吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (8): 2238-2244.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221364
基于随机充电需求的充电桩优化双层模型
- 1.华东交通大学 机电与车辆工程学院,江西 南昌 330013
2.华东交通大学 交通运输与物流学院,江西 南昌 330013
3.华东交通大学 软件学院,江西 南昌 330013
Double layer optimization model of charging pile based on random charging demand
Yun-juan YAN1( ),Wei-xiong ZHA2(
),Wei-xiong ZHA2( ),Jun-gang SHI2,Li-ping YAN3
),Jun-gang SHI2,Li-ping YAN3
- 1.College of Mechatronics & Vehicle Engineering,East China Jiaotong University,Nanchang 330013,China
2.Institute of Transportation and Economics,East China Jiaotong University,Nanchang 330013,China
3.School of Software,East China Jiaotong University,Nanchang 330013,China
摘要:
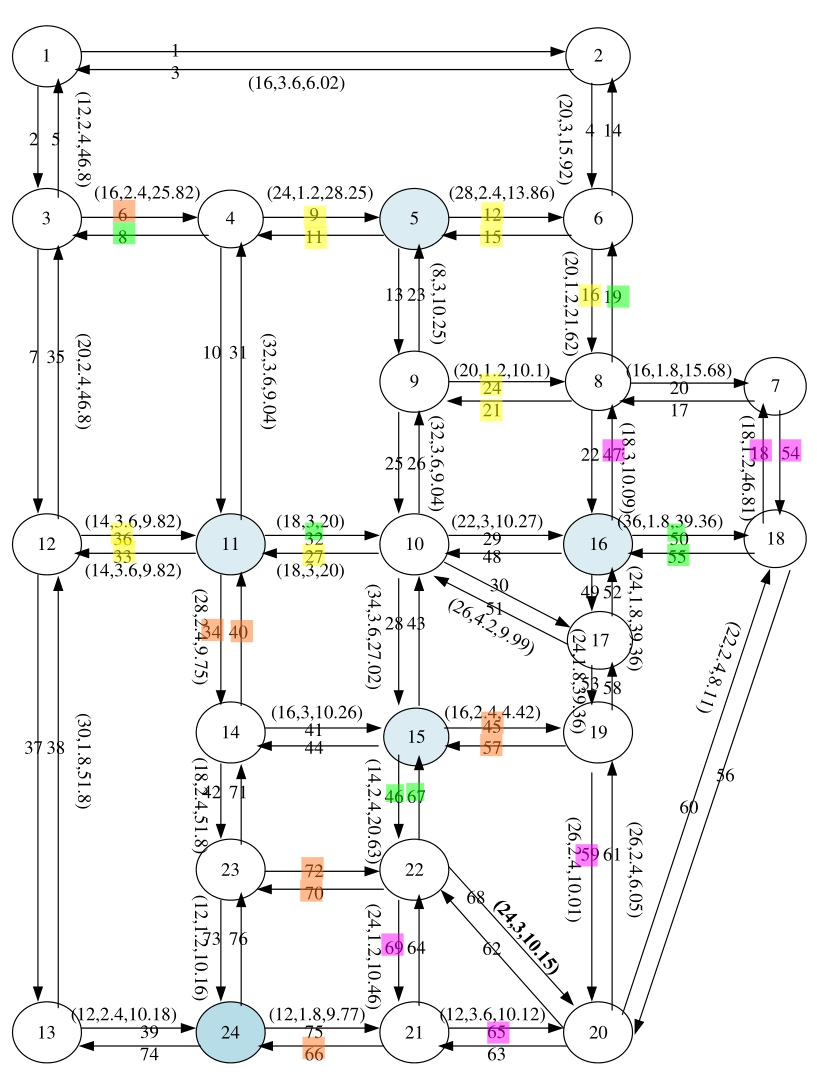
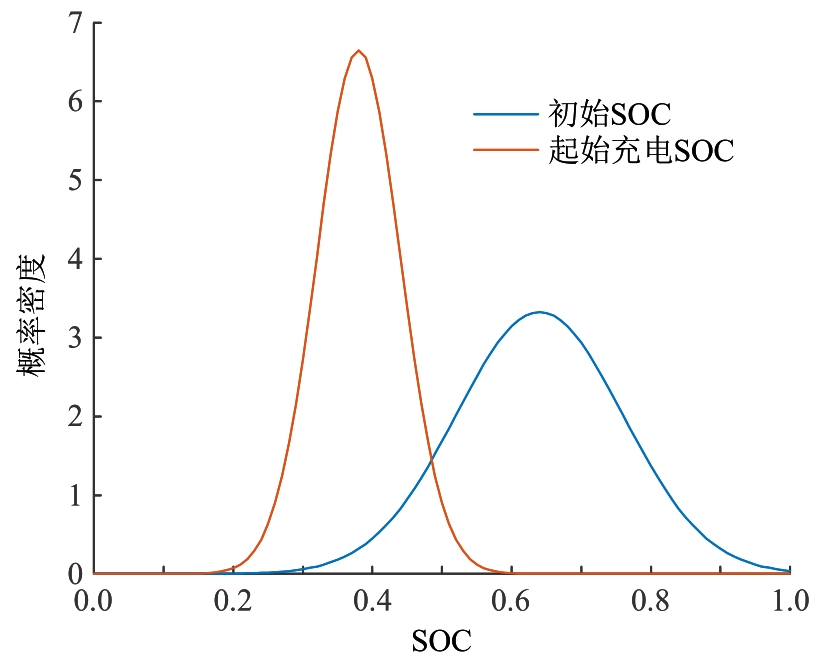
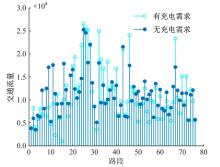
在具有随机充电需求的混合交通网络里,为确定合理的充电桩配置数,构建了双层规划模型。上层模型以建设成本净现值、顾客流失成本、超出忍耐时间成本之和最小为目标;下层模型以用户广义出行成本最小为目标,描述路网流量分配与充电设施部署位置的相互作用。模型利用差分进化算法与Frank-Wolfe算法相嵌套进行网络均衡配流及充电桩配置寻优仿真。结果表明:模型能有效模拟和预测网络均衡交通流、随机充电流、排队损失率和充电桩最优配置数。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | 国务院办公厅.国务院办公厅印发《新能源汽车产业发展规划(2021—2035年)》[R]. 北京:新华社, 2020. |
| 2 | Zhang H C, Moura S J, Hu Z C, et al. PEV fast-charging station siting and sizing on coupled transportation and power networks[J]. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, 2018, 9(4): 2595-2605. |
| 3 | Islam M M, Shareef H, Mohamed A, et al. Optimal location and sizing of fast charging stations for electric vehicles by incorporating traffic and power networks[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2018, 12(8): 947-957. |
| 4 | Xiang Y, Liu J, Li R, et al. Economic planning of electric vehicle charging stations considering traffic constraints and load profile templates[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 178: 647-659. |
| 5 | Zhang Q, Zhu Y, Wang Z, et al. Siting and sizing of electric vehicle fast charging station based on quasi-dynamic traffic flow[J]. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2021, 14(2): 4204-4215. |
