吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 136-143.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200785
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
具有随机充电需求的混合动态网络平衡模型
- 1.华东交通大学 机电与车辆工程学院,南昌 330013
2.华东交通大学 交通运输与物流学院,南昌 330013
Mixed network equilibrium model with stochastic charging demand
Yun-juan YAN1( ),Wei-xiong ZHA2(
),Wei-xiong ZHA2( ),Jun-gang SHI2,Jian LI2
),Jun-gang SHI2,Jian LI2
- 1.College of Mechatronics & Vehicle Engineering,East China Jiaotong University,Nanchang 330013,China
2.Institute of Transportation and Economics,East China Jiaotong University,Nanchang 330013,China
摘要:
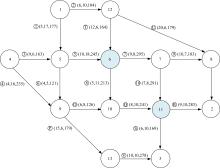
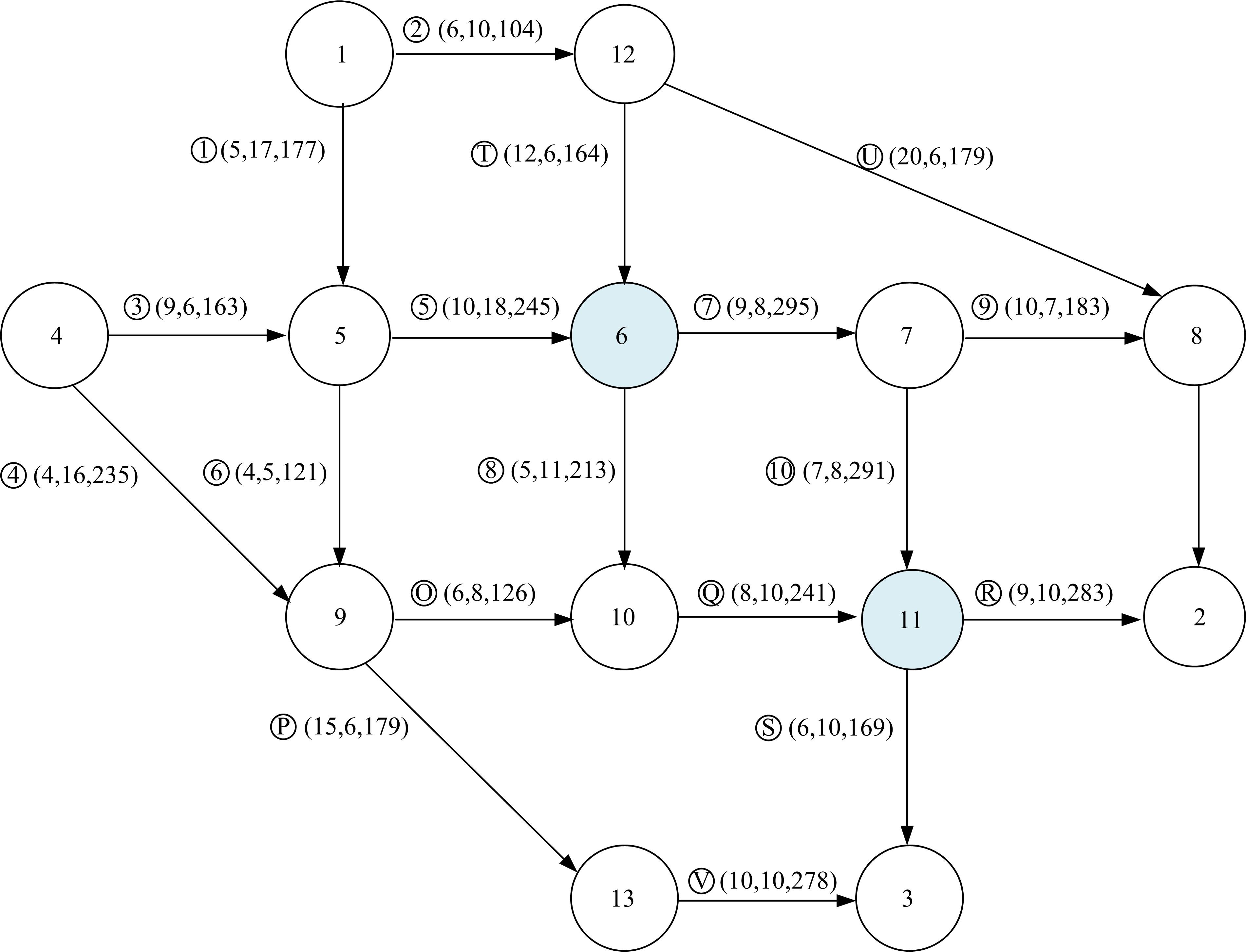
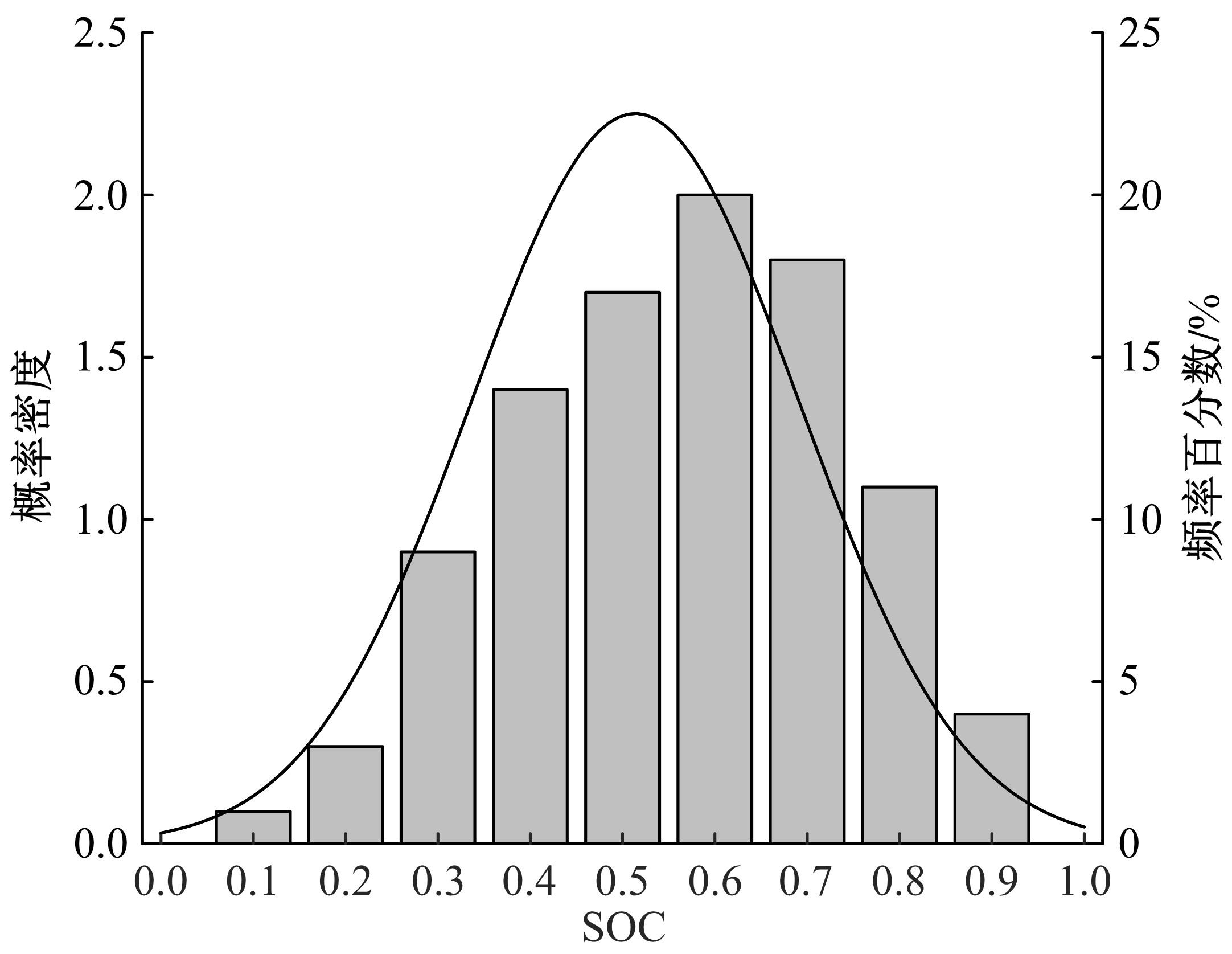
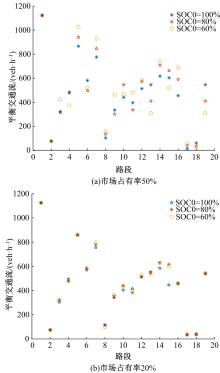
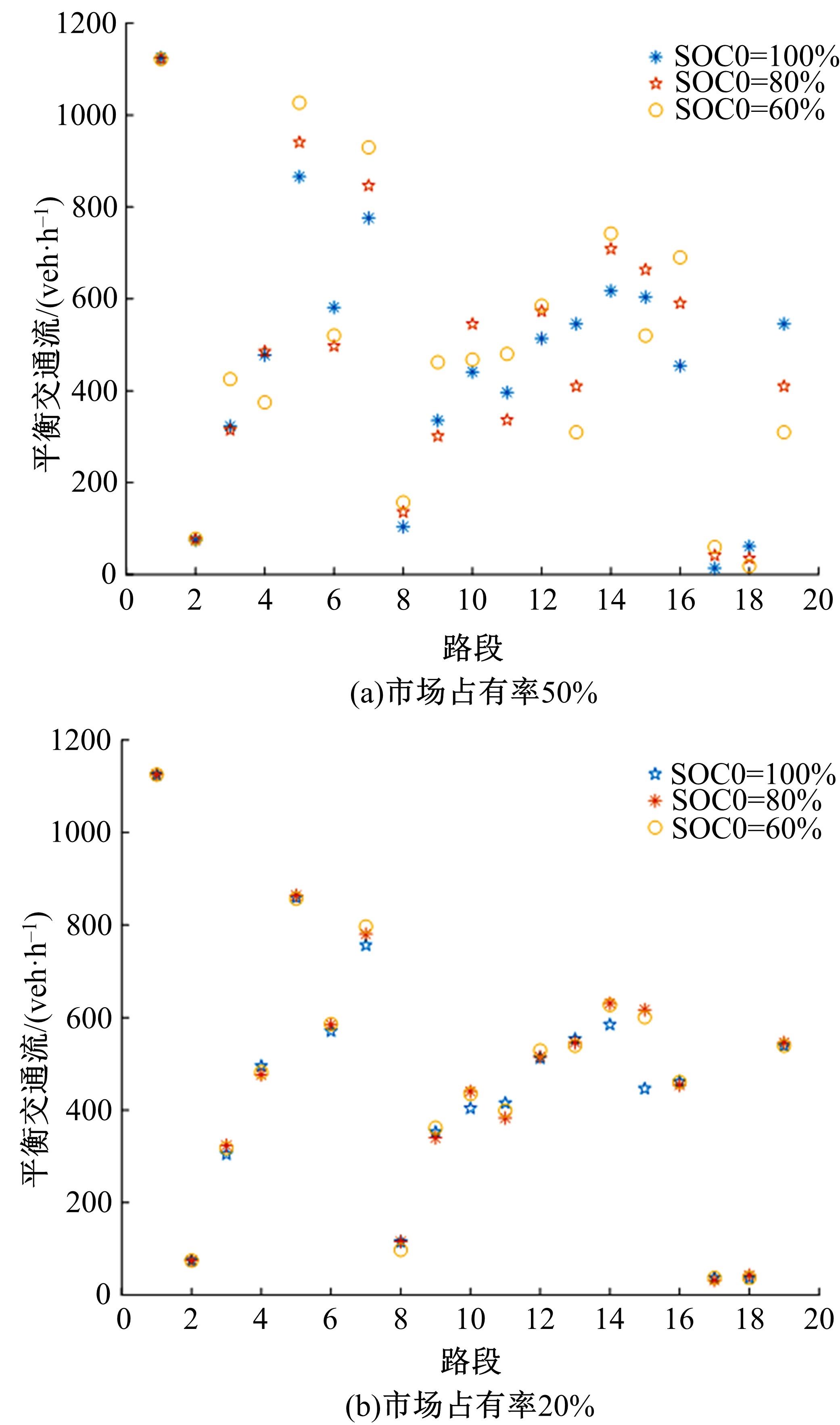
