吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 1047-1059.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210822
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
考虑能量消耗的纯电动物流车柔性时间窗路径规划问题
- 吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
Electric delivery vehicle routing problem with flexible time window integrated with energy consumption estimation
Bao-feng SUN( ),Jiao-jiao LIU,Tian-zi YAO,Xin-xin REN
),Jiao-jiao LIU,Tian-zi YAO,Xin-xin REN
- College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
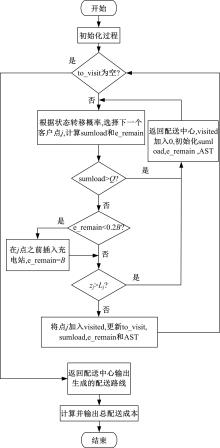
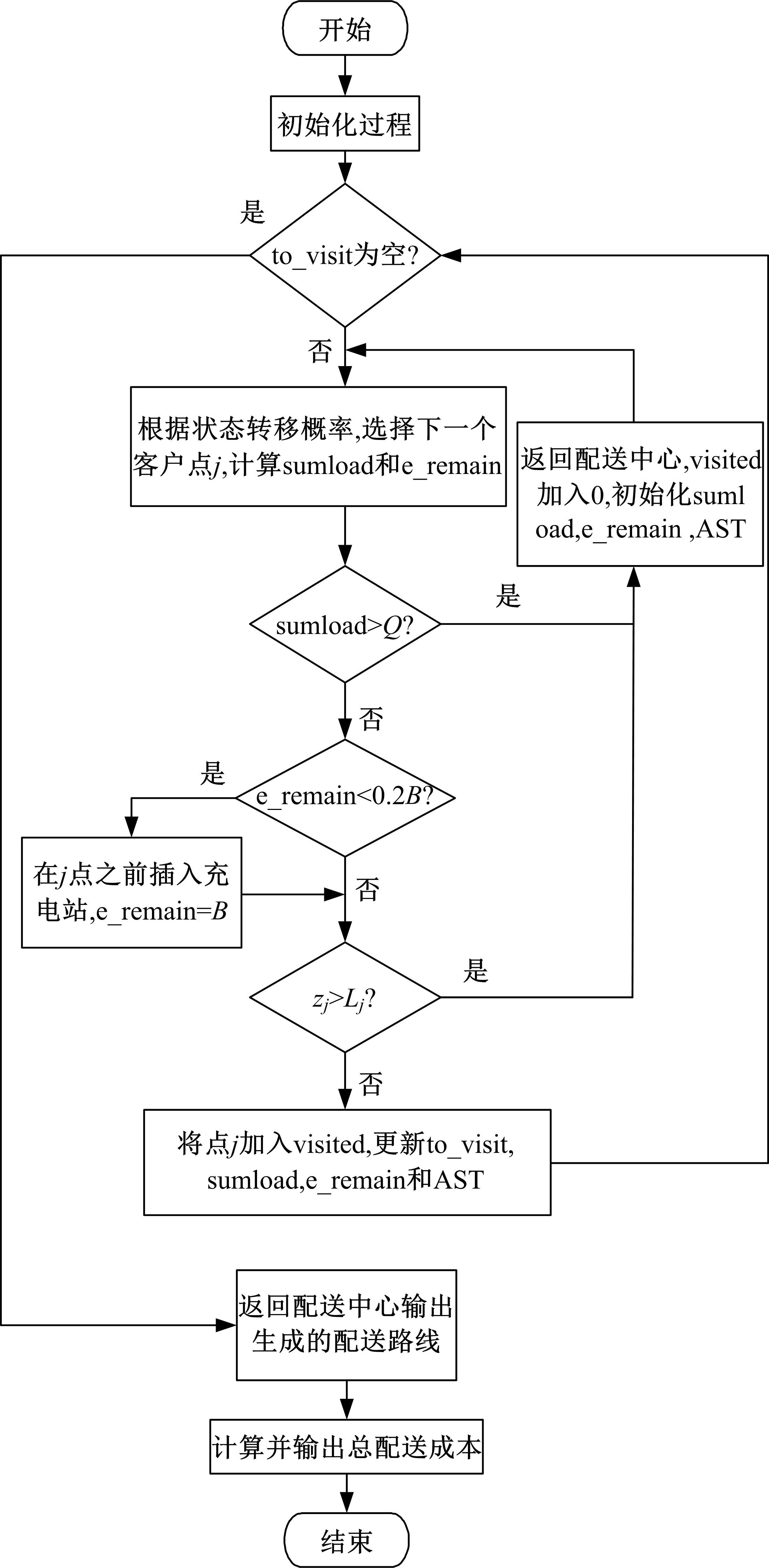
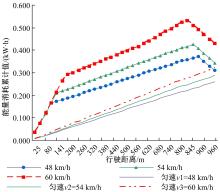
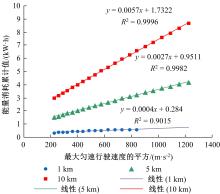
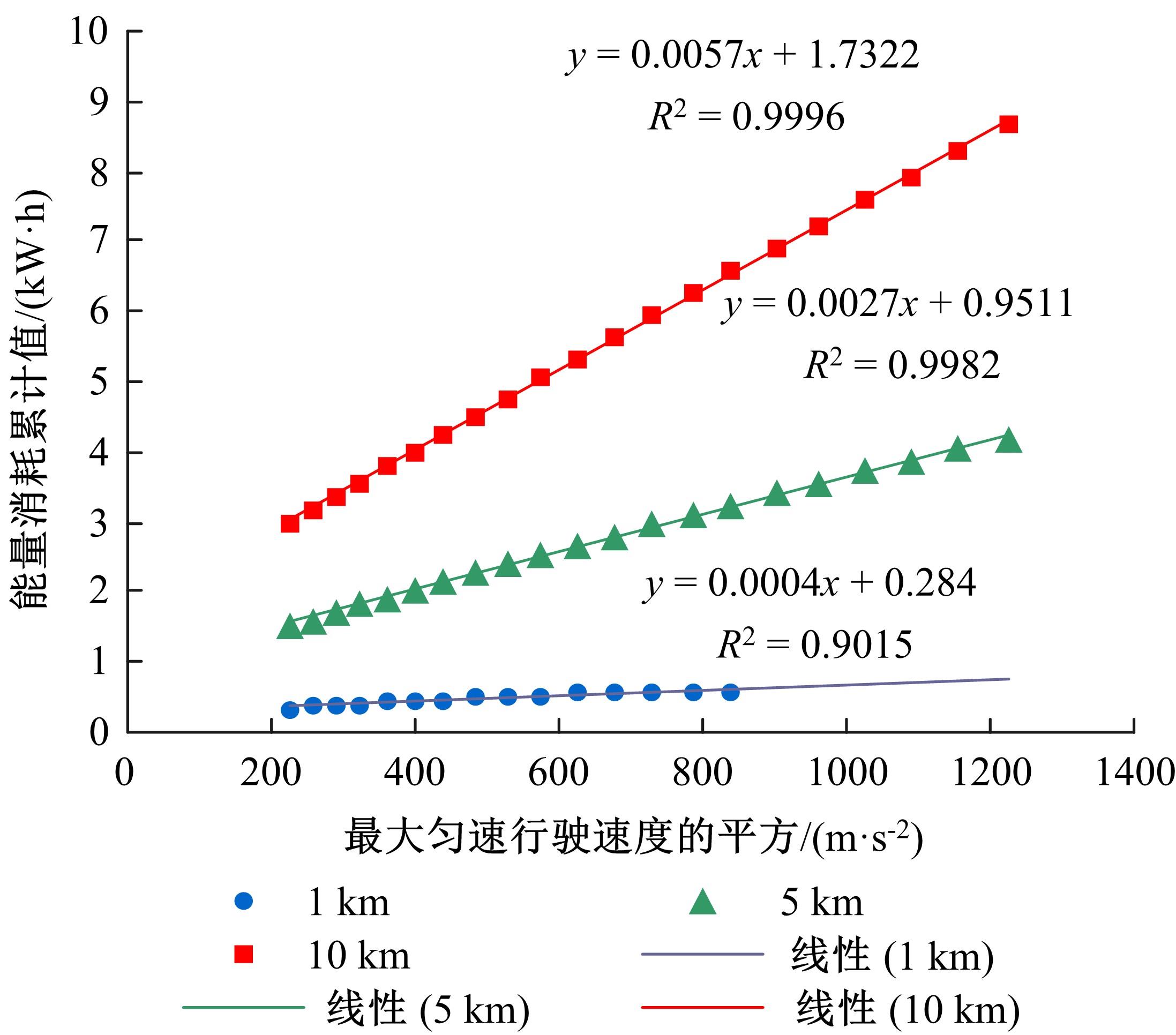
为提高物流企业收益,从模型驱动下的实验分析角度,研究了柔性时间窗约束下的纯电动物流车路径规划问题(EVRP-FlexTW)。首先,提出了考虑启动-制动的纯电动物流车能量消耗模型,揭示纯电动物流车在行驶过程中的能量消耗规律;其次,考虑了能量消耗的影响,增加车辆载重、柔性时间窗和耗电量等约束,建立了总配送成本最低的纯电动物流车路径优化模型,并设计了蚁群算法求解模型。行驶速度、柔性时间窗对决策目标的敏感性分析表明:减小纯电动物流车的最大行驶速度,会得到更好的路径规划结果;满足柔性时间窗约束虽然付出了更大的行驶距离和耗电量,但能够达成降低总配送成本的目标;上述发现体现了模型和算法的有效性。
中图分类号:
- N945.15
| 1 | 新能源汽车舆情中心. 2017年电动物流车产销或现“井喷” [EB/OL]. [2021-01-23]. . |
| 2 | 李明. 从政策法规层面浅析纯电动物流车发展趋势[J]. 科技资讯, 2018, 16(8): 92-93. |
| Li Ming. Analyze the development trend of pure electric logistics vehicle from the level of policies and regulations[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2018, 16(8): 92-93. | |
| 3 | 中共中央国务院. 交通强国建设纲要[EB/OL]. [2021-01-16].交通强国建设纲要. |
| 4 | Demir E, Bektaş T, Laporte G. A review of recent research on green road freight transportation[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2014, 237(3): 775-793. |