| 6 | 罗清玉,田万利,贾洪飞. 考虑通勤需求的电动汽车充电站选址与定容模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(5): 1471-1477. |
| Luo Qing-yu, Tian Wan-li, Jia Hong-fei. Location and capacity model of electric vehicle charging station | |
| considering commuting demand[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1471-1477. | |
| 7 | Oda T, Aziz M, Mitani T, et al. Mitigation of congestion related to quick charging of electric vehicles based on waiting time and cost–benefit analyses: a Japanese case study[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2018, 36: 99-106. |
| 8 | Bouguerra S, Layeb S B. Determining optimal deployment of electric vehicles charging stations: case of Tunis City, Tunisia[J]. Case Studies Transport Policy, 2019, 7(3): 628-642. |
| 9 | Jung J, Chow J Y J, Jayakrishnan R, et al. Stochastic dynamic itinerary interception refueling location problem with queue delay for electric taxi charging stations[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2014, 40: 123-142. |
| 10 | Payam S B, Abbas R G, Hosein K. Optimal fast charging station placing and sizing[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 125: 289-299. |
| 11 | Khaksari A, Tsaousoglou G, Makris P, et al. Sizing of electric vehicle charging stations with smart charging capabilities and quality of service requirements[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 70(102872): 1-8. |
| 12 | 梁辉, 杨超, 于绍政, 等. 电动汽车充电站选址和充电桩配置仿真优化[J] 计算机仿真, 2017, 34(8): 169-172. |
| Liang Hui, Yang Chao, Yu Shao-zheng, et al. Research on electric vehicle siting of charging stations and configuration of charging pile based on simulation optimization method[J]. Computer Simulation, 2017, 34(8): 169-172. | |
| 13 | SHEVDC上海市新能源汽车产业大数据研究报告2018上海市新能源汽车公共数据网[R]. https:∥www.shevdc.org/report/original_report/1898.jhtml. |
| 14 | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,等. 具有随机充电需求的混合动态网络平衡模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(1): 136-143. |
