吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 338-344.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211147
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于多属性群决策的加工中心故障模式风险分析
申桂香1,2( ),郑君1,2,张英芝1,2(
),郑君1,2,张英芝1,2( ),宋杰1,2,李哲文1,2
),宋杰1,2,李哲文1,2
- 1.吉林大学 数控装备可靠性教育部重点实验室,长春 130022
2.吉林大学 机械与航空航天工程学院,长春 130022
Risk analysis of machining center failure mode based on multi⁃attribute group decision making
Gui-xiang SHEN1,2( ),Jun ZHENG1,2,Ying-zhi ZHANG1,2(
),Jun ZHENG1,2,Ying-zhi ZHANG1,2( ),Jie SONG1,2,Zhe-wen LI1,2
),Jie SONG1,2,Zhe-wen LI1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of CNC Equipment Reliability,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
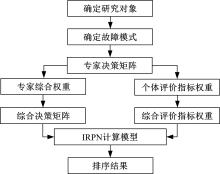
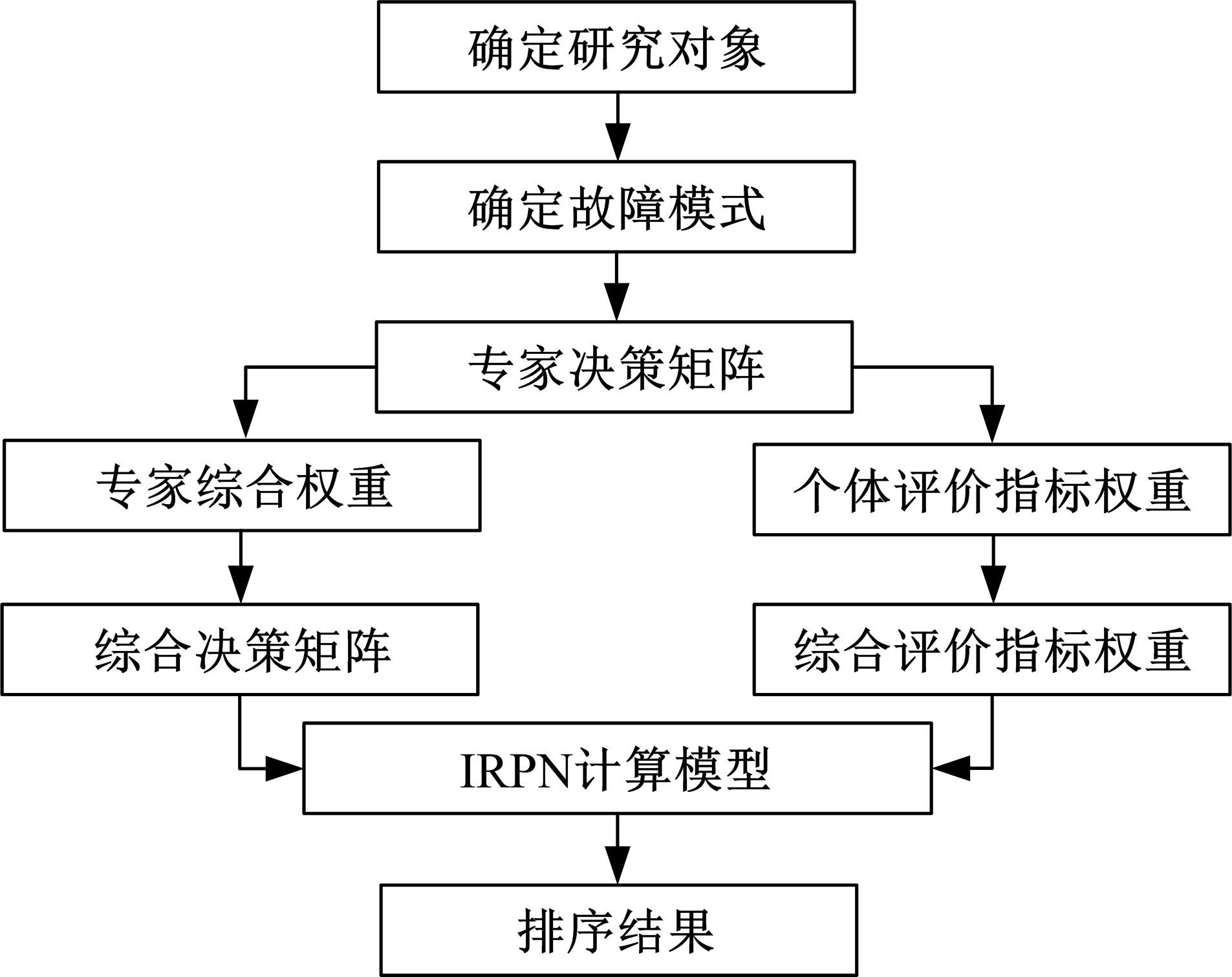
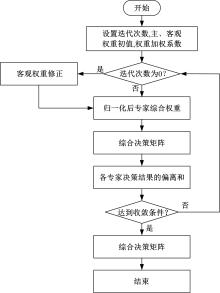
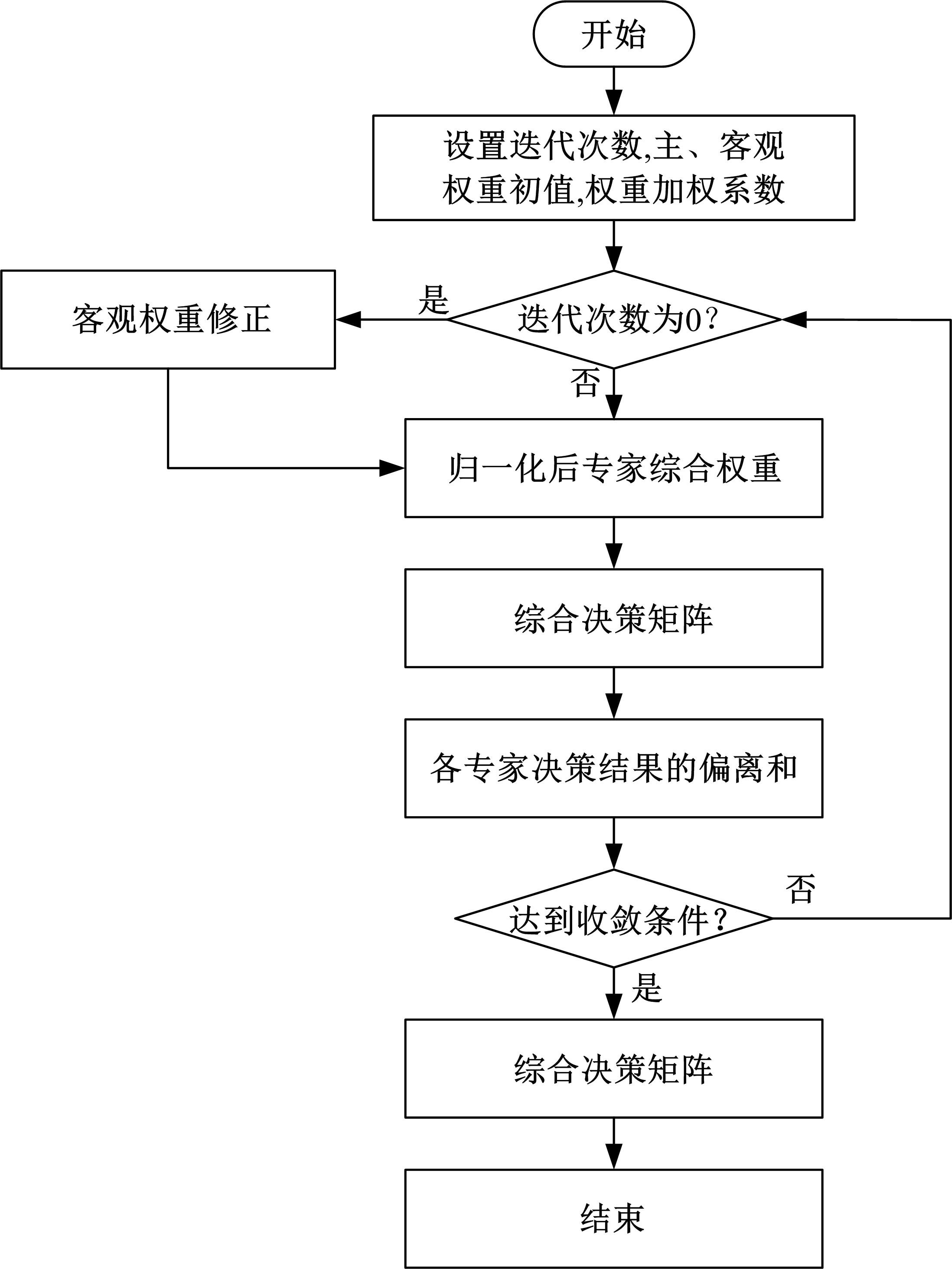
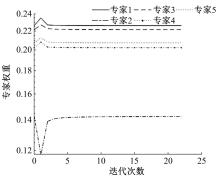
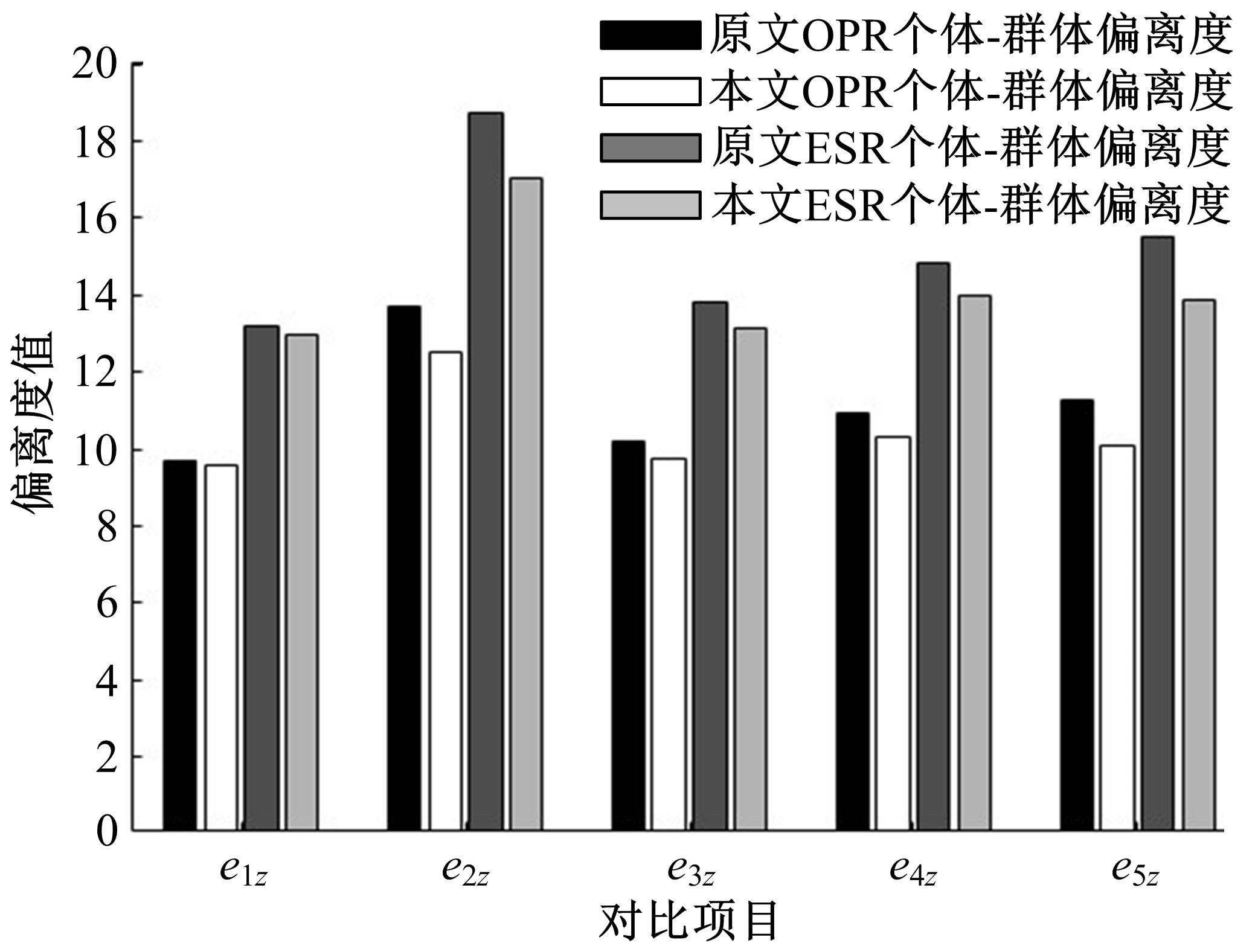
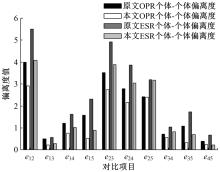
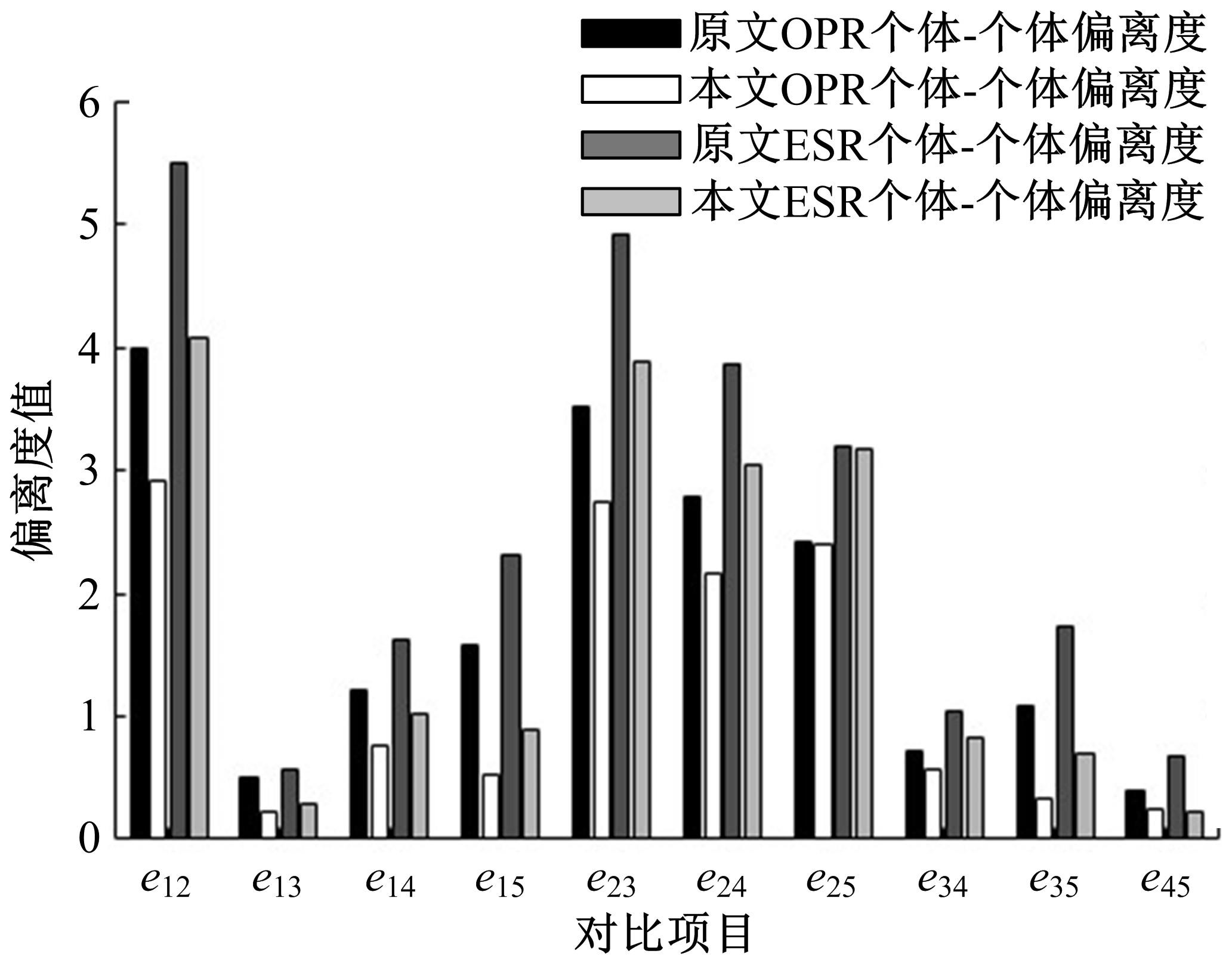
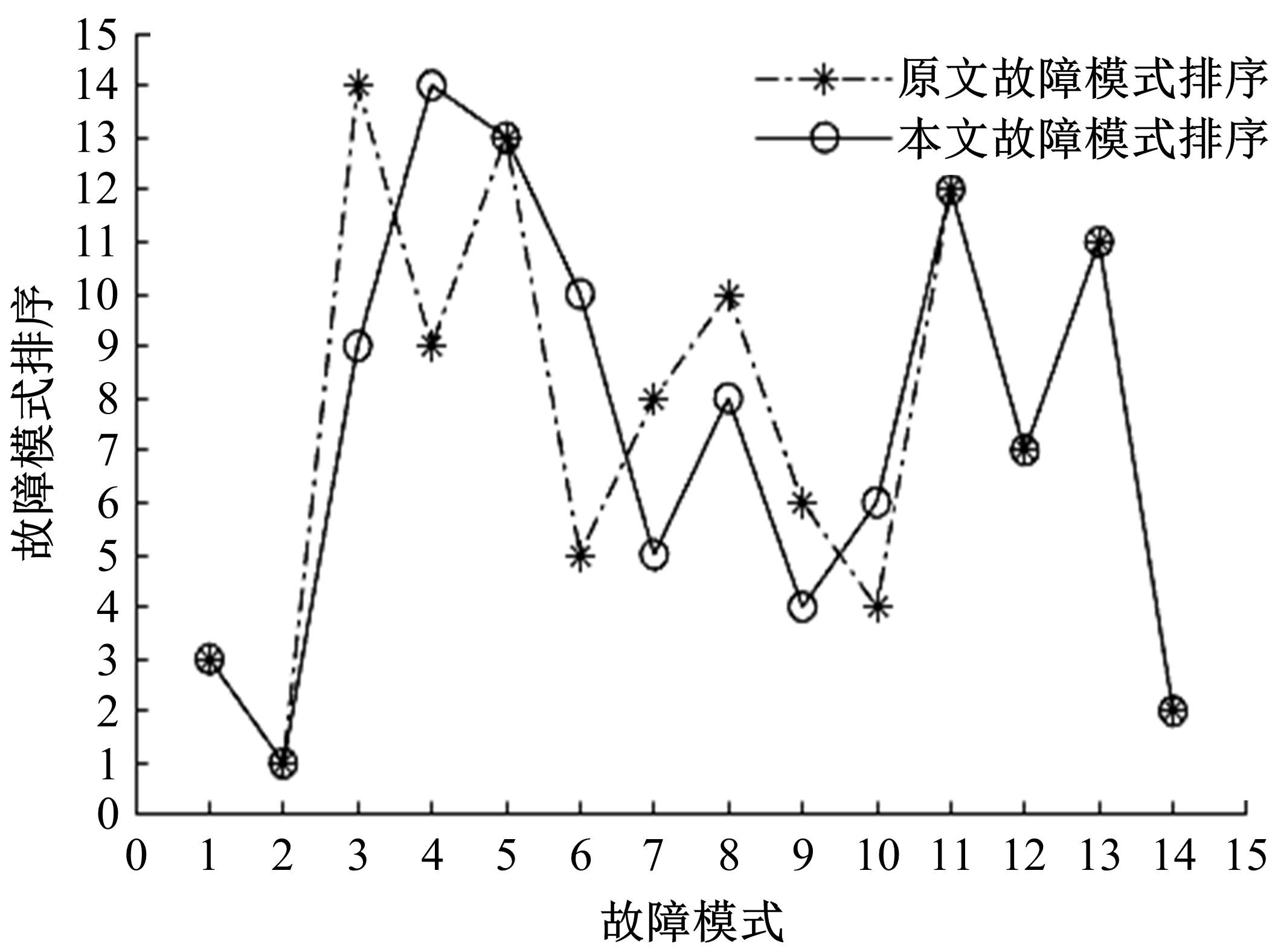