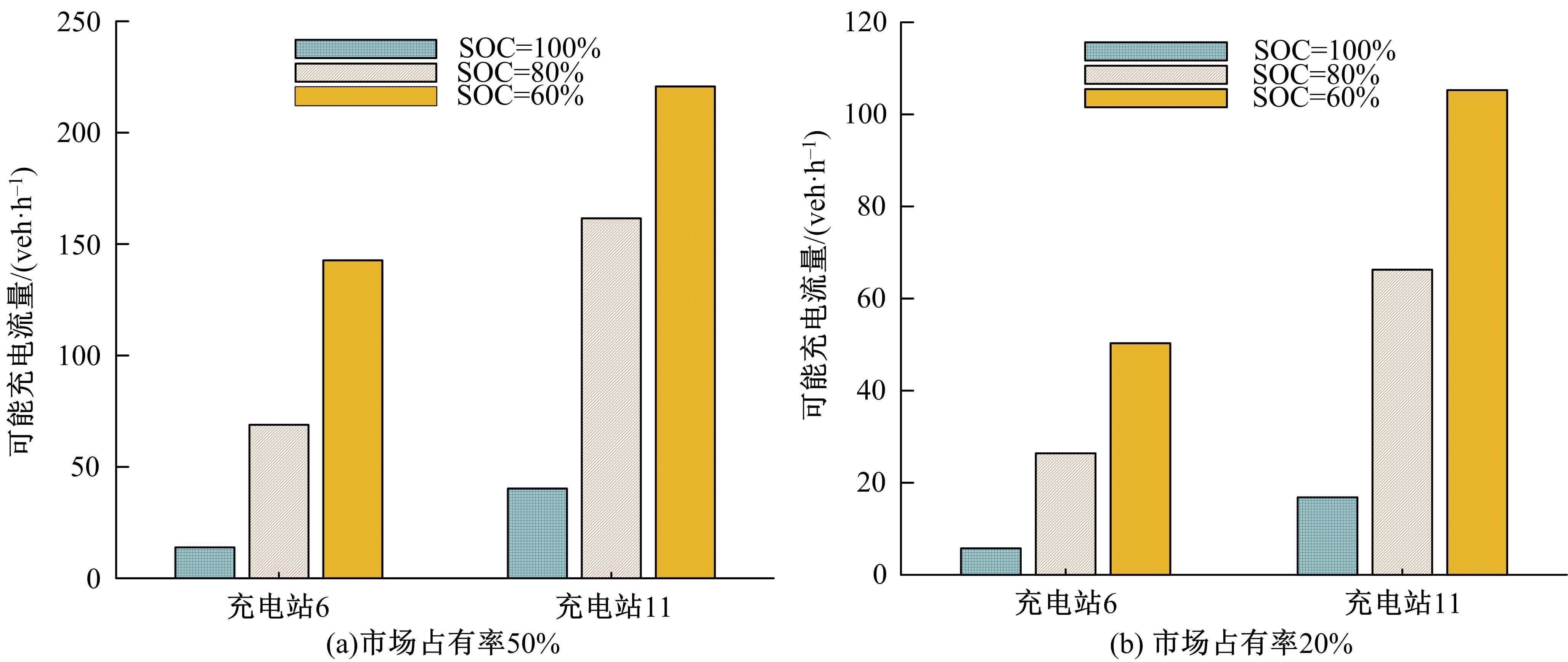
考虑电动汽车用户在途随机充电需求,基于随机充电行为及充电排队仿真构建了混合用户平衡模型。在电动汽车不同初始电量状态及市场占有率下,预测了网络平衡交通流和可能充电需求流的变化趋势。利用Frank-Wolfe算法和多标号算法,以Nguyen-Dupius网络为例,设计了电动汽车充电排队仿真的平衡交通流预测模型,本文研究结果可为交通管理者提供科学参考。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Windecker A, Ruder A. Fuel economy, cost, and greenhouse gas results for alternative fuel vehicles in 2011[J]. Transport Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2013, 23: 34⁃40. |
| 2 | Beckmann M J, Mcguire C B, Winston C B. Studies in economics of transportation[J]. Operational Research Society, 1956, 7(4):146-147. |
| 3 | Wardrop J G. Some theoretical aspects of road traffic research[J]. OR, 1953, 4(4):72⁃73. |
| 4 | Jonathan D, Pitu A B, Mirchandani H. The electric vehicle shortest-walk Problem with battery exchanges[J]. Networks and Spatial Economics March, 2016, 16(1):155⁃173. |