| 5 | Schneider M, Stenger A, Goeke D. The electric vehicle routing problem with time windows and recharging stations[J]. Transport Science, 2014, 48(4): 500-520. |
| 6 | Schiffer M, Schneider M, Laporte G. Designing sustainable mid-haul logistics networks with intra-route multi-resource facilities[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2018, 265(2): 517-532. |
| 7 | Macrina G, Pugliese L D P, Guerriero F, et al. The green mixed fleet vehicle routing problem with partial battery recharging and time windows[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2019, 101: 183-199. |
| 8 | Bektas T, Laporte G. The pollution-routing problem[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2011, 45(8): 1232-1250. |
| 9 | Goeke D, Schneider M. Routing a mixed fleet of electric and conventional vehicles[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2015, 245(1): 81-99. |
| 10 | Turkensteen M. The accuracy of carbon emission and fuel consumption computations in green vehicle routing[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017, 262(2): 647-659. |
| 11 | Bassoa R, Kulcsárb B, Egardtb B, et al. Energy consumption estimation integrated into the electric vehicle routing problem[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2019, 69(4): 141-167. |
| 12 | 王琪瑛, 李英, 李惠. 带软时间窗的电动车换电站选址路径问题研究[J]. 工业工程与管理, 2019, 24(3): 99-106. |
| Wang Qi-ying, Li Ying, Li Hui. Battery swap location-routing problem of electric vehicles with soft time windows[J]. Industrial Engineering and Management, 2019, 24(3): 99-106. | |