针对传统数控机床故障模式及影响分析(FMEA)中存在专家权重与风险因子权重分配不合理以及风险系数(RPN)计算模型不够稳健的问题,提出一种基于多属性群决策的改进FMEA方法。首先,引入区间数表征机床故障模式风险因子;其次,考虑专家的主、客观权重,根据一致性原则,计算专家综合权重,并利用加权平均算子(WAA)确定故障模式综合评价矩阵;再次,采用区间数熵值法确定风险因子权重,利用改进风险优先数(IRPN)计算模型得到故障模式风险值;最后,结合区间数距离测度,采用最优最劣区间数改进的逼近理想解排序方法(TOPSIS)对故障模式进行风险排序。以某型加工中心为例进行方法应用,验证了方法的合理性和有效性。
中图分类号:
- TG659
| 1 | Peeters J F W, Basten R J I, Tinga T. Improving failure analysis efficiency by combining FTA and FMEA in a recursive manners[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2018, 172(4): 36-44. |
| 2 | Wang Wei-zhong, Liu Xin-wang, Qin Yong, et al. A risk evaluation and prioritization for FMEA with prospect theory and choquet integral[J]. Safety Science, 2018, 110: 152-163. |
| 3 | 韦可佳, 耿俊豹, 徐孙庆. 基于模糊理论与D-S证据理论的FMEA方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(11): 2662-2668. |
| Wei Ke-jia, Geng Jun-bao, Xu Sun-qing. FMEA method based on fuzzy theory and D-S evidence theory[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(11): 2662-2668. | |
| 4 | 王晓峰, 申桂香, 张英芝, 等. 基于改进危害度和DEMATEL方法的abc轴进给系统的故障排序[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2012, 42(1): 122-127. |