| Yan Yun-juan, Zha Wei-xiong, Shi Jun-gang, et al. Mixed network equilibrium model with stochastic charging demand[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 136-143. | |
| 15 | He F, Yin Y, Lawphongpanich S. Network equilibrium models with battery electric vehicles[J]. Transp. Res. Part B, 2014, 67: 306-319. |
| 16 | Bar-Gear H. Transportation network test problems[R]. 2013. http:∥www.bgu.ac.il/bargera/tntp/ |
| [1] | 曲大义,刘浩敏,杨子奕,戴守晨. 基于车路协同的交通瓶颈路段车流动态分配机制及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2187-2196. |
| [2] | 阎奇武,邹忠亮. 减震结构阻尼器优化布置混合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2267-2274. |
| [3] | 温晓岳,钱国敏,孔桦桦,缪月洁,王殿海. TrafficPro:一种针对城市信控路网的路段速度预测框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2214-2222. |
| [4] | 陈桂珍,程慧婷,朱才华,李昱燃,李岩. 考虑驾驶员生理信息的城市交叉口风险评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1277-1284. |
| [5] | 赵晓华,刘畅,亓航,欧居尚,姚莹,郭淼,杨海益. 高速公路交通事故影响因素及异质性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 987-995. |
| [6] | 杨秀建,贾晓寒,张生斌. 考虑汽车队列动态特性的混合交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 947-958. |
| [7] | 吴文静,熊康贝,贾洪飞,罗清玉. 城市群轨道交通直通线路优化设置方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 711-718. |
| [8] | 范博松,邵春福. 城市轨道交通突发事件风险等级判别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [9] | 郑长江,胡欢,杜牧青. 考虑枢纽失效的多式联运快递网络结构设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2304-2311. |
| [10] | 王殿海,胡佑薇,蔡正义,曾佳棋,姚文彬. 基于BPR函数的城市道路间断流动态路阻模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1951-1961. |
| [11] | 李艳波,柳柏松,姚博彬,陈俊硕,渠开发,武奇生,曹洁宁. 考虑路网随机特性的高速公路换电站选址[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1364-1371. |
| [12] | 胡莹,邵春福,王书灵,蒋熙,孙海瑞. 基于共享单车骑行轨迹的骑行质量识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1040-1046. |
| [13] | 王占中,蒋婷,张景海. 基于模糊双边界网络模型的道路运输效率评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 385-395. |
| [14] | 杨敏,张聪伟,李大韦,马晨翔. 基于贝叶斯网的空铁联程乘客出行满意度模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2839-2846. |
| [15] | 秦严严,杨晓庆,王昊. 智能网联混合交通流CO2排放影响及改善方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 150-158. |
|