| 13 | Hiermann G, Puchinger J, Ropke S, et al. The electric fleet size and mix vehicle routing problem with time windows and recharging stations[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2016, 252(3): 995-1018. |
| 14 | Taş D, Jabali O, Woensel T V. A vehicle routing problem with flexible time windows[J]. Computers & Operation Research, 2014, 52(A): 39-54. |
| 15 | Zhang H Z, Zhang Q W, Ma L, et al. A hybrid ant colony optimization algorithm for a multi-objective vehicle routing problem with flexible time windows[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 490: 166-190. |
| 16 | 葛斌. 求解车辆路径问题的蚁群优化算法研究及应用[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学计算机与信息学院,2016. |
| Ge Bin. Research and application of ant colony optimization algorithm in solving the vehicle routing problem[D]. Hefei: School of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, 2016. | |
| 17 | 陈宝文. 蚁群优化算法在车辆路径问题中的应用研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学航天学院, 2009. |
| Chen Bao-wen. Application of ant colony optimization in vehicle routing problems[D]. Harbin: School of Astronautics, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009. | |
| 18 | 刘云忠, 宣慧玉. 蚂蚁算法在带时间窗车辆路径问题中的应用研究[C]∥中国运筹学会第七届学术交流会, 北京,中国,2004: 8-15. |
| Liu Yun-zhong, Xuan Hui-yu. Application research of the ant algorithm to vehicle routing problem with time windows[C]∥The 7th Conference of Operations Research Society of China, Beijing,China, 2004: 8-15. | |
| 19 | 王永聪. 基于纯电动汽车的城市配送车辆路径问题研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学交通运输学院, 2016. |