| Wang Xiao-feng, Shen Gui-xiang,Zhang Ying-zhi,et al. Prioritizing failures of abc-axis feeding systems based on improved criticality and DEMALTEL method[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2012, 42(1): 122-127. | |
| 5 | Liu Hu-chen, Li Zhao-jun, Song Wen-yan, et al. Failure mode and effect analysis using cloud model theory and PROMETHEE method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2017, 66(4): 1058-1072. |
| 6 | Lo H W, Liou J J H, Chuang Y C, et al. A novel failure mode and effect analysis model for machine tool risk analysis[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2019, 183: 173-183. |
| 7 | 郑玉彬, 申桂香, 张英芝, 等. 基于贝叶斯网络的链式刀库系统重要度分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(2): 466-471. |
| Zheng Yu-bin, Shen Gui-xiang, Zhang Ying-zhi,et al. Importance analysis of chain-type tool magazine system based on Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(2): 466-471. | |
| 8 | 王晓燕, 申桂香, 张英芝, 等. 基于DEMATEL方法的数控装备故障相关性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2012, 42(): 100-103. |
| Wang Xiao-yan, Shen Gui-xiang, Zhang Ying-zhi, et al. Analysis about failure correlation of CNC equipment base on DEMATEL[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2012, 42(Sup.1): 100-103. | |