| 5 | Schneider M, Stenger A, Goeke D. The electric vehicle-routing problem with time windows and recharging stations[J]. Transportation Science, 2014,48(4):500⁃520. |
| 6 | Jiang N, Xie C. Computing and analyzing mixed equilibrium network flows with gasoline and electric vehicles[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2014, 29(8): 626-646. |
| 7 | Xie C, Jiang N. Relay requirement and traffic assignment of electric vehicles[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2016, 31(8): 580-598. |
| 8 | He F, Wu D, Yin Y F, et al. Optimal deployment of public charging stations for plug-inhybrid electric vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2013, 47(C):87-101. |
| 9 | Cen X K, Hong K L, Li L, et al. Modeling electric vehicles adoption for urban commute trips[J]. Transportation Research Part B,2018,117(A): 431⁃454. |
| 10 | Mock P, Schmid S A, Friedruch H E. Chapter twenty one: market prospects of electric passenger vehicles[M]//Electric & Hybrid Vehicles, Berlin: Elsevier,2010:545-577. |
| 11 | Smart J, Stephen S. Battery electric vehicle driving and charging behavior observed early in the EV project [J]. SAE International Journal of Alternative Powertrains, 2012, 1(1): 27-33. |
| 12 | Nguyens Dupuis C. An efficient method for computing traffic equilibria in networks with asymmetric transportation costs[J]. Transportation Science, 1984, 18(2):185⁃202. |
| 13 | 陶顺, 肖湘宁, 温剑锋.电动汽车分散充电设施配比度分析与计算方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2014, 29(8):11-19. |
| Tao Shun, Xiao Xiang-ning, Wen Jian-feng. Analysis and calculation method of matching ratio of electric vehicle decentralized charging facilities [J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2014, 29(8): 11-19. |
| [1] | 李浩,陈浩. 考虑充电排队时间的电动汽车混合交通路网均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1684-1691. |
| [2] | 户佐安,夏一鸣,蔡佳,薛锋. 延误条件下综合多种策略的城轨列车运行调整优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1664-1672. |
| [3] | 朱才华,孙晓黎,李岩. 站点分类下的城市公共自行车交通需求预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 531-540. |
| [4] | 罗清玉,田万利,贾洪飞. 考虑通勤需求的电动汽车充电站选址与定容模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1471-1477. |
| [5] | 曹骞, 李君, 刘宇, 曲大为. 基于马尔科夫链的长春市乘用车行驶工况构建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1366-1373. |
| [6] | 孙宝凤, 高坤, 申琇秀, 梁婷. 基于能力平衡和变覆盖半径的加油站网络扩充选址模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 704-711. |
| [7] | 徐亮,程国柱. 基于车速离散度和经济车速的高速公路最低车速限制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 661-0665. |
|
||