 刘峰, 李红辉. 面向对象软件系统演化模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 545-550. |
| [7] | 罗养霞, 郭晔. 基于数据依赖特征的软件识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1894-1902. |
| [8] | 应欢, 王东辉, 武成岗, 王喆, 唐博文, 李建军. 适用于商用系统环境的低开销确定性重放技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 208-217. |
| [9] | 李勇, 黄志球, 王勇, 房丙午. 基于多源数据的跨项目软件缺陷预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 2034-2041. |
| [10] | 王念滨, 祝官文, 周连科, 王红卫. 支持高效路径查询的数据空间索引方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 911-916. |
| [11] | 陈鹏飞, 田地, 杨光. 基于MVC架构的LIBS软件设计与实现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 242-245. |
| [12] | 康辉, 王家琦, 梅芳. 基于Pi演算的并行编程语言[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 235-241. |
| [13] | 特日跟, 江晟, 李雄飞, 李军. 基于整数数据的文档压缩编码方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 228-234. |
| [14] | 冯晓宁, 王卓, 张旭. 基于L-π演算的WSN路由协议形式化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1565-1571. |
| [15] | 刘磊, 王燕燕, 申春, 李玉祥, 刘雷. Bellman-Ford算法性能可移植的GPU并行优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1559-1564. |
|
||