| 9 | Jiang Guang-jun, Cai Shuang, Zhang Nan, et al. Reliability analysis of the starting and landing system of UAV by FMECA and FTA[J]. Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering, 2019, 36(8): 503-511. |
| 10 | Zhao Xiao-song, Chen Te-hung, Kun Zhang, et al. Applying an improved failure mode effect analysis method to evaluate the safety of a three-in-one machine tool[J]. Human Factors and Ergonomics in Manufacturing & Service Industries, 2020, 30(1): 71-82. |
| 11 | Liu Hu-chen, You Jian-xin, You Xiao-yue, et al. Evaluating the risk of healthcare failure modes using interval 2-tuple hybrid weighted distance measure[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2014, 78(12): 249-258. |
| 12 | 王睿, 李延来, 朱江洪, 等. 考虑专家共识的改进FMEA风险评估方法[J]. 浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 52(6): 1058-1067. |
| Wang Rui, Li Yan-lai, Zhu Jiang-hong, et al. Improved FMEA method for risk evaluation considering expert consensus[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science), 2018, 52(6): 1058-1067. | |
| 13 | 聂文滨, 刘卫东, 汪建东, 等. 基于证据理论和矩阵相似度的工艺失效风险评估[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2016, 22(11): 2602-2612. |
| Nie Wen-bin, Liu Wei-dong, Wang Jian-dong, et al. Evaluation approach in process failure risk based on matrix similarity and evidence theory[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2016, 22(11): 2602-2612. | |
| 14 | 安相华, 蔡卫国, 宋晓杰. 基于云模型与协同决策的FMEA耦合评估方法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2018, 24(5): 1179-1190. |
| An Xiang-hua, Cai Wei-guo, Song Xiao-jie. FMEA coupling evaluation method based on cloud model and collaborative decision[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2018, 24(5): 1179-1190. | |
| 15 | 王晓峰, 申桂香, 张英芝, 等. 基于群体决策和多种赋值方式的加工中心关键部件RPN分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(6): 630-635. |
| Wang Xiao-feng, Shen Gui-xiang, Zhang Ying-zhi, et al. Analysis on risk priority number of critical component of machining center based on group decision-making and various assignment ways[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(6): 630-635. | |
| 16 | 陈晓红, 刘益凡. 基于区间数群决策矩阵的专家权重确定方法及其算法实现[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2010, 32(10): 2128-2131. |