| Wang Yong-cong. Research on vehicle routing problem of city distribution based on pure electric vehicle[D]. Beijing: School of Traffic and Transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| 20 | 宋稚雅. 基于纯电动物流车的城市配送车辆路径问题研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学经济与管理学院, 2019. |
| Song Zhi-ya. Study on urban distribution vehicle routing problem based on pure electric logistics vehicle[D]. Beijing: School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019. |
| [1] | 胡莹,邵春福,王书灵,蒋熙,孙海瑞. 基于共享单车骑行轨迹的骑行质量识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1040-1046. |
| [2] | 王占中,蒋婷,张景海. 基于模糊双边界网络模型的道路运输效率评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 385-395. |
| [3] | 孙宝凤,姚天姿,陈雨琦. 考虑时变交通拥堵的纯电动物流车路径规划模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 468-479. |
| [4] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,李剑. 具有随机充电需求的混合动态网络平衡模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 136-143. |
| [5] | 户佐安,夏一鸣,蔡佳,薛锋. 延误条件下综合多种策略的城轨列车运行调整优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1664-1672. |
| [6] | 李浩,陈浩. 考虑充电排队时间的电动汽车混合交通路网均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1684-1691. |
| [7] | 朱才华,孙晓黎,李岩. 站点分类下的城市公共自行车交通需求预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 531-540. |
| [8] | 罗清玉,田万利,贾洪飞. 考虑通勤需求的电动汽车充电站选址与定容模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1471-1477. |
| [9] | 曹骞, 李君, 刘宇, 曲大为. 基于马尔科夫链的长春市乘用车行驶工况构建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1366-1373. |
| [10] | 孙宝凤, 高坤, 申琇秀, 梁婷. 基于能力平衡和变覆盖半径的加油站网络扩充选址模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 704-711. |
| [11] | 徐亮,程国柱. 基于车速离散度和经济车速的高速公路最低车速限制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 661-0665. |
|
||