| Chen Xiao-hong, Liu Yi-fan. Expert weights determination method and realization algorithm based on interval numbers group decision matrices[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(10): 2128-2131. | |
| 17 | 王珊珊. 语言模糊多属性群决策中群共识问题研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学理学院, 2019. |
| Wang Shan-shan. Research on group consensus in linguistic fuzzy multi-attribute group decision making[D]. Chengdu: College of Science, Southwest Petroleum University, 2019. |
| [1] | 陈传海,王成功,杨兆军,刘志峰,田海龙. 数控机床可靠性建模研究现状及发展动态分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 253-266. |
| [2] | 李国龙,陶小会,徐凯,李喆裕. 数控机床转台位置相关几何误差的快速测量与辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 458-467. |
| [3] | 蔡洪彬,史国权. 主动控制加工误差慢刀伺服车削轨迹生成方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1221-1227. |
| [4] | 郑玉彬, 杨斌, 王晓峰, 申桂香, 赵宪卓, 秦猛猛. 基于威布尔分布的电主轴加速寿命试验时间设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 767-772. |
| [5] | 申桂香, 曾文彬, 张英芝, 吴茂坤, 郑玉彬. 最小故障率下数控组合机床平均维修时间确定[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1519-1526. |
| [6] | 张英芝, 刘津彤, 申桂香, 戚晓艳, 龙哲. 基于故障相关性分析的数控机床系统可靠性建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 169-173. |
| [7] | 曲兴田, 赵永兵, 刘海忠, 王昕, 杨旭, 陈行德. 串并混联机床几何误差建模与实验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 137-144. |
| [8] | 孟书, 申桂香, 张英芝, 龙哲, 曾文彬. 基于时间相关的数控机床系统组件更换时间[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1946-1952. |
| [9] | 李洪洲, 杨兆军, 许彬彬, 王彦鹍, 贾玉辉, 侯超. 数控机床可靠性评估试验周期设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1520-1527. |
| [10] | 王健健, 冯平法, 张建富, 吴志军, 张国斌, 闫培龙. 卡盘定心精度建模及其保持特性与修复方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 487-493. |
| [11] | 杨兆军, 杨川贵, 陈菲, 郝庆波, 郑志同, 王松. 基于PSO算法和SVR模型的加工中心可靠性模型参数估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 829-836. |
| [12] | 王晓燕,申桂香,张英芝,孙曙光,戚晓艳,荣峰. 基于故障链的复杂系统故障相关系数建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 442-447. |
| [13] | 赵帼娟, 张雷, 卢磊, 韩飞飞, 赵继. 四轴抛光平台综合误差建模及分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1676-1683. |
| [14] | 王继利, 杨兆军, 李国发, 朱晓翠. EM算法的多重威布尔可靠性建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 1010-1015. |
| [15] | 杨兆军,王继利,李国发,张新戈. 冲压机床可靠性增长的模糊层次分析预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 686-691. |
|
||